The global ear care devices market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising awareness of ear hygiene, increasing prevalence of earwax impaction, and a growing preference for at-home healthcare solutions. According to Grand View Research, the global ear care devices market was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by innovation in non-invasive ear cleaning tools, including soft rubber bulb ear syringes, which are widely recommended for their safety and ease of use. As demand rises across both clinical and consumer settings, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in producing high-quality, medical-grade soft rubber bulb syringes. These companies combine compliance with regulatory standards, scalable production, and a focus on ergonomic design to meet evolving market needs. The following analysis highlights the top eight manufacturers shaping this niche yet essential segment of the ear care industry.
Top 8 Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe Manufacturers and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2016
Website: goldenwellchina.com
Key Highlights: Goldenwell is one of the best soft rubber bulb ear syringe manufacturers and suppliers, which is equipped with a professional factory….
#2 China Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe Manufacturers Factory
Domain Est. 2022
Website: bkmbio.com
Key Highlights: As one of the most professional soft rubber bulb ear syringe manufacturers in China, we’re featured by quality products and good service….
#3 Ear syringe Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2013
Website: albertnovosino.com
Key Highlights: The Ear Syringe is an produce some products rubber suction ear syringe he made by Albert Novosino. Ingenious as well as distinct ear cleansing device that has ……
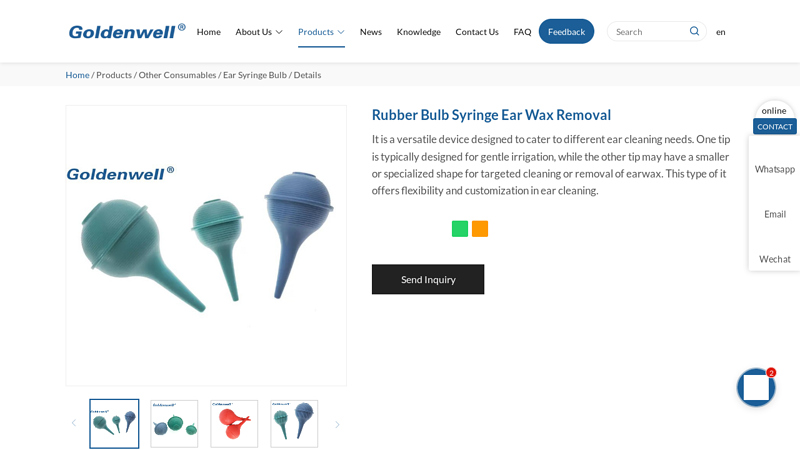
#4 Rubber Bulb Syringe Ear Wax Removal
Domain Est. 2019
Website: cngoldenwell.com
Key Highlights: We’re professional rubber bulb syringe ear wax removal manufacturers and suppliers in China, specialized in providing high quality medical devices….
#5 Tech
Domain Est. 2003
Website: warnertechcare.com
Key Highlights: Soft rubber bulb syringe used for gently flushing the ear with warm water after treating with Tech-care Earwax Removal drops. Sold each….
#6 Ear Bulb Syringe
Domain Est. 2006
Website: boenmedical.com
Key Highlights: The Ear / Ulcer Bulb Syringe is made of medical-grade soft PVC. The long tapered tip and increased suction power can be designed to safely irrigate ear canal….
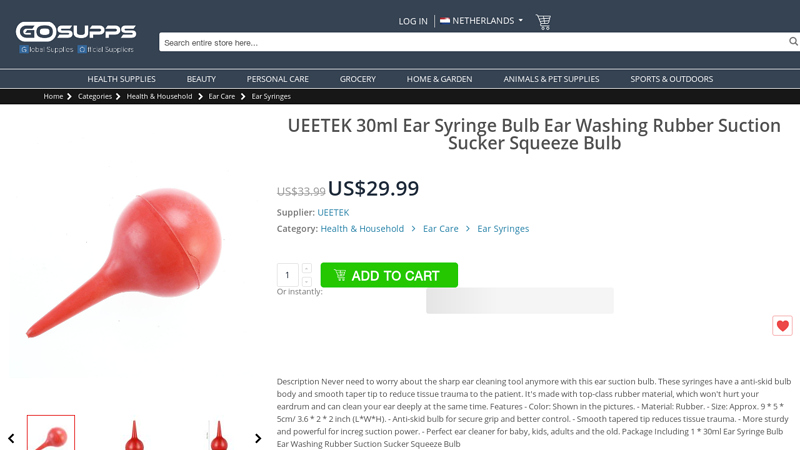
#7 UEETEK 30ml Ear Syringe Bulb Ear Washing Rubber Suction …
Domain Est. 2014
Website: gosupps.com
Key Highlights: In stock $19.99 deliveryIt’s made with top-class rubber material, which won’t hurt your eardrum and can clean your ear deeply at the same time. Sterility Rating: Sterile. Item Volu…
#8 Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe
Domain Est. 2018
Website: rubber-bulb.com
Key Highlights: Soft Rubber Ear Syringe Bulb Ear Cleaning Syringe Enema Bulb Syringe 25ml,35ml,65ml ,Air Blowing,Cleaning Bulb · MOQ:500pcs · Price:USD0.23-0.38 PCS….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe

2026 Market Trends for Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe
The global market for soft rubber bulb ear syringes is expected to experience steady growth and notable shifts by 2026, driven by increasing consumer awareness about ear hygiene, rising demand for at-home healthcare solutions, and advancements in product materials and design. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the industry in the coming years.
Rising Demand for At-Home Ear Care Solutions
The trend toward self-care and home-based medical treatments continues to accelerate, particularly in the wake of increased health consciousness post-pandemic. Soft rubber bulb ear syringes are gaining popularity as safe, non-invasive tools for earwax removal. Consumers are increasingly turning to over-the-counter (OTC) products rather than clinical visits, bolstering demand. Online retail platforms and telehealth endorsements are further enabling access to these devices, especially in North America and Europe.
Shift Toward Safer, Medical-Grade Materials
While traditional rubber bulb syringes are still in use, there is a growing shift toward silicone and latex-free alternatives due to concerns about allergenic reactions and material durability. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to phase out lower-grade rubber in favor of hypoallergenic, soft-touch silicone. This transition aligns with stricter regulatory standards in regions such as the EU and the U.S., where medical device safety and biocompatibility are closely monitored.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa are witnessing increased healthcare accessibility and rising disposable incomes. These factors are fueling demand for affordable ear care tools, including soft rubber bulb syringes. Local production and partnerships with global distributors are expected to expand market reach, especially in countries like India, Brazil, and Indonesia, where preventive healthcare adoption is on the rise.
Integration with Ear Care Kits
A growing trend is the bundling of soft rubber bulb syringes with complementary ear care products—such as saline solutions, ear drops, and cleaning wipes—into comprehensive ear hygiene kits. These kits offer convenience and are being marketed through e-commerce channels and pharmacies. By 2026, such bundled offerings are projected to dominate retail sales, appealing to consumers seeking holistic ear care routines.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
Regulatory scrutiny on single-use medical plastics and rubber products is increasing, prompting manufacturers to explore eco-friendly packaging and recyclable materials. Some companies are introducing reusable, sterilizable syringe designs to reduce environmental impact. Additionally, compliance with ISO 13485 and FDA standards will remain critical for market entry and consumer trust.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established healthcare brands and new entrants investing in ergonomic designs, improved suction control, and child-safe variants. Innovations such as anti-slip grips, transparent bulbs for visibility, and graduated markings for dosage accuracy are differentiating premium products. Strategic partnerships with online health retailers and digital marketing campaigns are key growth levers.
In conclusion, the soft rubber bulb ear syringe market in 2026 will be characterized by material innovation, expanded geographic reach, and a strong consumer focus on safety and convenience. As at-home healthcare continues to grow, this simple yet effective tool is poised for sustained relevance and evolution in the global medical consumer products space.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringes (Quality & IP)
Sourcing Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringes involves navigating several critical challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to regulatory non-compliance, customer dissatisfaction, safety issues, and legal liabilities.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Substandard Material Composition: Using low-grade or non-medical-grade rubber that may contain harmful phthalates, latex (causing allergies), or excessive plasticizers. This compromises safety, durability, and biocompatibility.
- Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances: Poorly controlled molding processes result in inconsistent bulb wall thickness, tip dimensions, or nozzle shape. This leads to unreliable suction, leakage, difficulty in insertion, or potential tissue damage.
- Poor Sealing and Air Leakage: Inadequate bonding between the bulb and the nozzle stem or defects in the bulb material cause air leaks. This significantly reduces suction efficacy, rendering the syringe ineffective for earwax removal.
- Lack of Sterility and Cleanliness: Manufacturing in non-controlled environments or inadequate packaging allows contamination (dust, microbes). This poses infection risks, especially if marketed as sterile or for medical use.
- Insufficient Durability and Reusability Claims: Bulbs made from inferior rubber crack, tear, or lose elasticity quickly after minimal use. Suppliers may falsely claim reusability without proper material testing or validation.
- Non-Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Failure to meet essential requirements of relevant regulations (e.g., FDA 510(k) clearance for medical devices in the US, CE marking under MDR in the EU, or local health authority approvals). This includes lack of biocompatibility testing (ISO 10993), labeling requirements, or quality management system (QMS) certification (e.g., ISO 13485).
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Infringement of Patented Designs: Sourcing syringes that copy the functional or ornamental design of a competitor’s patented product (e.g., unique nozzle shape, ergonomic bulb design, integrated features) without authorization, leading to potential infringement lawsuits.
- Trademark Infringement: Using packaging, branding, or product names that are confusingly similar to established brands (e.g., mimicking color schemes, logos, or well-known brand names), misleading consumers and violating trademark rights.
- Copyright Violation in Packaging and Documentation: Copying instructional leaflets, user manuals, or distinctive packaging artwork protected by copyright from another manufacturer.
- Sourcing from Suppliers with Questionable IP Practices: Engaging manufacturers who routinely produce counterfeit or reverse-engineered products, exposing the buyer to secondary liability and reputational damage.
- Lack of IP Due Diligence: Failing to verify that the supplier owns the rights to the design or has valid licenses for any proprietary technology incorporated into the syringe before placing orders or launching products.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe
This guide outlines the key logistics and regulatory compliance considerations for the import, distribution, storage, and sale of Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringes. Adherence is critical to ensure product safety, avoid regulatory penalties, and maintain market access.
H2.1 Regulatory Classification & Key Requirements
-
Global Classification:
- USA (FDA): Classified as a Class I medical device (510(k) exempt) under 21 CFR 874.1800 (Ear Syringe). Subject to General Controls.
- European Union (EU): Classified as a Class I medical device under Regulation (EU) 2017/745 (MDR). Requires conformity assessment, CE marking, and adherence to essential requirements. Note: May require involvement of a Notified Body if sterile or measuring function is claimed.
- United Kingdom (UK): Classified as a UKCA-marked Class I medical device under the UK MDR 2002 (as amended). Requires conformity assessment and registration with the MHRA.
- Canada (Health Canada): Classified as a Class I medical device under the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282). Requires a Medical Device Licence (MDL) for sale.
- Australia (TGA): Classified as a Class I medical device (non-sterile, non-measuring) on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG). Requires inclusion on the ARTG.
- Other Markets: Classification varies (e.g., Japan: Class I under PMDA; China: Class I under NMPA). Verify specific country requirements.
-
Key Regulatory Requirements:
- Quality Management System (QMS): Implement and maintain a QMS compliant with ISO 13485:2016 is highly recommended and often required (e.g., EU MDR, FDA for manufacturers).
- Technical Documentation: Maintain comprehensive technical files demonstrating conformity with applicable regulations (design, materials, manufacturing, risk management, labeling, testing).
- Labeling & Instructions for Use (IFU): Must comply strictly with regional requirements (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 801, EU MDR Annex I). Include:
- Device name (“Soft Rubber Bulb Ear Syringe”)
- Manufacturer name and address
- Intended purpose (“For irrigation of the external ear canal under medical supervision” or similar)
- Contraindications, Warnings, Precautions (e.g., “Do not use if eardrum is perforated,” “Not for deep insertion,” “Consult a healthcare professional before use”)
- Conformity markings (CE, UKCA, FDA Establishment Registration Number, etc.)
- Lot/Batch number
- Expiry date (if applicable, though often indefinite for non-sterile)
- Sterility status (e.g., “Non-sterile,” “Single-use only” if applicable)
- Material composition (e.g., “Latex-Free? Natural Rubber? Synthetic Rubber? PVC?”)
- Language(s) required for the target market.
- Unique Device Identification (UDI): Mandatory in the USA (FDA UDI Rule), EU (MDR), UK (UK MDR), and increasingly elsewhere. Requires a UDI on the label and in submissions to device databases (GUDID, EUDAMED, MHRA database).
- Post-Market Surveillance (PMS): Implement systems to monitor device performance, collect and report adverse events (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EU Vigilance, UK Yellow Card), and conduct trend reporting.
- Latex Allergen Warning: If the bulb contains natural rubber latex, prominent labeling “Contains Natural Rubber Latex Which May Cause Allergic Reactions” is mandatory in the USA (FDA) and strongly recommended/guided elsewhere. Consider latex-free alternatives.
H2.2 Logistics & Supply Chain Management
-
Sourcing & Manufacturing:
- Supplier Qualification: Rigorously audit and qualify manufacturers. Verify their QMS (ISO 13485), regulatory compliance history, and manufacturing controls.
- Material Specifications: Clearly define and control specifications for rubber (type, hardness, biocompatibility, latex status), plastic components (if any), and packaging materials. Obtain Certificates of Analysis (CoA).
- Biocompatibility: Ensure materials are biocompatible for intended contact (skin/mucosal membrane). Testing per ISO 10993-1 (e.g., Cytotoxicity, Sensitization, Irritation) is standard practice, even for Class I devices.
- Sterility (If Applicable): If marketed as sterile, define and validate the sterilization method (e.g., Ethylene Oxide, Gamma) and shelf life. Requires strict process control and sterility testing.
-
Packaging & Labeling:
- Primary Packaging: Ensure packaging protects the device from contamination and damage during transit. Material must not leach harmful substances.
- Secondary Packaging: Use sturdy outer cartons suitable for stacking and transport. Clearly label with product details, quantities, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”).
- Label Accuracy: Ensure all regulatory labels (UDI, CE/UKCA, warnings) are correctly applied and legible. Implement label verification processes.
- Serialization (If Required): Implement systems for unique serialization if mandated by specific markets (beyond basic UDI).
-
Storage & Distribution:
- Storage Conditions: Store in a clean, dry, cool environment, protected from direct sunlight, heat, ozone, and excessive humidity. Avoid contact with oils, greases, or solvents which can degrade rubber. Follow manufacturer’s recommended conditions.
- Inventory Management: Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or FEFO (First-Expired, First-Out) systems. Monitor stock levels and expiry dates (if applicable).
- Transportation: Use reputable carriers. Protect packages from physical damage, moisture, and extreme temperatures during transit. Document shipping conditions if necessary.
- Cold Chain (If Sterile/Specific): Only if sterility or material integrity requires temperature control (uncommon for standard non-sterile bulb syringes). Validate if used.
-
Import/Export:
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Identify the correct HS code for customs (e.g., 9018.39.0000 – Other appliances and instruments for medical, surgical, dental or veterinary purposes, not elsewhere specified or included – US; 9018.39.00 – EU). Accuracy is crucial for tariffs and regulations.
- Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading/air waybills. Include regulatory certificates (CE Cert, FDA Registration, Certificate of Free Sale – CFS) as required by the destination country.
- Import Licenses/Permits: Obtain necessary import licenses or permits from the destination country’s regulatory authority (e.g., FDA Prior Notice in US, specific permits in some countries).
- Duties & Taxes: Calculate and budget for applicable import duties, VAT, and other taxes.
H2.3 Compliance Verification & Documentation
-
Essential Documentation:
- Technical File / Design Dossier
- Quality Management System Certificate (ISO 13485)
- Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for each market
- UDI Certificates and Database Submissions
- Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) – Often required for export
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for constituent materials
- Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for materials and finished goods
- Sterilization Validation Reports (if sterile)
- Biocompatibility Test Reports
- Labeling Files (approved artwork)
- Post-Market Surveillance Plan and Reports
- Adverse Event Reports (if any)
- Supplier Qualification Records
-
Audits & Inspections:
- Be prepared for audits by regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, MHRA, Notified Bodies) or customers.
- Maintain comprehensive, organized, and readily accessible records for the required retention period (often 5-10 years post-device withdrawal).
-
Change Management:
- Implement a formal process for any changes to design, materials, manufacturing process, labeling, or suppliers. Assess impact on regulatory status and QMS. Notify authorities if required (e.g., FDA 30-day notice for certain changes, EU MDR Significant Change notifications).
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Regulations are complex and subject to change. Always consult with qualified regulatory experts and legal counsel specific to your target markets and business model to ensure full compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing soft rubber bulb ear syringes requires careful consideration of product quality, material safety, supplier reliability, and compliance with relevant health and safety standards. Soft rubber bulb ear syringes are essential for safe and effective ear irrigation, particularly for sensitive users, making it critical to select a product made from medical-grade, latex-free, and non-irritating materials. Evaluating potential suppliers based on reputation, manufacturing certifications (such as ISO 13485 or FDA registration), and ability to meet volume and delivery requirements ensures consistent supply and regulatory compliance. Additionally, conducting product sampling and due diligence can help verify performance and durability. Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy will balance cost-efficiency with patient safety and product efficacy, ensuring a reliable supply of high-quality soft rubber bulb ear syringes for medical or consumer use.