The global sodium perborate market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in household and industrial cleaning applications, as well as its use in cosmetics and textile bleaching. According to Mordor Intelligence, the bleach and bleaching agents market—of which sodium perborate is a key component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of hygiene, the expansion of the laundry care industry, and the shift toward oxygen-based bleaching agents due to their eco-friendly profile compared to chlorine-based alternatives. Sodium perborate, valued for its stability and effective bleaching performance at lower temperatures, is particularly favored in powder and liquid detergent formulations. With regulatory pressure mounting on environmentally hazardous chemicals, manufacturers are investing in greener production methods, further strengthening market dynamics. As demand rises, a select group of global manufacturers are leading innovation, scale, and supply reliability—shaping the competitive landscape of this niche but essential chemical segment.
Top 6 Sodium Perborate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
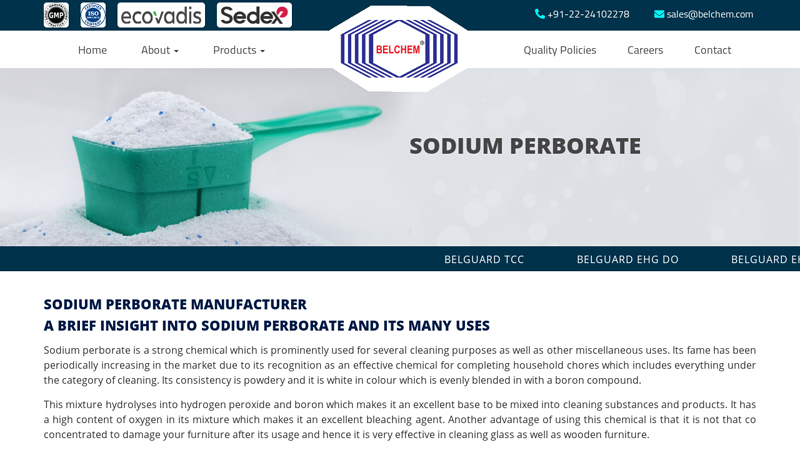
#1 Sodium Perborate Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: belchem.com
Key Highlights: We are the well known Sodium Perborate Manufacturer and supplier. Sodium Perborate is a strong chemical which is prominently used for several cleaning ……
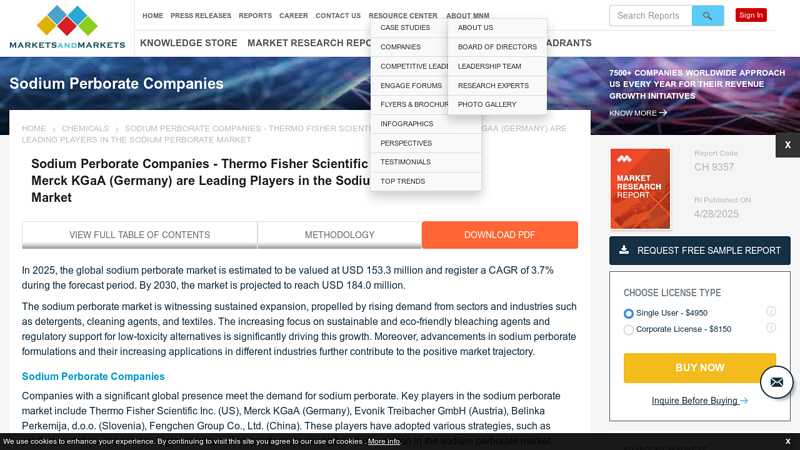
#2 Sodium Perborate Companies
Domain Est. 2009
Website: marketsandmarkets.com
Key Highlights: Key players in the sodium perborate market include Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (US), Merck KGaA (Germany), Evonik Treibacher GmbH (Austria), Belinka ……
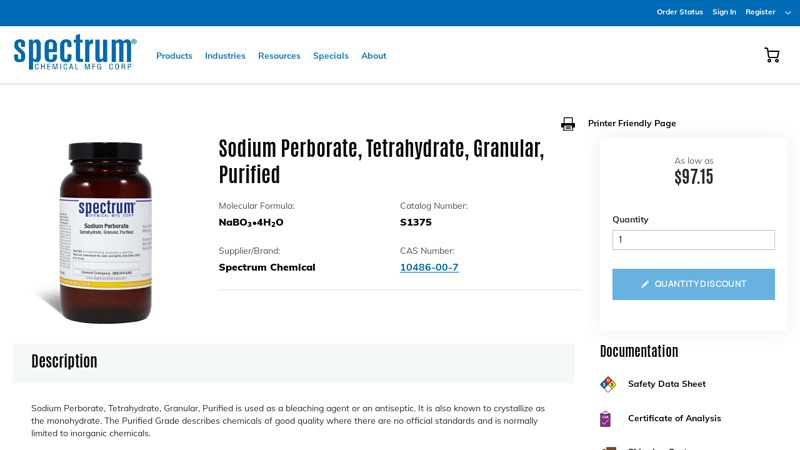
#3 Sodium-Perborate-Tetrahydrate-Granular-Purified
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spectrumchemical.com
Key Highlights: 15-day returnsSodium Perborate, Tetrahydrate, Granular, Purified is used as a bleaching agent or an antiseptic. It is also known to crystallize as the monohydrate….
#4 Parchem is the leading supplier of Sodium Perborate Monohydrate
Domain Est. 1996
Website: parchem.com
Key Highlights: Parchem – fine & specialty chemicals is the premier supplier of inorganic chemicals and high quality chemical intermediates such as sodium perborate ……
#5 Sodium perborate
Domain Est. 2006
Website: history.evonik.com
Key Highlights: Evonik continues to produce sodium perborate; however over the last years, sodium percarbonate has become a more important detergent substance. Further ……
#6 Sodium Perborate
Domain Est. 2015
Website: belinka-perkemija.com
Key Highlights: Sodium perborate is a white, crystalline powder that dissolves well in water, forming an alkaline solution with oxidative properties….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sodium Perborate

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Sodium Perborate
As the global chemicals market evolves in response to environmental regulations, shifting consumer preferences, and advancements in industrial applications, sodium perborate—a widely used bleaching and oxidizing agent—is expected to experience notable market dynamics by 2026. The following analysis outlines key trends shaping the sodium perborate market under the H2 framework, focusing on Health, Hygiene, Homecare, and High-Efficiency Applications.
1. Health & Safety Regulations Driving Formulation Changes
By 2026, tightening health and safety regulations—particularly in North America and the European Union—are expected to influence the use of sodium perborate in consumer products. Regulatory bodies such as the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are increasingly scrutinizing boron-based compounds due to potential reproductive toxicity concerns at high exposure levels.
- Impact: Manufacturers are reformulating products to reduce boron content or replace sodium perborate with alternative bleaching agents like percarbonate or enzymatic systems.
- Counter-Trend: In regions with less stringent regulations (e.g., parts of Asia-Pacific and Latin America), sodium perborate remains a cost-effective option, supporting continued demand in industrial laundry and detergent sectors.
2. Hygiene Demand Sustained Post-Pandemic
The heightened focus on hygiene following the global pandemic continues to support demand for effective disinfectants and cleaning agents. Sodium perborate, which releases hydrogen peroxide in water, is valued for its antimicrobial properties.
- Growth Area: Use in medical-grade cleaning formulations and institutional hygiene products (e.g., hospital laundry, surface disinfectants) is expected to grow steadily, especially in emerging markets.
- Innovation: Blending sodium perborate with silver ions or other biocides to enhance germ-killing efficacy is emerging as a niche trend.
3. Homecare & Detergent Industry Shifts
Sodium perborate has long been a staple in laundry detergents, particularly in powder formulations where it acts as a low-temperature bleach activator.
- Decline in Developed Markets: In Europe and North America, liquid detergents and compacted powders dominate, reducing reliance on sodium perborate due to solubility and stability concerns.
- Growth in Developing Markets: In India, Southeast Asia, and Africa, powdered detergents remain popular, and sodium perborate is favored for its cost-efficiency and performance. Market expansion is expected here, driven by urbanization and rising disposable incomes.
- Sustainability Pressures: Brands like Unilever and Procter & Gamble are shifting toward “greener” formulations, which may limit sodium perborate adoption unless eco-certified or sustainably sourced variants emerge.
4. High-Efficiency and Industrial Applications
Beyond consumer detergents, sodium perborate is finding new applications in high-efficiency and specialty industrial processes.
- Textile Processing: Used in eco-friendly bleaching processes that operate at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption.
- Pulp & Paper: Limited but steady use in bleaching mechanical pulps; however, competition from chlorine-free alternatives (e.g., ozone, peracetic acid) remains strong.
- Dental & Cosmetics: Niche use in tooth-whitening formulations and antiseptic mouthwashes, though safety concerns may restrict broader adoption by 2026.
Market Outlook Summary (2026):
- Global CAGR: Estimated at 1.8–2.5% from 2023 to 2026, with Asia-Pacific leading growth.
- Production Shifts: China remains the largest producer, but India and Southeast Asia are expanding manufacturing capacity.
- Price Trends: Stable to slightly increasing due to raw material (borax, hydrogen peroxide) cost volatility.
- Competitive Landscape: Key players include BASF, Solvay, and Liaoning Qixing Group, focusing on product differentiation and compliance with global standards.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the sodium perborate market will be shaped by a dichotomy between regulatory-driven decline in mature markets and sustained demand in developing economies. While health and environmental concerns pose challenges, its role in hygiene, cost-effective homecare, and industrial bleaching ensures continued relevance—especially where high-efficiency, low-temperature performance is valued. Strategic innovation and regional adaptation will be critical for stakeholders aiming to maintain or grow market share.

Certainly. Here’s a response using the H2 (Heading 2) format to address common pitfalls when sourcing Sodium Perborate, focusing on quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations:
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Sodium Perborate (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Sodium Perborate—commonly used as a bleaching agent in detergents and as an oxidizing agent in chemical synthesis—can present several challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property rights. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply and regulatory compliance.
1. Inconsistent Product Quality
- Variable Active Oxygen Content: Sodium Perborate is valued for its active oxygen release. Suppliers may offer grades with differing active oxygen levels (e.g., monohydrate vs. tetrahydrate), leading to performance variability if not properly specified.
- Impurity Profiles: Contaminants such as heavy metals, free alkali, or residual borax can affect performance and safety. Poor-quality batches may fail to meet pharmaceutical or food-grade standards.
- Moisture Sensitivity: Sodium Perborate degrades upon exposure to humidity. Inadequate packaging or storage during transit can compromise stability and efficacy.
Best Practice: Require certified COAs (Certificates of Analysis), conduct periodic third-party testing, and specify grade (e.g., technical, detergent, pharmaceutical) and hydrate form clearly in procurement contracts.
2. Misrepresentation of Grade or Purity
- Some suppliers may label lower-grade material as “high purity” without supporting data. This is particularly common in regions with lax regulatory oversight.
- Confusion between Sodium Perborate and similar boron compounds (e.g., sodium percarbonate or borax) can lead to incorrect substitutions.
Best Practice: Perform supplier audits and request full specification sheets, including assay, pH, solubility, and stability data.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Manufacturing Processes
- Certain synthesis methods or stabilized formulations of Sodium Perborate may be protected by patents, especially in specialty applications (e.g., detergent additives or medical disinfectants).
- Sourcing from manufacturers using patented processes without license could expose the buyer to indirect IP infringement, particularly in regulated markets like the EU or U.S.
Best Practice: Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s manufacturing process. Request documentation confirming freedom to operate (FTO), especially when sourcing for proprietary end-products.
4. Lack of Regulatory Compliance Documentation
- Sodium Perborate is regulated under REACH (EU), TSCA (U.S.), and other chemical control frameworks. Suppliers may not provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) or regulatory declarations in line with local requirements.
- Non-compliant sourcing may lead to customs delays, product recalls, or legal liabilities.
Best Practice: Verify that suppliers are registered under relevant chemical regulations and provide up-to-date compliance documentation.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
- Opaque supply chains may obscure the origin of raw materials (e.g., boron sources), raising concerns about sustainability, ethical sourcing, or contamination.
- Re-bottlers or intermediaries may not fully understand or communicate technical specifications.
Best Practice: Source directly from verified manufacturers when possible and require batch traceability.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls proactively, organizations can ensure a reliable, compliant, and effective supply of Sodium Perborate for their intended applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sodium Perborate (H2: Hazard Statement – H228: Flammable Solid)
⚠️ Important Note: The use of “H2” in your request likely refers to a Hazard Statement under the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). However, sodium perborate is not classified under H228 (Flammable Solid). This appears to be a misunderstanding. Below is a corrected and comprehensive logistics and compliance guide for Sodium Perborate, including accurate hazard classifications, regulatory considerations, and safe handling procedures.
1. Chemical Identity
- Chemical Name: Sodium Perborate
- CAS Number: 10486-00-7 (anhydrous), 7632-49-5 (tetrahydrate)
- Molecular Formula: NaBO₃ (often represented as NaBO₂·H₂O₂ or NaBO₃·nH₂O)
- Common Forms: Monohydrate (NaBO₃·H₂O) and Tetrahydrate (NaBO₃·4H₂O)
- Uses: Bleaching agent in detergents, disinfectant, oxidizing agent in chemical synthesis
2. Correct GHS Hazard Classification
Sodium perborate is not flammable and should not be classified under H228. Its correct GHS hazard statements are:
- H272: May intensify fire; oxidizer
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H335: May cause respiratory irritation
- H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long-lasting effects
✅ Note: H228 (Flammable Solid) does not apply to sodium perborate. Using this classification would be incorrect and could lead to non-compliance.
3. Transport Classification (UN Number & Regulations)
- UN Number: UN 3371
- Proper Shipping Name: SODIUM PEROXOBORATE
- Class: 5.1 (Oxidizing Substances)
- Packing Group: III (Low to moderate hazard)
- Transport Regulations:
- IMDG Code (Maritime): Class 5.1, PG III
- IATA DGR (Air): Class 5.1, PG III, permitted with restrictions
- ADR/RID (Road/Rail in Europe): Class 5.1, PG III
- Special Provisions: Keep away from combustible materials, heat, and ignition sources due to oxidizing nature.
4. Storage Requirements
- Environment: Cool, dry, well-ventilated area
- Containers: Sealed, non-combustible, corrosion-resistant (e.g., HDPE)
- Segregation:
- Keep away from flammable/combustible materials
- Store separately from reducing agents, acids, and organic materials
- Temperature: Store below 30°C; avoid prolonged exposure to heat or moisture
- Shelf Life: Limited; degrades in humid conditions releasing oxygen
5. Handling Precautions
- Use in well-ventilated areas or with local exhaust ventilation
- Avoid dust formation
- Prohibit smoking, open flames, or sparks in handling areas
- Use non-sparking tools
- Ground equipment to prevent static discharge
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing
6. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles or face shield
- Skin Protection: Nitrile or neoprene gloves, lab coat or protective clothing
- Respiratory Protection: NIOSH-approved dust mask (e.g., N95) if dust levels exceed limits
- Hygiene Measures: Wash hands after handling; do not eat, drink, or smoke in work areas
7. Spill Response
- Immediate Actions:
- Evacuate non-essential personnel
- Eliminate ignition sources
- Avoid creating dust
- Containment: Use non-combustible material (e.g., sand, vermiculite) to contain spill
- Cleanup:
- Scoop into a dry, clean container
- Place in a suitable, labeled container for disposal
- Do not use combustible materials (e.g., sawdust) for cleanup
- Disposal: Follow local, national, and international regulations for oxidizing waste
8. Regulatory Compliance
- GHS/CLP: Classified as Ox. Sol. 3, Skin Irrit. 2, Eye Irrit. 2, STOT SE 3, Aquatic Chronic 3
- REACH (EU): Registered; ensure compliance with exposure scenarios
- TSCA (USA): Listed; report if required under significant new use rules
- OSHA (USA): Regulated under HCS 2012; ensure SDS and training are up to date
- EPA: Review under FIFRA if used in pesticidal applications
9. Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
Ensure the latest version of the SDS is available and complies with:
– ISO 11014 or ANSI Z400.1 standards
– Includes correct hazard statements (H272, H315, H319, H335, H412)
– Accurate first aid, firefighting, and transport information
10. Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Environmental Hazards: Toxic to aquatic organisms; avoid release to waterways
- Waste Disposal:
- Treat as hazardous oxidizing waste
- Follow local regulations (e.g., RCRA in the US)
- Do not dispose of in household trash or drains
✅ Summary: Key Corrections & Recommendations
- ❌ Do not classify sodium perborate under H228 (Flammable Solid) — it is incorrect.
- ✅ Correct hazard: H272 (May intensify fire; oxidizer)
- ✅ Transport under UN 3371, Class 5.1
- ✅ Store away from combustibles; treat as oxidizer
- ✅ Train personnel on oxidizer hazards and emergency procedures
For full compliance, always verify classification with your supplier’s SDS and consult local regulatory authorities (e.g., EPA, ECHA, OSHA) before transport, storage, or use.
Let me know if you need a sample SDS section or label layout.
In conclusion, sourcing sodium perborate requires careful consideration of supplier reliability, product purity, regulatory compliance, and cost-efficiency. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards and provide consistent quality, especially given the compound’s widespread use in detergents, bleaching agents, and various industrial applications. Evaluating factors such as production capacity, environmental and safety certifications, and logistical capabilities will ensure a stable and efficient supply chain. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and potential regulatory changes can help mitigate risks and support long-term sourcing strategies. Overall, a well-vetted and strategic sourcing approach is key to obtaining high-quality sodium perborate while maintaining operational and economic sustainability.