The global smart rack market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient data center solutions, increasing adoption of IoT-enabled infrastructure, and the expansion of cloud computing services. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the smart rack market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 14.5% from 2023 to 2028, reaching a valuation of USD 3.2 billion by the end of the forecast period. This surge is further supported by Grand View Research, which highlights that innovations in intelligent power distribution, real-time monitoring, and thermal management are accelerating adoption across enterprise data centers, colocation facilities, and edge computing environments. As organizations prioritize uptime, scalability, and operational efficiency, smart racks—equipped with integrated sensors, remote management capabilities, and predictive analytics—are becoming critical components of modern IT infrastructure. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading the way in delivering next-generation solutions. Below are the top 8 smart rack manufacturers shaping the future of intelligent data center management.
Top 8 Smart Rack Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Panduit
Domain Est. 1994
Website: panduit.com
Key Highlights: Panduit develops smarter, scalable network infrastructure and industrial electrical wiring solutions that unlock the full potential of your business….
#2 Eaton: Electrical and Industrial
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton is an intelligent power management company dedicated to improving the quality of life and protecting the environment for people everywhere. We are ……
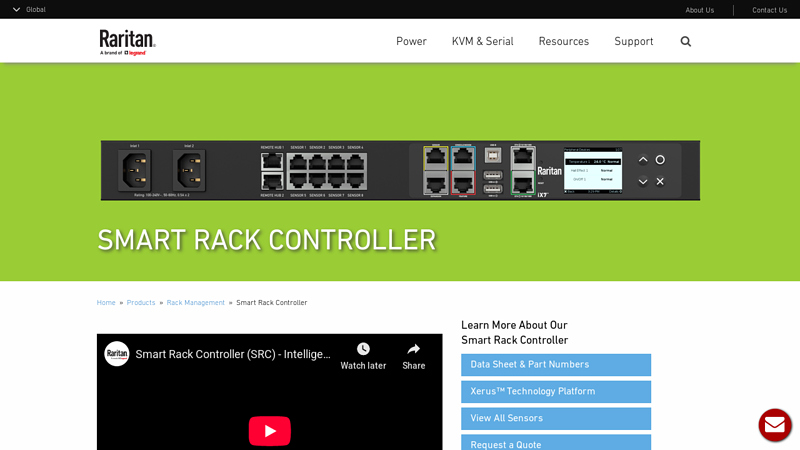
#3 Intelligent Sensor Management
Domain Est. 1995
Website: raritan.com
Key Highlights: Smart Rack Controller (SRC) is an intelligent sensor management solution for environmental conditions, asset location, physical access, and more……
#4 12U Server Rack Cabinet for Harsh Environments, Mid-Depth
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: This SmartRack 12U Mid-Depth Rack Enclosure Cabinet protects sensitive electronic equipment from harsh conditions that would overwhelm a typical rack enclosure….
#5 Rittal
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rittal.com
Key Highlights: IT rack systems. With our flexible system solutions, you will find the perfect rack for your individual requirements, covering all network applications ……
#6 Intertek
Domain Est. 2001
Website: intertek.com
Key Highlights: We deliver unrivalled Total Quality Assurance with precision, pace and passion, enabling our customers to make their businesses stronger….
#7 Ortronics Network Infrastructure Solutions
Domain Est. 2004
Website: legrand.us
Key Highlights: Legrand Ortronics® network infrastructure solutions combine flexibility and efficiency, with superior design, to ensure that facilities operate flawlessly….
#8 Smartrack
Domain Est. 2005
Website: digitalarmsroom.com
Key Highlights: Smartrack provides advanced asset visibility, RFID, GPS, and real-time tracking solutions for commercial, government, military, and law enforcement ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Smart Rack

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Smart Rack Systems
As we approach 2026, the market for Smart Rack systems—integrated hardware and software solutions that optimize data center infrastructure through intelligent power, cooling, monitoring, and automation—is poised for transformative growth and evolution. Driven by the rapid expansion of edge computing, the rise of AI-driven workloads, sustainability mandates, and the increasing need for operational efficiency, Smart Rack adoption is accelerating across enterprise, colocation, and hyperscale environments.
-
Increased Adoption in Edge Computing
By 2026, the proliferation of edge data centers—supporting applications in manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and smart cities—will drive demand for compact, self-sufficient Smart Racks. These racks will integrate advanced sensors, predictive maintenance capabilities, and autonomous cooling and power management to operate reliably in distributed, often unstaffed locations. Vendors are expected to offer modular, preconfigured Smart Racks tailored for edge use cases, emphasizing plug-and-play deployment and remote management. -
AI-Optimized Infrastructure Management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will play a central role in Smart Rack operations. By 2026, AI-driven analytics platforms will be embedded within Smart Rack ecosystems to forecast power usage, prevent thermal hotspots, and dynamically allocate resources. These systems will enable self-healing capabilities—automatically adjusting fan speeds, rerouting power, or alerting operators to potential failures—thereby reducing downtime and improving energy efficiency. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Imperatives
With global data center energy consumption expected to rise significantly, regulatory and corporate sustainability goals will push Smart Rack vendors to enhance energy efficiency. Innovations such as liquid cooling integration, real-time PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) monitoring, and dynamic load balancing will become standard. Smart Racks will increasingly support renewable energy integration and participate in demand-response programs, aligning with net-zero commitments. -
Convergence of IT and Facilities Management
The traditional silos between IT and facilities operations will continue to dissolve. Smart Racks will act as a bridge, providing unified visibility into both server performance and physical infrastructure (power, cooling, security). By 2026, integrated Digital Twin models of data centers—powered by Smart Rack telemetry—will enable simulation, optimization, and capacity planning in real time, improving operational agility. -
Standardization and Interoperability
As the Smart Rack market matures, industry standards for communication protocols (e.g., Redfish, SNMP, Modbus) and data formats will gain broader adoption. This will enable multi-vendor interoperability and support hybrid environments. Open APIs will allow seamless integration with DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management) and cloud orchestration platforms, fostering ecosystem collaboration. -
Growth in Hyperscale and Colocation Deployments
Hyperscalers and colocation providers will increasingly deploy Smart Racks at scale to maximize density and efficiency. Custom-designed Smart Racks with telemetry-rich components and centralized management platforms will become the norm. These deployments will emphasize scalability, security, and remote diagnostics to support global operations. -
Cybersecurity Integration
With increased connectivity comes heightened cybersecurity risks. By 2026, Smart Racks will incorporate embedded security features such as secure boot, hardware-based encryption, and zero-trust access controls. Continuous monitoring for anomalous behavior—both in IT loads and infrastructure sensors—will be critical to safeguarding the physical and digital layers.
Conclusion
The 2026 landscape for Smart Rack systems will be defined by intelligence, integration, and sustainability. As data centers evolve into dynamic, responsive environments, Smart Racks will transition from isolated units to integral nodes in a larger, intelligent infrastructure network. Vendors that prioritize interoperability, AI-driven automation, and energy efficiency will lead the market, while enterprises that adopt Smart Racks strategically will gain competitive advantages in reliability, cost management, and environmental stewardship.
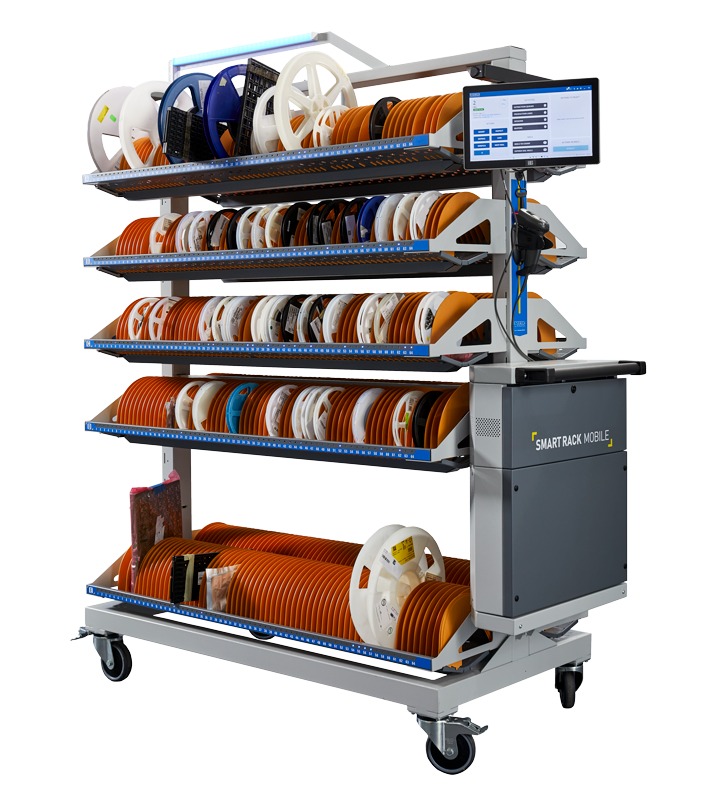

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Smart Racks: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Smart Racks—integrated IT infrastructure solutions that combine power, cooling, monitoring, and management—can offer significant operational benefits. However, organizations often encounter critical pitfalls related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) that can undermine long-term performance, security, and compliance. Being aware of these risks is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
Poor Build Quality and Component Reliability
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing Smart Racks, especially from lesser-known or offshore suppliers, is inconsistent build quality. Substandard materials, inadequate thermal management, poor cable management, and unreliable power distribution units (PDUs) can lead to system failures, increased downtime, and higher total cost of ownership. It’s crucial to verify manufacturing standards, certifications (such as UL, CE, or ISO), and conduct thorough site or third-party audits before finalizing procurement.
Lack of IP Ownership and Proprietary Software Lock-In
Many Smart Rack solutions are bundled with proprietary monitoring and management software. A key pitfall arises when buyers do not fully understand or secure rights to use, modify, or integrate this software. Vendors may retain full IP rights, leading to vendor lock-in, limited customization, and dependency on the supplier for updates or support. Always review software licensing agreements and, where possible, negotiate access to APIs or source code escrow to avoid long-term constraints.
Inadequate Cybersecurity and Firmware Vulnerabilities
Smart Racks often include IoT-enabled sensors and controllers that communicate across networks. If the firmware is poorly secured or based on unlicensed or open-source software with known vulnerabilities, it can expose the entire IT environment to cyber threats. Ensure that vendors comply with cybersecurity standards and provide regular, documented firmware updates. Verify whether the firmware and embedded software respect open-source licenses and do not infringe on third-party IP.
Hidden IP Infringement in Design and Technology
Some Smart Rack manufacturers may incorporate patented technologies—such as thermal regulation systems, intelligent load balancing, or remote monitoring algorithms—without proper licensing. Purchasing such products can expose the end-user to legal liability for contributory infringement. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s design origins and request documentation proving freedom to operate (FTO) regarding key technologies.
Insufficient Documentation and Support for Future Maintenance
Poor quality extends beyond hardware—it includes incomplete technical documentation, lack of accessible schematics, or absence of training materials. Without clear documentation, future maintenance, upgrades, or troubleshooting become difficult, especially if the original vendor discontinues support. Ensure that contracts include clauses requiring comprehensive documentation and long-term technical support, particularly if IP rights to the system design are not fully transferred.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, organizations should prioritize vendors with transparent supply chains, verifiable quality controls, and clear IP policies. Conducting thorough technical and legal due diligence—potentially involving third-party experts—can prevent costly issues down the line and ensure that Smart Rack investments deliver secure, scalable, and sustainable value.
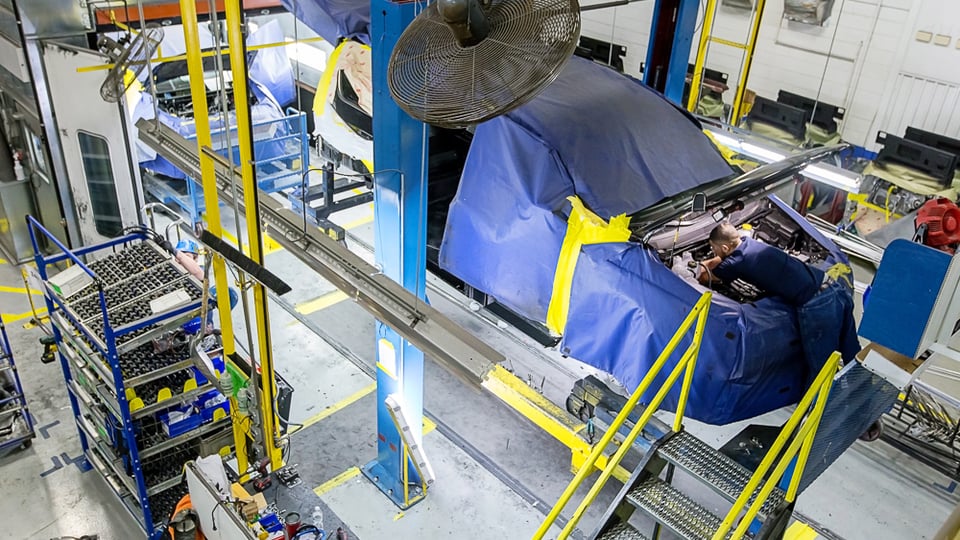

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Smart Rack
This guide outlines the logistics processes and compliance requirements for the Smart Rack system to ensure efficient operations, regulatory adherence, and seamless integration across supply chain functions.
Product Specifications and Packaging
The Smart Rack is a modular, IoT-enabled storage solution designed for industrial environments. All units must be shipped in standardized, recyclable packaging that meets ISTA 3A performance testing standards. Each package must include:
– Product model and serial number
– Weight and dimensions label
– “Fragile – Electronic Components” handling instructions
– Compliance labels (CE, FCC, RoHS)
Shipping and Transportation
Smart Racks are shipped via freight carriers using palletized loads. Standard lead time for delivery is 5–7 business days within the continental U.S. International shipments require customs documentation and must comply with Incoterms® 2020 (typically DDP for end customers). Carriers must provide real-time GPS tracking and proof of delivery.
Import/Export Compliance
All international shipments must adhere to export control regulations, including:
– U.S. Department of Commerce Export Administration Regulations (EAR)
– EU Dual-Use Regulation
– Accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification (e.g., 8431.49 for industrial racking components)
– Required export licenses for restricted destinations
Prohibited countries include those under OFAC sanctions.
Regulatory Certifications
Smart Rack systems must maintain valid certifications for all markets:
– CE marking (EU): Compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive 2014/30/EU
– FCC Part 15 Class A (U.S.): For embedded wireless communication modules
– RoHS and REACH (EU): Restricted substances compliance
– CSA certification (Canada): For electrical safety
Certificates must be renewed annually and available upon request.
Installation and Safety Compliance
Installation must be performed by certified technicians following OSHA and ANSI MH16.1 safety standards for industrial racking. Load capacity signage must be affixed to each unit. Post-installation inspections are required, with documentation retained for audit purposes.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
Smart Racks collect operational data via IoT sensors. Compliance with GDPR (for EU), CCPA (for California), and other applicable data privacy laws is mandatory. Data transmissions must be encrypted (TLS 1.2+), and access controls enforced. Regular cybersecurity audits must be conducted to meet ISO/IEC 27001 standards.
Warranty and Returns Logistics
Smart Rack offers a 3-year limited warranty. Returns require a pre-authorized RMA number. Defective units must be returned in original packaging with a completed return form. Reverse logistics are managed through designated regional hubs with 14-day processing windows.
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
End-of-life Smart Rack components must be recycled in accordance with WEEE Directive (EU) and applicable state regulations (e.g., California’s Electronic Waste Recycling Act). Take-back programs are available. Packaging materials must contain at least 75% recycled content.
Audit and Documentation Requirements
All logistics and compliance activities must be documented and retained for a minimum of 7 years. Records include:
– Shipping manifests and customs forms
– Certification documentation
– Installation and inspection reports
– Data processing agreements
– Audit trails for system access
Regular internal audits ensure alignment with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards.
In conclusion, sourcing a smart rack system represents a strategic investment in enhancing operational efficiency, inventory accuracy, and overall supply chain visibility. By carefully evaluating key factors such as scalability, integration capabilities with existing systems (e.g., WMS or ERP), real-time tracking features, and total cost of ownership, organizations can select a solution that aligns with their current needs and future growth objectives. Engaging with reputable suppliers, conducting thorough pilot testing, and considering after-sales support and maintenance will further ensure long-term success. Ultimately, the right smart rack system not only optimizes storage and retrieval processes but also drives smarter decision-making through data-driven insights, positioning businesses for greater agility and competitiveness in an evolving industrial landscape.