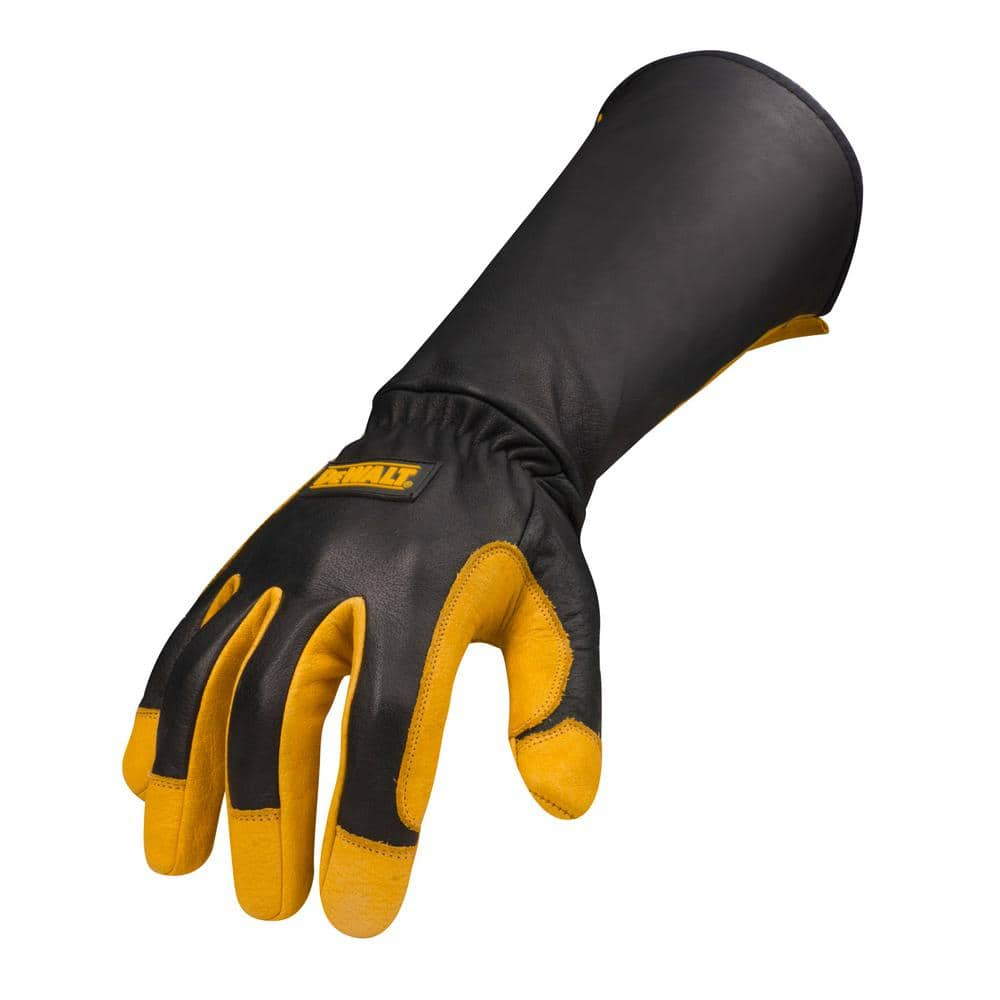
The global welding gloves market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global welding equipment market—of which personal protective equipment (PPE) like welding gloves is a critical component—was valued at USD 11.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory underscores the rising focus on worker safety and the need for high-performance protective gear. As large manufacturers dominate supply chains, a new wave of small, agile welding glove producers is emerging, offering specialized designs, improved dexterity, and advanced materials tailored to niche applications. These smaller manufacturers are gaining traction by prioritizing innovation, customization, and faster time-to-market—key differentiators in a competitive landscape. Below, we spotlight the top nine small welding gloves manufacturers making significant strides in quality, technology adoption, and market responsiveness.
Top 9 Small Welding Gloves Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 About RAPICCA INC.
Domain Est. 2019
Website: rapicca.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsFounded in Gardena,California in 2014, RAPICCA provide a wide range of hand protection solutions. At RAPICCA, we believe safety is not a luxury – it’s a…
#2 Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1993
#3 Welders Gloves
Domain Est. 1995
Website: airgas.com
Key Highlights: Welding gloves in multiple types of leather can be found at Airgas for the hand and heat protection you need when MIG, TIG or Stick welding….
#4 Welders Gloves and Hand Protection
Domain Est. 1996
Website: millerwelds.com
Key Highlights: Improve comfort and dexterity with Miller welding gloves. Our three-dimensional pattern provides the fit welders demand. Explore now….
#5 Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lincolnelectric.com
Key Highlights: Full Leather construction for general purpose steel fabricator work or light welding. Available in sizes Small to 2XL. Compare. JESSI COMBS ……
#6 Premium Quality Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wellslamont.com
Key Highlights: For ultimate protection and ease of use during TIG and MIG welding, shop Wells Lamont’s line of premium-quality welding gloves. Find your perfect fit today….
#7 Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1997
#8 Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1997
#9 Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1999
Website: stauffersafety.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 30-day returnsWelding Gloves – Choose from Stauffer’s selection of Welding products. We offer welding apparel such as Gloves, Helmets, Eyewear, Caps, Goggles…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Small Welding Gloves

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Small Welding Gloves
The global market for small welding gloves is poised for steady growth and strategic evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and heightened safety awareness. Key trends shaping this niche segment include:
1. Rising Demand for Advanced Material Innovation:
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to increasingly adopt high-performance materials such as engineered aramids (e.g., Kevlar®), modacrylic blends, and inherently flame-resistant (FR) fabrics. These materials offer superior heat resistance, dexterity, and durability—critical for small gloves that must balance protection with precision. Innovations like heat-reflective coatings and moisture-wicking liners will enhance comfort and extend glove lifespan, particularly in automated or semi-automated welding environments.
2. Growth in Precision and Automation-Driven Manufacturing:
As industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics continue to adopt robotic and semi-automated welding systems, there is a growing need for specialized small gloves. These gloves cater to technicians performing delicate tasks such as TIG welding, rework, and quality inspections where fine motor control is essential. The trend supports demand for gloves with fingertip sensitivity, ergonomic design, and consistent sizing tailored to smaller hand profiles.
3. Expansion of E-commerce and Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Channels:
Online retail platforms and industrial supply e-marketplaces are expected to dominate distribution by 2026. This shift enables brands to reach smaller workshops, independent welders, and hobbyists more effectively. Customization options—such as size-specific fittings and brand personalization—are likely to become more prevalent through digital channels, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
4. Emphasis on Ergonomics and User-Centric Design:
With increasing focus on worker well-being and productivity, ergonomic design will be a key differentiator. Small welding gloves in 2026 are projected to feature anatomical shaping, pre-curved fingers, and improved breathability to reduce hand fatigue during prolonged use. Brands investing in anthropometric research to better fit diverse hand sizes—particularly for female and younger welders—will gain competitive advantage.
5. Regulatory and Safety Compliance Pressures:
Stricter occupational health and safety regulations, especially in North America and Europe, will drive adoption of certified protective gear. By 2026, compliance with standards such as ANSI/ISEA 138 (impact protection) and EN 12477 (welding gloves) will be non-negotiable. This ensures small gloves meet rigorous performance thresholds for heat, abrasion, and cut resistance, even at reduced sizes.
6. Sustainability and Eco-Conscious Manufacturing:
Environmental responsibility is emerging as a market differentiator. Leading suppliers are anticipated to introduce recyclable packaging, bio-based materials, and take-back programs. Transparency in supply chains and reduced chemical usage in tanning and finishing processes will appeal to environmentally conscious industrial buyers.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the small welding gloves market will be defined by a fusion of safety, precision, and comfort. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate with advanced materials, adapt to automation trends, and meet the ergonomic and regulatory demands of a modern welding workforce. Brands that prioritize fit, functionality, and sustainability are best positioned to capture growth in this specialized segment.
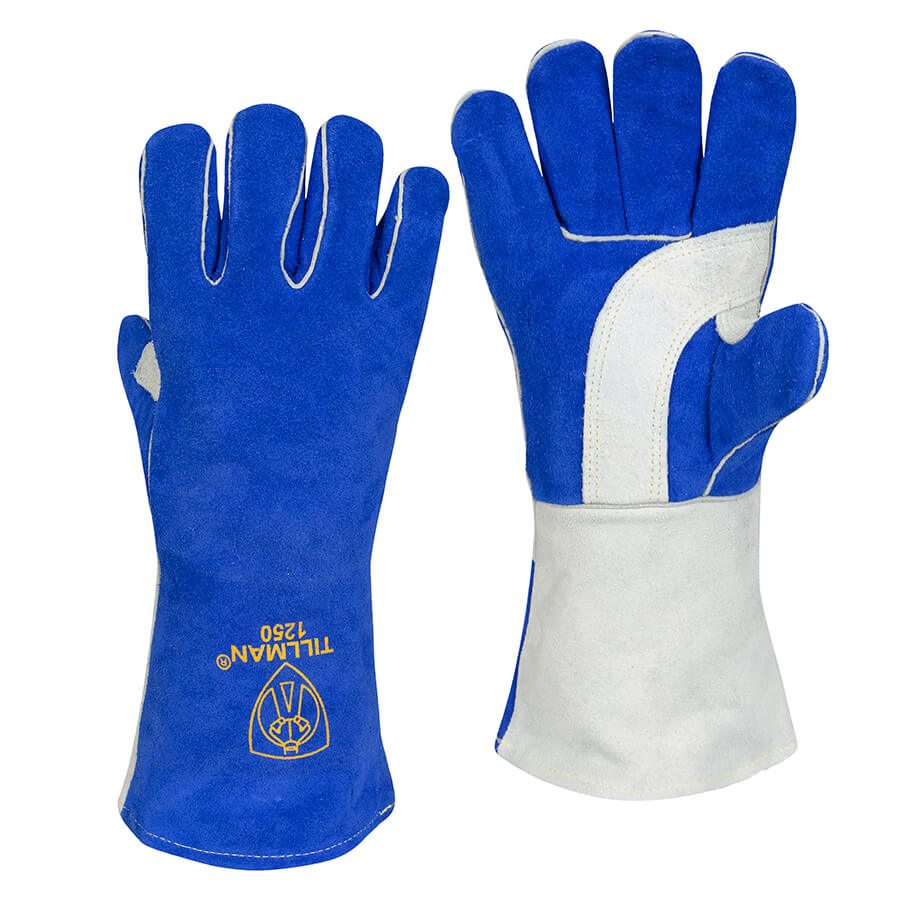

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Small Welding Gloves (Quality, IP)
Sourcing small welding gloves—particularly for specialized or precision welding tasks—requires careful attention to quality and safety standards. Buyers often encounter several pitfalls that can compromise worker safety, performance, and compliance. Below are the most common issues related to quality and impact protection (IP) when sourcing small-sized welding gloves:
1. Compromised Heat and Flame Resistance
Many low-cost small welding gloves use inferior leather or synthetic materials that degrade quickly under high heat. This is especially problematic in small sizes, where manufacturers may cut corners to maintain dexterity, sacrificing protective qualities. Always verify that gloves meet recognized standards like EN 12477 (Type A or B) for heat and flame resistance.
2. Inadequate Dexterity Leading to Safety Risks
While small gloves aim to improve precision, poor design can result in excessive bulk or stiff materials, reducing tactile sensitivity. This forces welders to remove gloves during fine work, increasing exposure to sparks and molten metal. Ensure gloves balance flexibility with protection, particularly in finger and palm areas.
3. Lack of Impact Protection (IP) Compliance
Some small welding gloves are marketed without proper impact protection ratings (e.g., EN 13594 or ANSI/ISEA 138). In environments with pinch or crush hazards, this omission creates a serious safety gap. Always confirm whether gloves are tested and certified for impact resistance, especially if used in industrial or fabrication settings.
4. Inconsistent Sizing and Fit
Small gloves often suffer from inconsistent sizing across brands. A glove labeled “small” may not fit true-to-size or may restrict movement. Poor fit reduces control and increases fatigue, raising the risk of accidents. Request sizing charts and samples before bulk ordering.
5. Poor Stitching and Seam Integrity
Low-quality stitching using non-flame-resistant thread can fail under heat or stress. In small gloves, tighter stitching patterns are more prone to defects if not manufactured precisely. Inspect seams closely and ensure aramid or Kevlar thread is used for durability.
6. Misleading Claims and Lack of Certification
Suppliers may advertise gloves as “heat-resistant” or “industrial-grade” without providing test reports or certification marks. Always request documentation for standards compliance (e.g., CE, ANSI) and beware of vague marketing language.
7. Shortened Lifespan Due to Thin Materials
To enhance flexibility in small sizes, some manufacturers use thinner leather or fewer protective layers. This reduces glove longevity and increases replacement costs. Evaluate material thickness and layering to ensure durability without sacrificing comfort.
8. Incompatibility with Other PPE
Small gloves may not integrate well with other personal protective equipment (e.g., sleeves or arm guards), leaving gaps in coverage. Ensure gloves provide adequate wrist coverage and are designed to work seamlessly within a full PPE system.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers, request test certifications, and conduct field trials. Prioritizing certified quality and verified impact protection ensures that small welding gloves deliver both safety and functionality.
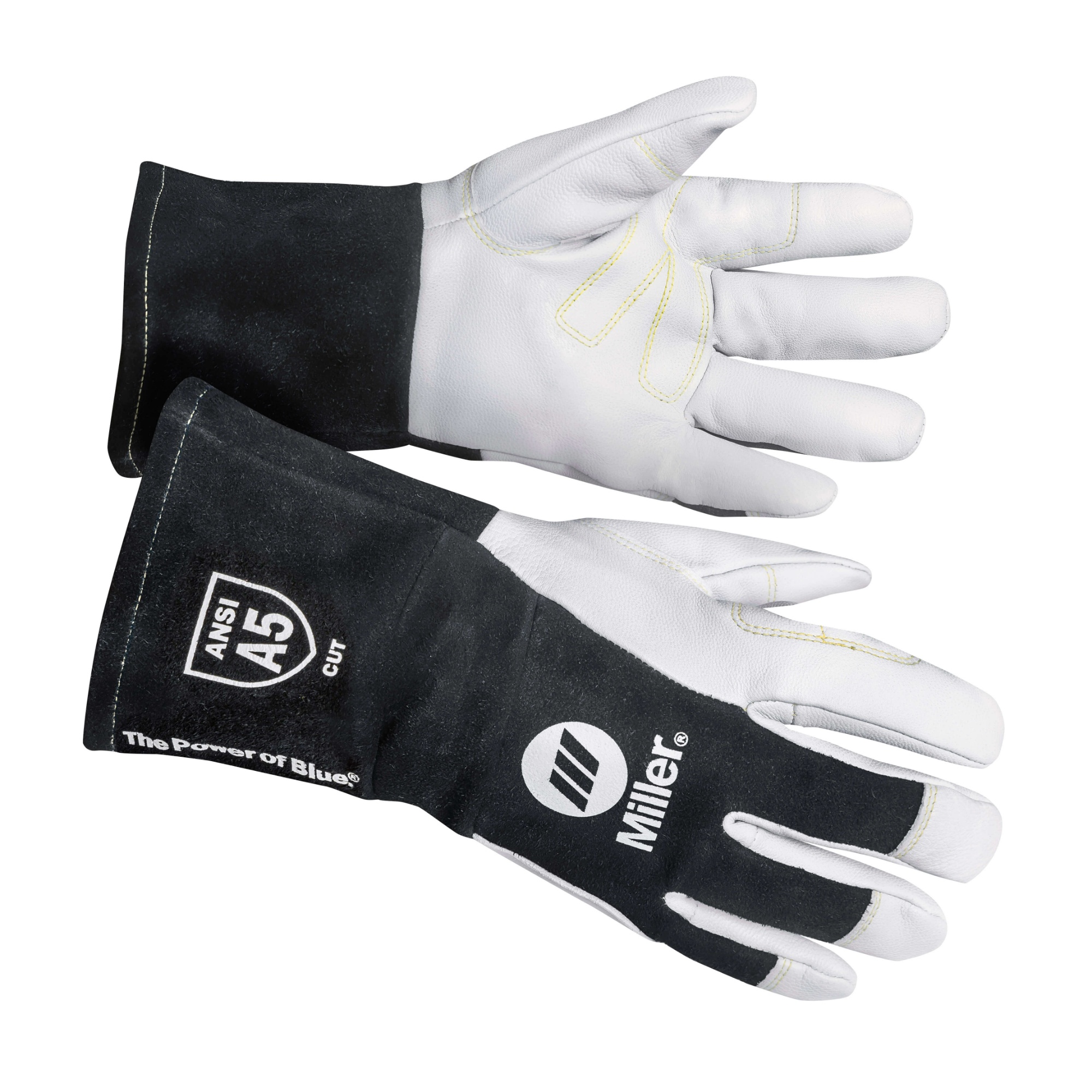

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Small Welding Gloves
Product Classification & HS Code
Small welding gloves are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 6216.00, which covers gloves, mittens, and mitts made of leather, textile, or other materials suitable for protective purposes. Accurate classification is essential for international shipping, customs clearance, and duty assessment. Confirm the exact code with local customs authorities or a trade compliance expert, as variations exist based on material composition (e.g., leather vs. synthetic).
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Ensure small welding gloves are packaged in durable, moisture-resistant materials to prevent damage during transit. Each unit or batch should include:
– Product name and size (“Small Welding Gloves”)
– Manufacturer or brand name
– Material composition (e.g., “100% Cow Split Leather, Kevlar Stitching”)
– Care instructions and usage warnings
– Compliance markings (e.g., CE, EN 12477 for Europe)
– Batch/lot number and date of manufacture
Retail packaging must comply with destination country labeling laws, including language requirements and safety warnings.
Import/Export Documentation
Key documents required for international trade include:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed product description, value, quantity, and HS code)
– Packing List (itemizing contents per package)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (if claiming preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS), if applicable for treated materials
Ensure all documents are accurate and consistent to avoid customs delays or penalties.
Safety & Regulatory Compliance
Small welding gloves must meet regional safety standards:
– European Union: Comply with Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Regulation (EU) 2016/425 and carry CE marking. Must meet EN 12477 (welding gloves standard), specifying performance levels for heat, flame, and mechanical resistance.
– United States: No federal certification required, but gloves should meet ANSI/ISEA 105-2016 for hand protection and OSHA recommendations. Voluntary ASTM F2877-19 compliance enhances market acceptance.
– Canada: Comply with CSA Z94.3-2020 for industrial protective gloves; CSA-certified gloves are preferred for workplace safety compliance.
– Australia/New Zealand: Follow AS/NZS 2161.3:1999 standards for protective gloves.
Always verify current standards, as regulations may be updated.
Shipping & Handling Considerations
- Use standardized cartons with weight and dimension limits suitable for standard freight handling.
- Label packages with “Fragile” and “Keep Dry” warnings if required.
- For air freight, ensure compliance with IATA regulations—no hazardous materials unless treated with flame retardants requiring special documentation.
- Maintain a cold chain only if gloves contain temperature-sensitive materials (rare).
Storage Conditions
Store in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Avoid contact with oils, solvents, or corrosive substances. Keep in original packaging until distribution to maintain hygiene and compliance integrity.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
Dispose of gloves per local waste regulations. If treated with chemicals (e.g., flame retardants), follow hazardous waste protocols where applicable. Manufacturers should provide disposal guidance in product documentation to support end-user compliance.
Recordkeeping & Audits
Maintain records of compliance certifications, test reports, shipment documentation, and supplier audits for a minimum of 5 years (or per regional requirements). These are essential for regulatory inspections and quality assurance.
In conclusion, sourcing small welding gloves requires careful consideration of material quality, heat resistance, dexterity, and proper sizing to ensure both safety and comfort for users with smaller hands. It is essential to prioritize reputable suppliers who offer certified protective gear compliant with relevant safety standards such as EN 12477 or ANSI. Evaluating options based on durability, user feedback, and cost-effectiveness will help identify the best value solution. By focusing on specialized suppliers or customizable options, businesses can ensure that all welders—regardless of hand size—receive reliable protection and optimal performance, ultimately contributing to a safer and more efficient working environment.