The global market for cutting tools is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising demand from metal manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global cutting tools market size was valued at USD 29.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing automation, advancements in tool coatings, and the shift toward high-precision machining in small-part fabrication. As manufacturers seek to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and maintain tighter tolerances, the importance of selecting the right small cutting tools—designed for accuracy, durability, and performance in tight spaces—has never been greater. In this context, optimizing tooling selection is not just a matter of operational efficiency but a strategic lever for competitiveness. The following list highlights the top 10 small cutting tools that are enabling metal manufacturers to meet the demands of modern production environments with precision and reliability.
Top 10 Small Cutting Tools For Metal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Lexington Cutter
Domain Est. 2000
Website: lexingtoncutter.com
Key Highlights: Lexington Cutter is a manufacturer of precision carbide-tipped and solid carbide cutting tools. Our products are used primarily for metal removal and ……
#2 Cutting Tools
Domain Est. 2004
Website: samtectools.com
Key Highlights: SAMTEC is focussed on providing standard and customized cutting tools and accessories for improving productivity of niche machining applications….
#3 Kennametal
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kennametal.com
Key Highlights: Kennametal is a leading provider of productivity solutions for metalworking, earth cutting, and wear components, coatings, and powders….
#4 Seco Tools – Cutting Tools solutions company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: secotools.com
Key Highlights: Double Turbo 11 Milling Cutter and indexable inserts. Ideal for daily machining challenges even on smaller machines. Discover more. Seco Assistant….
#5 Cutting Tools
Domain Est. 2000
Website: sumitool.com
Key Highlights: Cutting Tools, Grades, Chipbreakers, External Holders, Boring Bars, Grooving / Cut-off / Threading, Small Tools, Milling, Cutters, Endmills, Drills, CBN/PCD…
#6 Whitney Tool Company
Domain Est. 2002
Website: whitneytool.com
Key Highlights: … Cutting Tools – We are the industry leader in the manufacture of custom Made in the USA – Whitney cutting tools are crafted in America’s heartland, where small ……
#7 Swanstrom Tools USA
Domain Est. 2002
Website: swanstromtools.com
Key Highlights: Swanstrom Tools offers a full spectrum of specialty pliers, cutters, and metal-forming tools for the jewelry industry….
#8 Woodward Fab: Sheet Metal Fabrication Tools
Domain Est. 2003
Website: woodwardfab.com
Key Highlights: Specialize in sheet metal fabrication, metal forming, shaping and metal working tools. Shop best quality Woodward fab’s tools and equipment at best price ……
#9 KYOCERA Precision Tools
Domain Est. 2013
Website: kyoceraprecisiontools.com
Key Highlights: Precision cutting tools for milling, turning, and holemaking operations in the automotive, aerospace, medical, energy, and PCB industries….
#10 MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORPORATION
Domain Est. 2022
Website: mmc-carbide.com
Key Highlights: Check out our online store! Browse and buy cutting tools for your drilling, milling, and turning machining needs! Check out our online store!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Small Cutting Tools For Metal

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Small Cutting Tools for Metal
The global market for small cutting tools for metal is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving manufacturing demands, and shifting industrial priorities. These tools—typically defined as drills, end mills, taps, reamers, and other precision instruments under a specific diameter (often ≤25 mm)—are critical in high-precision industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical device manufacturing, and mold & die. The H2 2026 outlook reveals several key trends shaping the sector.
-
Increased Demand for High-Precision and Micro-Cutting Tools
As industries adopt miniaturization and tighter tolerances—particularly in electronics and medical sectors—demand for micro-cutting tools with diameters below 1 mm is rising. Advancements in tool coating (e.g., diamond-like carbon and nano-layered PVD coatings) and substrate materials (e.g., ultra-fine carbide) are enabling longer tool life and improved performance at smaller scales. -
Adoption of Smart and Digital-Enabled Tools
The integration of IoT and digital twin technologies is beginning to influence small cutting tools. By 2026, tool manufacturers are increasingly embedding sensors or offering companion software that tracks tool wear, cutting conditions, and performance analytics. This shift supports predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and enhances machining accuracy in smart factories. -
Growth in Sustainable and Eco-Efficient Solutions
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing demand for tools with longer lifespans, recyclable materials, and reduced need for cutting fluids. Dry and minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) machining are gaining traction, favoring tools with advanced thermal resistance and self-lubricating coatings. -
Regional Shifts in Manufacturing and Supply Chains
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, continues to dominate consumption due to expanding manufacturing bases. However, nearshoring and reshoring trends in North America and Europe—driven by supply chain resilience concerns—are boosting local demand for high-performance small cutting tools, especially in aerospace and EV component production. -
Rise of Advanced Materials and Hard-to-Cut Alloys
The proliferation of high-strength materials (e.g., titanium alloys, Inconel, and hardened steels) in aerospace and energy sectors is driving demand for small cutting tools capable of efficient machining under extreme conditions. Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and cubic boron nitride (CBN) tools are seeing increased use, albeit at higher costs. -
Consolidation and Innovation Among Tool Makers
Major players like Sandvik Coromant, Kennametal, and Mitsubishi Materials are investing heavily in R&D, focusing on multi-functional tools, modular designs, and AI-driven toolpath optimization. Smaller niche manufacturers are responding with agile innovation in specialized applications, such as micro-machining for dental implants. -
Impact of Additive Manufacturing (AM)
While AM reduces the need for traditional cutting in some areas, it simultaneously increases demand for post-processing tools. Small cutting tools are essential for precision finishing of 3D-printed metal parts, creating a complementary growth avenue by 2026.
In conclusion, the H2 2026 outlook for small metal cutting tools reflects a market evolving toward higher precision, digital integration, and sustainability. Manufacturers that innovate in material science, smart tooling, and application-specific solutions are best positioned to capture value in this dynamic landscape.
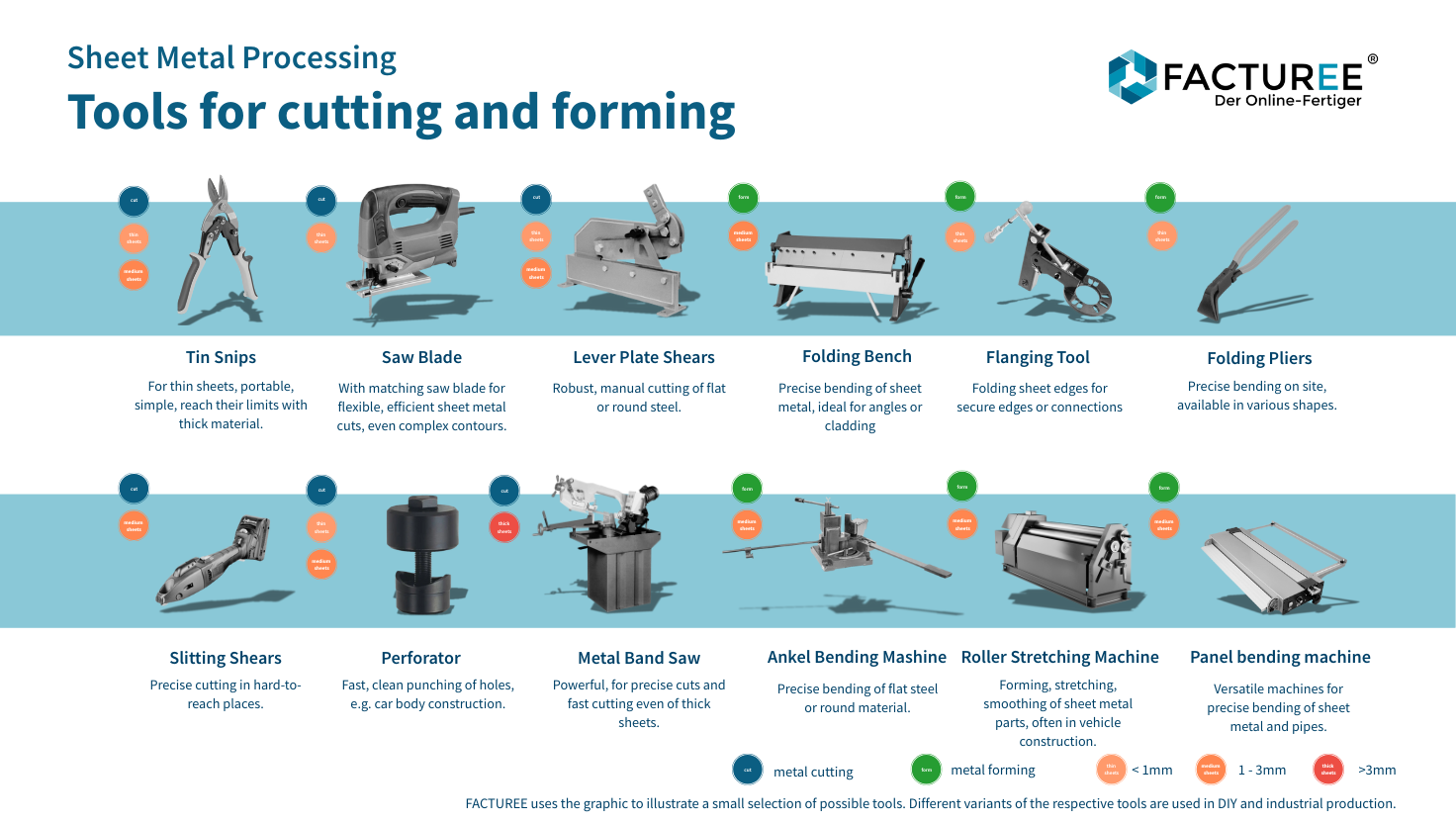
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Small Cutting Tools for Metal (Quality and IP Concerns)
Sourcing small cutting tools for metal—such as end mills, drills, reamers, taps, and burrs—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to production delays, safety risks, subpar performance, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material and Coating Quality
Many suppliers, especially low-cost offshore manufacturers, use inferior-grade substrates (e.g., low cobalt or inconsistent carbide composition) and apply substandard coatings (e.g., uneven TiN or fake “nano” coatings). This results in rapid tool wear, chipping, or inconsistent cutting performance, increasing downtime and rework costs.
Inaccurate Tool Geometry and Tolerances
Low-quality tools often fail to meet ISO or ANSI tolerances for diameter, concentricity, helix angle, and flute geometry. Even minor deviations can affect surface finish, dimensional accuracy of machined parts, and tool life—particularly in precision CNC applications.
Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Tools
Reputable brands (e.g., Sandvik, Kennametal, Walter) are frequently counterfeited. These knock-offs may bear fake logos, misleading part numbers, or packaging mimicking genuine products. Using such tools exposes buyers to IP infringement risks, voided warranties, and potential liability if failures cause equipment damage or safety incidents.
Lack of Traceability and Certifications
Genuine high-performance tools come with lot traceability, material certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and test reports. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide documentation makes it difficult to verify quality, comply with industry standards (e.g., aerospace AS9100), or conduct root cause analysis after tool failure.
Inadequate Heat Treatment and Grinding Processes
Precision tools require controlled sintering, heat treatment, and CNC grinding. Poor process control leads to internal stresses, micro-cracks, or inconsistent edge prep—issues not visible during inspection but that cause premature failure under load.
Misrepresentation of Tool Performance Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate cutting speeds, feed rates, or tool life based on unrealistic test conditions. Without independent validation or real-world data, buyers may select tools unsuited for their application, leading to poor ROI and production bottlenecks.
Ignoring IP Licensing and Authorized Distribution
Purchasing branded tools through unauthorized distributors or gray market channels may violate licensing agreements. This not only risks receiving counterfeit goods but can also breach procurement policies in regulated industries and invalidate technical support or warranty claims.
Overlooking Post-Sale Support and Technical Expertise
Low-cost suppliers often lack technical teams to assist with tool selection, troubleshooting, or application optimization. This absence of support increases the risk of improper usage and reduces overall machining efficiency.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and prioritizing authorized channels—even at a higher initial cost. The long-term gains in reliability, safety, and compliance far outweigh short-term savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Small Cutting Tools for Metal
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the international trade, storage, and distribution of small cutting tools used in metalworking applications. These tools include items such as drill bits, end mills, taps, reamers, inserts, and burrs.
Import and Export Regulations
Small cutting tools are generally classified under specific Harmonized System (HS) codes, commonly falling within Chapter 82 (Tools, Implements, Cutlery, etc.). Accurate classification is essential to determine applicable duties, restrictions, and compliance requirements. Export controls may apply if tools are deemed dual-use (civilian and military applications), particularly high-precision or hardened tools. Always verify export licensing needs with national authorities (e.g., BIS in the U.S., Export Control Joint Unit in the UK).
Product Classification and HS Codes
Typical HS codes for small metal cutting tools include:
– 8207: Interchangeable tools for hand tools, power-operated tools, or machine tools
– 8201: Hand tools (where applicable)
– 8208: Cutting blades for machines or mechanical appliances
Classification depends on tool type, material (e.g., high-speed steel, carbide, ceramic), and use. Misclassification can lead to customs delays, penalties, or seizure. Consult a customs broker or use official tariff databases to confirm the correct code for your products.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packaging must ensure protection against corrosion, shock, and moisture, especially for carbide or precision-ground tools. Use anti-tarnish paper, sealed plastic wraps, or desiccant packs where necessary. Labels must include:
– Product name and description
– HS code
– Country of origin
– Manufacturer/importer details
– Material composition (e.g., “Carbide Tipped”)
– Safety warnings (if applicable)
Ensure labels meet destination country language and regulatory requirements (e.g., bilingual labeling in Canada).
Transportation and Handling
Use standardized packaging (e.g., boxes, blister packs, trays) suitable for stacking and automated handling. Clearly mark packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.” For air freight, comply with IATA regulations; for sea freight, follow IMDG Code guidelines if hazardous materials (e.g., cutting fluids) are included. Temperature and humidity control may be needed during long transit.
Customs Documentation
Complete and accurate documentation is critical for customs clearance. Required documents typically include:
– Commercial Invoice (with value, quantity, description, HS code)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Export Declaration (as required by exporting country)
Ensure all documents are consistent in product description and declared value to avoid delays.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to relevant safety and environmental standards in both origin and destination markets:
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals — ensure no restricted substances in tool coatings or packaging.
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances — primarily applies to electrical components, but verify if relevant.
– OSHA (U.S.): Workplace safety standards; provide safety data if tools involve hazardous materials.
– Product Safety Standards: Comply with ISO, ANSI, DIN, or JIS standards as applicable.
Tools with moving parts or requiring special handling may need additional safety certifications.
Country-Specific Requirements
Different countries may impose unique requirements:
– China: May require CCC certification for certain power tool accessories; accurate Chinese labeling.
– Russia/Eurasian Economic Union: Requires EAC certification for listed products.
– Brazil: NBR standards and import licensing (SISCOMEX).
– India: May require BIS certification depending on tool type.
Research destination market regulations early in the supply chain process.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Maintain records of all transactions, compliance certifications, test reports, and correspondence for a minimum of 5–7 years, depending on jurisdiction. Implement a traceability system (e.g., batch/lot numbering) to support recalls or audits.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Promote sustainable practices by:
– Using recyclable or biodegradable packaging
– Offering tool recycling programs (especially for carbide)
– Reducing excess packaging
– Complying with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives if applicable
Final Recommendations
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders and customs brokers familiar with industrial tools.
- Conduct regular compliance audits.
- Stay updated on international trade regulation changes.
- Train staff on export controls and safety compliance.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, businesses can ensure smooth international operations and minimize risks associated with the trade of small metal cutting tools.
In conclusion, sourcing small cutting tools for metal requires a careful balance of quality, cost, reliability, and technical specifications. It is essential to identify suppliers that offer durable, precision-engineered tools made from high-performance materials such as carbide,高速钢 (HSS), or coated variants to ensure longevity and consistent performance. Evaluating vendors based on reputation, certification standards (e.g., ISO), and technical support can significantly reduce downtime and improve machining efficiency.
Additionally, considering factors such as lead times, minimum order quantities, and after-sales service contributes to a more resilient supply chain. Leveraging both local and global suppliers—while conducting thorough due diligence—enables procurement teams to secure competitive pricing without compromising on quality. Ultimately, establishing strong partnerships with reliable manufacturers and maintaining inventory flexibility will support operational efficiency and adaptability in dynamic production environments.