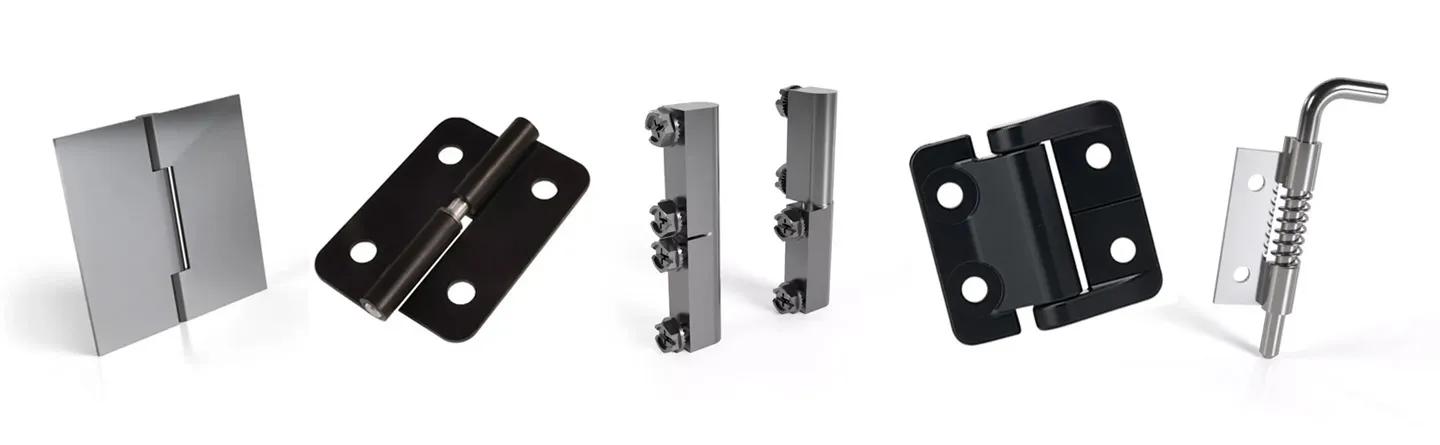
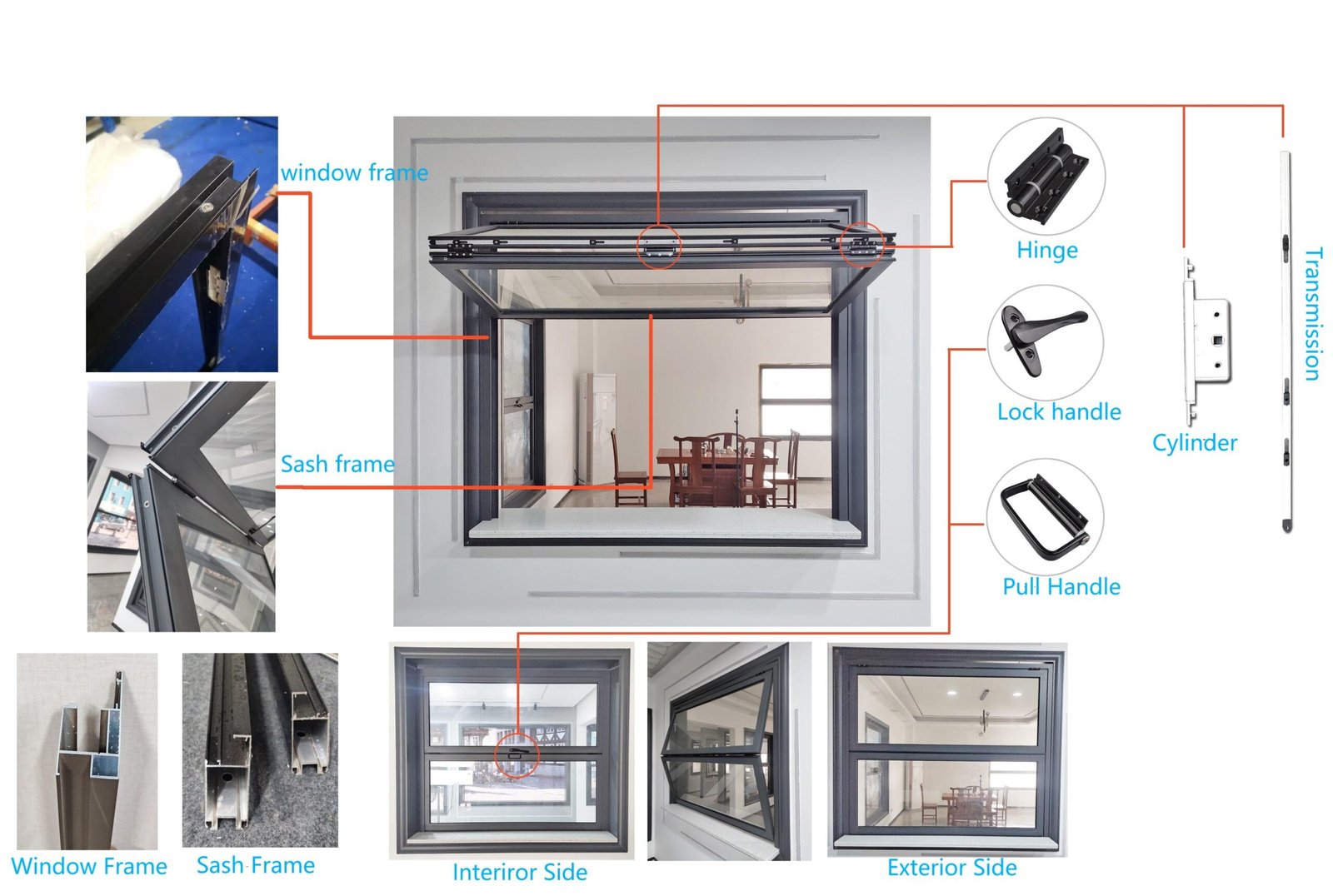
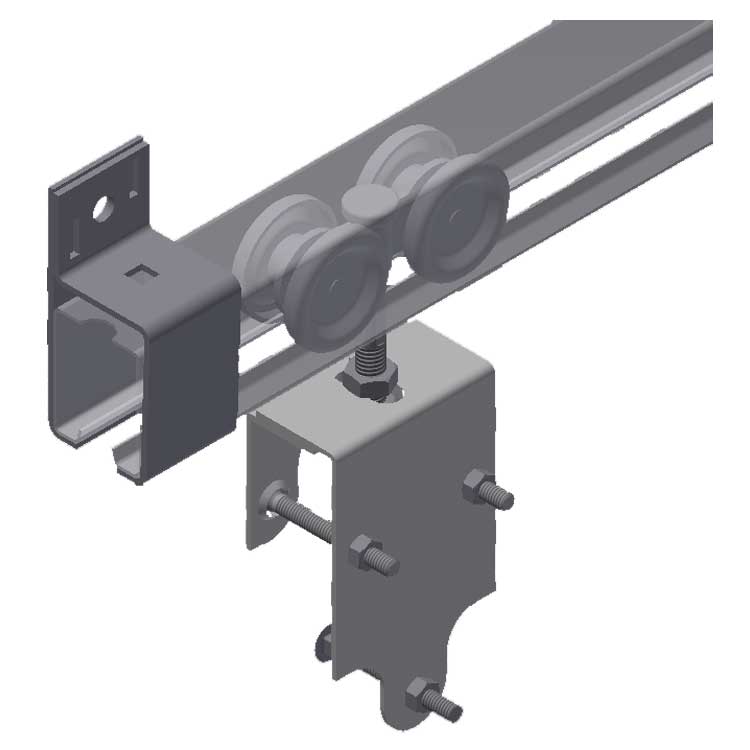
The global sliding hinge mechanisms market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in consumer electronics, automotive, and furniture sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global hinges market size was valued at USD 10.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by innovation in compact and space-saving hardware solutions. Sliding hinges, in particular, are gaining traction due to their ability to enable smooth linear and rotational motion in space-constrained applications such as laptop screens, sliding doors, and medical devices. As industries prioritize ergonomic design and multifunctional mechanisms, manufacturers are investing in high-precision, durable sliding hinge systems. This growing demand has catalyzed competition among leading global suppliers, setting the stage for continuous innovation. Here’s a look at the top 8 sliding hinge mechanisms manufacturers shaping the future of motion control technology.
Top 8 Sliding Hinge Mechanisms Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Window / door technology and building management systems …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: g-u.com
Key Highlights: Opening, moving, closing, securing: The GU Group is a manufacturer of window and door technology, automatic entrance and building management systems….
#2 Hawa Sliding Solutions
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hawa.com
Key Highlights: Hawa Sliding Solutions is the global technology and market leader of sliding hardware for doors, furniture, partition walls and facades. Innovative sliding ……
#3 soft close hinge cabinet door hinge kav furniture hardware,furniture …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: kavhinge.com
Key Highlights: kav Hardware International Co.,Ltd. kav hardware international co.,ltd is the professional manufacturer the cabinet hinges & drawer slides and established in ……
#4 Wide range of sliding door systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hettich.com
Key Highlights: Sliding door systems from Hettich are suitable for doors of various cabinets, but also as a room divider Find out more now!…
#5 Hinges, runners and sliding systems for furniture
Domain Est. 1997
Website: salice.com
Key Highlights: A simple yet reliable mechanism that provides complete door retraction into the compartment. MORE. The linear damping gently controls the movement of the door….
#6 Sliding systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: agb.it
Key Highlights: There are two types of products: lift&slide with a sliding movement for opening and closing of the doors and the coplanar system Galileo that combines a sliding ……
#7 Motion in cabinetry
Domain Est. 1998
Website: blum.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture products such as drawer runners, hinges and lift systems that create an easier workflow for all cabinetry throughout the home….
#8 Hinge Systems
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sametglobal.com
Key Highlights: SAMET Hinge Systems is a well-known name in the furniture accessories industry, providing perfect solutions for all users with a wide variety of products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sliding Hinge Mechanisms

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Sliding Hinge Mechanisms
The global market for sliding hinge mechanisms is poised for substantial transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in smart technology, rising demand for space-efficient designs, and growing applications across consumer electronics, automotive, and architectural sectors. Sliding hinge mechanisms—engineered components that enable linear and rotational motion in devices—have evolved beyond traditional applications to support innovative product functionalities.
One of the dominant trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the integration of sliding hinges into foldable and rollable consumer electronics. With major manufacturers expanding their portfolios of foldable smartphones, laptops, and tablets, demand for durable, compact, and precision-engineered sliding hinge systems has surged. These hinges must support repeated folding motions while maintaining structural integrity, prompting innovations in materials like titanium alloys and advanced polymers, as well as lubrication and anti-wear technologies.
In the automotive sector, sliding hinge mechanisms are increasingly used in electric and autonomous vehicles for features such as gull-wing doors, sliding consoles, and adaptive interior configurations. The push for modular and customizable interiors aligns with consumer preferences for comfort and personalization, further accelerating adoption. Additionally, lightweight hinge designs are gaining traction as automakers strive to reduce vehicle weight and improve energy efficiency.
The architecture and furniture industries are also embracing sliding hinge systems for space-saving solutions in urban living environments. Smart cabinetry, sliding room partitions, and hidden appliance installations are leveraging these mechanisms to maximize functionality in compact spaces. The integration of IoT-enabled actuators with sliding hinges allows for automated, touchless operation—enhancing convenience and accessibility.
From a regional perspective, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, South Korea, and Japan—is expected to dominate the market in 2026 due to robust electronics manufacturing and strong R&D investments. North America and Europe are following closely, driven by demand in smart homes and high-end automotive segments.
Sustainability is another emerging trend. Manufacturers are focusing on recyclable materials and energy-efficient production methods to align with global environmental regulations. Concurrently, the competitive landscape is intensifying, with companies investing in patents for proprietary hinge designs and forming strategic partnerships with OEMs.
In summary, by 2026, the sliding hinge mechanisms market will be characterized by innovation in materials and design, broader cross-industry applications, and a heightened focus on durability, miniaturization, and sustainability—positioning sliding hinges as critical enablers of next-generation product engineering.
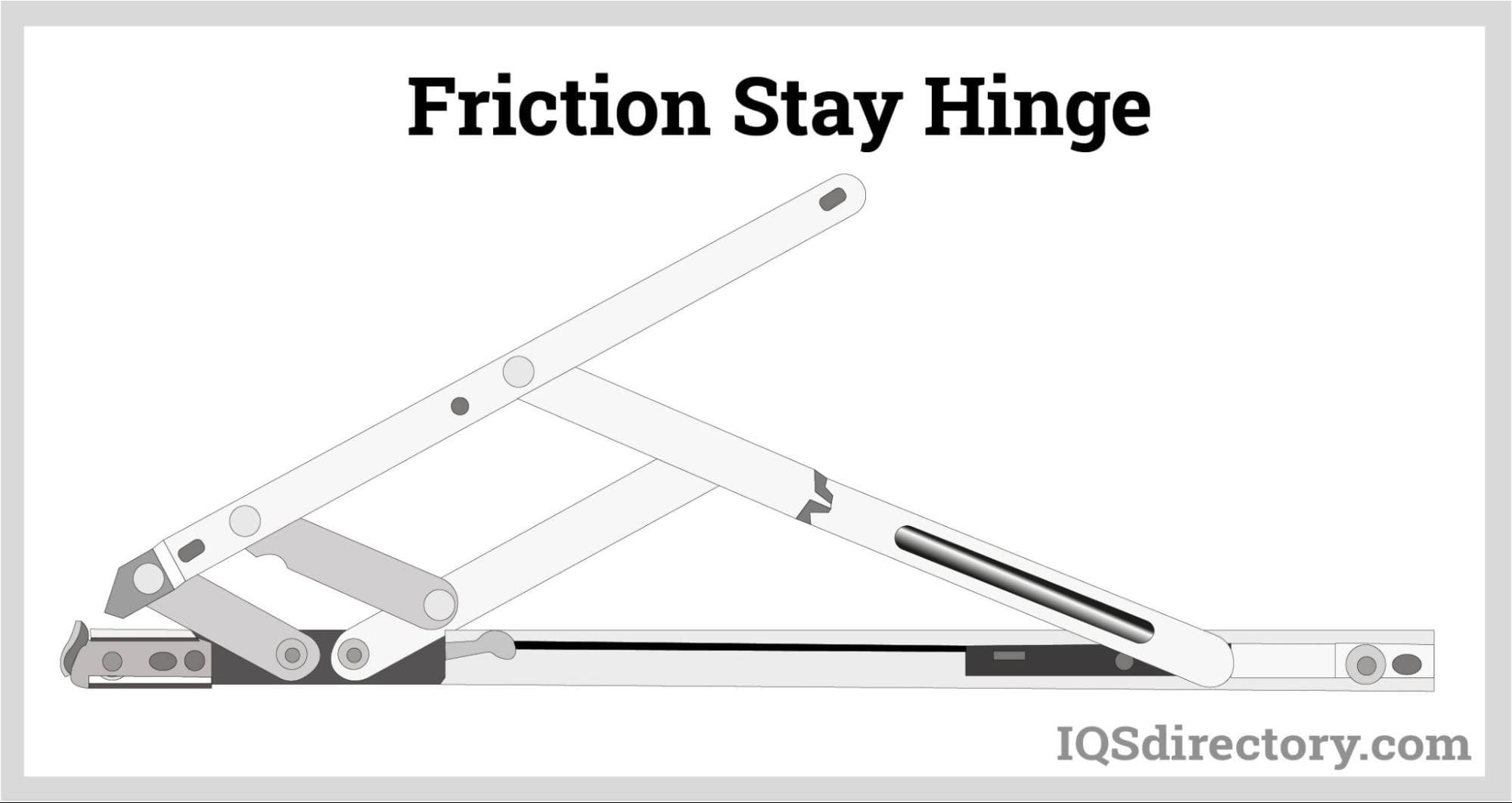
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Sliding Hinge Mechanisms: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing sliding hinge mechanisms—commonly used in laptops, foldable devices, and high-end cabinets—can be fraught with challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to avoid costly delays, product failures, or legal disputes.
Quality Inconsistencies and Material Deficiencies
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing sliding hinge mechanisms is inconsistent quality across production batches. Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, may use substandard materials such as inferior-grade stainless steel or low-tolerance engineering plastics that degrade over time. This results in mechanisms that fail prematurely due to wear, binding, or loss of smooth operation. Additionally, poor manufacturing tolerances can lead to misalignment, wobbling, or inconsistent sliding action, negatively affecting the end-user experience. Without rigorous quality control and third-party testing, these defects may go unnoticed until after integration, causing rework and reputational damage.
Lack of Durability and Fatigue Resistance Testing
Sliding hinges are subject to repeated mechanical stress, making fatigue resistance critical. However, many sourced components lack proper lifecycle testing data. Suppliers may claim high cycle endurance (e.g., 20,000+ open/close cycles), but without verified test reports under real-world conditions, these claims can be misleading. Sourcing hinges without access to independent durability testing increases the risk of field failures, especially in consumer electronics where longevity is a key selling point.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sliding hinge designs, particularly in consumer electronics, often incorporate patented technologies related to the mechanism’s motion, locking features, or integration with device housing. Sourcing from generic suppliers increases the risk of inadvertently procuring IP-infringing components. For example, certain multi-axis sliding and rotating hinge designs are protected by patents held by major OEMs. Using such mechanisms without proper licensing can lead to legal action, product recalls, or customs seizures. Conducting thorough IP due diligence—such as freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis—is crucial before finalizing a supplier.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive technical documentation, including material certifications, dimensional drawings, or test results. This lack of traceability complicates quality assurance and regulatory compliance, especially in industries with strict standards (e.g., medical or aerospace applications). Without clear documentation, it becomes difficult to diagnose failures or ensure consistent performance across supply chains.
Overreliance on Supplier Claims Without Prototyping
A common mistake is accepting hinge performance claims at face value without physical validation. Prototyping and real-world testing are essential to evaluate factors like smoothness, acoustic noise, and long-term reliability. Skipping this step can result in discovering critical flaws only after mass production has begun, leading to costly redesigns and delays.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), request verifiable test data, conduct IP audits, and insist on detailed technical documentation. Investing time in due diligence during the sourcing phase can prevent significant problems down the line.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sliding Hinge Mechanisms
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the transportation, handling, and regulatory adherence of sliding hinge mechanisms used in furniture, cabinetry, electronics enclosures, and similar applications.
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate product classification for international shipping and customs clearance. Sliding hinge mechanisms typically fall under HS (Harmonized System) codes related to hardware, fittings, or mechanical components (e.g., 8302.41 or 8302.49 for base metal mountings). Maintain detailed technical specifications, material composition (e.g., steel, aluminum, plastic), and product drawings. Include safety data sheets (SDS) if applicable, particularly for lubricated components.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Use robust, anti-corrosive packaging to prevent damage during transit. Individual or grouped components should be protected with bubble wrap, foam inserts, or cardboard dividers. For bulk shipments, utilize stackable, moisture-resistant master cartons with clearly labeled orientation indicators (e.g., “This Side Up”). Avoid overpacking to prevent deformation. Clearly mark packages with product codes, batch numbers, and handling instructions to ensure proper storage and traceability.
Transportation and Storage Conditions
Transport sliding hinge mechanisms in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent condensation and rust. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity, which may affect lubricants or material integrity. Store inventory off the ground on pallets in well-ventilated areas. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize aging and obsolescence. Monitor storage conditions regularly, especially in humid climates.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Ensure compliance with relevant international and regional regulations. In the EU, sliding hinge mechanisms may be subject to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, particularly if containing certain metals or coatings. In the U.S., compliance with CPSIA (Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act) may apply if used in consumer goods. Verify that all materials and finishes meet environmental and safety standards applicable to the end-use market.
Import/Export Controls
Check for export licensing requirements based on destination country and material composition—especially if components include controlled materials or dual-use technologies. Use accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin to facilitate customs clearance. Be aware of trade restrictions or tariffs that may apply to shipments involving certain countries or materials.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Implement a quality control process to verify dimensional accuracy, smooth operation, and durability before shipment. Maintain lot traceability through batch coding and documentation to support recalls or compliance audits if necessary. Conduct periodic audits of suppliers and logistics partners to ensure adherence to agreed standards.
End-of-Life and Environmental Responsibility
Design for recyclability where possible, using separable materials and minimizing mixed composites. Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives if integrated into electronic devices. Provide guidance to customers on proper disposal or recycling of hinge mechanisms at end-of-life to support environmental sustainability goals.
Conclusion for Sourcing Sliding Hinge Mechanisms
In conclusion, sourcing sliding hinge mechanisms requires a strategic approach that balances performance, cost, durability, and compatibility with the intended application. After evaluating various suppliers, materials, design specifications, and manufacturing capabilities, it is evident that selecting the right sliding hinge involves careful consideration of load capacity, smoothness of motion, corrosion resistance, and ease of integration.
Prioritizing suppliers with a proven track record in precision engineering and quality control ensures reliability and long-term functionality. Additionally, engaging with vendors offering customization options and technical support can significantly enhance product performance and reduce integration challenges.
Ultimately, a well-sourced sliding hinge mechanism not only improves the user experience through seamless operation but also contributes to the overall durability and reputation of the final product. By aligning technical requirements with supplier capabilities, organizations can achieve optimal performance while maintaining cost efficiency and scalability in their manufacturing processes.