The global capacitor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, industrial equipment, and renewable energy. According to Mordor Intelligence, the capacitor market was valued at USD 25.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 35.8 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of electric vehicles, advancements in 5G infrastructure, and the proliferation of compact electronic devices requiring efficient energy storage solutions. Amid this growth, the role of key manufacturers in scaling production, innovating materials, and meeting regional demand has become increasingly critical. The following analysis highlights the top eight capacitor manufacturers shaping the industry through strategic capacity expansion, technological leadership, and strong global supply chain integration.
Top 8 Sizing A Capacitor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Chemi
Domain Est. 1996
Website: chemi-con.com
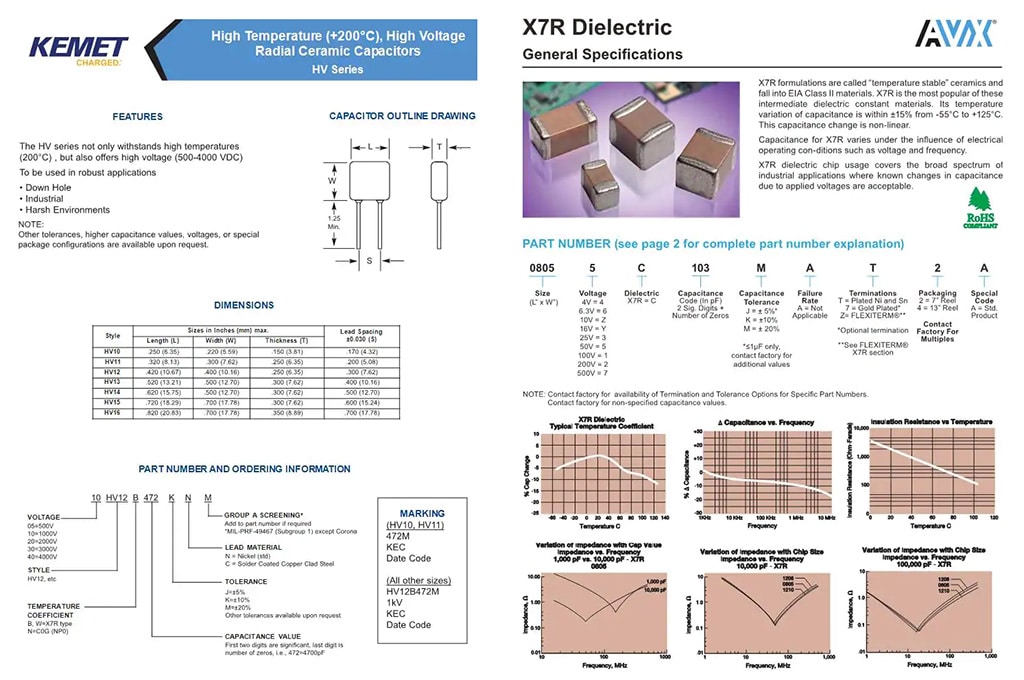
Key Highlights: As North America’s largest supplier of aluminum electrolytic capacitors, CHEMI-CON is uniquely positioned to offer more innovative, customer-centric technology ……
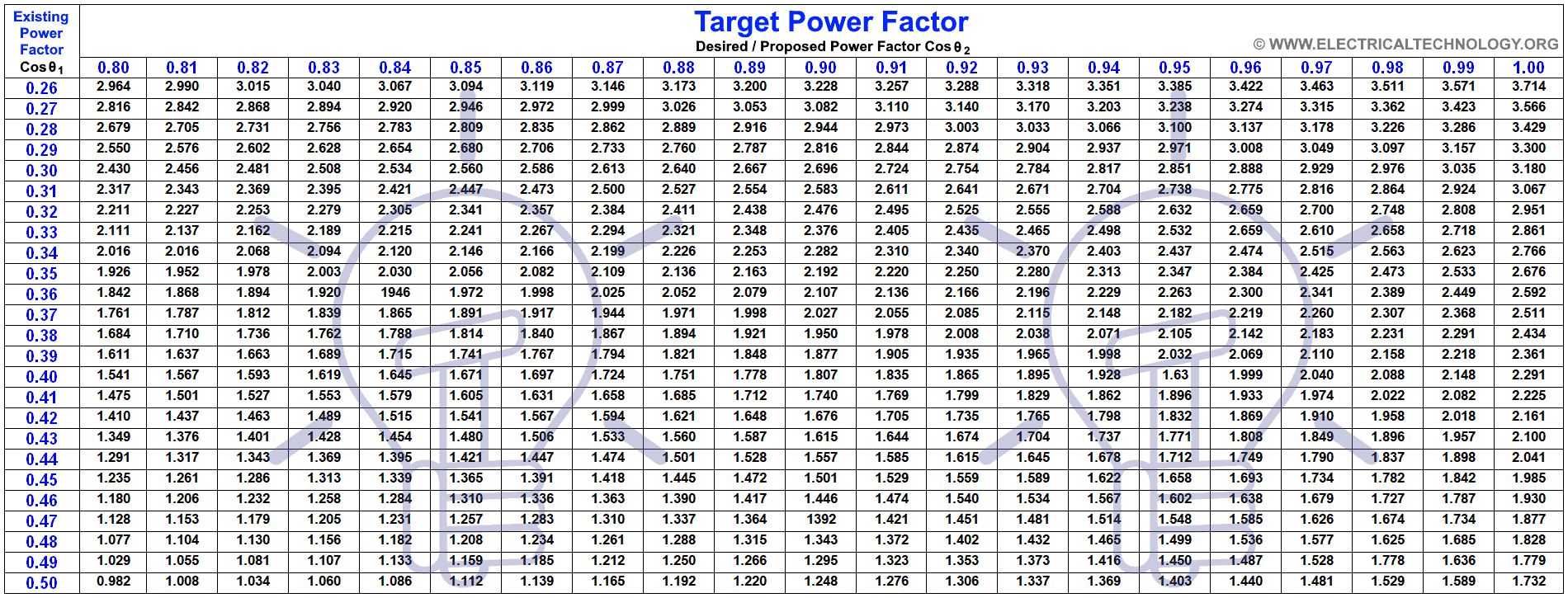
#2 TechTopics No. 20
Domain Est. 1986
Website: siemens.com
Key Highlights: Learn how to size power factor correction capacitors for motors to reduce energy costs, improve efficiency, and minimize electrical system losses….
#3 Capacitor Calculator
Domain Est. 2012
Website: keysight.com
Key Highlights: Discover the ultimate guide to using our capacitor calculator: Calculate capacitance, energy, charge, and more for your electronic projects….
#4 Selection Guide
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: This is Murata’s capacitor selection guide. Please use this guide to select the optimal product from among our various capacitors….
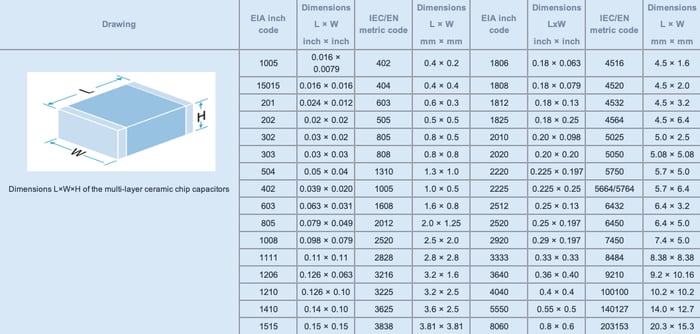
#5 SMD Capacitor Size Charts
Domain Est. 1989
Website: resources.pcb.cadence.com
Key Highlights: Below is the SMD capacitor size chart for the most common type of SMD capacitor: multilayer ceramic SMD capacitors, or MLCCs….
#6 Capacitors Selection Guide
Domain Est. 1996
Website: product.tdk.com
Key Highlights: A Selection Guide for the various capacitors produced by TDK. It includes a product map organized by capacitance and rated voltage, and information such as ……
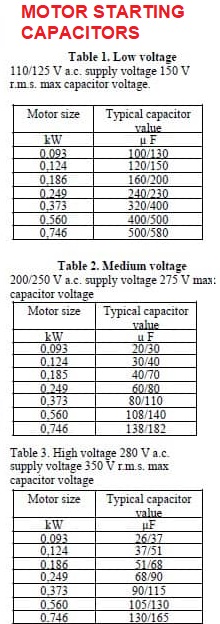
#7 Your Capacitor Sizing Chart Guide for Better Motor Performance
Domain Est. 2013
Website: ic-online.com
Key Highlights: Use a capacitor sizing chart to improve motor performance by matching your motor’s HP and voltage to find the correct MFD rating for a replacement ……
#8 Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor Selection Guide
Domain Est. 2019
Website: zxcompo.com
Key Highlights: Choosing the right multilayer ceramic capacitor can still be a daunting task. This article provides a complete buying guide, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sizing A Capacitor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Sizing a Capacitor
By 2026, the process and market dynamics surrounding capacitor sizing are being reshaped by powerful technological, industrial, and sustainability forces. Key trends influencing how engineers and designers approach capacitor selection and sizing include:
1. Rising Demand in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Energy Storage Systems (ESS):
The explosive growth of EVs and grid-scale battery storage is driving demand for high-performance, high-reliability capacitors—particularly film and electrolytic types. Sizing these capacitors requires careful consideration of voltage transients, ripple currents, thermal management, and lifecycle durability under harsh conditions. Designers are increasingly using advanced simulation tools to model real-world stress and optimize capacitor size for efficiency and longevity.
2. Miniaturization and High-Power Density Requirements:
Consumer electronics, wearables, and compact power supplies continue to demand smaller form factors with higher power delivery. This pushes capacitor sizing toward compact multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) with high volumetric efficiency. Engineers must balance reduced physical size with adequate capacitance, voltage rating, and derating practices to avoid failure under load.
3. Integration of AI and Predictive Sizing Tools:
By 2026, AI-powered design software is becoming mainstream in power electronics. These tools analyze circuit requirements, environmental conditions, and reliability targets to recommend optimal capacitor types and values. Predictive analytics help in derating components appropriately and forecasting failure rates, streamlining the sizing process and reducing design cycles.
4. Emphasis on Reliability and Longevity in Industrial and Automotive Applications:
With increasing use of capacitors in mission-critical systems (e.g., autonomous driving, industrial automation), proper sizing now includes rigorous derating—especially for temperature and voltage. Designers are prioritizing capacitors with extended lifespans and tighter tolerances, supported by standards such as AEC-Q200 for automotive applications.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Material Sourcing:
Ongoing supply chain volatility—especially for raw materials like tantalum and rare earth elements—is influencing capacitor selection. Designers are opting for more readily available alternatives (e.g., niobium or polymer capacitors) and re-evaluating sizing strategies to accommodate second-sourcing and multi-vendor approaches without compromising performance.
6. Sustainability and End-of-Life Considerations:
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are prompting a reevaluation of capacitor materials and lifecycle impacts. Sizing decisions increasingly factor in recyclability, lead-free construction, and reduced use of hazardous substances. Long-life capacitors that reduce replacement frequency are favored, aligning sizing with sustainability objectives.
7. Growth in Wide-Bandgap (WBG) Semiconductor Adoption:
The proliferation of SiC (silicon carbide) and GaN (gallium nitride) devices in power converters introduces faster switching speeds and higher frequencies. This necessitates capacitors with ultra-low ESR and ESL, impacting how engineers size capacitors for effective decoupling and noise suppression in high-frequency circuits.
In summary, by 2026, capacitor sizing is no longer a purely electrical calculation—it is a multidimensional engineering decision influenced by performance, reliability, sustainability, and intelligent design tools. Success requires a holistic approach that integrates component characteristics with system-level demands and market realities.
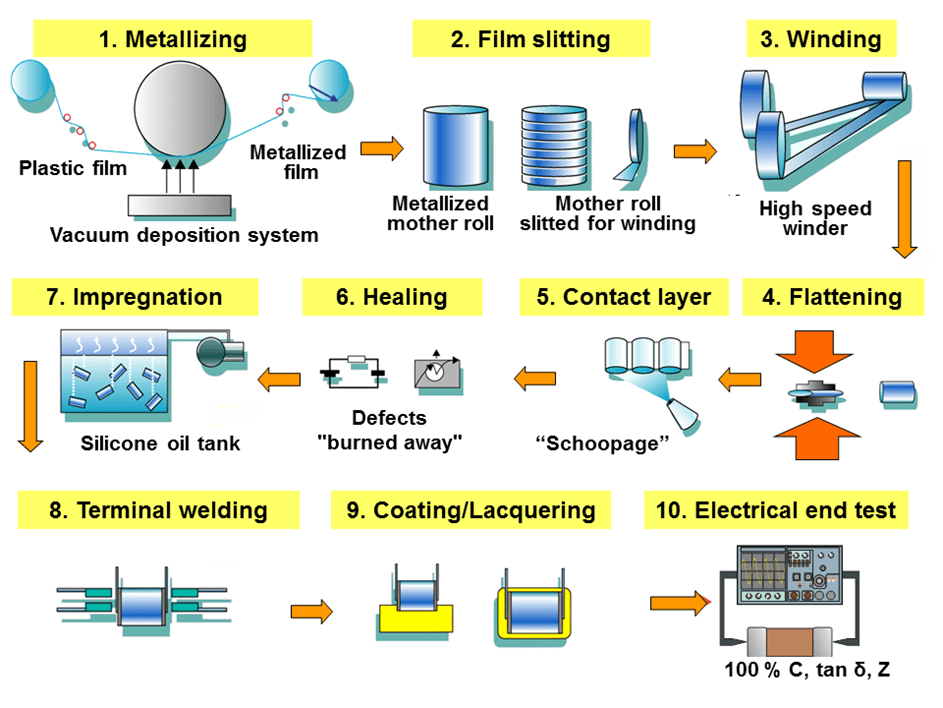
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Capacitor (Focusing on Quality and Intellectual Property)
When sourcing capacitors for electronic designs, overlooking key aspects of quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant issues, including product failures, reliability concerns, and legal complications. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Selecting Low-Quality or Counterfeit Components
One of the most critical risks in capacitor sourcing is inadvertently purchasing counterfeit or substandard parts. These may appear identical to genuine components but fail prematurely due to inferior dielectric materials, incorrect tolerances, or poor manufacturing practices.
– Impact: Reduced product lifespan, field failures, safety hazards, and reputational damage.
– Mitigation: Source exclusively from authorized distributors, verify component traceability, and use independent testing (e.g., X-ray, electrical testing) when high reliability is required.
2. Ignoring Manufacturer Qualification and Certifications
Not all capacitor manufacturers adhere to the same quality standards. Suppliers without proper certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AEC-Q200 for automotive, or IATF 16949) may lack rigorous quality control processes.
– Impact: Inconsistent performance, especially under stress conditions like temperature cycling or voltage surges.
– Mitigation: Prioritize manufacturers with relevant industry certifications and a proven track record in your application domain (e.g., industrial, automotive, aerospace).
3. Overlooking Long-Term Supply Chain Stability
A capacitor may meet technical and quality specs today, but if the manufacturer discontinues it or has unreliable supply chains, your production could halt unexpectedly.
– Impact: Production delays, redesign costs, and obsolescence issues.
– Mitigation: Choose components with long-term availability commitments (LTB—Long-Term Buy), and verify the manufacturer’s product lifecycle policy. Consider second sourcing when possible.
4. Failing to Protect or Respect Intellectual Property
Using capacitor designs or proprietary technologies without proper licensing—or failing to protect your own IP when customizing components—can lead to legal disputes.
– Impact: Infringement lawsuits, forced redesigns, loss of competitive advantage.
– Mitigation: Ensure all custom capacitor designs include clear IP ownership agreements. When using patented technologies (e.g., specialized dielectrics or packaging), confirm licensing is in place.
5. Underestimating the Importance of Data Sheet Accuracy and Transparency
Some suppliers provide incomplete or misleading specifications, especially regarding lifetime, ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance), ripple current, and temperature derating.
– Impact: Design miscalculations, overheating, and premature failure.
– Mitigation: Cross-check datasheet claims with third-party resources or application notes. Request detailed reliability reports and test data directly from the manufacturer.
6. Bypassing Application-Specific Qualification
A capacitor rated for consumer electronics may not perform reliably in harsh environments (e.g., high temperature, vibration, humidity). Using generic parts without application-specific validation is a common oversight.
– Impact: System failure in real-world conditions despite passing lab tests.
– Mitigation: Require application-specific qualification testing (e.g., HALT—Highly Accelerated Life Testing) and select series designed for your operating environment.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, design and procurement teams can ensure that capacitor sourcing supports both product quality and IP integrity throughout the product lifecycle.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sizing a Capacitor
Sizing a capacitor correctly is essential for ensuring the safe, efficient, and compliant operation of electrical systems. This guide outlines the logistical considerations and regulatory compliance requirements involved in selecting and deploying capacitors across industrial, commercial, and utility applications.
Understanding Application Requirements
Identify the specific electrical system needs, including voltage level, load characteristics, power factor correction goals, and harmonic environment. Accurate load profiling and power quality assessments are critical first steps. Logistical planning should include site surveys, load data collection, and coordination with electrical engineers to define capacitor specifications.
Voltage and Capacitance Rating
Select capacitors with voltage ratings that match or exceed the system’s operating voltage, including tolerance for surges. Capacitance must be calculated based on required reactive power (kVAR) using standard formulas (e.g., Q = V²ωC). Ensure components are rated for continuous operation at or above nameplate values to prevent premature failure.
Environmental and Installation Conditions
Assess installation environment for temperature, humidity, altitude, and exposure to contaminants. Capacitors must be installed in well-ventilated areas with adequate spacing for cooling. Compliance with IP (Ingress Protection) ratings and NEMA enclosures may be required based on location (indoor/outdoor, hazardous areas).
Safety Standards and Certifications
Capacitors must comply with recognized safety standards such as:
– IEC 60831 (shunt power capacitors)
– UL 810 (safety standard for capacitors)
– IEEE 18 (application, rating, and testing of AC capacitors)
Ensure products carry valid certifications (e.g., CE, UL, CSA) and are listed in approved equipment directories.
Harmonic Considerations and Resonance
Evaluate system harmonic content before installing capacitors. Improperly sized capacitors can exacerbate harmonic resonance, leading to equipment damage. Use detuned reactors or harmonic filters when necessary. Follow IEEE 519 guidelines for harmonic control in electrical power systems.
Reactive Power Compensation Strategy
Develop a strategic plan for power factor correction—whether fixed, automatic (switched), or dynamic (using contactors or thyristors). Logistical planning includes selecting switching mechanisms, control relays, and protective devices (fuses, disconnect switches) in compliance with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC Article 460, IEC 60364-5-52).
Protection and Coordination
Implement overcurrent, overvoltage, and discharge protection per manufacturer recommendations and electrical codes. Capacitor banks must include discharge resistors or devices that reduce residual voltage to safe levels (<50V) within 5 minutes (IEC 60831-1). Coordination with upstream protective devices is essential.
Labeling and Documentation
Ensure all capacitors are clearly labeled with kVAR rating, voltage, frequency, manufacturer, and safety warnings. Maintain detailed documentation including sizing calculations, one-line diagrams, compliance certificates, and maintenance records for audits and inspections.
Transportation and Handling
Capacitors are sensitive to mechanical shock and orientation. Follow manufacturer handling instructions—avoid tilting or dropping units. Use appropriate lifting equipment and store in dry, temperature-controlled environments prior to installation. Confirm packaging integrity upon delivery.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Schedule periodic inspections for bulging, leaking, or terminal corrosion. Follow preventive maintenance routines aligned with manufacturer guidelines. Track capacitor age and performance; typical service life is 10–15 years. Decommission and replace units proactively to avoid system downtime.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Dispose of failed capacitors in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., RoHS, WEEE) due to potential presence of dielectric fluids or hazardous materials. Use certified e-waste handlers. Maintain records of disposal for compliance audits.
Training and Personnel Qualifications
Only qualified electrical personnel should handle capacitor installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Provide training on capacitor hazards (stored energy, arc flash risks) and lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures per OSHA 29 CFR 1910 or equivalent local regulations.
Final Verification and Commissioning
After installation, verify connections, grounding, and protection settings. Perform insulation resistance and capacitance tests. Energize gradually and monitor performance under load. Document results and update facility electrical records to ensure ongoing compliance and reliability.
Conclusion: Sourcing and Sizing a Capacitor
In conclusion, properly sourcing and sizing a capacitor is a critical step in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of electrical and electronic systems. The process involves a comprehensive understanding of the application requirements, including voltage rating, capacitance value, current handling, temperature range, physical size, and environmental conditions. Key parameters such as Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), ripple current capability, and lifetime expectancy must also be evaluated to match the capacitor to the operational demands.
When sourcing, it is essential to consider reputable manufacturers and suppliers to guarantee quality, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, cost, availability, and lead times should be balanced against performance requirements, especially in high-volume or mission-critical applications.
Improperly sized or low-quality capacitors can lead to premature failure, reduced system efficiency, or even catastrophic circuit damage. Therefore, engineers must carefully analyze circuit behavior—whether for power supply filtering, motor starting, power factor correction, or signal coupling—to select the optimal capacitor type (e.g., electrolytic, ceramic, film, or supercapacitor).
Ultimately, a well-sourced and correctly sized capacitor enhances system performance, improves longevity, and contributes to overall design robustness. Attention to detail during the selection process pays significant dividends in reliability and operational efficiency.