The global sintered bronze market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand in automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace applications due to the material’s excellent wear resistance, self-lubricating properties, and dimensional stability under high loads. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global powder metallurgy market—of which sintered bronze is a key segment—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by rising adoption of lightweight, durable components in electric vehicles and advanced manufacturing processes. Additionally, Grand View Research valued the global powder metallurgy market at USD 25.3 billion in 2022 and forecasts continued growth through 2030, citing innovations in metal injection molding and porous bearing technologies. With such momentum, identifying leading sintered bronze manufacturers becomes crucial for industries prioritizing performance and supply chain reliability. Below are the top eight manufacturers recognized for their technological expertise, global reach, and consistent product quality in the sintered bronze space.
Top 8 Sintered Bronze Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Powder Metallurgy Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2000
Website: powdermetallurgy.com
Key Highlights: BLUE is a specialized powder metallurgy manufacturer supplying powder metal parts worldwide. Access 100000+ standard parts with no tooling fees….
#2 Sintered Bronze Part Manufacturer Supplier
Domain Est. 2000
Website: powderedmetalparts.com
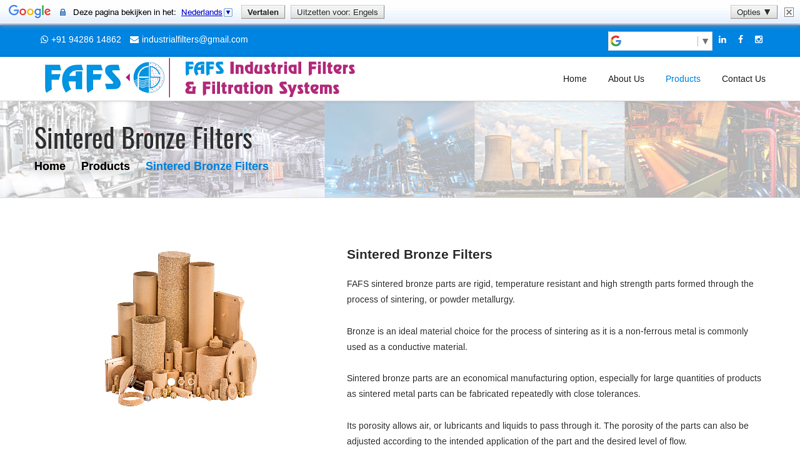
Key Highlights: Sintered bronze parts are rigid, temperature resistant and high strength parts formed through the process of sintering, or powder metallurgy….
#3 Sintered Parts, Gear, Bush, Bronze Bush Manufacturers in India
Domain Est. 2012
Website: specialitysintered.com
Key Highlights: Speciality Sintered Products Pvt Ltd:- We are sintered parts, gear, bush, bronze bush manufacturer in Pune, India. We deliver cost effective components on ……
#4 Sintered Bronze Filter Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2017
Website: sinteredbronzefilter.com
Key Highlights: Satkirti Sintered Bronze filter Manufacturers are known for their superior quality, customization options, and cost-effectiveness….
#5 Sintered Bronze Bushings & Components
Domain Est. 2007
Website: diversifiedbronze.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in providing a wide range of sintered bronze products, including standard-sized parts and custom-pressed components, to meet your specific needs….
#6 Sinter Metals
Domain Est. 2018
Website: gknpm.com
Key Highlights: Utilizing materials such as stainless steel, bronze, nickel-based alloys, and titanium, we manufacture sintered filter elements with high mechanical strength ……
#7 Sintered Bronze Filter Element Supplier
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sinteredfilter.net
Key Highlights: The sintered bronze filter element is a highly specified filtering device for the efficient filtration of liquid, gaseous, and semi-solid materials….
#8 Sintered Bronze Filters
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sinteredfilters.in
Key Highlights: FEATURES & BENEFITS: Sintered Bronze has high permeability that attracts maximum impurities and ensures utmost filtration of oil, gas and other powder products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sintered Bronze
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Sintered Bronze
The global sintered bronze market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by rising demand across key industrial sectors, advancements in powder metallurgy technologies, and a growing emphasis on lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials. Sintered bronze, known for its excellent wear resistance, self-lubricating properties, and porosity that enables oil retention, remains a critical material in automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and consumer electronics applications.
1. Automotive Industry Expansion
The automotive sector continues to be the largest consumer of sintered bronze components, especially in transmission systems, engine parts, and bushings. With the global push toward fuel efficiency and emission reduction, automakers are increasingly adopting lightweight sintered metal solutions. While electric vehicles (EVs) use fewer traditional transmission components, sintered bronze is finding new applications in EV motors, powertrain systems, and ancillary units. This adaptation ensures sustained demand through 2026.
2. Growth in Industrial Automation
As industries embrace automation and robotics, the need for reliable, low-maintenance bearings and gears intensifies. Sintered bronze’s self-lubricating characteristics make it ideal for use in automated systems where maintenance downtime must be minimized. The expansion of smart manufacturing in regions like North America, Europe, and East Asia is expected to boost consumption of sintered bronze parts.
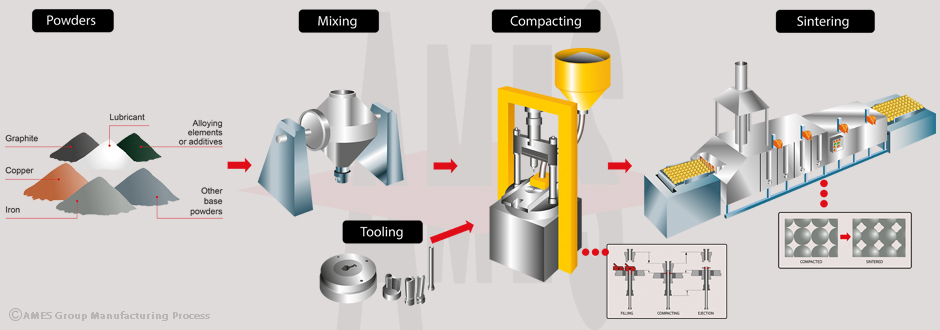
3. Technological Advancements in Powder Metallurgy
Innovations in additive manufacturing (metal 3D printing) and improved sintering techniques are enhancing the mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of sintered bronze components. These advancements allow for more complex geometries and higher performance under extreme conditions, opening new markets in aerospace and defense, where weight savings and reliability are paramount.
4. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain the fastest-growing regional market for sintered bronze due to rapid industrialization, expanding automotive production, and government initiatives supporting manufacturing. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, supported by high-end industrial applications and R&D investments in material science.
5. Supply Chain and Raw Material Considerations
Copper and tin, primary constituents of bronze, face fluctuating prices due to geopolitical tensions and mining constraints. This volatility may pressure margins, prompting manufacturers to invest in recycling and alternative alloy formulations. Increased focus on circular economy models could lead to higher recovery rates of sintered bronze scrap, supporting sustainability goals.
6. Competitive Landscape
The market is moderately consolidated, with key players such as GKN Powder Metallurgy, Hitachi Powdered Metals, and ABC Technologies investing in R&D and capacity expansion. Strategic partnerships with OEMs and adoption of digital twin technologies for process optimization are emerging as competitive differentiators.
Conclusion
By 2026, the sintered bronze market is projected to experience moderate but resilient growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) estimated between 3.5% and 4.5%, depending on regional and sector-specific dynamics. The material’s unique combination of performance, cost-efficiency, and adaptability to evolving manufacturing needs ensures its continued relevance in a transforming industrial landscape.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Sintered Bronze: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing sintered bronze components—widely used for bearings, filters, and wear parts due to their porosity, self-lubrication, and strength—can be fraught with challenges. While cost and lead time are common concerns, deeper pitfalls lie in ensuring consistent quality and protecting intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failure, supply chain disruption, and legal exposure.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Material Composition and Density
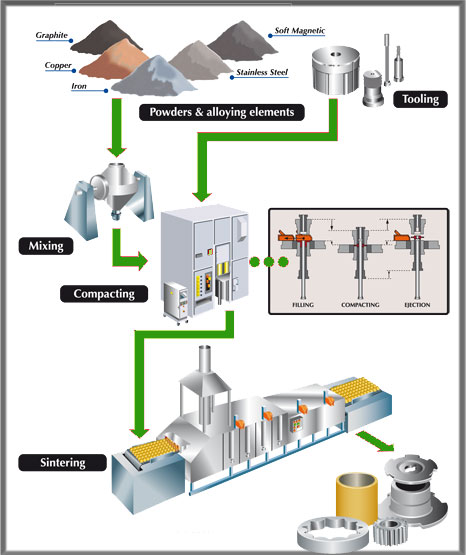
Sintered bronze performance heavily depends on precise control of alloy composition (e.g., Cu-Sn, Cu-Pb-Sn) and final density. Suppliers may use substandard or variable-grade powders to reduce costs, resulting in components with poor mechanical strength, inconsistent porosity, or inadequate wear resistance. Without clear specifications and third-party material certification (e.g., ASTM B939), buyers risk receiving non-conforming parts. -
Poor Control of Sintering Parameters
The sintering process—time, temperature, and atmosphere—must be tightly controlled. Inadequate sintering leads to weak bonds between particles, high variability in dimensional tolerances, and compromised structural integrity. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners here, especially without proper process validation or statistical process control (SPC). -
Inadequate Post-Sintering Treatments
Many sintered bronze parts require oil impregnation, infiltration (e.g., with bronze or resin), or secondary machining. Poor oil retention or incomplete infiltration diminishes self-lubricating properties and load-bearing capacity. Suppliers may skip or inadequately perform these treatments unless explicitly specified and audited. -
Lack of Dimensional Consistency and Tolerance Control
Sintered components often exhibit shrinkage and warping during sintering. Suppliers without robust tooling design and process monitoring may deliver parts outside dimensional tolerances, leading to assembly issues or premature failure in service. -
Insufficient Testing and Documentation
Reliable suppliers conduct routine testing (e.g., density, hardness, permeability, tensile strength) and provide traceability. Many low-cost vendors offer minimal or falsified test reports. Without access to certified test data and batch traceability, buyers assume significant risk.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Tooling Ownership Ambiguity
Dies and molds used to press powder into “green” compacts are often custom and expensive. If tooling ownership is not contractually assigned to the buyer, the supplier may retain rights, enabling them to produce identical parts for competitors or demand high fees for future use. -
Unauthorized Reverse Engineering and Duplication
Sintered bronze parts, especially complex geometries, can be reverse-engineered with relative ease. Unscrupulous suppliers may replicate designs for sale to other clients or even counterfeit components under different branding, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement. -
Lack of Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and IP Clauses
Failing to implement strong NDAs and IP protection clauses in supplier contracts leaves design data, material specs, and manufacturing processes vulnerable. This is particularly risky when sharing CAD models or technical drawings needed for production. -
Third-Party Manufacturing Without Consent
Some suppliers subcontract production to unauthorized or lower-tier facilities without buyer knowledge. This not only risks quality but may involve IP leakage if the subcontractor copies designs or shares them with others. -
Export of IP Through Finished Goods
Even if a supplier doesn’t directly copy a design, shipping finished parts to regions with lax IP laws can enable local actors to deconstruct and replicate the component, undermining market exclusivity.
Mitigation Strategies
- Define Clear Specifications: Use industry standards (e.g., MPIF, ASTM) and include detailed requirements for material, density, porosity, hardness, and post-processing.
- Conduct Supplier Audits: On-site visits to assess quality systems, process controls, and IP safeguards.
- Secure IP Legally: Ensure contracts include tooling ownership, confidentiality, non-compete clauses, and restrictions on subcontracting.
- Require Certification and Traceability: Mandate material test reports, process validation data, and batch-level traceability.
- Limit Design Exposure: Share only necessary geometry; use controlled release versions of CAD files with watermarks or encryption.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, buyers can ensure reliable performance of sintered bronze components while protecting their innovation and competitive advantage.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sintered Bronze
Material Overview and Classification
Sintered bronze is a porous metal component produced through powder metallurgy, where bronze powder is compacted and heated below its melting point to form a solid structure. Due to its unique physical properties—such as self-lubrication, filtration capability, and wear resistance—it is widely used in automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and fluid handling applications. For logistics and compliance purposes, sintered bronze is typically classified under HS (Harmonized System) codes related to metal products or semi-finished metal goods. Common classifications include:
– HS 7409 90: Other articles of copper (may apply depending on form and function)
– HS 8483: Gears and gearing (if the sintered bronze component is a gear)
– HS 8409: Parts of engines or motors (if used as such)
Consult local customs authorities for exact classification, as it varies by end use and configuration.
International Shipping and Packaging Requirements
When shipping sintered bronze components internationally, proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit. Use moisture-resistant packaging such as vacuum-sealed bags or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper to protect against oxidation, especially in humid climates. Secure components in rigid containers with cushioning material to prevent mechanical damage.
Ensure all shipments include accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. For bulk shipments, pallets should be ISPM 15-compliant if wood is used, requiring heat treatment and official marking. Label packages clearly with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”) and include relevant safety data if applicable.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Data
Sintered bronze itself is not classified as hazardous under major transport regulations (e.g., IATA, IMDG, ADR) when shipped in solid form. However, if impregnated with oil or other substances (e.g., for self-lubrication), the impregnating agent may trigger hazardous material classification. Always verify the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for any treated components.
Compliance with REACH (EU), RoHS (EU), and TSCA (USA) regulations must be confirmed, particularly concerning restricted substances like lead or certain phthalates that may be present in trace amounts depending on the alloy composition. Suppliers should provide documentation certifying compliance with applicable chemical regulations.
Import and Export Controls
Export of sintered bronze components may be subject to dual-use or strategic goods controls if intended for military, aerospace, or high-performance applications. Check the EAR (Export Administration Regulations) in the U.S. or the EU Dual-Use Regulation to determine if export licenses are required. Components used in defense systems or advanced machinery may fall under specific control lists (e.g., ECCN 1A007, 9A012).
Importers must ensure adherence to destination country standards, such as China’s CCC mark (if applicable), or India’s BIS certification, depending on the application. Tariff rates and preferential treatment under free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) should be evaluated based on origin and classification.
Environmental and End-of-Life Considerations
Sintered bronze components are recyclable and should be managed at end-of-life in accordance with local waste regulations. In the EU, producers may be subject to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) or ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles) directives if the components are part of covered equipment. Proper recycling channels should be established to recover copper and tin content.
Environmental compliance also includes adherence to manufacturing emissions and wastewater standards under regulations such as the EU Industrial Emissions Directive or the U.S. Clean Air Act, particularly for facilities performing sintering operations.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for traceability and audit purposes, including:
– Material test reports (MTRs) or certificates of conformance (CoC)
– SDS for any treated or impregnated materials
– Export licenses and customs declarations
– REACH/RoHS compliance declarations
Retention periods vary by jurisdiction but typically range from 5 to 10 years. Digital documentation systems are recommended for efficient compliance management.
Conclusion for Sourcing Sintered Bronze:
Sourcing sintered bronze requires a strategic approach that balances material quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and application-specific requirements. Sintered bronze components offer unique advantages such as self-lubrication, porosity for oil retention, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, making them ideal for use in bearings, bushings, gears, and other industrial applications.
When sourcing, it is critical to partner with experienced and certified manufacturers who adhere to international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and possess advanced powder metallurgy capabilities. Evaluating suppliers based on their technical expertise, quality control processes, production capacity, and track record ensures consistent performance and longevity of the components.
Additionally, considerations such as raw material sourcing, lead times, customization options, and total cost of ownership—not just unit price—play a vital role in long-term success. With increasing demand for efficient and maintenance-free mechanical systems, sintered bronze remains a valuable material choice, and strategic sourcing strengthens supply chain resilience and product reliability.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of sintered bronze involves a thorough supplier assessment, clear technical specifications, and a focus on performance and sustainability, ultimately contributing to improved operational efficiency and product quality across various industries.