The global silver capacitor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in electronics, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global capacitor market size was valued at USD 31.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, with silver-based capacitors playing a critical role in high-performance applications due to their superior conductivity and reliability. Silver capacitors, particularly multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) using silver palladium electrodes, are increasingly adopted in advanced consumer electronics and power systems. This growth is further fueled by ongoing miniaturization trends and technological advancements in materials science. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation and scaling production to meet evolving industry standards. Below are the top 10 silver capacitor manufacturers shaping the future of electronic components.
Top 10 Silver Capacitor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
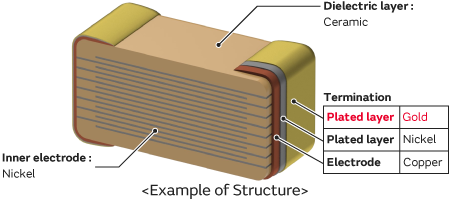
#1 Silver foil capacitor
Domain Est. 2016
Website: bevenbi.com
Key Highlights: Silver foil capacitor Manufacturers, Factory, Suppliers From China, To learn more about what we can easily do in your case, make contact with us at any time ……
#2 GMD Series
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: These capacitors have gold-plated electrodes and are designed specifically for wire bonding and use of gold-tin (AuSn) solder. Specific Applications; Features ……
#3 Silver Mica Capacitors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: suntan.com.hk
Key Highlights: Suntan is a manufacturer of Mica Capacitors. Following is a Mica Capacitors Pictures and Specifications, we are supply the best Mica Capacitors for you….
#4 Samwha Capacitor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: samwha.co.kr
Key Highlights: Samwha Capacitor is a specialized manufacturer of Passive Components such as Capacitor, MLCC, DCC(Y-CAP), EMI Filter, Varistor, Chip Bead & Inductor, ……
#5 Capacitors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: product.tdk.com
Key Highlights: TDK offers a large selection of highly reliable capacitors ranging from miniaturized MLCCs (multilayer ceramic chip capacitors) used in smartphones and cars….
#6 Nichicon
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nichicon.com
Key Highlights: Nichicon is a global leader in advanced capacitor technologies. We offer a capacitor for every design need—from high temperature and high ripple current to ……
#7 Silver Mica, Dipped Capacitors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jameco.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50Jameco’s wide selection of silver mica dipped capacitors. These high quality devices feature up to 3300pF capacitance and are available in many voltage levels…
#8 Capacitors
Domain Est. 2001
Website: charcroft.com
Key Highlights: Charcroft Electronics manufacture a wide variety of Capacitors, which include Silver Mica and professional radial multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs)….
#9 Jupiter Condenser
Domain Est. 2002
Website: jupitercondenser.com
Key Highlights: The finest capacitors, wire, and cable Copper Foil Paper Wax, Aluminum Foil Paper Wax, Cosmos Electrolytic, Bumblebee, Red Astron, Vintage Yellow Capacitors ……
#10 Capacitors passive electronic components
Domain Est. 2009
Website: exxelia.com
Key Highlights: Exxelia is expert in manufacturing different types of capacitors including tantalum capacitors, ceramic capacitors, film capacitors, RF capacitors and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Silver Capacitor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Silver Capacitors
As the electronics and industrial sectors continue to evolve, the market for silver capacitors is poised for notable transformation by 2026. Silver capacitors—particularly silver mica and silver-based multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs)—are valued for their stability, high precision, and performance in high-frequency and high-reliability applications. The following analysis outlines key trends expected to shape the silver capacitor market in the second half (H2) of 2026.
1. Rising Demand in Aerospace and Defense
In H2 2026, the aerospace and defense sectors are projected to be primary drivers of silver capacitor demand. These capacitors are essential in avionics, radar systems, and satellite communications due to their excellent temperature stability and low signal loss. With increased global defense spending and the expansion of space exploration initiatives (e.g., satellite constellations and lunar missions), demand for high-reliability passive components like silver capacitors will remain robust.
2. Growth in High-Frequency 5G and Telecommunications Infrastructure
The rollout of advanced 5G networks and the early development stages of 6G in select regions will continue to boost demand for silver capacitors. Silver’s superior conductivity makes it ideal for RF and microwave applications where signal integrity is critical. In H2 2026, telecom infrastructure upgrades—especially in Asia-Pacific and North America—are expected to increase procurement of silver-based capacitors for base stations and signal filtering systems.
3. Supply Chain Constraints and Silver Price Volatility
Silver prices are expected to remain volatile in H2 2026 due to fluctuating mining output, speculative trading, and increasing demand from green technologies (e.g., solar panels). This volatility will directly impact the production costs of silver capacitors. Manufacturers may respond by investing in silver recovery technologies or exploring alternative materials, although performance trade-offs will limit full substitution in high-end applications.
4. Advancements in Miniaturization and Hybrid Technologies
Technological innovation will drive the integration of silver into advanced hybrid capacitors and ultra-miniaturized components. In H2 2026, we expect to see increased R&D in nano-silver electrode formulations and thin-film deposition techniques to enhance capacitance density while maintaining thermal stability. These advancements are particularly relevant for medical devices, IoT sensors, and wearable electronics.
5. Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, especially China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain dominant in both production and consumption of silver capacitors due to their strong electronics manufacturing ecosystems. However, H2 2026 may also see increased regionalization of supply chains in North America and Europe, spurred by geopolitical considerations and initiatives like the U.S. CHIPS Act. This could lead to modest growth in local silver capacitor production, particularly for defense and automotive applications.
6. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations regarding the use of precious metals and electronic waste (e.g., EU RoHS and WEEE directives) will influence silver capacitor design and lifecycle management. In H2 2026, manufacturers are likely to emphasize recyclability, reduce silver content through precision engineering, and improve end-of-life recovery rates to comply with tightening sustainability standards.
Conclusion
The silver capacitor market in H2 2026 will be characterized by strong demand from high-tech sectors, ongoing innovation in materials science, and challenges related to raw material costs and supply chain resilience. While silver remains difficult to replace in critical applications, manufacturers that invest in efficiency, sustainability, and advanced packaging technologies will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Silver Capacitors: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing silver capacitors—particularly those using silver as an electrode material in multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) or specialized film capacitors—can present significant challenges related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Buyers and procurement teams must be vigilant to avoid common pitfalls that can compromise product performance, reliability, and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Counterfeit or Substandard Components
A major risk when sourcing silver capacitors is receiving counterfeit or non-compliant parts. This is especially true when purchasing from unauthorized distributors or gray market suppliers. Counterfeit capacitors may use inferior dielectric materials, incorrect silver plating thickness, or fail to meet temperature and voltage ratings. These defects can lead to field failures, reduced lifespan, and system malfunctions.
2. Inconsistent Material Purity and Composition
Silver content and purity directly affect electrical performance and longevity. Lower-tier suppliers may use silver alloys or reduced silver content to cut costs, leading to higher equivalent series resistance (ESR) and poor high-frequency performance. Without proper material certifications (e.g., Certificate of Conformance, RoHS, REACH), buyers risk integrating components that do not meet design specifications.
3. Lack of Traceability and Testing Data
Reliable suppliers provide full traceability, including lot numbers, manufacturing dates, and test reports (e.g., life cycle testing, capacitance tolerance, insulation resistance). Sourcing from vendors who lack proper documentation makes it difficult to validate quality or conduct root cause analysis during failure events.
4. Non-Compliance with Industry Standards
Silver capacitors used in automotive, medical, or aerospace applications must adhere to stringent standards such as AEC-Q200, ISO 13485, or MIL-PRF. Sourcing components without verified compliance exposes end products to certification failures and safety risks.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Unauthorized Replication or Reverse Engineering
Silver capacitor designs—especially those optimized for high reliability or miniaturization—often incorporate proprietary technology. Sourcing from unverified manufacturers increases the risk of purchasing components that infringe on patented electrode structures, termination processes, or material formulations. This exposes the buyer to potential IP litigation, even if unintentional.
2. Use of Grey Market or Overproduced Parts
Some suppliers source capacitors produced in excess of original orders (overproduction) or diverted from legitimate contracts. These parts may be genuine in construction but are distributed without the manufacturer’s authorization, violating IP and distribution agreements. Purchasing such components can lead to warranty issues and legal exposure.
3. Lack of IP Assurance in Supply Contracts
Procurement agreements that do not include IP indemnification clauses leave buyers vulnerable. If a capacitor design is later found to infringe on third-party patents, the buyer—not the supplier—may bear legal and financial responsibility unless protected by contract.
4. Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier Origins
Failing to audit a supplier’s manufacturing processes, design ownership, and supply chain transparency can result in unknowingly sourcing IP-compromised components. This is particularly common with offshore manufacturers who may replicate branded parts without authorization.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, procurement teams should:
– Source exclusively from authorized distributors or directly from OEM manufacturers.
– Require full material and test documentation for every batch.
– Conduct supplier audits and request proof of IP ownership or licensing.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in purchasing contracts.
– Use third-party testing labs to verify component authenticity and performance.
By recognizing and addressing these quality and IP-related risks, organizations can ensure the reliability and legal safety of their electronic designs when sourcing silver capacitors.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Silver Capacitor
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, transportation, and documentation of silver capacitors. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, minimizes risks, and supports smooth supply chain operations.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Silver capacitors may be subject to various international and national regulations depending on their composition, particularly if they contain hazardous materials or are classified as electronic components. Accurately classify the product using the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for customs declarations. Common classifications may fall under HS 8532 (electrical capacitors). Ensure Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) are up to date and readily available, clearly indicating any hazardous substances (e.g., lead, brominated flame retardants) if applicable. Maintain records of RoHS, REACH, and conflict minerals (e.g., Dodd-Frank Section 1502) compliance documentation.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Use electrostatic discharge (ESD)-safe packaging materials to protect silver capacitors from static damage during storage and transit. Inner packaging should include anti-static bags or conductive foam, while outer packaging must be robust to prevent physical damage. Clearly label packages with ESD-sensitive warnings, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), and product identification. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and direct sunlight during storage and transport to maintain component integrity.
Transportation and Shipping
Select carriers experienced in handling electronic components and compliant with IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations if transporting by air, sea, or road. If silver capacitors contain any restricted substances above regulatory thresholds, proper hazardous materials declarations and packaging (e.g., UN-certified containers) may be required. For international shipments, ensure all export controls are met—verify if the product is subject to ITAR, EAR, or other trade restrictions based on destination country. Utilize tracking systems and insure high-value shipments.
Import and Customs Clearance
Provide complete and accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and any required permits or licenses at the destination country. Be prepared for customs inspections and ensure all documentation aligns with local regulations. Duties and taxes vary by jurisdiction; consult with a customs broker to ensure correct tariff application and potential eligibility for duty-free treatment under trade agreements (e.g., GSP, USMCA).
Environmental and Waste Compliance
Dispose of defective or end-of-life silver capacitors in accordance with local and international e-waste regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive in the EU). Partner with certified electronic waste recyclers to ensure environmentally sound recycling practices. Maintain records of waste disposal and recycling to support audit readiness and sustainability reporting.
Audit and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records of compliance documentation, shipping manifests, SDS sheets, and certification reports for a minimum of five years or as required by local laws. Conduct periodic internal audits to verify adherence to logistics and compliance procedures. Stay updated on regulatory changes that may affect the classification or handling of electronic components.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure the reliable and compliant movement of silver capacitors across global supply chains while mitigating legal, financial, and operational risks.
Conclusion for Sourcing Silver Capacitors:
Sourcing silver capacitors requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Silver capacitors, particularly silver mica types, are valued for their high stability, low losses, and excellent performance in high-frequency and high-precision applications, making them essential in aerospace, defense, medical, and RF communication systems.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include verifying the technical specifications—such as capacitance value, tolerance, temperature stability, and voltage rating—ensuring authenticity and quality from trusted manufacturers or authorized distributors, and assessing long-term supply chain reliability. Given the limited number of producers and potential scarcity of raw materials, proactive supply chain management and qualification of multiple suppliers are recommended.
Additionally, compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH) and counterfeiting prevention measures are crucial in maintaining product integrity. While silver capacitors may carry a higher cost compared to other types, their performance advantages justify their use in critical applications.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of silver capacitors involves thorough supplier vetting, continuous market monitoring, and close collaboration with engineering and procurement teams to ensure availability, quality, and performance alignment with project requirements.