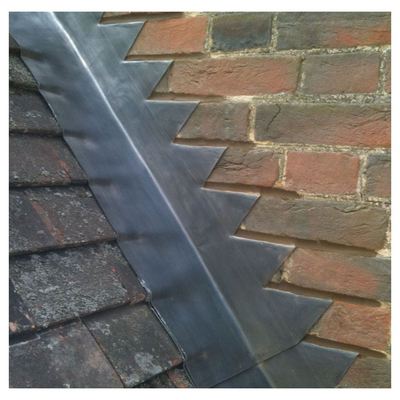
The global roofing materials market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising construction activities, infrastructure development, and increasing demand for durable, weather-resistant solutions. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global roofing market was valued at USD 112.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2029, with metal roofing—particularly sheet lead—gaining traction due to its longevity, low maintenance, and aesthetic versatility. Sheet lead roofing, long favored for historic and high-performance applications, is witnessing renewed interest in both restoration projects and premium new builds across Europe and North America. As sustainability and building resilience become key priorities, leading manufacturers are investing in advanced production techniques and eco-friendly practices to meet evolving regulatory and performance standards. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as industry leaders, combining technical expertise, compliance with international standards, and scalable output to capture growing demand. The following list highlights the top 10 sheet lead roofing manufacturers shaping the future of high-performance roofing solutions.
Top 10 Sheet Lead Roofing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Berridge Manufacturing Co.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: berridge.com
Key Highlights: For over 50 years Berridge has worked to set the standard by designing, developing and manufacturing superior architectural metal products and technology….
#2 Metal Roofing Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mbci.com
Key Highlights: MBCI manufactures the highest quality metal roofing & wall panels to meet your project’s aesthetic & structural standards. Request a quote today!…
#3 Onduline Group
Domain Est. 1997
Website: onduline.com
Key Highlights: Founded in France, Onduline has been designing innovative roofing and waterproofing solutions for more than 80 years….
#4 Lead Sheet
Domain Est. 1998
Website: canadametal.com
Key Highlights: Explore premium sheet lead and lead sheet metal for roofing and radiation shielding. Canada Metal supplies durable lead sheets for industrial and medical ……
#5 CertainTeed
Domain Est. 1995
Website: certainteed.com
Key Highlights: CertainTeed is North America’s leading brand of exterior and interior products, including roofing, siding, trim, insulation, gypsum, and ceilings….
#6 Sheet Lead for Roofing & Flashing
Domain Est. 1999
Website: marsmetal.com
Key Highlights: Made from 98% recyclable material, sheet lead is the most malleable of common metals and can be easily shaped, formed, bend and cut to suit a variety of ……
#7 Sheet Lead Squares/Rolls
Domain Est. 2001
Website: maycoindustries.com
Key Highlights: Sheet Lead can be used for soundproofing, waterproofing, and radiation shielding. Most commonly seen in the roofing industry as 2.5 lb and 4 lb squares, we ……
#8 Stock Lead Roll Sizes and Specifications
Domain Est. 2007
Website: santarosalead.com
Key Highlights: Sheet lead is readily available in 1#, 2#, 2-1/2#, 4#, 6#, and 8# (lbs./sq. ft.). Other thicknesses are available, including lead plate (up to 1″ thick)….
#9 Lead roof flashings
Domain Est. 2014
Website: pureleadproducts.com
Key Highlights: Pure Lead Product’s roof flashings are made of 99% pure lead. Made from precise coiled sheet lead. Available in 2.5#, 3# & 4# lead….
#10 The Neverleak Company
Domain Est. 2020
Website: neverleak.northparkgroup.com
Key Highlights: We offer quality, time-tested roof flashing products at excellent prices, same day shipping, and a team of knowledgable sales representatives ready to serve….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sheet Lead Roofing

2026 Market Trends for Sheet Lead Roofing
Growing Niche Demand in Heritage and High-End Construction
Despite broader shifts toward sustainable and lightweight roofing materials, sheet lead roofing is expected to maintain a stable, specialized market presence by 2026. Its primary growth will be driven by heritage restoration projects, particularly in Europe and North America, where regulatory requirements and preservation standards mandate the use of traditional materials. Architects and conservationists continue to favor lead for its longevity, malleability, and authentic aesthetic in restoring historic buildings, ensuring steady demand in this segment. Additionally, luxury residential and institutional projects seeking premium, long-term roofing solutions will support niche adoption.
Increased Regulatory and Environmental Scrutiny
Environmental and health concerns surrounding lead usage will intensify by 2026, influencing market dynamics. Stricter regulations on lead handling, worker safety, and end-of-life recycling are expected in key markets such as the EU and UK. These regulations may increase installation costs and compliance requirements, potentially deterring some contractors. However, improved recycling infrastructure and closed-loop systems for reclaimed lead could mitigate environmental impact and enhance the material’s sustainability credentials within its niche.
Supply Chain and Cost Volatility
The sheet lead roofing market will remain sensitive to fluctuations in lead commodity prices, which are influenced by global mining output, battery demand (especially from electric vehicles), and geopolitical factors. By 2026, price volatility may lead to increased interest in lead alternatives like zinc, copper, or advanced composites—particularly in cost-sensitive projects. Nonetheless, lead’s unmatched durability (often exceeding 100 years) and repairability will sustain its value proposition in applications where lifecycle cost outweighs initial investment.
Innovation and Alternatives Pressure
Technological advancements in synthetic lead substitutes—such as lead-coated copper or polymer-based mimic materials—will continue to challenge traditional sheet lead. These alternatives offer similar workability and appearance with reduced environmental and health risks. While they have not yet displaced lead in heritage work due to authenticity concerns, their adoption in new construction may limit market expansion. Contractors and specifiers will increasingly weigh performance, compliance, and public perception when selecting materials.
Regional Market Divergence
Market trends will vary significantly by region. Europe, especially the UK and Germany, will remain the largest market due to extensive historic building stock and strong preservation policies. In contrast, North America will see more limited use, concentrated in high-value restoration projects. Emerging markets are unlikely to adopt lead roofing widely due to cost, regulatory barriers, and environmental priorities. Overall, the global sheet lead roofing market in 2026 is projected to remain small but resilient, sustained by specialized demand rather than broad industry growth.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Sheet Lead Roofing (Quality, IP)
Sourcing sheet lead roofing requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly failures, legal issues, or performance shortcomings. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Purity
One of the most frequent issues is receiving lead sheets that do not meet required standards for purity or thickness. Substandard lead may contain excessive impurities (e.g., antimony, arsenic), reducing malleability and corrosion resistance. Always verify compliance with relevant standards such as BS EN 12588 or ASTM B749, and request mill test certificates to confirm lead content (typically ≥ 99.94% pure).
Inconsistent Sheet Thickness and Tolerances
Lead sheets that vary in thickness—even slightly—can compromise waterproofing integrity and installation performance. Some suppliers may cut corners by supplying thinner material than specified. Ensure dimensional tolerances are clearly defined in procurement contracts and independently verified upon delivery.
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Reputable lead roofing products should come with full traceability, including origin, batch numbers, and compliance documentation. Sourcing from uncertified or untraceable suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or recycled lead that may not meet construction-grade requirements.
Ignoring Intellectual Property in Design and Installation Methods
Many modern lead roofing systems—especially patented flashings, jointing techniques, or fixing methods—are protected by intellectual property rights. Using a proprietary design or installation detail without proper licensing can lead to legal disputes or liability. Always confirm whether architectural details or system components are IP-protected and obtain necessary permissions.
Sourcing from Unverified or Non-Compliant Suppliers
Choosing suppliers based solely on price can expose projects to non-compliant materials, especially when dealing with international or uncertified vendors. Unethical suppliers may misrepresent product origin or bypass environmental and safety regulations. Conduct due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and references.
Overlooking Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Lead is a regulated material due to its environmental and health impacts. Sourcing lead that doesn’t comply with REACH, RoHS (where applicable), or local environmental standards can result in project delays or penalties. Ensure supplier practices align with legal requirements for mining, refining, and transportation.
Failure to Specify Recycled Content and Sustainability Claims
Many green building certifications require documentation of recycled content. Some suppliers make unsubstantiated claims about sustainability. Request certified documentation for recycled lead content and ensure alignment with environmental standards like BES 6001.
Using Non-Approved Alloys or Coatings
Some suppliers may offer lead-coated copper or lead alloys marketed as cost-effective alternatives. However, these may not perform the same way as pure sheet lead in roofing applications and could breach specification requirements. Confirm that materials are solid, soft lead (Grade A or equivalent), not composites or coated substrates.
By addressing these common pitfalls proactively, specifiers and contractors can ensure the durability, compliance, and legal safety of lead roofing installations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sheet Lead Roofing
Overview
Sheet lead roofing is a traditional, durable, and highly effective roofing material valued for its longevity and malleability. However, due to the hazardous nature of lead, its use, transport, installation, and disposal are subject to stringent environmental, health, and safety regulations. This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for handling sheet lead roofing.
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
Lead is a hazardous material regulated under various environmental laws. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). In the European Union, the REACH and RoHS directives govern lead use and disposal. Compliance includes proper classification of lead waste as hazardous, secure storage, and use of licensed waste carriers for disposal.
Health and Safety Standards
Workers handling sheet lead must be protected from lead exposure, which can cause serious health issues. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) in the U.S. mandates lead exposure limits and requires medical surveillance, personal protective equipment (PPE), and hygiene practices. Training in lead-safe work practices is mandatory. In the UK, the Control of Lead at Work Regulations (CLAW) applies similar standards.
Building Codes and Standards
Local building codes often regulate the use of lead roofing, particularly regarding weight, fire resistance, and installation methods. British Standard BS 922:2015 specifies requirements for lead sheet used in roofing and plumbing. In North America, standards from ASTM International (e.g., ASTM B749) cover lead and lead alloy roll materials.
Transportation and Handling
Packaging and Labeling
Lead sheets must be securely bundled and protected from damage during transit. Packages should be clearly labeled as containing lead, with hazard warnings where applicable. Proper documentation, including safety data sheets (SDS), must accompany shipments.
Transportation Regulations
Transport of lead materials may fall under hazardous materials regulations (e.g., DOT regulations in the U.S. or ADR in Europe). Shipments must comply with packaging, labeling, placarding, and documentation requirements. Non-hazardous quantities may be exempt, but verification is essential.
On-Site Handling
Lead sheets should be stored on elevated, dry platforms away from foot traffic. Handling should be done with gloves and appropriate lifting equipment to prevent strain and contamination. Avoid dragging or dropping sheets to prevent deformation.
Installation Best Practices
Worker Training and PPE
Only trained and certified personnel should install lead roofing. Required PPE includes nitrile gloves, protective clothing, safety goggles, and respiratory protection if cutting or welding. Eating, drinking, or smoking in work areas must be prohibited.
Dust and Waste Control
Cutting or trimming lead generates lead dust and shavings. Use wet-cutting methods or local exhaust ventilation to minimize airborne particles. Collect all waste in labeled, sealed containers for proper disposal.
Sealing and Joining
Lead sheets are typically joined by welding, soldering, or patress rolling. All joints must be watertight and meet code requirements. Use lead-compatible materials for fixings and underlayments.
Waste Management and Disposal
Waste Classification
Lead scrap, offcuts, and old roofing materials are generally classified as hazardous waste. Confirm local classification rules and ensure waste is stored separately in secure, labeled containers.
Recycling and Reuse
Lead is highly recyclable. Work with licensed recyclers who can process lead roofing materials. Recycling reduces environmental impact and may offer cost recovery.
Disposal Documentation
Maintain records of waste transfer, including waste manifests and disposal certificates. These are essential for regulatory audits and environmental compliance.
Record Keeping and Monitoring
Exposure Monitoring
Regular air monitoring for lead dust is required in enclosed or high-risk work environments. Maintain records of exposure assessments and employee blood lead level testing if mandated.
Compliance Documentation
Keep copies of training records, safety permits, SDS, waste disposal receipts, and inspection reports. These documents demonstrate due diligence and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Sheet lead roofing offers exceptional performance but demands rigorous attention to logistics and compliance. Adherence to environmental, health, and safety regulations protects workers, the public, and the environment while ensuring project legality and long-term sustainability. Always consult local authorities and industry standards before starting any lead roofing project.
Conclusion for Sourcing Sheet Lead Roofing:
Sourcing sheet lead for roofing applications requires careful consideration of material quality, supplier reliability, compliance with environmental and safety regulations, and long-term performance. Lead remains a durable, malleable, and weather-resistant material ideal for complex roofing details, heritage restorations, and high-performance installations. However, due to its environmental impact and health risks, responsible sourcing—preferably from certified, recycled, or ethically produced lead—is essential to ensure sustainability and regulatory compliance.
When selecting suppliers, prioritize those with proven experience in architectural lead, adherence to British/European standards (e.g., BS EN 12588), and transparent supply chains. Additionally, factor in cost, delivery timelines, and technical support, especially for large or specialized projects. With proper sourcing and handling practices, sheet lead can provide a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing roofing solution, particularly in conservation and premium construction contexts. Always ensure installation is carried out by trained professionals to maintain safety and performance standards.