The global seatbelt material market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing automotive production, stringent vehicle safety regulations, and rising consumer demand for enhanced occupant protection. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global automotive safety systems market—of which seatbelt materials are a critical component—was valued at USD 48.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects that the automotive seatbelt market will grow at a CAGR of over 5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, underpinned by advancements in pretensioners, load limiters, and high-tensile textile materials. As automakers prioritize lightweight yet durable components to meet safety and fuel efficiency standards, the demand for high-performance seatbelt fabrics—primarily made from technical polyesters and nylon—is intensifying. This growing demand has positioned key material manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, scaling production and investing in R&D to meet evolving industry specifications. Here are the top 8 seatbelt material manufacturers shaping the future of automotive safety.
Top 8 Seatbelt Material Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1
Domain Est. 2005
Website: belt-tech.com
Key Highlights: High performance products to suit all your needs. We are a manufacturer of narrow fabrics webbing for all markets and applications….
#2 rosemont textiles
Domain Est. 2006
Website: rosemonttextiles.com
Key Highlights: Rosemont Textiles is an industrial distributor of First Quality and Aftermarket Seatbelt Webbing. We also produce custom made One Way Straps….
#3 / Joyson
Domain Est. 2017
Website: joysonsafety.com
Key Highlights: Joyson Safety Systems is a global leader in mobility safety providing safety-critical components, systems and technology to automotive and non-automotive ……
#4 Seatbelts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: autoliv.com
Key Highlights: The seatbelt material (known as webbing) is housed in a rotating spool called a retractor, a highly designed mechanical product that Autoliv considers to be a ……
#5 Seat Belts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sfifoundation.com
Key Highlights: SFI is a non-profit organization established to issue and administer standards for all kinds of specialty/performance automotive and racing equipment….
#6 Seatbelt Webbing for Manufacturing Purposes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tnwebbing.com
Key Highlights: Almost all of our seatbelt webbing is 2 inch, 5000-6000 lb. tensile, 100% polyester webbing and is UV inhibited and will not shrink, rot, mold, or mildew….
#7 Seat Belt Webbing by the Yard
Domain Est. 2006
#8 Midwest Precision Products
Domain Est. 2015
Website: seatbeltsforpallets.com
Key Highlights: Seatbelts for Pallets is the world leader in providing retractable, self contained cargo restraints for material handling applications. Our “seatbelt ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Seatbelt Material
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Seatbelt Material
The global seatbelt material market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automotive safety standards, material innovation, and the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles. Several key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape during this period.
-
Increased Demand for High-Strength Synthetic Fibers
By 2026, there will be a growing preference for high-performance synthetic fibers such as high-tenacity polyester and nylon 6,6. These materials offer superior tensile strength, resistance to abrasion, and durability under extreme conditions. Their lightweight nature also supports fuel efficiency, aligning with stricter global emissions regulations. -
Integration of Smart Textiles and Sensor-Embedded Materials
As vehicle connectivity advances, seatbelt materials are evolving into smart systems. By 2026, expect wider adoption of seatbelts with integrated sensors that monitor occupancy, tension, and user health metrics. These smart seatbelts—woven with conductive fibers or embedded with micro-sensors—will enhance passive safety systems and support autonomous driving protocols by providing real-time feedback to vehicle control units. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers toward sustainable alternatives. Recycled polyester derived from post-consumer plastic bottles and bio-based polyamides are gaining traction. By 2026, regulatory pressure and consumer demand will likely compel major automotive suppliers to adopt circular economy principles, including recyclable or biodegradable seatbelt webbing. -
Rising Production in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will play a central role in the seatbelt material market expansion. Increasing vehicle production, urbanization, and government-mandated safety regulations are fueling demand. Local manufacturers are investing in advanced weaving and coating technologies to meet international standards, positioning the region as a key hub for material supply. -
Growth in Electric and Autonomous Vehicles (EVs and AVs)
The shift toward EVs and AVs introduces new safety considerations. By 2026, seatbelt systems will need to adapt to unconventional seating arrangements (e.g., rotating or lounge-style seats in autonomous pods). This will drive innovation in retractable, multi-directional, and adaptive seatbelt materials capable of functioning in dynamic interior environments. -
Stringent Safety Regulations and Global Standards
Regulatory bodies such as the NHTSA (U.S.), EU-NCAP, and Bharat NCAP (India) continue to strengthen safety requirements. These evolving standards will mandate higher material performance benchmarks, including improved energy absorption and reduced elongation under impact, thereby influencing material selection and design. -
Consolidation and Collaboration in the Supply Chain
Anticipated market growth will lead to increased partnerships between textile producers, automotive OEMs, and technology firms. By 2026, vertical integration and co-development initiatives will accelerate the commercialization of next-generation seatbelt materials with enhanced functionality and cost efficiency.
In conclusion, the 2026 seatbelt material market will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and intelligent integration. As vehicles become safer and more technologically advanced, seatbelt materials will transition from passive restraints to active components of holistic safety ecosystems.
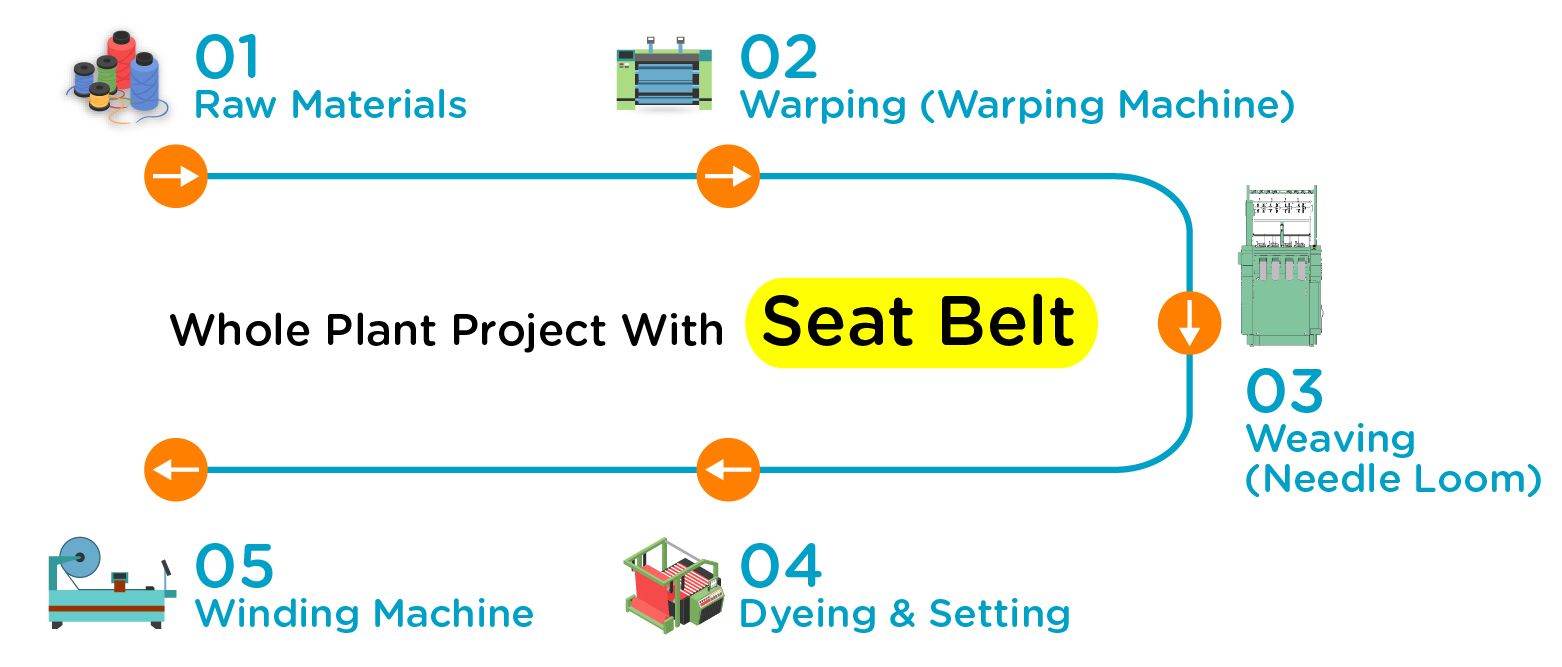
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Seatbelt Material (Quality, IP)
Sourcing seatbelt materials involves critical considerations due to the safety-critical nature of the product. Overlooking key aspects can lead to compromised performance, regulatory non-compliance, and intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and IP:
Inadequate Quality Control and Material Specifications
One of the most significant risks is failing to enforce strict quality control measures and clearly defined material specifications. Seatbelt materials must meet rigorous safety standards (e.g., FMVSS 209, ECE R16). Suppliers may offer substandard webbing with inconsistent tensile strength, poor UV resistance, or inadequate abrasion performance. Without third-party testing and batch certifications, manufacturers risk integrating defective materials that could fail under load.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Seatbelt components require full traceability from raw material to finished product. Sourcing without proper documentation—such as ISO/TS 16949 certification, material test reports (MTRs), or OE (Original Equipment) approvals—increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant materials entering the supply chain. This can result in product recalls and liability issues.
Overlooking Long-Term Material Performance
Some suppliers may provide materials that meet initial performance tests but degrade prematurely due to environmental exposure (e.g., heat, humidity, UV light). Failure to evaluate long-term durability—such as colorfastness, tensile retention, and resistance to mildew—can compromise safety over the product lifecycle.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Using patented weaving patterns, webbing designs, or proprietary fiber blends without proper licensing exposes companies to IP litigation. Many OE seatbelt systems incorporate patented technologies (e.g., load-limiting webbing, pretensioner-compatible fibers). Sourcing generic materials that mimic these designs without authorization can lead to legal disputes and costly product redesigns.
Unverified Supplier Credentials and Capacity
Partnering with suppliers lacking automotive-grade production capabilities or audited quality management systems increases risk. Some suppliers may claim compliance but lack the infrastructure for consistent, high-volume output. This can lead to supply chain disruptions and inconsistent material quality.
Failure to Conduct On-Site Audits
Relying solely on documentation without conducting on-site audits of supplier facilities can hide deficiencies in manufacturing processes, inventory controls, or worker training. Physical audits help verify compliance with safety and quality standards and assess the supplier’s ability to scale responsibly.
Ignoring Regional Regulatory Differences
Seatbelt standards vary by region (e.g., U.S., EU, China). Sourcing materials designed for one market without adapting to local regulations can result in non-compliance. Suppliers may not always be aware of these nuances, so due diligence is required to ensure regional conformity.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a structured sourcing strategy that emphasizes certified suppliers, rigorous testing, IP due diligence, and ongoing quality monitoring.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Seatbelt Material
This guide outlines the key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for handling, transporting, and managing seatbelt materials used in automotive manufacturing. Adhering to these standards ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational safety.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Seatbelt materials must comply with stringent international and regional safety standards. Key regulations include:
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) 209 (USA): Specifies performance requirements for seatbelt webbing, including tensile strength, elongation, and abrasion resistance.
- ECE Regulation No. 16 (Europe): Governs approval of vehicle seatbelts and restraint systems; mandates testing for strength, durability, and material consistency.
- ISO 13216 and ISO 16644: International standards covering child restraint systems and seatbelt anchorages, indirectly influencing material specifications.
- REACH and RoHS (EU): Restrict the use of hazardous substances in materials; ensure seatbelt webbing is free from SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern).
- Oeko-Tex Standard 100: Voluntary certification indicating textiles are free from harmful levels of toxic substances, often required by OEMs.
All seatbelt materials must be accompanied by a Certificate of Compliance (CoC) and traceability documentation, including lot numbers and test reports.
Material Handling & Storage
Proper handling and storage are critical to maintaining the mechanical properties of seatbelt webbing:
- Environmental Conditions: Store materials in a clean, dry environment with temperatures between 15°C and 25°C and relative humidity of 40–60%. Avoid direct sunlight and exposure to UV radiation.
- Packaging Integrity: Keep materials in original sealed packaging until use to prevent contamination, moisture absorption, or mechanical damage.
- Stacking and Shelving: Store rolls vertically on pallets or racks to prevent deformation. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of seatbelt material containers.
- Shelf Life: Adhere to manufacturer-specified shelf life (typically 2–5 years). Implement a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory system to prevent aging.
Transportation & Logistics
Seatbelt materials must be transported under controlled conditions to preserve quality:
- Mode of Transport: Use enclosed, climate-controlled vehicles (road or rail) to prevent exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, and contaminants.
- Loading/Unloading: Use appropriate handling equipment (e.g., forklifts with soft forks) to avoid damaging packaging or webbing edges.
- Documentation: Shipments must include detailed packing lists, CoC, hazardous material declarations (if applicable), and customs documentation for cross-border transport.
- Tracking & Traceability: Utilize barcode or RFID systems to track material batches throughout the supply chain, ensuring full traceability from supplier to assembly line.
Quality Control & Inspection
Implement rigorous QC protocols at all stages:
- Incoming Inspection: Verify material against purchase specifications, including color, width, weight per meter, and tensile strength. Perform visual checks for defects (e.g., fraying, contamination).
- Periodic Testing: Conduct periodic third-party testing for compliance with FMVSS 209, ECE R16, and OEM-specific standards.
- Non-Conformance Management: Establish a process for quarantining and disposing of non-compliant material, including root cause analysis and supplier corrective action requests (SCARs).
Supplier & OEM Requirements
Automotive OEMs often impose additional compliance and logistical expectations:
- APQP & PPAP Documentation: Suppliers must complete Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) and submit Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) dossiers, including material test results and process flow diagrams.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) / Kanban Delivery: Comply with OEM delivery schedules using JIT or Kanban systems to minimize inventory and ensure timely production support.
- Audit Readiness: Maintain documentation and processes to support customer and regulatory audits (e.g., IATF 16949, ISO 9001).
Sustainability & End-of-Life Considerations
Environmental responsibility is increasingly important:
- Recyclability: Use recyclable or bio-based fibers where technically feasible. Document material composition for end-of-life processing.
- Waste Management: Segregate production waste (e.g., cut-offs) for recycling; avoid landfill disposal of textile waste.
- Carbon Footprint: Optimize transport routes and consider low-emission logistics partners to reduce environmental impact.
By following this guide, manufacturers and logistics providers can ensure that seatbelt materials meet all safety, regulatory, and operational standards throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Seatbelt Material:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, material specifications, compliance standards, cost considerations, and sustainability factors, it is concluded that sourcing seatbelt material requires a strategic balance between safety, quality, and cost-efficiency. The selected material must meet stringent international safety standards—such as ISO 13216 and FMVSS 209—to ensure passenger protection in all driving conditions. High-tensile polyester webbing remains the industry benchmark due to its durability, strength, and resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Engaging with certified, reputable suppliers who adhere to consistent quality control and offer traceability is essential for long-term reliability. Additionally, incorporating sustainable and recyclable materials where feasible supports environmental goals without compromising safety. Ultimately, the decision to source seatbelt material should prioritize passenger safety above all, supported by supplier reliability, compliance assurance, and lifecycle cost analysis. A well-structured sourcing strategy will not only ensure regulatory compliance but also enhance overall vehicle safety and brand reputation.