The global market for SDI (Serial Digital Interface) converters is experiencing steady growth, driven by increased demand for high-quality video transmission in broadcast, live production, and surveillance applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global SDI market was valued at USD 1.8 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 7.2% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by the ongoing transition to 4K and high dynamic range (HDR) content, alongside rising investments in IP-based broadcast infrastructures. As studios, broadcasters, and AV professionals seek reliable signal conversion between SDI, HDMI, and IP formats, the need for high-performance converters has intensified. In this evolving landscape, manufacturers that combine engineering precision, low-latency performance, and forward-compatible designs are emerging as industry leaders. Based on market presence, product innovation, and technical capabilities, the following five companies represent the top SDI converter manufacturers shaping the future of professional video workflows.
Top 5 Sdi Converter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Macom
Domain Est. 1991
Website: macom.com
Key Highlights: MACOM designs and manufactures high-performance semiconductor products for the Telecommunications, Industrial and Defense, and Data Center industries….
#2 Solid State Logic
Domain Est. 1999
Website: solidstatelogic.com
Key Highlights: From groundbreaking audio production consoles to innovative personal studios, Solid State Logic are the world’s leading manufacturer of creative tools for music ……
#3 AJA Video Systems
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aja.com
Key Highlights: AJA offers a range of solutions for 12G-SDI single cable simplicity. Explore solutions for editing, routing, distributing, and muxing/demuxing to 3G-SDI….
#4 Micro Converters
Domain Est. 2000
Website: blackmagicdesign.com
Key Highlights: The new Blackmagic Micro Converters are incredibly tiny broadcast video converters that let you connect between consumer HDMI and professional SDI equipment….
#5 Decimator Design
Domain Est. 2001
Website: decimator.com
Key Highlights: Decimator Design’s new 4K scaling engine can scale and/or frame rate convert between 351 input formats and 57 output formats….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sdi Converter
2026 Market Trends for SDI Converters
The market for SDI (Serial Digital Interface) converters is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving broadcast standards, enterprise AV demands, and technological innovation. While IP-based workflows continue to gain ground, SDI remains a critical infrastructure in professional video environments, and converters that bridge SDI with modern formats will play an essential role. Key trends shaping the SDI converter market through 2026 include:
Accelerated Adoption of High-Bandwidth SDI Standards
By 2026, 12G-SDI and emerging 24G-SDI will become mainstream in high-end production environments. As 4K60 and 8K video applications grow in broadcast, live events, and medical imaging, demand for converters capable of handling higher data rates over a single coaxial cable will surge. Manufacturers will prioritize compact, low-latency converters supporting HDR, wide color gamut, and deep color—features essential for premium content creation. Legacy 3G-SDI to 12G-SDI up/down/cross-conversion tools will see sustained demand during infrastructure transitions.
Hybrid SDI-IP Workflow Integration
The coexistence of SDI and IP (particularly SMPTE ST 2110) standards will drive demand for hybrid SDI-to-IP and IP-to-SDI gateways. By 2026, converters with dual connectivity—supporting both traditional BNC interfaces and 10GbE/25GbE networking—will dominate professional installations. These devices will enable incremental migration, allowing broadcasters and enterprises to protect existing SDI investments while integrating IP-based routing and control systems. Embedded audio, metadata, and timing (PTP) support will be standard features.
Expansion into Non-Traditional Verticals
Beyond traditional broadcast and live production, SDI converters will see increased adoption in medical imaging, defense, gaming studios, and corporate AV. In healthcare, 4K surgical cameras rely on SDI for real-time, uncompressed video; converters will be needed to interface with recording systems and displays. Similarly, simulation and training applications in defense and aviation will require ruggedized SDI conversion solutions. Enterprise meeting rooms adopting high-end video walls will also leverage SDI-to-HDMI or SDI-to-DVI converters for signal reliability.
Miniaturization and Power Efficiency
Demand for compact, portable, and power-efficient converters will grow, especially for field production, OB vans, and remote studios. By 2026, modular converter platforms—such as those using mini-SDI or DIN connectors—and USB-powered designs will gain traction. These form factors support mobile workflows and reduce cabling complexity. Additionally, energy efficiency will become a competitive differentiator, driven by sustainability goals and thermal management in dense installations.
Enhanced Intelligence and Remote Management
Future SDI converters will incorporate embedded intelligence, including real-time diagnostics, signal monitoring, and remote configuration via web UIs or SNMP. AI-powered signal analysis may detect issues like jitter, cable faults, or format mismatches preemptively. Integration with network management systems (NMS) and cloud-based monitoring platforms will enable centralized control across distributed AV infrastructures—critical for large venues and broadcast networks.
Price Pressure and Market Consolidation
As technology matures and production scales, price competition will intensify, especially in the mid-tier market. Established brands will focus on premium features and reliability, while Asian manufacturers offer cost-effective alternatives. This dynamic may lead to market consolidation, with niche players being acquired by larger AV or networking companies seeking to expand their signal management portfolios.
Conclusion
While the long-term trajectory points toward IP-based video transport, SDI converters will remain indispensable through 2026. Their evolution will center on higher bandwidth support, hybrid interoperability, intelligent features, and broader application across verticals. Companies that innovate at the intersection of SDI reliability and IP flexibility will lead the market, ensuring seamless video signal conversion in an increasingly complex media ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing SDI Converters (Quality, IP)
When procuring SDI (Serial Digital Interface) converters—especially those with IP (Internet Protocol) capabilities—several common pitfalls can impact performance, reliability, and long-term cost of ownership. Being aware of these issues helps ensure you select high-quality, future-proof equipment.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many low-cost SDI converters use substandard materials and components, leading to unreliable performance, signal degradation, and shorter lifespans. Watch out for poorly shielded connectors, flimsy housings, and inadequate power regulation that can cause dropouts or interference.
Inconsistent Signal Conversion and Latency
Low-quality converters may introduce unacceptable latency or fail to maintain signal integrity during format conversion (e.g., SDI to HDMI or IP). This is especially problematic in live production environments where synchronization is critical.
Lack of True IP Interoperability
Some converters claim IP support (e.g., SRT, RTP, RTMP, or NDI), but lack full compliance with standards or have limited compatibility with mainstream encoders, decoders, or streaming platforms. This can lead to integration issues and troubleshooting delays.
Inadequate Firmware and Software Support
Units with infrequent firmware updates or no remote management capabilities become difficult to maintain and scale. Without proper software tools, configuring IP settings, monitoring status, or diagnosing faults becomes time-consuming.
Overstated Specifications
Manufacturers may exaggerate bandwidth, supported resolutions, or transmission distances. For example, claiming “4K support” without specifying frame rate or chroma subsampling can be misleading. Always verify specs under real-world conditions.
Insufficient Power and Environmental Resilience
Many budget converters are designed for controlled environments and fail in field deployments. Look for units with wide voltage input ranges, surge protection, and ruggedized enclosures—especially for outdoor or mobile use.
Missing Redundancy and Monitoring Features
Professional applications require failover support, status LEDs, SNMP monitoring, or dual power inputs. Consumer-grade converters often lack these, increasing downtime risk.
Ignoring Security in IP-Enabled Devices
IP-based converters that lack password protection, encryption (e.g., TLS, SRT), or access control pose network security risks. Ensure devices support modern security protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: prioritize reputable brands, verify third-party certifications, test units in your specific workflow, and confirm long-term vendor support.
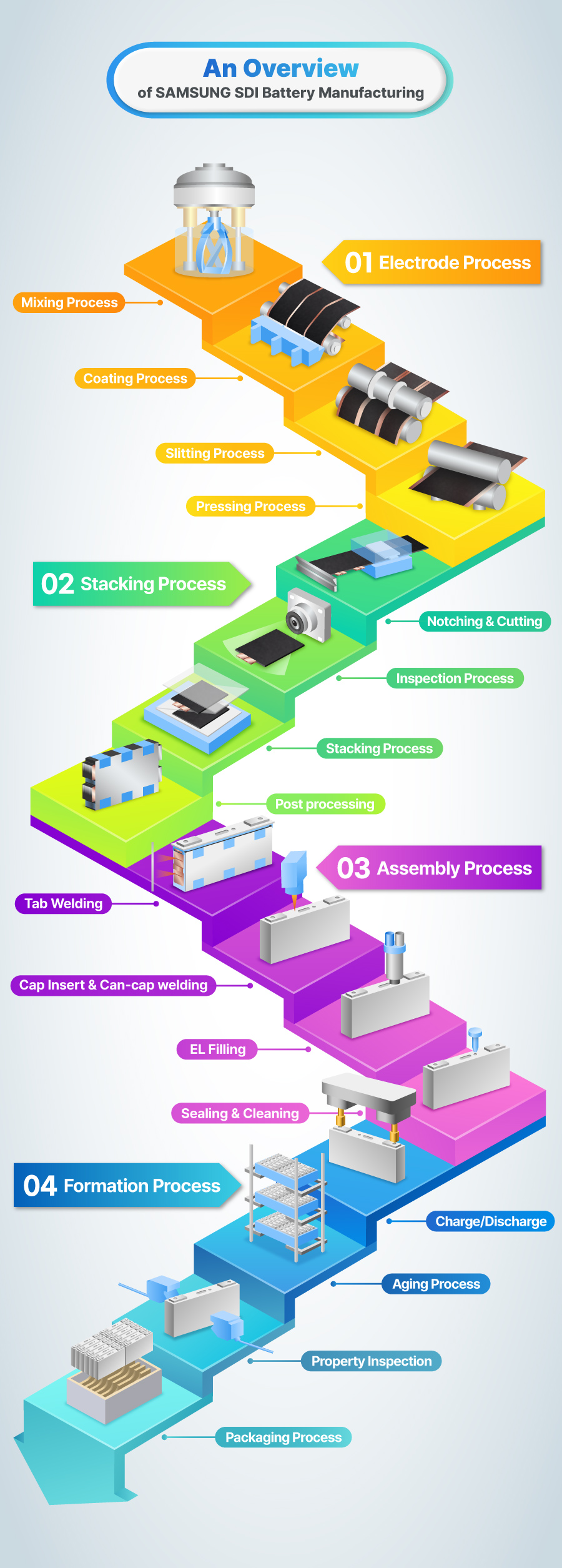
Logistics & Compliance Guide for HDMI to SDI Converter
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the distribution, import/export, and usage of HDMI to SDI converters. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, smooth supply chain operations, and product safety.
Regulatory Compliance
Electrical and Safety Standards
HDMI to SDI converters must comply with electrical safety standards in the target markets. Key certifications include:
– UL/ETL (North America): Required for electrical safety under OSHA regulations.
– CE (European Union): Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Includes compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
– UKCA (United Kingdom): Required for sale in Great Britain post-Brexit.
– PSE (Japan): Mandatory for electrical appliances under Japan’s Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law.
– KC (South Korea): Required by the Korea Electrotechnical Certification body.
Manufacturers must provide test reports and certification marks on product labels and packaging.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
SDI converters generate and are susceptible to electromagnetic interference. Compliance with EMC regulations is critical:
– FCC Part 15 (USA): Regulates unintentional radiators; Class A or B depending on use environment.
– CISPR 32 (International/EMEA): Governs radio disturbance characteristics for multimedia equipment.
– ICES-003 (Canada): Equivalent to FCC rules in Canada.
Ensure the device passes radiated and conducted emissions testing.
Environmental and Chemical Regulations
- RoHS (EU/China/UK/USA): Restricts the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium in electrical equipment.
- REACH (EU): Addresses the registration, evaluation, and restriction of chemical substances.
- WEEE (EU): Requires producers to manage end-of-life disposal and recycling of electronic equipment.
Maintain compliance documentation and provide product-specific substance declarations.
Logistics and Shipping
Packaging Requirements
- Use anti-static packaging to protect sensitive electronic components.
- Include cushioning materials to prevent physical damage during transit.
- Label packages with handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
- Include compliance marks (CE, FCC, etc.) and manufacturer/importer details on outer packaging.
Import and Export Documentation
Ensure the following documents are prepared for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Import Licenses (if required by destination country)
– FCC Declaration of Conformity or EU Declaration of Performance (as applicable)
Harmonized System (HS) Code
Use the correct HS code for customs clearance:
– Typical code: 8517.62 (Transmission apparatus for television) or 8543.70 (Electrical apparatus for line transmission of data).
– Confirm with local customs authorities, as classification may vary by design and function.
Battery and Power Supply Considerations
If the converter includes a rechargeable battery (e.g., lithium-ion):
– Comply with UN 38.3 testing requirements.
– Package according to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations for air transport.
– Label packages with proper shipping names and hazard class (Class 9).
Storage and Handling
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 0–40°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures.
- Follow FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices to minimize aging risks.
Product Labeling and User Documentation
Labeling Requirements
Each unit must display:
– Manufacturer/importer name and address
– Model and serial number
– Input/output specifications (e.g., HDMI 2.0, 3G-SDI)
– Power requirements (voltage, current)
– Regulatory marks (FCC, CE, RCM, etc.)
– Warning labels (e.g., “Do not expose to water”)
User Manuals and Safety Information
Include multilingual user manuals with:
– Installation and operation instructions
– Safety warnings and precautions
– Troubleshooting guide
– Compliance statements
– Recycling and disposal information (per WEEE or local regulations)
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Implement a quality control process to verify device functionality prior to shipment.
- Maintain batch records and serial number traceability for recalls or field service.
- Conduct periodic audits of manufacturing and logistics partners to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential for the global distribution of HDMI to SDI converters. By adhering to electrical, environmental, and shipping regulations, manufacturers and distributors can ensure product safety, avoid customs delays, and maintain customer trust. Always consult local regulatory bodies and legal counsel to stay up to date with evolving standards.
Conclusion on Sourcing an SDI Converter:
In conclusion, sourcing an SDI (Serial Digital Interface) converter requires careful consideration of technical specifications, application requirements, quality, reliability, and budget. Whether for broadcast, live production, or surveillance systems, selecting the right SDI converter involves evaluating signal compatibility (e.g., HD-SDI, 3G-SDI, 12G-SDI), conversion types (such as SDI to HDMI or fiber), and features like audio embedding, loop-through, and power resilience.
OEM reputation, product certifications, warranty support, and after-sales service are critical when choosing a supplier. While cost-effective options are available from various manufacturers, particularly in regions like Asia, investing in reputable brands often ensures better signal integrity, longer lifespan, and compliance with industry standards. In mission-critical environments, reliability outweighs initial savings.
Ultimately, a balanced approach—prioritizing performance, compatibility, and support—will lead to a successful integration of the SDI converter into your AV workflow, ensuring stable, high-quality video transmission across your system.