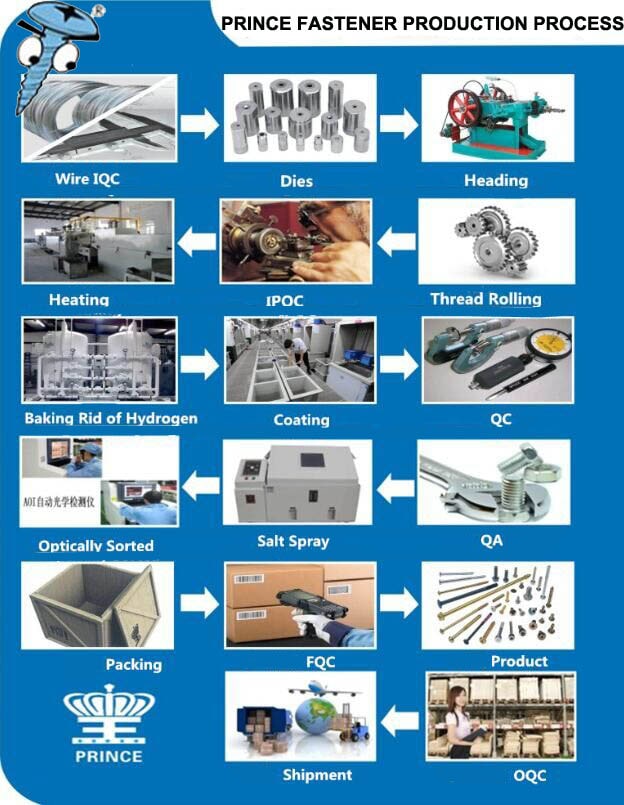
The global screws manufacturing market continues to expand amid rising demand from construction, automotive, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global fasteners market—of which screws are a critical component—was valued at USD 97.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is driven by increasing infrastructure investments, particularly in emerging economies, and the escalating production volumes in the automotive and aerospace industries, where high-precision fasteners are essential. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that the demand for corrosion-resistant and lightweight screws made from stainless steel and alloys is accelerating, especially in regions like Asia-Pacific, which accounted for over 40% of global fastener consumption in 2022. As the industry evolves with technological advancements and stricter regulatory standards, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in innovation, production capacity, and global reach. Here are the top 10 screws manufacturers shaping the future of this vital segment.
Top 10 Screws Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AMPG
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ampg.com
Key Highlights: AMPG is a trusted USA manufacturer of high-quality fasteners. We provide precision-engineered sex bolts, shoulder screws, washer, shims and other industrial ……
#2 Star Drive Wood Screws – Screw Products, Inc.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: screw-products.com
Key Highlights: Screw Products Inc. specializes in star drive stainless steel and heat treated wood screws for decks, log homes, remodeling, kitchen cabinets, docks, ……
#3 Midwest Fastener
Domain Est. 2000
Website: fastenerconnection.com
Key Highlights: Midwest Fastener is a fastener supplier and fastener manufacturer offering construction fasteners, drywall screws, and much, much more….
#4 Screw Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: katsuhana.com.tw
Key Highlights: Katsuhana Fasteners Corp, Taiwan professional screw manufacturer, provides High Stable Quality of Drywall Screw, SDS screw, Painted Screw, Tapping Screw, ……
#5 McMaster
Domain Est. 1994
Website: mcmaster.com
Key Highlights: McMaster-Carr is the complete source for your plant with over 700000 products. 98% of products ordered ship from stock and deliver same or next day….
#6 Specialty Fastening Solutions for the Commercial Construction …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: itwbuildex.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture self-drilling and tapping screws, anchors, toggles, and other fastening systems under the Teks, Sammys, Dec-King, EZ Ancor, and Rock-On-brands….
#7
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arp-bolts.com
Key Highlights: ARP was the first company to design and engineer fasteners specifically for racing. We developed many patented process for manufacturing high strength ……
#8 Reliable Wholesale Fastener Distributors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: intercorpusa.com
Key Highlights: Trusted Fastener Suppliers. Intercorp’s stringent manufacturing standards ensure that every Strong-Point fastener is designed to perform at the highest level….
#9 Interstate Screw
Domain Est. 1997
Website: interstate-screw.com
Key Highlights: Interstate Screw Corporation has been in business for over 60 years, and we are the oldest and largest fastener distributor in the state of Florida….
#10 SPAX US
Domain Est. 2004
Website: spax.us
Key Highlights: Our Engineered Screws & Fasteners are manufactured and rigorously tested right here in the heart of America. Rely on us to help you drive the highest quality….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Screws
H2 2026 Market Trends for Screws
As we progress through 2026, the global screws market is experiencing a dynamic shift influenced by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements, sustainability mandates, and geopolitical factors. The second half of 2026 (H2 2026) reveals several key trends shaping the production, distribution, and consumption of screws across various sectors.
Rising Demand in Construction and Infrastructure
H2 2026 continues to see robust growth in the construction and infrastructure sectors, particularly in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America. Government-led infrastructure projects—such as smart cities, transportation networks, and renewable energy installations—are driving demand for high-strength, corrosion-resistant screws. Structural screws used in steel framing, modular construction, and prefabricated buildings are witnessing above-average growth, supported by urbanization and housing shortages.
Expansion in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive industry, especially electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, is a major driver of innovation in screw design and materials. In H2 2026, the shift toward lightweight materials such as aluminum and composites in EVs has increased demand for specialized screws that offer reliable fastening without compromising structural integrity. Thread-forming and thread-cutting screws with enhanced torque control and anti-loosening features are in high demand. Additionally, automation in EV assembly lines is boosting the need for precision-engineered screws compatible with robotic installation.
Growth in Renewable Energy Applications
The renewable energy sector, particularly solar and wind power, is fueling demand for specialized fasteners. In H2 2026, solar panel mounting systems and wind turbine assembly continue to require stainless steel and coated screws with high resistance to environmental stress. The global push to meet climate targets has accelerated renewable installations, directly benefiting the screws market. Expansion in offshore wind projects, especially in Europe and East Asia, is increasing demand for marine-grade fasteners.
Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
Sustainability remains a critical priority in H2 2026. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, including using recycled metals and reducing carbon emissions in screw production. Customers—particularly in Europe and North America—are demanding transparency in sourcing and lifecycle impacts. Screw producers are responding with product lines certified under environmental standards (e.g., ISO 14001) and exploring biodegradable coatings and reusable fastening systems. The circular economy model is influencing design for disassembly, especially in electronics and appliances.
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical tensions and logistics disruptions have prompted companies to reevaluate global supply chains. In H2 2026, there is a notable trend toward regionalization and nearshoring of screw manufacturing. Companies are investing in local production facilities in North America, Eastern Europe, and Southeast Asia to mitigate risks and reduce lead times. Digital inventory platforms and just-in-time delivery models are being enhanced with AI-driven forecasting tools to improve responsiveness.
Technological Innovation and Smart Fasteners
Advancements in smart manufacturing are leading to the development of “smart screws” embedded with sensors to monitor stress, temperature, or loosening in real time—particularly in aerospace, defense, and industrial machinery. While still in early adoption, these innovations are gaining traction in H2 2026, driven by Industry 4.0 integration. Additionally, digital twin technology is being used to simulate screw performance under real-world conditions, improving R&D efficiency.
Price Volatility and Raw Material Challenges
Fluctuations in steel, zinc, and copper prices—due to energy costs and trade policies—are impacting screw pricing in H2 2026. Producers are hedging against volatility through long-term supplier contracts and diversifying material sources. Some manufacturers are transitioning to alternative alloys or improving coating technologies to extend product life and reduce material usage.
Conclusion
H2 2026 marks a pivotal phase for the screws market, characterized by strong demand from key industries, a deepening focus on sustainability, and technological innovation. Companies that adapt to regional supply chain needs, invest in R&D, and align with environmental goals are best positioned to thrive. As automation and electrification reshape global industries, the humble screw remains a critical enabler of modern engineering and construction.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Screws: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP)
Sourcing screws may seem straightforward, but it carries hidden risks—especially concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Standards
One of the biggest risks in screw sourcing is inconsistent quality, particularly when working with low-cost suppliers or new manufacturers. Common quality-related issues include:
- Inaccurate Thread Dimensions: Screws that don’t meet specified thread pitch, diameter, or tolerance can fail to fit or strip during assembly.
- Insufficient Strength or Hardness: Substandard materials or poor heat treatment result in screws that shear or deform under load.
- Corrosion Resistance Failures: Inadequate plating or coating leads to rust, especially in harsh environments, compromising structural integrity.
- Lack of Certification: Suppliers may claim compliance with ISO, ASTM, or DIN standards without providing valid test reports or mill certifications.
- Batch-to-Batch Variability: Inconsistent manufacturing processes lead to performance differences between production runs, increasing defect rates.
To mitigate this, always require material certifications, conduct third-party inspections, and establish clear quality agreements with suppliers.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Screws—especially proprietary or specialty fasteners—can be protected by patents, trademarks, or design rights. Sourcing them without due diligence can result in IP violations:
- Copying Patented Designs: Some high-performance screws (e.g., Torx with tamper-resistant features, or structural blind rivet screws) are patented. Manufacturing or sourcing replicas without a license constitutes infringement.
- Using Branded Drive Systems Illegally: Drive types like Torx, Phillips, or Pozidriv are trademarked or licensed. Unauthorized use in manufacturing or labeling can lead to legal action.
- Reverse Engineering Without Clearance: While common, reverse engineering a patented screw design for production may violate IP laws unless the patent has expired or a license is obtained.
- Supplier Misrepresentation: Some suppliers falsely claim their products are “compatible” or “equivalent” to branded fasteners, masking IP violations.
To avoid IP issues, conduct patent landscaping, verify the legal status of designs, and ensure suppliers warrant that their products do not infringe on third-party rights.
Conclusion
Sourcing screws involves more than just price and availability. Ensuring quality consistency and avoiding IP pitfalls requires proactive supplier vetting, technical specifications, and legal diligence. Investing in due diligence upfront prevents costly disruptions down the line.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Screws
Overview
Screws are widely used fasteners in manufacturing, construction, automotive, and consumer goods industries. Efficient logistics and strict compliance with international and regional regulations are essential to ensure timely delivery, product safety, and adherence to quality standards.
Classification and HS Code
- HS Code (Harmonized System Code): Typically classified under 7318.15 (Screws, of iron or steel, threaded) or 7318.29 (Other screws and bolts, whether or not with nuts or washers).
- Material-Based Classification: Stainless steel, carbon steel, alloy steel, and non-ferrous (e.g., brass, aluminum) screws may have different codes.
- Accurate classification is critical for customs clearance, duty calculation, and compliance with import/export regulations.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Standard Packaging: Screws are commonly packed in plastic bags, cartons, or bulk containers. Anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper) is recommended for metal screws.
- Labeling: Packages must include:
- Product description and specifications (e.g., size, thread type, material grade)
- Quantity and net weight
- Manufacturer or supplier name and address
- Batch or lot number
- Country of origin
- Compliance markings (e.g., CE, RoHS, REACH where applicable)
- Barcodes and SKUs: Essential for inventory management and traceability.
Transportation and Handling
- Mode of Transport: Air, sea, and ground freight are viable options depending on volume, urgency, and destination.
- Containerization: Use of standard dry containers for sea freight; palletization recommended to prevent shifting and damage.
- Handling: Use proper lifting equipment; avoid moisture exposure during transit to prevent rust (especially for carbon steel screws).
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent corrosion and maintain quality.
Import/Export Regulations
- Export Controls: Screws made from certain materials (e.g., high-strength alloys) may be subject to export restrictions under dual-use or strategic goods regulations.
- Import Duties and Taxes: Vary by country; check local tariff schedules. Preferential rates may apply under free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-UK TCA).
- Documentation: Required documents include:
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Bill of lading or air waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Material test reports (if required)
- Export declaration (if applicable)
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in electrical and electronic equipment. Applies if screws are used in such products.
- REACH (EU): Requires registration, evaluation, and restriction of chemicals. Suppliers may need to provide SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) declarations.
- CE Marking: Required for screws used in construction or machinery within the EU. Compliance with EN standards (e.g., EN ISO 898-1 for mechanical properties) is mandatory.
- ASTM/ASME (USA): Screws used in structural or mechanical applications must meet relevant ASTM or ASME standards.
- Conflict Minerals (Dodd-Frank Act): If screws contain tin, tungsten, tantalum, or gold, reporting may be required if sourced from conflict-affected regions.
Quality and Certification
- ISO Standards: Certification to ISO 9001 (Quality Management) is recommended for manufacturers and suppliers.
- Testing and Inspection: Dimensional accuracy, tensile strength, corrosion resistance (e.g., salt spray test), and thread integrity should be verified.
- Certificates of Conformity (CoC): Should be provided upon request, confirming compliance with specified standards.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Recyclability: Steel screws are highly recyclable; promote sustainable end-of-life practices.
- Packaging Waste: Use recyclable or biodegradable packaging materials where possible.
- Carbon Footprint: Optimize logistics routes and consolidate shipments to reduce emissions.
Risk Management
- Supply Chain Visibility: Implement tracking systems to monitor shipments in real time.
- Supplier Audits: Regularly assess suppliers for compliance, quality, and ethical practices.
- Incident Response: Have procedures in place for recalls, customs delays, or non-compliance issues.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for screws require accurate classification, proper documentation, adherence to international regulations, and robust quality control. By following this guide, businesses can ensure smooth cross-border trade, minimize risks, and maintain product integrity across the supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing screws requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, availability, and reliability. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on certifications, production capabilities, and track record to ensure consistent product standards. Understanding the specific application requirements—such as material, size, coating, and strength—helps in selecting the most suitable screws and avoids performance issues. Establishing long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers can lead to better pricing, just-in-time delivery, and improved supply chain resilience. Additionally, considering sustainability and ethical sourcing practices supports corporate responsibility goals. Ultimately, effective screw sourcing contributes to overall operational efficiency, product durability, and cost savings across manufacturing and construction processes.