The global screwdriver market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as construction, automotive, electronics, and DIY applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global hand tools market—of which screwdrivers are a key component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure development, advancements in tool ergonomics, and a surge in home improvement activities, particularly in emerging economies. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that the growing emphasis on precision tools in the electronics and aerospace sectors is further boosting demand for high-quality screwdrivers. With tightening quality standards and the proliferation of specialized drive types (e.g., Phillips, Torx, Pozidriv), leading manufacturers are investing in innovative materials, ergonomic designs, and durability enhancements to gain competitive advantage. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top screwdriver manufacturers becomes essential for professionals and consumers seeking reliability, performance, and value.
Top 10 Screwdriver Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Speciality Screwdriver Sets Made in the USA by Chapman …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chapmanmfg.com
Key Highlights: Made in the USA for over 85 years, Chapman provides a variety of screwdriver sets for industrial assembly, maintenance, home repairs, and more….
#2 Klein Tools – For Professionals since 1857
Domain Est. 1998
Website: kleintools.com
Key Highlights: Klein is the only major tool manufacturer worldwide focused on electrical and utility applications. No other manufacturer of hand tools and related products…
#3 The Phillips Screw Company
Domain Est. 1998
Website: phillips-screw.com
Key Highlights: Phillips Screw Company is a leader in the design and engineering of proprietary fastener technology, including high-performance drive systems….
#4 Milwaukee® Tool
Domain Est. 2000
Website: milwaukeetool.com
Key Highlights: Milwaukee Tool is the most respected manufacturer of heavy-duty power tools … Screwdrivers & Screwguns. Combo Kits. View All — Combo Kits · 2 Piece Kits….
#5 VESSEL TOOLS U.S.A., INC
Domain Est. 2017
Website: vesseltoolsusa.com
Key Highlights: VESSEL TOOLS USA, INC. 2384 E. Artesia Blvd., Long Beach, CA 90805 Tel : 424-427-5441 www.vesseltoolsusa.com…
#6 Screwdrivers in high quality from Weidmüller
Domain Est. 1996
Website: weidmuller.com
Key Highlights: Screwdrivers – Our screwdrivers are up to the task ✓ Power and precision ✓ Discover products now | Weidmüller….
#7 CHANNELLOCK®: High
Domain Est. 1996
Website: channellock.com
Key Highlights: Explore the high quality tools Channellock has been making since 1886 including pliers, wrenches, screwdriver, toolsets and more….
#8 Screwdrivers individually or as a set
Domain Est. 2000
Website: wiha.com
Key Highlights: Wiha offers a fully insulated, variable screwdriver system called the “ElectricVario Family”. It consists of a total of 83 components that can be combined with ……
#9 Screwdrivers, Nut Drivers & Bits
Domain Est. 2012
#10 Screwdriver
Website: wera.de
Key Highlights: Professional filter · With flexible shaft · Ball tip · Torsion zone · Hollow shaft · Reduced blade and handle diameter · Halfmoon and HIOS · Suitable for Wera 2go….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Screwdriver

2026 Market Trends for Screwdrivers
The global screwdriver market is poised for notable evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and growing consumer interest in smart and ergonomic tools. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the screwdriver industry in 2026, focusing on innovation, market segmentation, regional developments, and sustainability.
Technological Innovation and Smart Tools
One of the most significant trends shaping the 2026 screwdriver market is the integration of smart technology into hand tools. Manufacturers are increasingly embedding sensors, Bluetooth connectivity, and torque control systems into screwdrivers to enhance precision and data tracking. Smart screwdrivers are gaining traction in industrial and automotive applications where consistent torque application is critical. These tools can connect to mobile apps or centralized systems, enabling real-time monitoring, performance analytics, and quality control—particularly valuable in manufacturing and assembly lines.
Additionally, the rise of cordless and battery-powered screwdrivers continues to accelerate. Advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have improved run time, reduced charging times, and increased power efficiency. By 2026, expect a broader adoption of modular battery systems compatible across tool ranges, enhancing user convenience and reducing costs.
Ergonomics and User-Centric Design
As workplace safety and user comfort gain prominence, ergonomic design is becoming a key differentiator in the screwdriver market. In 2026, leading brands are expected to prioritize lightweight materials, anti-vibration handles, and customizable grips to reduce user fatigue and the risk of repetitive strain injuries. This trend is particularly influential in professional sectors such as construction, electronics repair, and manufacturing.
Moreover, demand for compact and multi-functional screwdrivers is rising, especially in electronics and DIY markets. Products featuring interchangeable bits, built-in LED lights, and magnetic bit holders are becoming standard, offering enhanced utility in tight spaces and low-light conditions.
Growth in the DIY and Home Improvement Sector
The DIY (Do-It-Yourself) movement continues to expand globally, fueled by online tutorials, social media, and home renovation trends. By 2026, this sector will represent a significant portion of screwdriver demand. Consumers are increasingly investing in high-quality, aesthetically pleasing, and versatile tools for home projects. Retailers and manufacturers are responding with value packs, beginner-friendly sets, and branded toolkits appealing to both novice and experienced users.
E-commerce platforms are also playing a crucial role in driving accessibility and competition. Online marketplaces enable smaller brands to reach global audiences, fostering innovation and customization in screwdriver offerings.
Industrial Automation and Precision Requirements
In industrial settings, the demand for precision screwdriving solutions is growing due to automation and miniaturization trends—especially in electronics, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. By 2026, automated screwdriving systems and servo-controlled electric screwdrivers are expected to see increased adoption. These systems offer programmable torque settings, error detection, and integration with robotic assembly lines, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
Additionally, traceability requirements in regulated industries will boost demand for screwdrivers that can log data and ensure compliance with quality standards.
Regional Market Dynamics
Regionally, the Asia-Pacific market is projected to lead growth in 2026, driven by rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sectors (particularly in China, India, and Southeast Asia), and rising urbanization. The region’s electronics production hubs will require high volumes of precision screwdriving tools.
North America and Europe will see steady growth, supported by infrastructure development, automotive manufacturing, and a strong DIY culture. These regions are also likely to be early adopters of smart and sustainable tools due to stricter environmental regulations and higher consumer awareness.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is emerging as a key factor in tool manufacturing. By 2026, more companies are expected to adopt eco-friendly materials, modular designs for easier repair, and recyclable packaging. The circular economy model—emphasizing tool longevity, refurbishment, and component reuse—will gain momentum. Brands that emphasize durability and sustainability are likely to gain competitive advantage, especially among environmentally conscious consumers and corporate procurement teams.
Conclusion
By 2026, the screwdriver market will be characterized by technological sophistication, ergonomic advancement, and diversified demand across industrial, professional, and consumer segments. Smart tools, sustainability practices, and the growing DIY culture will be central drivers of innovation and market expansion. Companies that invest in R&D, user-centric design, and digital integration will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
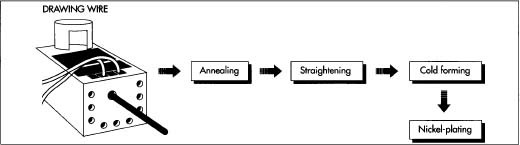
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Screwdrivers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing screwdrivers—especially for industrial, medical, or high-precision applications—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these factors can lead to product failures, legal risks, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls buyers face:
Poor Material and Build Quality
Many low-cost screwdrivers use substandard steel that degrades quickly, leading to stripped screw heads and tool failure. Soft alloy tips deform easily, while poorly heat-treated shafts can twist or break under torque. Inconsistent manufacturing also results in imprecise tip dimensions, reducing compatibility and increasing the risk of damage to sensitive components.
Inaccurate or Missing IP Ratings
When sourcing screwdrivers for use in hazardous or sensitive environments (e.g., electronics, medical devices), IP (Ingress Protection) ratings are critical. A common pitfall is assuming a generic “insulated” or “anti-static” claim equates to compliance with standards like IEC 60900. Some suppliers misrepresent or omit proper IP ratings, leading to safety hazards and non-compliance with industry regulations.
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Reputable screwdrivers—especially insulated or ESD-safe versions—must come with valid certifications (e.g., VDE, CE, RoHS). Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide documentation or batch traceability increases the risk of counterfeit products and exposes the buyer to liability in the event of electrical accidents or product recalls.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Copying patented designs—such as unique handle ergonomics, tip geometries (e.g., Posidriv, Pentalobe), or safety features—can lead to legal action. Some suppliers, particularly in unregulated markets, replicate branded tools without authorization. Sourcing from such vendors may expose your company to IP litigation, shipment seizures, and brand damage.
Inconsistent Quality Control Across Suppliers
When sourcing from multiple or low-tier suppliers to cut costs, quality often varies significantly between batches. This inconsistency undermines reliability and increases the total cost of ownership due to rework, tool replacement, and downtime.
Overlooking Total Cost of Ownership
Focusing solely on unit price leads many buyers to choose cheaper screwdrivers that wear out quickly or fail prematurely. High-quality tools may have a higher upfront cost but offer better durability, precision, and safety, ultimately reducing lifecycle costs and improving productivity.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers, demanding certifications, verifying IP ratings, and ensuring IP compliance. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and conducting regular quality audits can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, compliant tooling.
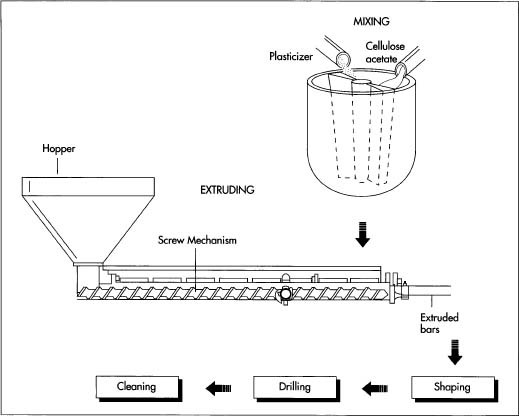
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Screwdrivers
Product Classification and HS Codes
Screwdrivers are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 8205.40, which covers hand tools for working in the hand, not elsewhere specified or included. This classification applies to both manual and non-powered screwdrivers. Accurate classification is essential for international shipping, customs clearance, and determining applicable tariffs. Always verify the specific HS code with local customs authorities, as sub-classifications may vary by country and screwdriver type (e.g., precision, insulated, or magnetic tip).
Import/Export Regulations
Compliance with import and export regulations is critical when shipping screwdrivers internationally. Exporters must adhere to the regulations of the country of origin, including proper documentation such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Some countries may require additional certifications (e.g., CE marking in the EU or UKCA in the UK) to demonstrate conformity with safety and quality standards. Be aware of trade restrictions or sanctions that may affect shipments to certain destinations.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Screwdrivers must be packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use sturdy, standardized packaging with internal dividers or blister packs for protection. Labeling should include product identification, model number, country of origin, manufacturer details, and applicable safety warnings. For markets such as the European Union, labeling must comply with relevant directives, including the Machinery Directive or Low Voltage Directive if applicable. Barcodes and shipping labels should be clearly visible and adhere to carrier specifications.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
Ensure screwdrivers meet relevant safety standards such as ISO 2380-1 (for slotted screwdriver tips) or IEC 60900 (for insulated hand tools used in live electrical work). Tools marketed as insulated for electrical use must comply with voltage ratings and undergo dielectric testing. Additionally, comply with environmental regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) in the EU, which restricts the use of lead, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in tool production.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Screwdrivers are generally non-restricted goods and can be shipped via air, sea, or ground freight. However, lithium-powered electric screwdrivers may be subject to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations due to their batteries. For such items, ensure proper packaging, labeling, and documentation (e.g., UN38.3 test certification for lithium batteries). Standard metal screwdrivers pose no hazardous material concerns and can be transported under general cargo rules.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain detailed records of product specifications, compliance certifications, shipping documents, and supplier information. These records support customs audits, product recalls, and regulatory inquiries. Implement a traceability system to track batches or serial numbers, especially for industrial or safety-critical applications. Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing compliance with logistics and regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Updates and Monitoring
Stay informed about changes in international trade policies, customs procedures, and product safety standards. Subscribe to updates from regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), European Commission, or local standards organizations. Proactive monitoring helps prevent delays, fines, or shipment rejections due to non-compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing screwdrivers requires a careful evaluation of several key factors including quality, cost, supplier reliability, material durability, ergonomic design, and compliance with industry standards. Whether for industrial use, retail distribution, or internal operations, selecting the right screwdriver involves balancing performance needs with budget constraints. Developing strong relationships with reputable suppliers, considering both local and global options, and conducting thorough product assessments ensure a consistent supply of reliable tools. Additionally, prioritizing sustainability and long-term value over short-term savings contributes to operational efficiency and user satisfaction. Effective sourcing strategies ultimately lead to improved tool performance, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced overall productivity.