The global fasteners market, driven by rising demand from industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics, was valued at approximately USD 108.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% through 2030, according to a report by Grand View Research. A key segment within this expansive market is specialized fasteners, including screws without heads—also known as set screws or headless screws—used where a flush or concealed finish is required. These components are critical in precision machinery, medical devices, and compact electronics, where space constraints and aesthetic integrity are paramount. With increasing miniaturization in manufacturing and stringent performance standards, demand for high-quality, headless screw solutions has surged. This growing need has positioned a select group of manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, precision engineering, and global supply. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, certifications, and technological expertise, we identify the top 10 screw without head manufacturers shaping the future of industrial fastening.
Top 10 Screw Without Head Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AMPG
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ampg.com
Key Highlights: AMPG is a trusted USA manufacturer of high-quality fasteners. We provide precision-engineered sex bolts, shoulder screws, washer, shims and other industrial ……
#2 Star Drive Wood Screws – Screw Products, Inc.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: screw-products.com
Key Highlights: Screw Products Inc. specializes in star drive stainless steel and heat treated wood screws for decks, log homes, remodeling, kitchen cabinets, docks, ……
#3 Pro-Twist
Domain Est. 2003
Website: pro-twist.com
Key Highlights: Pro-Twist is an industry-leading manufacturer of professional-grade fasteners that are used for a wide variety of applications. Get started with us today!…
#4 Fasco Fastener & Industrial Supply Corp
Domain Est. 2012
Website: fascofas.com
Key Highlights: Fasco Fastener & Industrial Supply is your one stop shop for durable, high-quality fasteners for many types of construction projects….
#5 Fastening Systems — Screws & Nails
Domain Est. 1995
Website: strongtie.com
Key Highlights: Information about our wide variety of nail types and screw styles designed for every project including our Strong-Drive® and Deck-Drive™ product lines….
#6 Specialty Fastening Solutions for the Commercial Construction …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: itwbuildex.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture self-drilling and tapping screws, anchors, toggles, and other fastening systems under the Teks, Sammys, Dec-King, EZ Ancor, and Rock-On-brands….
#7 Special Screws
Domain Est. 2000
Website: nbk1560.com
Key Highlights: Screws made of special materials such as Inconel, Molybdenum and Hastelloy to provide excellent heat, chemical, corrosion resistance….
#8 HOLO
Domain Est. 2003
Website: holo-krome.com
Key Highlights: All HOLO-KROME products are made in the USA and used in a wide variety of market application which demand high-quality, high-strength precision components. Holo ……
#9 SPAX US
Domain Est. 2004
Website: spax.us
Key Highlights: Our Engineered Screws & Fasteners are manufactured and rigorously tested right here in the heart of America. Rely on us to help you drive the highest quality….
#10 Headless Compression & Twist
Domain Est. 2014
Website: zimmerbiomet.com
Key Highlights: The Zimmer Biomet Headless Compression and Twist-Off Screw System offers cannulated, fully threaded and partially-threaded headless compression screws….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Screw Without Head
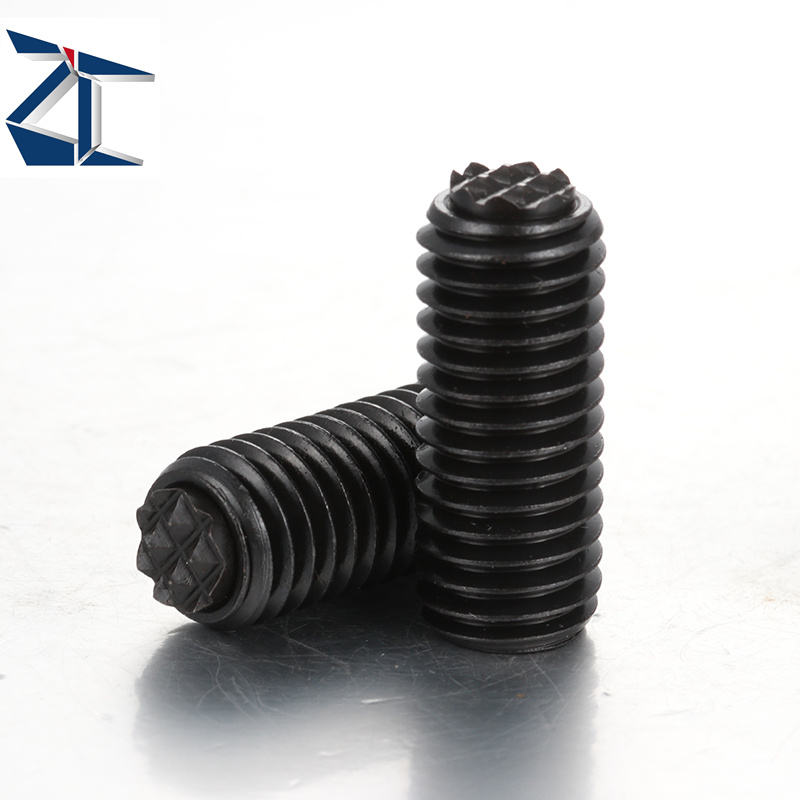

H2: Market Trends for Screws Without Heads (2026 Outlook)
The global market for screws without heads—also known as set screws, grub screws, or headless screws—is projected to experience steady growth and notable transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing, increasing demand in precision engineering, and the expansion of automated assembly processes. These fasteners are valued for their flush mounting capability, compact design, and ability to secure components without protruding hardware, making them ideal for high-precision and space-constrained applications.
1. Rising Demand in High-Tech and Precision Industries
By 2026, the electronics, robotics, aerospace, and medical device sectors are expected to be primary growth drivers for headless screws. Miniaturization trends in consumer electronics and wearable devices require compact, reliable fastening solutions. Headless screws, particularly in miniature and micro sizes, are increasingly used in circuit boards, sensors, and actuator assemblies. The aerospace and defense industries also favor these screws for internal mechanisms where aerodynamics and weight savings are critical.
2. Growth in Automation and Robotics
The increasing deployment of industrial robots and automated manufacturing systems is boosting demand for reliable, tamper-resistant fasteners. Headless socket set screws are widely used in shaft collars, couplings, and motor assemblies within robotic systems. As global Industry 4.0 adoption accelerates, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America, the need for durable, precision-engineered headless screws will rise significantly.
3. Material and Coating Innovations
By 2026, sustainability and performance demands are pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced materials such as stainless steel (especially grades 304 and 316), titanium, and high-strength alloys. Additionally, anti-corrosion coatings like black oxide, zinc-nickel, and PTFE are becoming standard to enhance durability in harsh environments. Biocompatible coatings are also gaining traction in medical applications.
4. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is expected to dominate the headless screw market in 2026 due to its robust electronics manufacturing base and expanding automotive sector. North America and Western Europe will follow, driven by aerospace innovation, medical technology advancements, and stringent quality standards. Localized production and supply chain resilience are becoming priorities, encouraging regional manufacturing investments.
5. Sustainability and Circular Economy Influences
Environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria are shaping production practices. By 2026, leading manufacturers are expected to adopt energy-efficient machining, recyclable materials, and reduced-waste manufacturing techniques. The push for longer product lifecycles and serviceability in consumer electronics also supports the use of reusable, high-quality headless fasteners.
6. Competitive Landscape and Customization Trends
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with a shift toward customized solutions. OEMs and industrial clients are demanding tailored thread types (metric, imperial, fine-pitch), drive types (hex, socket, Torx), and specialized geometries. This trend favors manufacturers with agile production capabilities and strong R&D focus.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for screws without heads will be shaped by the convergence of technological innovation, industrial automation, and sustainability imperatives. With growing applications in high-value sectors and continuous improvements in materials and design, the headless screw market is poised for moderate but sustained growth, offering opportunities for manufacturers who can deliver precision, reliability, and customization at scale.
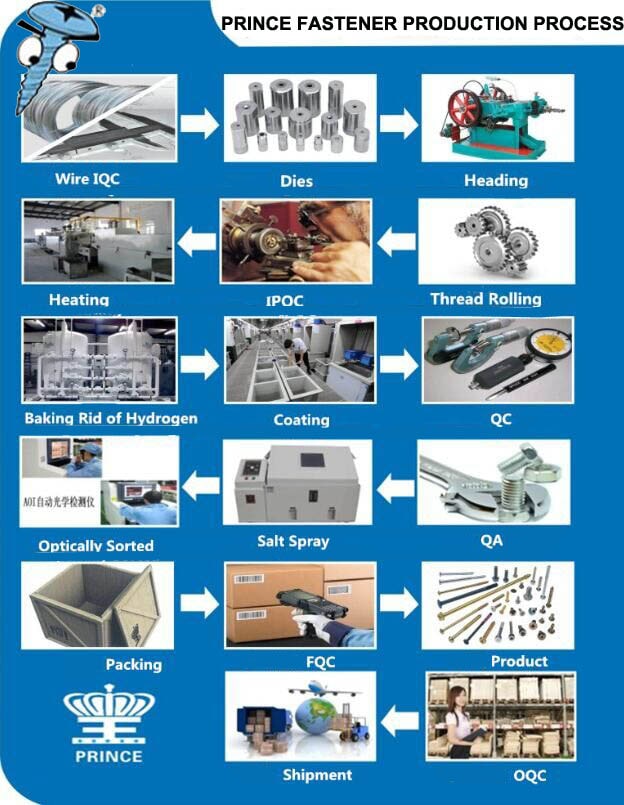
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Screw Without Head (Quality, IP)
Sourcing screws without heads—such as set screws, grub screws, or headless socket screws—can present unique challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply and legal compliance.
Poor Material and Dimensional Quality
One of the most frequent issues is inconsistent material composition and poor dimensional accuracy. Headless screws are often used in precision applications (e.g., securing shafts or components in machinery), where even minor deviations can lead to failure. Suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, may use substandard alloys or fail to adhere to tight tolerances specified in standards like ISO 4026 or ASME B18.3. This can result in stripped drive sockets, thread damage, or insufficient clamping force.
Inadequate Heat Treatment and Surface Finish
Headless screws typically require specific hardness levels to resist deformation under load. Poor or inconsistent heat treatment processes can lead to screws that are either too brittle (leading to cracking) or too soft (causing thread stripping). Additionally, surface treatments like black oxide, zinc plating, or passivation may be improperly applied, reducing corrosion resistance and shortening service life.
Non-Compliance with International Standards
Many suppliers falsely claim compliance with ISO, DIN, or ANSI standards without proper certification or testing. This misrepresentation becomes evident only during quality inspections or in-field failures. Always verify test reports and request samples for third-party validation before bulk procurement.
Risk of Counterfeit or Non-Genuine Fasteners
The generic nature of headless screws makes them prone to counterfeiting. Some suppliers rebrand inferior products as OEM-equivalent or certified items. This not only affects performance but can also void equipment warranties and compromise safety, especially in regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Sourcing headless screws designed to match proprietary fasteners (e.g., custom thread profiles, drive types, or sizes used in branded equipment) carries IP risks. Replicating a patented or trademarked screw design—even if functionally similar—can lead to legal action for infringement. This is particularly critical when reverse-engineering screws used in high-tech or industrial equipment without proper licensing.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Many low-tier suppliers fail to provide full material traceability, mill test reports (MTRs), or compliance documentation. In regulated industries, this lack of documentation can lead to audit failures and supply chain disruptions. Always require proper certification and lot traceability to ensure accountability.
Supply Chain and Lead Time Instability
Reliance on single or unverified suppliers—especially overseas—can lead to long lead times, inconsistent batches, and communication challenges. Without backup sources or quality agreements, any disruption can halt production.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Source from certified, audited suppliers with proven quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Request and verify material certifications and dimensional reports.
– Conduct pre-shipment inspections and sample testing.
– Consult legal counsel when replicating proprietary designs.
– Use procurement contracts that include quality clauses and IP indemnification.
Proactively addressing these issues ensures reliable performance and minimizes legal and operational risks when sourcing headless screws.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Screw Without Head
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the international shipment and regulatory adherence of “Screw Without Head” (also known as set screws, grub screws, or headless screws), commonly used in mechanical assemblies.
Product Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Code
Correct product classification is critical for customs clearance and duty assessment. A headless screw typically falls under HS code 7318.15 or 7318.19, depending on material and size. For example:
– 7318.15: Screws and bolts, whether or not with their nuts or washers, of stainless steel.
– 7318.19: Other screws and bolts, not of stainless steel.
Accurate classification ensures compliance with import/export regulations and helps avoid delays or penalties. Always verify the exact HS code with your local customs authority or a licensed customs broker.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Headless screws should be packaged to prevent damage, corrosion, and contamination. Recommended practices include:
– Use moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., vacuum-sealed bags or anti-corrosion paper).
– Clearly label each package with:
– Product description (e.g., “Stainless Steel Set Screw, M4x10”)
– Quantity
– Batch/lot number
– Country of origin
– Supplier identification
– Include a packing list and commercial invoice with every shipment.
Proper labeling ensures traceability and compliance with international shipping standards.
Export Controls & Restricted Parties Screening
Certain industrial fasteners may be subject to export control regulations, especially if they are used in aerospace, defense, or high-tech applications. Conduct the following:
– Screen end-users against government restricted parties lists (e.g., U.S. Denied Persons List, EU Consolidated List).
– Determine if an export license is required based on destination country and intended use.
– Maintain records of screening and licensing for audit purposes.
Failure to comply with export controls can result in severe legal and financial consequences.
Customs Documentation
Ensure all required documentation is accurate and complete for smooth customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice: Includes value, description, HS code, origin, and Incoterms.
– Packing List: Details of contents, weights, and dimensions.
– Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries to determine tariff eligibility (e.g., under free trade agreements).
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill: Legal receipt and contract of carriage.
Use Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP) to clarify responsibilities between buyer and seller.
Transportation & Handling
Headless screws are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via air, sea, or land freight. However:
– Use standard industrial packaging suitable for bulk or retail needs.
– Protect from extreme temperatures and humidity during transit.
– Ensure secure loading to prevent shifting in containers.
Consider insurance for high-value shipments.
Regulatory Compliance (REACH, RoHS, etc.)
Depending on the destination market, headless screws may need to comply with chemical and environmental regulations:
– REACH (EU): Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., certain metals or coatings) are present above thresholds.
– RoHS (EU): Applies if screws are part of electrical/electronic equipment; verify lead and cadmium content.
– Proposition 65 (California, USA): Disclose if screws contain chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm.
Maintain compliance documentation and Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if applicable.
Import Duties & Taxes
Import duties vary by country and HS code classification. Research:
– Applicable tariff rates for the destination country.
– Potential exemptions or preferential rates under trade agreements.
– Value Added Tax (VAT) or Goods and Services Tax (GST) requirements.
Consult with a customs broker to optimize duty costs and ensure accurate declarations.
Recordkeeping & Audit Trail
Maintain comprehensive records for a minimum of 5–7 years, including:
– Invoices and shipping documents
– Export licenses (if applicable)
– Compliance certifications
– Restricted party screening logs
Robust recordkeeping supports audits and regulatory inquiries.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for headless screws ensures timely delivery, avoids penalties, and supports global trade sustainability. Partner with experienced freight forwarders, customs brokers, and compliance consultants to navigate complex international regulations effectively.
Conclusion for Sourcing Screws Without Heads:
Sourcing screws without heads, such as set screws, grub screws, or headless thread-forming/fastening screws, requires careful consideration of material specifications, thread type, drive style, length, diameter, and application requirements. These fasteners are often used in applications where a low-profile or flush finish is necessary, such as in machinery, shaft collars, or precision instruments. Successfully sourcing headless screws involves identifying reliable suppliers, ensuring compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ANSI), and verifying the mechanical and environmental suitability of the material (e.g., stainless steel, alloy steel, brass). Additionally, working with experienced distributors or manufacturers can help overcome potential challenges related to customization, availability, and quality control. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of technical requirements and supplier capabilities is essential to ensure performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in the final application.