The global market for schedule 120 pipes—valued for their thick walls and high-pressure capabilities—is experiencing steady expansion, driven by growing demand across oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global stainless steel pipes and tubes market was valued at USD 37.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% through 2029, with Sch 120 pipes playing a critical role in high-performance applications. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights the increasing infrastructure investments and pipeline modernization projects—particularly in North America and Asia Pacific—as key growth catalysts. With stringent regulatory standards and rising emphasis on corrosion resistance and system durability, end-users are increasingly turning to trusted Sch 120 pipe manufacturers known for quality compliance, dimensional precision, and reliability under extreme conditions. In this competitive landscape, the top 9 manufacturers stand out through scalable production, advanced metallurgical engineering, and strong global distribution networks.
Top 9 Sch 120 Pipe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pipe Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: southernpipe.com
Key Highlights: Southern Pipe & Supply is a leading online HVAC, air conditioning, mechanical, industrial pipe, valves and fittings, waterworks, and plumbing supply store…
#2 H1200600PG2000 Georg Fischer PVC Pipe & Fittings
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rhfs.com
Key Highlights: $1,000 deliveryManufacturer, Georg Fischer. Manufacturer’s part number, H1200600PG2000. Type, Pipe. Classification, Schedule 120. Material, PVC. Nominal Size, 6″. Color, Gray….
#3 Schedule 120 Pipe
Domain Est. 2019
Website: pandapipe.com
Key Highlights: Schedule 120 Pipe is specially designed for high temperature and high pressure environments in the industrial and construction fields….
#4 Carbon Steel Pipe Supplier
Domain Est. 1996
Website: saginawpipe.com
Key Highlights: Saginaw carries a complete inventory of carbon steel pipe, ranging in size from 1/8 inch to 48 inch OD for A252 Grade and A500 Grade Carbon Steel pipe….
#5 Bath Iron Works
Domain Est. 1998
Website: gdbiw.com
Key Highlights: Bath Iron Works is a leader in designing and building US Navy ships. We also provide maintenance, modernization and lifecycle support services for Navy ships….
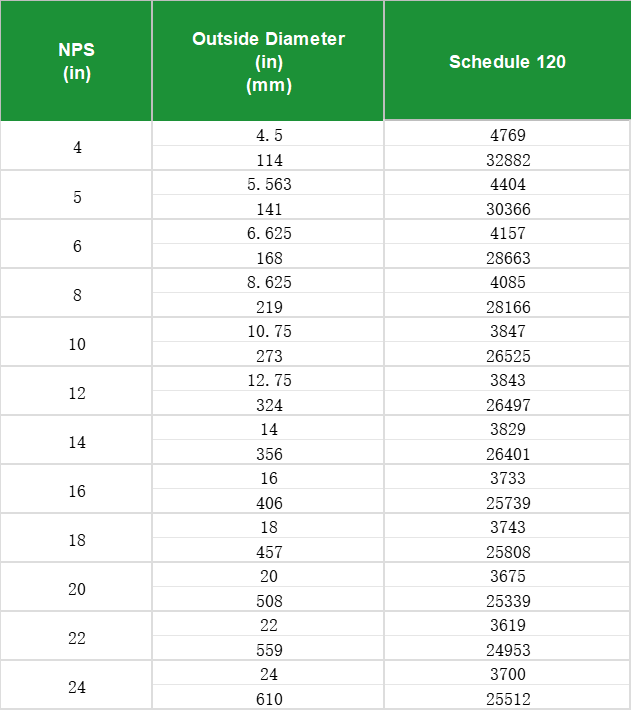
#6 Pipe Schedule Chart
Domain Est. 1999
Website: naspd.com
Key Highlights: Steel Pipe Schedules – Sch 100, Sch 120. Sch 100, Sch 120. Nom Size, OD, Wall, lbs / ft, Wall, lbs / ft. 1/8, 0.405. 1/4, 0.54. 3/8, 0.675. 1/2, 0.84. 3/4, 1.05….
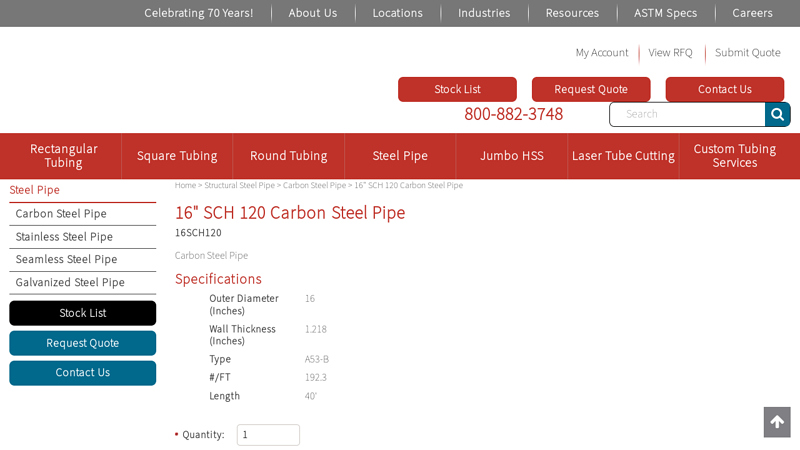
#7 16″ SCH 120 Carbon Steel Pipe
Domain Est. 2000
#8 Schedule 120 Stainless Steel Pipe
Domain Est. 2005
Website: amardeepsteel.com
Key Highlights: Schedule 120 pipes have dimensions that typically span from 5 to 120 inches, while the outer diameter can reach up to 24 inches….
#9 Schedule 120 Steel Pipe
Domain Est. 2018
Website: newzelindustries.com
Key Highlights: Schedule 120 Steel Pipe Supplier & Exporter. Check out SCH 120 pipe dimensions, wall thickness, pipe pressure rating & weight chart. But SCH 120 pipe now!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sch 120 Pipe

H2: Projected Market Trends for Schedule 120 Pipe in 2026
As we approach 2026, the global market for Schedule 120 (SCH 120) steel pipe—a heavy-wall piping solution commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature industrial applications—is expected to undergo significant transformation driven by macroeconomic factors, evolving industry demands, and technological advancements. SCH 120 pipes, known for their robust wall thickness and durability, are primarily utilized in oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment industries. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the SCH 120 pipe sector in 2026:
-
Growing Demand in Energy Infrastructure
The continued expansion of oil and gas infrastructure, particularly in emerging markets and regions with deep-water offshore exploration (such as the Gulf of Mexico, West Africa, and the Eastern Mediterranean), is expected to drive demand for high-pressure piping systems. SCH 120 pipes are well-suited for these applications due to their ability to withstand extreme pressures and corrosive environments. The global push to enhance energy security amid geopolitical volatility is likely to accelerate pipeline construction and retrofitting projects, boosting SCH 120 adoption. -
Increased Focus on Industrial Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory standards in the U.S. (e.g., ASME B31.3), EU (PED), and other regions are placing greater emphasis on safety and material integrity in high-risk industrial environments. SCH 120 pipes, which exceed the wall thickness of standard schedules like SCH 40 or 80, are increasingly being specified in new installations to ensure compliance with safety codes and reduce the risk of failure. This trend is expected to intensify in 2026, particularly in chemical and petrochemical plants undergoing safety upgrades. -
Rise in Replacement and Retrofitting Projects
Aging infrastructure in North America and Europe is necessitating pipe replacement, with operators opting for heavier-wall solutions like SCH 120 to extend service life and improve reliability. Asset integrity management programs are favoring high-schedule pipes in critical service lines, contributing to sustained demand despite higher initial costs. -
Material Innovation and Cost Pressures
While carbon steel remains dominant, there is growing interest in corrosion-resistant alloys (CRAs) and duplex stainless steels for SCH 120 applications in highly corrosive environments. However, high raw material costs—especially for nickel and chromium—may constrain adoption. Manufacturers are responding with hybrid solutions and improved manufacturing techniques (e.g., seamless vs. welded) to optimize cost-performance ratios. -
Impact of Sustainability and ESG Initiatives
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are influencing procurement decisions. Producers of SCH 120 pipe are investing in cleaner production methods, such as electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking and recycling programs, to reduce carbon footprints. Buyers in regulated industries are increasingly favoring suppliers with strong sustainability credentials, a trend expected to grow in 2026. -
Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: Remains a key market due to shale gas development and refinery modernization.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid industrialization in India, Southeast Asia, and China is driving demand for high-integrity piping systems.
- Middle East & Africa: Major investments in downstream oil and gas projects (e.g., Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030) are creating strong demand for SCH 120 pipes.
-
Europe: Growth is more moderate, focused on retrofitting and renewable energy integration (e.g., hydrogen-ready piping systems).
-
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Post-pandemic and post-conflict supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional manufacturing and inventory buffering. In 2026, we expect to see increased localization of SCH 120 pipe production to mitigate logistics risks and tariffs, especially in North America and India.
Conclusion
By 2026, the SCH 120 pipe market is poised for steady growth, underpinned by robust demand from energy and industrial sectors, stricter safety regulations, and infrastructure modernization efforts. While cost and material availability remain challenges, technological innovation and a focus on sustainability will enable market participants to meet evolving requirements. Companies that invest in quality, compliance, and supply chain agility are likely to gain a competitive edge in this specialized segment.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Schedule 120 Pipe (Quality, Intellectual Property)
Sourcing Schedule 120 pipe—particularly for high-pressure, corrosive, or critical applications—requires careful attention to material specifications, manufacturing standards, and supply chain integrity. Failure to address key quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, or legal exposure. Below are common pitfalls buyers encounter in these areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
One of the most frequent issues is receiving pipes without proper Material Test Reports (MTRs) or with incomplete or falsified documentation. Schedule 120 pipe, often used in high-stress environments (e.g., oil & gas, chemical processing), must meet ASTM, ASME, or API standards such as ASTM A53, A106, or A312. Failure to verify mill test reports or source from mills with full traceability increases the risk of substandard material entering the system.
Best Practice: Always require certified MTRs (preferably 3.1 or 3.2 per EN 10204) and confirm heat numbers match physical product markings.
2. Non-Compliance with Dimensional and Wall Thickness Tolerances
Schedule 120 pipe has a significantly thicker wall than lower schedules (e.g., Sch 40 or Sch 80). Some suppliers may deliver undersized pipe or misrepresent lower-schedule pipes as Sch 120 to cut costs. Even minor deviations in wall thickness can compromise pressure ratings.
Best Practice: Conduct third-party inspections or ultrasonic thickness testing upon delivery, especially for large or critical orders.
3. Poor Weld Quality in ERW or Seamless Fabrication
For welded Sch 120 pipe, inadequate welding techniques (e.g., insufficient heat treatment, lack of weld seam inspection) can result in weak joints prone to cracking under stress. Seamless pipe may have internal laminations or inclusions if produced from low-quality billets.
Best Practice: Specify non-destructive testing (NDT) requirements such as hydrostatic testing, ultrasonic testing (UT), or radiographic inspection (RT) in procurement contracts.
4. Corrosion Resistance Mismatch (Especially for Stainless Steel)
When sourcing stainless steel Sch 120 pipe (e.g., SS 304, 316), buyers may unknowingly receive material that hasn’t undergone proper passivation or has incorrect alloy composition. This is especially common with offshore or uncertified mills.
Best Practice: Require Positive Material Identification (PMI) testing and verify compliance with ASTM A380 for surface finish and corrosion resistance.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Brand Integrity Pitfalls
1. Counterfeit or “Grey Market” Products
Some suppliers rebrand or counterfeit pipes from lesser-known mills, falsely labeling them as products from reputable manufacturers (e.g., Sandvik, V&M, Tenaris). These counterfeit products may mimic branding and packaging but lack certified quality controls.
Best Practice: Source directly from authorized distributors or manufacturers and verify supplier credentials. Avoid unusually low bids that may indicate IP infringement.
2. Unauthorized Use of Standards and Certifications
Unscrupulous suppliers may claim compliance with API 5L, ASME B36.10M, or NACE MR0175 without proper certification. This misuse of standards constitutes IP misrepresentation and can void insurance or compliance in regulated industries.
Best Practice: Audit supplier certifications and cross-check with issuing bodies (e.g., API Monogram Licensees list).
3. Design and Specification Theft
In custom or engineered piping systems, there is a risk that suppliers may copy proprietary designs, dimensions, or material specs for resale or replication without consent—particularly when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement.
Best Practice: Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), watermark technical drawings, and limit distribution of detailed specs to vetted partners only.
4. Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
Complex sourcing channels, especially through trading companies, can obscure the origin of pipe, making it difficult to trace IP violations or quality lapses back to the manufacturer.
Best Practice: Demand full supply chain transparency and, when possible, audit the actual production facility.
Conclusion
Sourcing Schedule 120 pipe demands diligence beyond price and availability. Ensuring quality requires verification of material standards, dimensional accuracy, and testing protocols. Protecting intellectual property involves vetting suppliers, securing design rights, and avoiding counterfeit goods. Proactive due diligence mitigates risks to safety, performance, and legal compliance.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Schedule 120 Pipe
Schedule 120 (Sch 120) pipe is a heavy-wall steel or stainless steel pipe commonly used in high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive environments across industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment. Due to its specialized nature and stringent application requirements, the logistics and compliance associated with Sch 120 pipe demand careful planning and adherence to regulatory standards. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements to ensure safe, efficient, and lawful handling, transportation, and use.
1. Regulatory & Standards Compliance
Sch 120 pipe must comply with various national and international standards to ensure structural integrity and safety. Key regulations and standards include:
- ASTM Standards
- ASTM A53/A53M: Standard specification for pipe, steel, black and hot-dipped, zinc-coated, welded and seamless.
- ASTM A106: Seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service.
- ASTM A312: Standard for seamless, welded, and heavily cold-worked austenitic stainless steel pipes.
-
ASTM A333: Seamless and welded steel pipe for low-temperature service.
-
ASME B36.10M / B36.19M
Governs dimensions and wall thicknesses for welded and seamless steel pipe, including Sch 120 specifications. -
ASME IX & B31.3
Relevant for welding procedures and process piping design, respectively. Required for installation in pressurized systems. -
API 5L
Applicable if used in pipeline transportation systems for the petroleum and natural gas industries. -
OSHA & DOT Regulations (U.S.)
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.110: Storage and handling of liquefied petroleum gases.
-
DOT 49 CFR: Transportation of hazardous materials, especially if pipes are used in systems carrying hazardous fluids.
-
International Standards (e.g., ISO 4200, EN 10255)
Required for export or use in European and other global markets.
✅ Compliance Tip: Always verify material test reports (MTRs), mill certificates, and traceability documentation (e.g., heat numbers) prior to shipment and installation.
2. Material Handling & Packaging
Proper handling prevents damage and ensures product integrity:
- End Protection: Use plastic or metal caps on pipe ends to prevent thread damage and internal contamination.
- Bundling: Secure pipes in bundles using steel strapping or coated wire; include dunnage between layers to prevent scratching.
- Coating Protection: For coated pipes (e.g., galvanized, epoxy-lined), use protective wraps or sleeves.
- Lifting: Use spreader bars and soft slings to avoid deformation; never use chains directly on pipe surfaces.
3. Transportation & Logistics
Due to the weight and length of Sch 120 pipe, transport logistics require special planning:
-
Weight Considerations:
Sch 120 pipe is significantly heavier than lower schedules. Calculate total load weight to comply with road transport limits (e.g., FMCSA in the U.S.). -
Truck Loading & Securing:
- Use flatbed or step-deck trailers.
- Secure with load binders, chains, and edge protectors.
-
Comply with FMCSA §393.100–136 on securement of metal coils and cylindrical objects.
-
Length Restrictions:
Oversize loads (typically over 40–53 ft) may require permits, pilot cars, and adherence to state-specific routing rules. -
International Shipping:
- For ocean freight: Use ISO containers or flat-rack containers for long lengths.
- Ensure compliance with IMDG Code if transporting near hazardous zones or containing residual substances.
4. Storage & Site Management
- Environment: Store indoors or under cover to prevent corrosion, especially for carbon steel variants.
- Support: Use cradles or skids to elevate pipes off the ground; avoid direct soil contact.
- Segregation: Separate by material grade, size, and coating type to prevent mix-ups.
- Orientation: Store horizontally with proper support; avoid stacking more than 3–4 layers high.
5. Documentation & Traceability
Critical documents to maintain throughout the supply chain:
- Material Test Reports (MTRs)
- Mill Certificates (e.g., 3.1 or 3.2 per EN 10204)
- Heat/lot numbers for traceability
- Certificates of Compliance (CoC)
- Shipping manifests and bills of lading
- Dangerous Goods Declaration (if applicable)
🔍 Audit Tip: Maintain a digital or physical traceability log from manufacturer to end-user for quality and safety audits.
6. Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS) Considerations
- Worker Safety: Use PPE (gloves, hard hats, steel-toe boots) during handling; follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during installation.
- Fumes & Dust: Grinding or cutting stainless steel may release hazardous particulates—use local exhaust ventilation.
- Spill Prevention: If transporting or storing near water sources, implement SPCC (Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure) plans if oil-coated.
7. Import/Export Compliance
For cross-border shipments:
- HS Codes:
- 7306.30: Seamless stainless steel pipes
-
7306.50: Welded carbon steel pipes
(Verify based on material and origin) -
Customs Documentation:
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Certificate of Origin
-
Import licenses (if required)
-
Trade Sanctions:
Screen suppliers and destinations against OFAC, EU, or UN sanctions lists.
Conclusion
Sch 120 pipe demands a high level of attention to detail in logistics and compliance due to its structural importance and regulatory scrutiny. By adhering to material standards, secure transport practices, proper documentation, and safety protocols, stakeholders can ensure successful delivery and compliance across the supply chain.
📌 Best Practice: Conduct pre-shipment inspections and partner with certified logistics providers experienced in heavy industrial materials.
— End of H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sch 120 Pipe —
Conclusion for Sourcing SCH 120 Pipe:
Sourcing SCH 120 pipe requires a strategic approach that balances material specifications, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and project timelines. Due to its significantly thicker wall compared to lower schedule pipes, SCH 120 is ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, commonly used in oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation industries. When sourcing, it is critical to ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASME B36.10M or B36.19M, and material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) must be verified for quality assurance.
Key considerations include selecting the appropriate material grade (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy), confirming dimensional accuracy, and evaluating supplier lead times and logistics capabilities—especially for large or custom orders. Procurement should prioritize reputable suppliers with a proven track record in delivering high-integrity piping products to avoid costly delays or failures in service.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of SCH 120 pipe hinges on thorough technical evaluation, adherence to industry standards, supplier due diligence, and proactive supply chain management. Investing time in proper planning and vendor selection ensures long-term reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness in demanding operational environments.