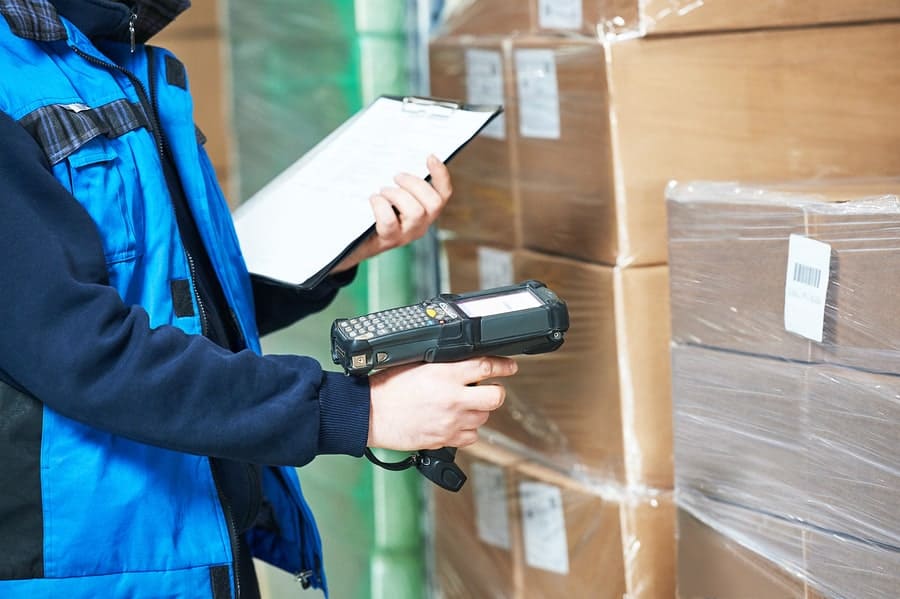
The global barcode and imaging scanner market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for automation and operational efficiency across retail, logistics, and manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global barcode scanner market size was valued at USD 5.93 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady market expansion, citing the rising adoption of wireless and cloud-connected scanning solutions in warehouse and inventory management systems. As supply chains grow more complex and data accuracy becomes mission-critical, warehouse operators are turning to high-performance scanning equipment from leading manufacturers to optimize workflows and reduce errors. This increasing reliance on real-time data capture has positioned scanner technology as a cornerstone of modern warehouse operations, fueling demand for innovative and reliable hardware. In this landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, offering scalable, durable, and intelligent scanning solutions tailored to the rigorous demands of warehouse environments.
Top 10 Scanner Warehouse Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Datalogic
Domain Est. 1994
Website: datalogic.com
Key Highlights: Datalogic is a world-class producer of bar code readers, mobile computers, sensors, vision and laser marking systems….
#2 AML Mobile Computers and Kiosks
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amltd.com
Key Highlights: AML is an American manufacturer of barcoding solutions including mobile computers, self-service kiosks, and forklift-mounted computers….
#3 1D/2D Barcode Scanners & NFC Readers for Retail & Industrial …
Domain Est. 2006
Website: socketmobile.com
Key Highlights: Mobile data capture with native OS integration. Barcode scanners and contactless reader writers providing control, speed, and accuracy….
#4 General Purpose Handheld Scanners – Automation
Domain Est. 1988
Website: automation.honeywell.com
Key Highlights: Honeywell general purpose handheld scanners are the ideal tool for businesses looking to improve their day-to-day barcode reading applications….
#5 Barcode Scanners
Domain Est. 1995
Website: zebra.com
Key Highlights: Built for retail, healthcare, manufacturing and more, Zebra scanners are designed to meet real-world demands with unmatched versatility….
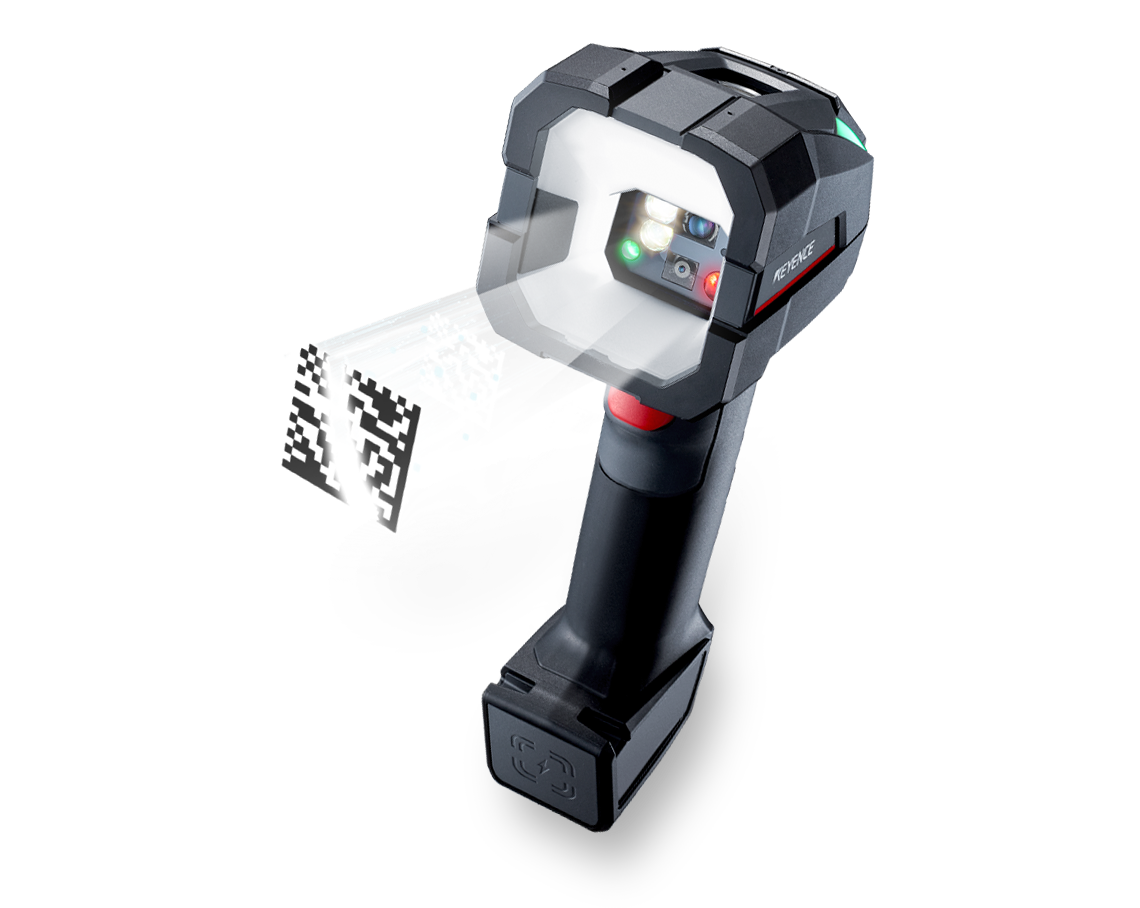
#6 Warehouse Barcode Scanners
Domain Est. 1996
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Reliably scan inventory barcodes from forklifts. Instantly switch from short to long range scanning. Easily scan barcodes under wrinkles and glare….
#7 Mobile Barcoding and Data Collection Solutions
Domain Est. 1998
Website: rfgen.com
Key Highlights: RFgen seamlessly integrates barcode scanning, RFID, GPS, and native labeling to ensure you maintain accurate, real-time data across your entire operation….
#8 Smart Data Capture on Smart Devices
Domain Est. 2002
Website: scandit.com
Key Highlights: Data capture. Smarter. Scandit advanced barcode scanning, ID scanning or shelf intelligence software runs on any smart device. Unmatched speed and accuracy….
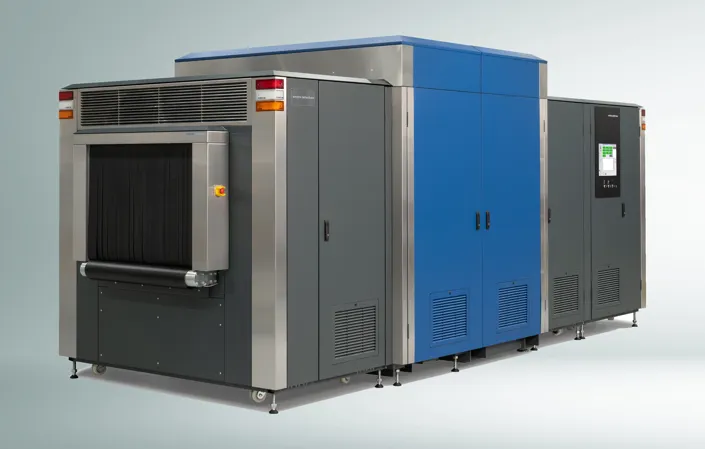
#9 Smiths Detection
Domain Est. 2002
Website: smithsdetection.com
Key Highlights: An automatic, drive through scanner portal for the inspection of vehicles and containers, guaranteeing constant vehicle flow on site. See product. HI-SCAN 7555 ……
#10 Barcode Scanners
Domain Est. 2022
Website: meferi.com
Key Highlights: Ideal for diverse environments like retail, logistics, warehouse, and healthcare, MEFERI scanners are built for durability and ease of use….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Scanner Warehouse

2026 Market Trends for Scanner Warehouse: Strategic Outlook
Entering 2026, Scanner Warehouse operates in a dynamic and rapidly evolving market landscape characterized by technological acceleration, shifting customer demands, and heightened competition. Success will hinge on the company’s ability to anticipate and adapt to key trends across technology, customer behavior, and industry dynamics. Here’s an analysis of the most significant trends shaping the market:
1. Dominance of Advanced Scanning Technologies
The core market is moving decisively beyond basic barcode scanning. In 2026, demand will be heavily skewed towards sophisticated solutions:
* AI-Powered Scanning: Scanners integrated with Artificial Intelligence will be essential. This enables features like automatic document classification (e.g., receipts, IDs, invoices), intelligent data extraction (OCR++), anomaly detection in inventory, and predictive maintenance alerts for industrial scanners. Scanner Warehouse must prioritize partnerships with vendors offering AI-enhanced devices.
* LiDAR and 3D Scanning Adoption: Driven by applications in construction, logistics (volume/weight capture), retail (virtual fitting rooms, store mapping), and manufacturing (quality control), LiDAR and structured light 3D scanners will transition from niche to mainstream. Warehouse must expand its portfolio to include robust, user-friendly 3D scanning solutions.
* Enhanced Mobile & Handheld Capabilities: The line between dedicated scanners and smartphones/tablets continues to blur. High-performance, ruggedized mobile computers (Android/iOS) with superior built-in or attachable scanners (including long-range, omnidirectional, and 2D imagers) will dominate enterprise needs. Focus on devices with superior ergonomics, battery life, and integration capabilities is critical.
* Sustainability & Repairability: Environmental regulations (like EU Right-to-Repair) and corporate ESG goals will increase demand for scanners designed for longevity, easy repair, and recycling. Offering refurbished units, robust warranty/repair programs, and highlighting sustainable products will be a competitive differentiator.
2. Hyper-Focus on Seamless Integration & Cloud Ecosystems
Owning a scanner is no longer enough; its value lies in seamless data flow:
* Cloud-First Integration: Customers demand scanners that plug effortlessly into cloud-based ERP (e.g., NetSuite, SAP S/4HANA Cloud), WMS, CRM (e.g., Salesforce), and specialized SaaS platforms (e.g., inventory management, field service). Scanner Warehouse services must emphasize API compatibility, pre-built connectors, and robust middleware solutions.
* IoT & Edge Computing: Scanners will be key nodes in the Industrial IoT (IIoT) and broader enterprise IoT networks. Devices capable of local data processing (edge computing) for speed and reduced bandwidth, while securely transmitting insights to central systems, will be highly valued, especially in manufacturing and logistics.
* Unified Platform Approach: Customers seek vendors who can offer not just hardware, but integrated software platforms (or partnerships) for device management, data analytics, and workflow automation. Scanner Warehouse should develop or partner around platform solutions.
3. Evolving Customer Needs & Procurement Models
The “buyer” and their expectations are changing:
* Demand for Outcomes, Not Just Hardware: Customers increasingly evaluate scanners based on ROI: reduced errors, faster throughput, improved inventory accuracy, enhanced compliance, or better customer experiences. Sales and marketing must shift to focus on quantifiable business outcomes.
* Subscription & As-a-Service Models (XaaS): Beyond traditional purchase, subscription models for scanner hardware, software, maintenance, and even scanning-as-a-service (e.g., managed document capture) will gain significant traction, especially among SMBs and for specialized, high-cost equipment (like advanced 3D). Scanner Warehouse should explore flexible leasing, rental, and managed service offerings.
* Heightened Cybersecurity Focus: As scanners connect to networks and handle sensitive data (PII, financials, operational data), security is paramount. Customers will demand devices with secure boot, hardware-based encryption, regular firmware updates, and compliance with standards (e.g., FIPS, GDPR). This must be a core part of the sales value proposition.
* Supply Chain Resilience: The focus on mitigating disruption remains high. Customers will favor vendors (like Scanner Warehouse) who demonstrate supply chain transparency, offer multi-sourcing options, maintain strategic inventory of key SKUs, and have robust logistics.
4. Competitive Landscape Intensification
The market for scanning solutions is becoming more crowded and complex:
* Consolidation & Specialization: Expect continued M&A activity among scanner manufacturers and software providers. Simultaneously, niche players focusing on specific verticals (e.g., healthcare specimen tracking, retail loss prevention) or technologies (e.g., ultra-high-speed industrial readers) will emerge, requiring Scanner Warehouse to define its strategic focus.
* Direct Competition from Tech Giants: Companies like Honeywell (after Zebra challenges), Panasonic, and potentially even consumer electronics giants expanding into enterprise rugged devices will compete aggressively on price, brand, and ecosystem.
* Value-Added Services as Differentiator: Price competition on hardware will be fierce. Scanner Warehouse’s key differentiators will be expertise (consulting, workflow design), integration services, training, responsive support, and reliable supply chain. Building long-term partnerships is crucial.
Conclusion for Scanner Warehouse in 2026:
To thrive in 2026, Scanner Warehouse must evolve from a hardware distributor to a strategic solutions partner. Success requires:
1. Curating a Future-Proof Portfolio: Aggressively incorporating AI, 3D, LiDAR, and cloud-connected devices.
2. Embracing Service-Oriented Models: Developing XaaS offerings, robust integration/consulting services, and managed services.
3. Investing in Expertise: Building deep knowledge in AI integration, cloud ecosystems, IoT, and vertical-specific applications.
4. Prioritizing Security & Sustainability: Making these non-negotiable aspects of product selection and service delivery.
5. Focusing on Outcomes: Shifting the conversation from scanner specs to demonstrable business value and ROI.
The 2026 market rewards agility, deep technical understanding, and a customer-centric, solution-oriented approach. Scanner Warehouse that proactively aligns with these H2 trends will be well-positioned for growth and leadership.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing from Scanner Warehouse (Quality, IP)
Sourcing from a scanner warehouse—whether a physical surplus dealer or an online marketplace specializing in used or refurbished scanners—can offer cost savings, but it comes with significant risks related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to avoid operational disruptions, legal issues, or compromised data security.
Poor or Inconsistent Quality
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing from scanner warehouses is inconsistent or subpar equipment quality. These warehouses often resell used, refurbished, or surplus scanners without standardized testing or warranties. Devices may appear functional but suffer from degraded components such as misaligned optics, worn rollers, or failing sensors, leading to poor scan accuracy, frequent jams, or early failure. Without proper diagnostics, buyers may receive units that do not meet performance requirements, resulting in downtime and hidden costs from repairs or replacements.
Lack of Quality Control and Testing Standards
Many scanner warehouses operate without rigorous quality assurance processes. Units may be resold “as-is” with minimal or no functional testing. This increases the likelihood of receiving scanners that are near end-of-life or have been improperly refurbished. Without documented testing procedures or performance benchmarks, it’s difficult to verify reliability before deployment, especially in high-volume or mission-critical environments.
Absence of Warranty and Support
Warehouse-sourced scanners typically come with limited or no manufacturer warranty. Aftermarket sellers may offer short-term guarantees, but these are often insufficient for business use. Additionally, technical support and access to spare parts can be nonexistent, making it difficult to resolve issues quickly. This lack of post-purchase support increases operational risk and total cost of ownership.
Risk of Counterfeit or Tampered Devices
Some warehouse suppliers may unknowingly or deliberately sell counterfeit scanners or devices with modified firmware. These units might mimic genuine models but lack proper security features or performance capabilities. Tampered devices could also contain malware or backdoors, posing cybersecurity risks—especially when handling sensitive documents.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Licensing Violations
A critical but often overlooked risk involves IP and software licensing. Used scanners may come preloaded with proprietary software licensed only to the original owner. Reusing or transferring such software without proper re-licensing can violate copyright agreements. Additionally, firmware or embedded software in the scanner might be subject to restrictive licenses that do not permit resale or commercial reuse, exposing the buyer to legal liability.
Non-Compliance with Regulatory or Industry Standards
Warehouse-sourced scanners may not comply with current regulatory standards (e.g., data privacy laws like GDPR or HIPAA) or industry-specific requirements. For example, a scanner used in healthcare must ensure secure document handling and audit trails. Older or uncertified models may lack these features, creating compliance risks and potential fines.
Incomplete or Missing Documentation
Original user manuals, calibration certificates, drivers, and software installation media are often missing when purchasing from a warehouse. This complicates integration into existing systems and hampers troubleshooting. Without proper documentation, ensuring compatibility with current operating systems or software platforms becomes challenging.
Hidden Total Cost of Ownership
While the upfront price may be low, hidden costs—such as repairs, downtime, software re-licensing, or premature replacement—can quickly outweigh initial savings. Poor-quality scanners may also consume more energy, require frequent maintenance, or reduce productivity due to unreliability, increasing long-term expenses.
Mitigation Strategies
To reduce these risks, buyers should:
– Request detailed inspection reports or third-party certifications.
– Verify the seller’s return policy and support offerings.
– Audit software and firmware for licensing compliance.
– Ensure devices meet necessary security and regulatory standards.
– Consider purchasing through authorized refurbishers with warranties and compliance guarantees.
By understanding and addressing these common pitfalls, organizations can make more informed decisions when sourcing scanners from warehouse suppliers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Scanner Warehouse
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance procedures to ensure efficient operations and regulatory adherence at the Scanner Warehouse. All staff must follow these protocols to maintain accuracy, safety, and legal compliance.
Inventory Management
Maintain accurate inventory records using barcode scanning and warehouse management system (WMS) software. Conduct regular cycle counts and scheduled physical inventories. Ensure all scanner units are stored according to manufacturer specifications, with proper labeling and segregation of new, refurbished, and defective equipment.
Receiving Procedures
All incoming shipments must be inspected upon arrival. Verify packing slips against purchase orders and physically count scanner units received. Document any discrepancies immediately and notify Procurement. Label all new inventory with unique serial numbers and update the WMS within four hours of receipt.
Storage & Handling
Store scanners in a climate-controlled environment (15–25°C, 40–60% humidity) to prevent damage. Use anti-static shelving and avoid stacking beyond manufacturer-recommended limits. Handle all devices with ESD-safe gloves and tools. Clearly mark quarantine areas for non-conforming or suspect units.
Order Fulfillment
Process outbound orders based on first-in, first-out (FIFO) unless otherwise specified. Pick, pack, and scan each order using WMS integration to ensure accuracy. Include required documentation (packing slip, compliance labels) with every shipment. Confirm weight and dimensions match carrier requirements prior to dispatch.
Shipping & Carrier Compliance
Partner only with approved logistics carriers. Ensure all packages are labeled with proper shipping codes, barcodes, and regulatory markings (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). Maintain records of shipping manifests and tracking numbers for a minimum of seven years. Comply with carrier-specific packaging standards to prevent damage.
Export Controls & Regulatory Compliance
All scanners classified as dual-use or technical devices are subject to export regulations (e.g., EAR, ITAR). Verify end-user and destination country prior to shipment. Obtain required export licenses when necessary. Maintain an up-to-date compliance checklist and conduct annual training for relevant staff.
Data Security
Ensure all scanners are wiped of sensitive data before refurbishment or disposal, following NIST 800-88 standards. Maintain logs of data destruction activities. Restrict access to warehouse IT systems with role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication.
Health, Safety & Environmental (HSE)
Adhere to OSHA and local safety regulations. Provide proper PPE (gloves, safety glasses) and train staff on material handling and emergency procedures. Dispose of electronic waste via certified e-waste recyclers in compliance with WEEE and EPA guidelines. Report all incidents immediately.
Audits & Documentation
Prepare for internal and external audits by maintaining complete, accurate records. Required documentation includes inventory logs, shipping records, compliance certifications, training completion reports, and equipment maintenance logs. Conduct quarterly compliance reviews and address findings promptly.
Training & Accountability
All warehouse personnel must complete onboarding training covering logistics procedures and compliance requirements. Refresher training is mandatory annually. Assign compliance officers to oversee adherence and serve as points of contact for regulatory inquiries.
Conclusion for Sourcing Scanner Warehouse:
In conclusion, sourcing a warehouse scanner system requires a strategic approach that balances technological capabilities, operational needs, and long-term scalability. After evaluating options based on features such as barcode/RFID compatibility, real-time data syncing, durability, ease of use, and integration with existing warehouse management systems (WMS), it is evident that investing in a reliable and efficient scanning solution significantly enhances inventory accuracy, reduces operational errors, and improves overall productivity.
Key considerations such as total cost of ownership, vendor support, training requirements, and future-proofing the technology should guide the final decision. Whether opting for handheld, mobile, or fixed scanners, aligning the chosen solution with specific warehouse workflows ensures optimal performance and return on investment.
Ultimately, a well-implemented scanning system not only streamlines daily operations but also positions the warehouse for greater efficiency and adaptability in an increasingly competitive supply chain environment. The right scanner warehouse solution is not just a tool—it is a critical component of a modern, responsive logistics operation.