The global demand for precision cutting tools and maintenance services has seen steady expansion, driven by growth in woodworking, construction, and metalworking industries. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global saw blade market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2024 to 2029. This sustained growth underscores the increasing need for reliable saw sharpening services to extend tool life and maintain operational efficiency. As manufacturers face pressure to reduce downtime and optimize costs, the role of specialized sharpening services has become critical. The following list highlights the top nine saw sharpening service manufacturers that have distinguished themselves through technological innovation, service quality, and market reach—key players supporting industries that rely on high-performance cutting tools.
Top 9 Saw Sharpening Service Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Simonds International
Domain Est. 2003
Website: simondsint.com
Key Highlights: As the oldest cutting tool manufacturer in North America, Simonds International offers one of the broadest and most trusted lines of cutting tools….
#2 Forrest Factory Carbide Saw Blade Sharpening
Domain Est. 1997
Website: forrestblades.com
Key Highlights: The Forrest Manufacturing Sharpening Service also sharpens other types of carbide saw blades, upgrading the life and performance of any saw blade….
#3 Valley Grinding & Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1998
Website: valleygrinding.com
Key Highlights: From industrial blade sharpening to manufacturing, we help our customers become world-class operators with fully automated solutions….
#4 Vortex Tool Company Sharpening Service
Domain Est. 1998
Website: vortextool.com
Key Highlights: Vortex Tool Company Inc. offers a comprehensive sharpening and service program. We have developed our manufacturing process to include the sharpening business….
#5 Saw Blade Sharpening Service
Domain Est. 1999
Website: burnstools.com
Key Highlights: Burns performs high-end, industrial sharpening of most cutters, knives and saw blades, specializing in carbide-tipped blades & cutters….
#6 Quinn Saw
Domain Est. 2000
Website: quinnsaw.com
Key Highlights: W.D. Quinn Saw Co. provides fast, precise circular saw blade sharpening and repair services using advanced technology. Design your blade online….
#7 Sharpening Revised
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ridgecarbidetool.com
Key Highlights: Ridge Carbide is a full service saw blade repair & sharpening center. We will return your dull, damaged, warped or wobbly sawblades back to you like new….
#8 Saw Blade Sharpening Service; Expert Sharpeners Of Router Bits …
Domain Est. 2002
Website: dynamicsaw.com
Key Highlights: We sharpen all brands of saw blades and router bits on our “new” state of the art CNC grinders! Plus, we design custom sawblades!…
#9 Festool Sharpening Service
Domain Est. 2023
Website: festoolsharpen.com
Key Highlights: Send us your blades and get them back as sharp as new! It’s as simple as that: Buy a sharpening, get a prepaid shipping label and send your saw blades….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Saw Sharpening Service

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Saw Sharpening Services
The saw sharpening service industry in 2026 is poised for steady growth, driven by a confluence of economic, technological, and environmental factors. While remaining a specialized niche, the sector is adapting to evolving customer demands and operational advancements. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Increased Demand from Construction and Woodworking Sectors:
Despite economic fluctuations, the residential and commercial construction markets, particularly in North America and Europe, are projected to maintain moderate growth through 2026. Concurrently, the rise of artisanal woodworking, custom furniture making, and DIY culture continues to expand the base of small workshops and independent craftspeople. These segments rely heavily on high-performing cutting tools, making professional sharpening a cost-effective alternative to frequent blade replacement. This sustained demand underpins market stability.
2. Emphasis on Sustainability and Tool Longevity:
Environmental awareness and cost-saving initiatives are pushing businesses and consumers toward sustainability. Sharpening saw blades extends their usable life significantly, reducing waste and the environmental footprint associated with manufacturing new tools. By 2026, this “repair and reuse” ethos is expected to be a major selling point for sharpening services, especially among eco-conscious contractors, municipalities, and green-certified operations.
3. Technological Advancements in Sharpening Equipment:
Automation and precision engineering are transforming the industry. CNC-controlled sharpening machines, laser-guided alignment systems, and digital profiling software allow for more consistent, accurate, and faster results. These technologies reduce human error, increase throughput, and enable shops to handle a wider variety of blade types (e.g., carbide-tipped, specialty profiles). Early adopters in 2026 will gain a competitive edge through improved quality and turnaround times.
4. Growth of Mobile and On-Site Sharpening Services:
To address the downtime associated with sending blades off-site, mobile sharpening services are becoming more prevalent. Equipped with compact, high-precision tools, technicians can sharpen blades directly at job sites, sawmills, or woodworking shops. This trend is particularly strong in rural areas and among large-scale operations where minimizing equipment downtime is critical. By 2026, on-demand and mobile services are expected to capture a growing share of the market.
5. Consolidation and Professionalization of Service Providers:
The market is gradually shifting from small, independent operators toward more standardized and professionalized businesses. Certification programs, adherence to industry standards (e.g., precision tolerances), and digital customer management systems are becoming more common. This professionalization builds trust and allows sharpening services to position themselves as essential partners in tool maintenance rather than just a repair function.
6. Integration with Digital Platforms and E-commerce:
Many sharpening services are enhancing their online presence through e-commerce platforms for blade collection, tracking, and payment. By 2026, expect wider adoption of customer portals, automated scheduling, and real-time job status updates. Some forward-thinking providers may partner with tool suppliers or offer bundled maintenance plans, integrating sharpening into broader tool lifecycle management solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 saw sharpening service market will be characterized by resilience, innovation, and a growing alignment with sustainability and efficiency trends. Success will favor providers who leverage technology, offer convenience through mobility or digital integration, and clearly communicate the economic and environmental benefits of professional blade maintenance.
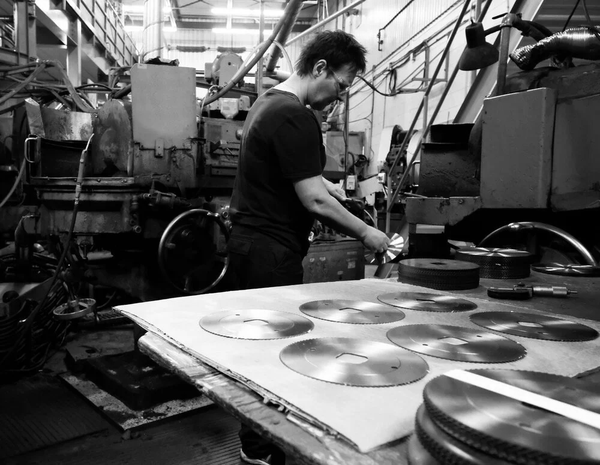

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Saw Sharpening Services
Poor Quality Workmanship
One of the most frequent issues when outsourcing saw sharpening is inconsistent or subpar quality. Inexperienced or poorly equipped providers may deliver uneven tooth profiles, incorrect rake angles, or overheated blades due to improper grinding techniques. This results in reduced cutting performance, premature blade wear, and increased downtime. Without strict quality control processes or skilled technicians, the sharpened saws may not meet operational standards, leading to frustration and higher long-term costs.
Lack of Quality Assurance and Standards Compliance
Many saw sharpening service providers do not adhere to industry standards or lack formal quality assurance procedures. Without documented processes, calibration records, or performance testing, it’s difficult to verify the consistency and reliability of their work. Sourcing from such providers increases the risk of receiving blades that degrade quickly or fail under heavy use, especially in industrial or high-precision applications.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Proprietary Blade Design Risks
When sending specialized or custom-designed saw blades for sharpening, there’s a risk of intellectual property exposure. Some service providers may reverse-engineer proprietary tooth geometries or replicate unique blade designs without authorization. This is particularly concerning for manufacturers who rely on patented or trade-secret blade configurations for competitive advantage. Without strong contractual protections or non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), sensitive design information may be compromised.
Inadequate Data and Process Security
Beyond physical IP risks, some advanced sharpening services use digital profiling or automated systems that store blade specifications. If the provider lacks robust data security measures, digital blueprints or performance data could be accessed or leaked. This digital footprint can be just as valuable—and vulnerable—as the physical blade, especially in industries where blade performance is a closely guarded secret.
Geographic and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Outsourcing sharpening services overseas or to distant locations increases lead times and reduces control over quality. Long shipping routes expose blades to handling damage and delays, while communication barriers may lead to misunderstandings about specifications. Additionally, reliance on a remote provider limits the ability to conduct audits or on-site inspections, making it harder to ensure consistent quality and IP protection.
Failure to Establish Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Many companies overlook the importance of formal SLAs when sourcing sharpening services. Without clear agreements on turnaround time, quality metrics, rework policies, or confidentiality, disputes are more likely to arise. A well-defined SLA helps align expectations and provides recourse if the provider fails to meet performance or security standards.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, businesses should vet saw sharpening providers thoroughly, prioritize those with certifications, enforce IP protections through legal agreements, and maintain oversight through regular audits and performance reviews. Choosing a trusted, transparent partner is essential for preserving both blade performance and proprietary advantages.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Saw Sharpening Service
Service Area and Delivery Options
Define the geographical scope of your saw sharpening service, including local pickup/drop-off zones, courier partnerships, and shipping regions. Offer multiple delivery methods such as in-person drop-off, scheduled pickups, or prepaid shipping labels for remote customers. Clearly communicate turnaround times and associated costs for each option.
Equipment Intake and Tracking System
Implement a standardized intake process for all incoming tools. Assign a unique tracking number or job tag to each saw upon receipt. Use a digital log or inventory management software to record tool type, customer details, condition upon arrival, and service requested. This ensures accountability and enables real-time status updates.
Safety and Handling Protocols
Train staff in safe handling of sharp and heavy equipment. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including cut-resistant gloves and eye protection. Establish procedures for securing blade edges during transport and storage. Maintain a clean, organized workspace to reduce accident risks.
Environmental and Waste Compliance
Adhere to local environmental regulations for disposal of metal shavings, grinding dust, and used oils. Use dust collection systems to minimize airborne particulates. Recycle metal waste through approved vendors and maintain disposal records. If using chemical cleaners, ensure proper storage and disposal in compliance with EPA or equivalent standards.
Regulatory and Business Licensing
Obtain all required local, state, and federal business licenses. Register for sales tax collection if applicable. Comply with zoning laws if operating from a physical workshop. Maintain liability insurance to protect against property damage or injury claims related to tool handling or service defects.
Quality Control and Service Standards
Establish consistent sharpening procedures based on saw type (e.g., circular, band, chainsaw). Calibrate equipment regularly to ensure precision. Perform post-sharpening inspections to verify edge quality, tooth alignment, and overall functionality. Document quality checks for each job.
Customer Communication and Recordkeeping
Provide clear service agreements outlining turnaround times, pricing, and liability limitations. Notify customers when tools are received, in progress, and ready for pickup or shipment. Retain service records for at least one year for warranty, compliance, or audit purposes.
Data Privacy and Customer Information
Protect customer contact and payment information in compliance with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). Secure digital records with password protection and encryption. Only collect essential information and avoid storing sensitive data unless necessary.
In conclusion, sourcing a reliable saw sharpening service is a critical decision that directly impacts cutting efficiency, tool longevity, and overall operational productivity. By evaluating key factors such as service quality, turnaround time, technician expertise, equipment used, and cost-effectiveness, businesses can identify a provider that aligns with their specific needs. Establishing a consistent maintenance partnership not only ensures optimal performance of saw blades but also reduces downtime and long-term equipment costs. Ultimately, investing in a professional and dependable saw sharpening service contributes to safer working conditions, improved cut quality, and greater return on investment—making it a strategic component of effective tool management.