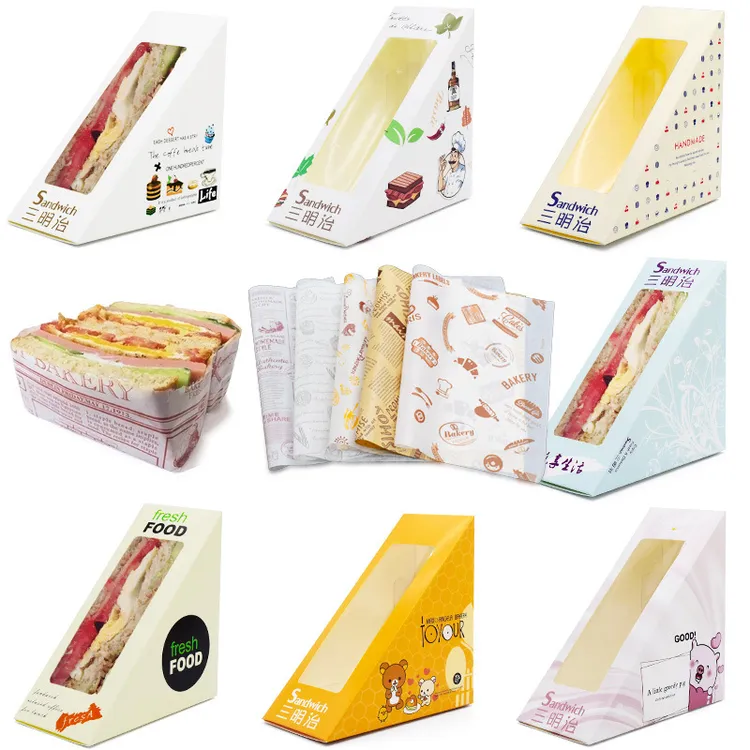
The global sandwich packaging market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for convenience foods and the expansion of foodservice and retail sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global food packaging market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, with ready-to-eat meals—including sandwiches—playing a significant role in this expansion. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the global rigid plastic packaging market, a key segment for sandwich solutions, will reach USD 164.3 billion by 2030, fueled by innovations in sustainable materials and increasing on-the-go consumption. As consumer preferences shift toward portable, eco-friendly, and visually appealing packaging, manufacturers are ramping up production and investing in advanced packaging technologies. In this dynamic landscape, identifying the top players in sandwich packaging is critical for brands seeking quality, scalability, and sustainability. Here are the top 9 sandwich packaging manufacturers leading the industry through innovation, compliance, and global reach.
Top 9 Sandwich Packaging Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Sabert
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sabert.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading global manufacturer of innovative food packaging products and solutions with more than 30 years in the packaging and food service industry….
#2 KM Packaging
Domain Est. 2001 | Founded: 1984
Website: kmpackaging.com
Key Highlights: We have provided an extensive range of specialist lidding films and flexible packaging worldwide to major and specialist food manufacturers since 1984….
#3 Paperboard Food Packaging Solutions
Domain Est. 2011
Website: colpacpackaging.com
Key Highlights: Colpac is an award-winning designer and manufacturer of innovative food packaging solutions. View our product range….
#4 PPC Flex
Domain Est. 2018
Website: ppcflex.com
Key Highlights: PPC Flex is an advanced flexible packaging manufacturer, focused on providing purposeful, powerful packaging solutions….
#5 Tetra Pak processing and packaging solutions for food and …
Domain Est. 1993
Website: tetrapak.com
Key Highlights: Tetra Pak is the world’s leading food processing and packaging solutions company working closely with our customers and suppliers to provide safe food….
#6 Glenroy Flexible Packaging
Domain Est. 1996
Website: glenroy.com
Key Highlights: Glenroy excels in sustainable flexible packaging, offering custom laminations and stand-up pouches for leading brands in various industries….
#7 Anchor Packaging: Foodservice To Go Packaging Solutions
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1963
Website: anchorpackaging.com
Key Highlights: The Anchor Advantage. A global innovation leader in designing and manufacturing rigid food containers and food service cling film in the USA since 1963….
#8 Berlin Packaging
Domain Est. 1997
Website: berlinpackaging.com
Key Highlights: Shop Berlin Packaging, a hybrid packaging company supplying wholesale bottles, containers, innovative design & more across all markets….
#9 Food
Domain Est. 1997
Website: graphicpkg.com
Key Highlights: Innovative, paperboard food packaging solutions for dry foods and snacks, fresh produce, fresh and processed meats, frozen foods, ready meals, and more….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sandwich Packaging

2026 Market Trends for Sandwich Packaging
The global sandwich packaging market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by shifting consumer preferences, escalating environmental regulations, and technological innovation. Key trends shaping the landscape include a relentless push toward sustainability, heightened demand for convenience and functionality, and the rise of premiumization and smart packaging solutions.
Sustainability Takes Center Stage
Environmental concerns are the dominant force reshaping sandwich packaging. By 2026, consumers and regulators alike will demand a sharp reduction in single-use plastics. This drives widespread adoption of compostable materials (like PLA and cellulose), recyclable paper-based solutions, and innovative mono-material films. Brands will prioritize packaging with clear end-of-life instructions and invest in closed-loop systems. Regulatory pressures, particularly in the EU and parts of North America, will accelerate the phase-out of non-recyclable components, making sustainable design a non-negotiable competitive requirement.
Demand for Enhanced Functionality & Convenience
As on-the-go consumption remains prevalent, functionality is paramount. Packaging in 2026 will increasingly feature resealable closures, moisture barriers to prevent sogginess, and ergonomic designs for easy opening and eating. Microwave-safe and freezer-to-oven capabilities will grow in importance for meal-kit and premium sandwich segments. Convenience extends to portion control and multi-packs tailored for families or office settings, supported by intuitive, user-friendly packaging formats.
Rise of Premiumization and Brand Differentiation
With competition intensifying, packaging becomes a critical brand touchpoint. Expect a surge in premium designs using high-quality graphics, matte finishes, and tactile materials to convey freshness and quality. Transparent windows to showcase the sandwich’s ingredients will remain popular, but with eco-friendly film alternatives. Customization and storytelling through packaging—highlighting sourcing, artisanal methods, or dietary benefits—will help brands stand out on crowded shelves.
Innovation in Active and Smart Packaging
By 2026, active packaging solutions such as oxygen scavengers and moisture absorbers will become more common to extend shelf life without preservatives. Early adoption of smart packaging, including time-temperature indicators and QR codes linking to traceability or nutritional information, will begin to emerge, especially in premium and health-focused segments, enhancing consumer trust and engagement.
Growth in E-commerce and Delivery-Optimized Packaging
The expansion of direct-to-consumer and food delivery channels necessitates packaging engineered for durability during transit. Sandwich packaging will increasingly feature robust, leak-proof designs with insulation properties to maintain temperature. Lightweight yet protective materials will be favored to reduce shipping costs and carbon footprint, aligning with both logistical and sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the 2026 sandwich packaging market will be defined by a convergence of eco-consciousness, functional innovation, and brand-centric design. Success will belong to producers and brands that integrate sustainability into core packaging strategy while meeting the evolving demands for convenience, transparency, and quality.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Sandwich Packaging: Quality and Intellectual Property Issues
When sourcing sandwich packaging, businesses often encounter challenges that can impact product safety, brand reputation, and legal compliance. Two critical areas where pitfalls frequently arise are quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these risks is essential for ensuring a reliable supply chain and safeguarding your brand.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Standards
One of the most common quality issues is variability in packaging materials. Sourced packaging may not consistently meet food safety regulations (e.g., FDA or EU compliance), especially when working with overseas suppliers. Non-compliant materials can leach harmful chemicals into food or fail to preserve freshness.
Poor Structural Integrity
Low-quality packaging may lack durability, leading to crushed sandwiches, leaks, or difficulty in sealing. This affects both customer experience and product shelf life, especially if the packaging fails during transport or storage.
Inadequate Barrier Properties
Packaging that doesn’t provide proper moisture, oxygen, or grease resistance can compromise sandwich quality. For example, soggy bread or greasy exteriors reduce consumer satisfaction and may lead to increased waste.
Misleading Sustainability Claims
Suppliers may advertise packaging as “biodegradable” or “compostable” without proper certifications. This greenwashing not only misleads consumers but can also expose your brand to regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
Lack of Rigorous Supplier Audits
Failing to conduct on-site audits or third-party testing can result in undetected quality issues. Without verified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 22000 or HACCP), suppliers may not maintain consistent production standards.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Design Elements
When sourcing custom packaging designs, there’s a risk that suppliers may use copyrighted graphics, logos, or patented structural designs without proper licensing. This can lead to IP infringement claims against your business, even if unintentional.
Ownership Ambiguity in Custom Designs
If contracts do not clearly assign IP rights, the supplier may retain ownership of the packaging design. This limits your ability to switch manufacturers or scale production and could result in costly renegotiations.
Counterfeit or Copycat Packaging
Some suppliers may replicate popular packaging designs from competitors, putting your brand at risk of being associated with knock-offs. This undermines brand uniqueness and may lead to legal disputes.
Weak Contractual Safeguards
Generic or poorly drafted agreements often lack clauses protecting IP, confidentiality, and design usage. Without explicit terms, enforcing IP rights in cross-border disputes becomes difficult and expensive.
Insufficient IP Due Diligence
Failing to conduct IP searches before finalizing designs can result in unintentional infringement. This includes checking for existing patents on packaging mechanisms (e.g., resealable windows or ventilation systems) and trademark conflicts.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Conduct thorough supplier vetting, including on-site audits and material testing.
- Require compliance certifications (e.g., FDA, FSC, BPI) and verify claims independently.
- Use detailed contracts that assign full IP ownership to your company and include confidentiality clauses.
- Perform IP clearance searches before finalizing packaging designs.
- Work with legal counsel experienced in international trade and IP law to mitigate risks.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP challenges, businesses can ensure their sandwich packaging is safe, compliant, and aligned with brand values.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sandwich Packaging
This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant packaging, handling, and distribution of sandwich products.
Packaging Design & Material Compliance
Sandwich packaging must comply with food contact regulations such as FDA 21 CFR (U.S.) or EU Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. Materials must be food-grade, non-toxic, and prevent migration of harmful substances into the product. Use of BPA-free, phthalate-free, and PFAS-free materials is increasingly mandated or expected. Packaging design should minimize oxygen and moisture transmission to preserve freshness and prevent spoilage.
Temperature Control & Cold Chain Management
Maintain a consistent cold chain (typically 0–5°C / 32–41°F) from production through delivery. Use refrigerated storage and transport equipped with temperature monitoring systems (e.g., data loggers). Validate cold chain procedures regularly and ensure packaging provides adequate insulation during short ambient exposure (e.g., last-mile delivery). Comply with HACCP and local food safety regulations regarding time-temperature control.
Labeling Requirements
All sandwich packaging must include mandatory labeling per jurisdiction: product name, ingredient list (including allergens in bold or highlighted text), net weight, best-before or use-by date, storage instructions, business name/address, and country of origin. In the U.S., FDA nutrition labeling is required unless exempt; in the EU, the Nutrition Declaration is mandatory. Allergens (e.g., gluten, dairy, soy, mustard) must be clearly declared.
Shelf Life & Stability Testing
Determine accurate shelf life through microbiological and sensory testing under defined storage conditions. Document challenge studies and accelerated aging tests where applicable. Use packaging that supports the validated shelf life and update labeling accordingly. Regularly revalidate shelf life when formulations or packaging materials change.
Transportation & Handling Protocols
Ensure transport vehicles are clean, sanitized, and dedicated to food transport to prevent cross-contamination. Use tamper-evident packaging and secure stacking methods to prevent damage. Train handlers on proper loading, unloading, and handling procedures. Comply with FSMA (U.S.) or equivalent regulations such as the EU’s Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 on hygiene of foodstuffs.
Sustainability & Environmental Compliance
Adhere to evolving environmental regulations such as plastic taxes, extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, and recyclability standards (e.g., EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive). Prioritize recyclable, compostable, or reusable packaging where feasible. Clearly label disposal instructions (e.g., “Recycle Me” or “Compostable in Industrial Facilities”). Avoid misleading environmental claims (greenwashing) and ensure certifications (e.g., compostability standards like EN 13432) are valid.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain complete records for full traceability: batch numbers, ingredient sources, packaging lot numbers, production dates, and distribution logs. Implement a recall plan and conduct regular mock recalls to validate systems. Comply with GS1 standards for barcoding and product identification to support supply chain visibility.
International Export Considerations
For cross-border distribution, verify compliance with destination country regulations (e.g., labeling in local language, specific preservative bans, import permits). Assess packaging durability for longer transit times and potential customs delays. Account for differences in voltage, refrigeration standards, and labeling laws to avoid border rejection.
In conclusion, sourcing sandwich packaging requires a careful balance between functionality, sustainability, cost-efficiency, and brand alignment. It is essential to select materials that maintain food freshness, provide adequate protection during transport, and offer convenience for end-users. With growing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions, prioritizing compostable, recyclable, or reusable packaging materials not only supports environmental responsibility but also enhances brand reputation. Additionally, working with reliable suppliers who can ensure consistent quality, scalability, and compliance with food safety standards is crucial. By evaluating all these factors, businesses can make informed sourcing decisions that support operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and long-term sustainability goals.