The global sand and aggregates market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising infrastructure development, urbanization, and construction activities worldwide. According to Grand View Research, the global construction aggregates market size was valued at USD 278.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts sustained momentum, citing increased demand from emerging economies and public-private investments in transportation and housing projects as key growth catalysts. With sustainability and sand scarcity becoming critical concerns, leading manufacturers are leveraging innovation and vertical integration to meet quality standards and supply chain demands. Against this backdrop, the following eight companies stand out as top sand manufacturers, combining scale, technological advancement, and global reach to dominate the industry landscape.
Top 8 Sands Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Energy Utility and Industrial Products Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2000
Website: sandsindia.com
Key Highlights: SANDS designs and manufactures niche hardware technologies for the generation, distribution and transmission segments of the electric power industry….
#2 A Packaging manufacturer For all your packing requirements.
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sandsplastics.com
Key Highlights: Sands is a flexible and environment-friendly packaging solutions provider for food and beverage, petrochemical and other industrial applications….
#3 Pacific Sands Inc
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pacificsandsinc.com
Key Highlights: We’ve been a proud manufacturer of powder and liquid products for 20+ years, our commitment to excellence ensures your needs are met with precision and care….
#4 S&C Electric Company
Domain Est. 1995 | Founded: 1911
Website: sandc.com
Key Highlights: S&C Electric Company is a global provider of equipment and services for electric power systems. Founded in 1911, the Chicago-based company designs and…
#5 Las Vegas Sands
Domain Est. 1999
Website: sands.com
Key Highlights: Las Vegas Sands Corporation is the world leader in developing and operating international, world-class integrated resorts….
#6 Roland Sands Design
Domain Est. 2004
Website: rolandsands.com
Key Highlights: The home for Roland Sands Design motorcycle parts, motorcycle gear and custom motorcycles….
#7 S&S Precision
Domain Est. 2007
Website: sandsprecision.com
Key Highlights: Leading Edge Solutions for Military Units, Federal Government and Law Enforcement Professionals….
#8 Company Information
Domain Est. 2008
Website: sandschina.com
Key Highlights: Sands China Ltd. (HKEx: 1928) is the leading developer, owner and operator of multi-use integrated resorts and casinos in Macao….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sands
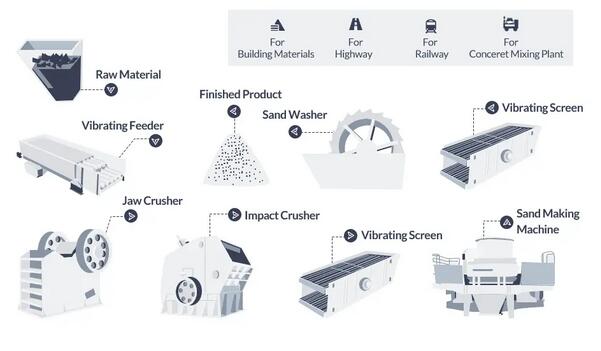
H2: Market Trends Shaping Las Vegas Sands in 2026
As Las Vegas Sands (LVS) navigates the evolving global gaming and hospitality landscape in 2026, several key market trends are expected to shape its strategic direction, financial performance, and competitive positioning. Building on its transition from Macau to a diversified international portfolio—particularly in the U.S. with the development of The Venetian Las Vegas and new ventures in resort-integrated destinations—Sands is adapting to macroeconomic, regulatory, and consumer-driven shifts.
-
U.S. Market Expansion and Integrated Resort Growth
By 2026, Sands has significantly accelerated its focus on the domestic U.S. market, particularly with the development of large-scale integrated resorts beyond Las Vegas. The company’s strategic pivot toward destinations like Las Vegas and potential new developments in emerging gaming markets (e.g., Texas, Florida, or Chicago) reflects a broader industry trend toward destination-based entertainment complexes combining gaming, luxury accommodations, convention space, and retail. Sands’ expertise in building convention-driven resorts positions it favorably as corporate travel and MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conventions, Exhibitions) activity rebounds post-pandemic. -
Macau Regulatory and Economic Adjustments
Although Sands China remains a major revenue contributor, the Macau market continues to operate under tighter regulatory scrutiny in 2026. The Chinese government’s emphasis on responsible gaming, capital controls, and reduced reliance on gambling revenue has prompted Sands to diversify its Macau offerings—emphasizing family-friendly attractions, entertainment, and non-gaming experiences. This aligns with the “moderate diversification” policy promoted by Macau authorities. While VIP gaming volumes remain subdued compared to pre-2019 levels, mass-market visitation has recovered, supported by easing travel restrictions and increased tourism from mainland China. -
Rise of Non-Gaming Revenue Streams
Sands is capitalizing on the growing importance of non-gaming revenue, which now accounts for over 50% of total earnings in key properties. In 2026, revenue from luxury retail (especially at Marina Bay Sands in Singapore), high-end dining, premium entertainment, and large-scale conventions continues to grow. The company has invested in digital ticketing platforms, loyalty programs, and personalized guest experiences to enhance per-capita spending. This trend reflects broader consumer preferences toward experiential spending, especially among younger, affluent demographics. -
Sustainability and ESG Initiatives
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are increasingly influencing investor sentiment and regulatory expectations. By 2026, Sands has enhanced its sustainability commitments, including energy efficiency upgrades, waste reduction programs, and responsible water management—particularly in water-stressed regions like Las Vegas and Singapore. The company has also strengthened its responsible gaming initiatives and community engagement, responding to stakeholder demands for ethical operations. -
Geopolitical and Macroeconomic Pressures
Ongoing U.S.-China tensions and currency fluctuations continue to impact Sands’ cross-border operations. The strength of the U.S. dollar affects inbound tourism to Macau and Singapore, while inflation and interest rate volatility influence consumer spending and capital costs. However, Sands’ geographic diversification—spanning North America, Southeast Asia, and Greater China—provides a hedge against regional downturns. -
Technology and Digital Transformation
Sands is leveraging AI, data analytics, and mobile platforms to optimize operations and enhance customer experience. In 2026, the company has rolled out smart room technology, cashless gaming systems, and dynamic pricing models across its properties. These innovations improve operational efficiency and support personalized marketing, driving repeat visitation and higher yield management.
Conclusion
By H2 2026, Las Vegas Sands is emerging as a leader in the next-generation integrated resort model, balancing its legacy in Asian markets with aggressive U.S. expansion. While challenges remain—particularly in Macau’s regulatory environment and global economic uncertainty—the company’s focus on non-gaming revenue, sustainability, and digital innovation positions it for long-term resilience and growth. Investors are watching closely as Sands executes its vision of becoming a global entertainment and hospitality powerhouse beyond traditional gaming.
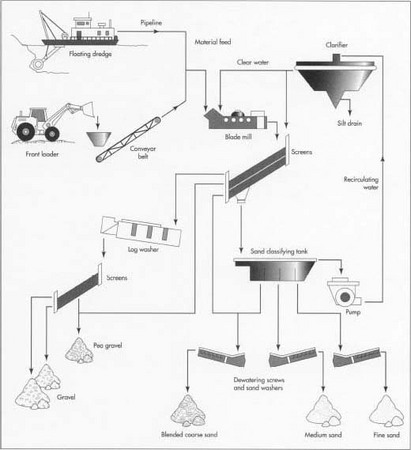
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Sands (Quality, IP)
Sourcing sand—especially for industrial, construction, or high-tech applications—can involve significant challenges related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to project delays, increased costs, legal disputes, or product failure.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Material Specifications
Sand sourced from different regions or suppliers often varies in grain size, shape, mineral composition, and impurity levels. Without strict quality control and standardized testing (e.g., sieve analysis, silt content), inconsistent sand can compromise the performance of concrete, foundry molds, or filtration systems. -
Contamination and Impurities
Sand may contain organic matter, clay, salts, or heavy metals, especially if extracted from riverbeds or coastal areas. These contaminants can weaken structural integrity, interfere with chemical processes, or pose environmental hazards. -
Unverified Source Authenticity
Some suppliers may misrepresent the origin or type of sand (e.g., passing off ordinary sand as high-purity silica sand). This is particularly risky in industries like glass manufacturing or hydraulic fracturing, where precise sand properties are critical. -
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Failure to obtain documentation such as certificates of analysis (CoA), material safety data sheets (MSDS), or ISO certifications can leave buyers vulnerable to substandard materials and compliance issues. -
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance Risks
Illegally or unsustainably sourced sand may violate environmental regulations. Buyers risk reputational damage or supply chain disruptions if their suppliers engage in unauthorized dredging or violate local mining laws.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
-
Proprietary Sand Treatments and Coatings
Specialized sands—such as resin-coated proppants used in oil and gas fracking—may be protected by patents. Sourcing equivalent materials without proper licensing or due diligence can lead to IP infringement claims. -
Reverse Engineering Risks
Attempting to replicate patented sand formulations or processing techniques (e.g., grain sizing methods, surface treatments) without authorization can expose companies to litigation, even if the base material is naturally occurring. -
Trade Secrets in Processing Methods
While raw sand itself is not patentable, the methods used to purify, grade, or modify sand often constitute trade secrets. Suppliers may restrict how sand is used or prohibit disclosure to third parties—violating these terms can result in legal action. -
Lack of IP Clauses in Supply Agreements
Contracts that fail to clarify ownership of improvements, usage rights, or liability for IP violations leave buyers exposed. For example, if a supplier uses a patented process to produce sand, the buyer could be implicated in infringement if not properly indemnified. -
Global Sourcing and Jurisdictional Differences
IP laws vary by country. Sand processed in one jurisdiction using a method not patented there may still infringe patents in the importing country. This creates risk when sourcing internationally without IP clearance.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires rigorous due diligence, clear contractual terms, third-party testing, and proactive IP assessments—ensuring both the physical and legal integrity of sand supply chains.
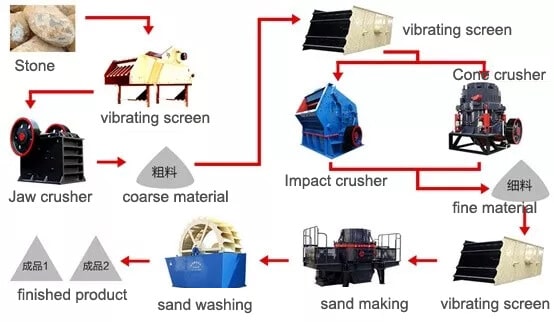
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sands
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for operations involving Sands, whether referring to industrial sand (e.g., frac sand, construction sand), beach sand, or sand as a metaphorical term within a corporate context (e.g., “Sands” as a company name). The principles below ensure efficient, legal, and sustainable sand-related activities.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to local, national, and international regulations is essential. Key areas include:
Environmental Regulations
- Permitting: Obtain necessary permits for sand extraction, transportation, and processing (e.g., mining permits, water discharge permits).
- Erosion & Sediment Control: Implement best management practices (BMPs) to prevent soil erosion and protect water quality.
- Habitat Protection: Avoid or mitigate impacts on sensitive ecosystems, including wetlands, dunes, and aquatic habitats.
- Reclamation Plans: Develop and follow post-extraction site restoration plans as required by law.
Transportation Regulations
- Weight & Dimension Limits: Comply with road, rail, and maritime regulations governing load sizes and axle weights.
- Hazardous Materials: While sand is generally non-hazardous, ensure compliance if transported with or classified alongside other regulated materials.
- Cross-Border Shipments: For international logistics, adhere to customs regulations, import/export controls, and documentation (e.g., commercial invoices, bills of lading, certificates of origin).
Health & Safety Standards
- OSHA/Workplace Safety: Follow occupational safety standards for mining, handling, and transport operations to prevent respiratory issues (e.g., silica exposure) and mechanical injuries.
- Driver Training: Ensure transport personnel are trained and certified as required.
Logistics Management
Efficient logistics ensure timely delivery while minimizing cost and environmental impact.
Sourcing & Procurement
- Supplier Vetting: Select suppliers with certified sustainable practices and compliance records.
- Chain of Custody: Maintain documentation to trace sand origin and handling, especially for regulated or high-value applications.
Storage & Handling
- Facility Design: Use covered or enclosed storage to reduce dust and runoff; ensure proper drainage.
- Material Handling Equipment: Employ appropriate machinery (e.g., conveyors, loaders) to minimize spillage and worker exposure.
Transportation Planning
- Mode Selection: Choose the most efficient transport mode—truck, rail, barge, or ship—based on volume, distance, and destination.
- Route Optimization: Use logistics software to plan fuel-efficient routes and avoid restricted zones.
- Load Securing: Ensure loads are properly covered and secured to prevent spillage during transit.
Inventory Management
- Tracking Systems: Implement real-time inventory tracking using barcode or RFID systems.
- Demand Forecasting: Align procurement and transport schedules with project timelines to reduce overstocking or shortages.
Sustainability & Corporate Responsibility
Demonstrate commitment to ethical and sustainable practices.
Sustainable Sourcing
- Prioritize sand from recycled sources or certified sustainable quarries.
- Avoid sourcing from ecologically sensitive or illegal mining operations.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
- Optimize transport routes and consolidate shipments to lower emissions.
- Invest in fuel-efficient or alternative-energy vehicles where feasible.
Community Engagement
- Maintain transparent communication with local communities affected by extraction or transport activities.
- Address concerns regarding noise, traffic, and environmental impacts.
Documentation & Auditing
Maintain thorough records to support compliance and operational efficiency.
Required Documentation
- Permits and licenses
- Safety data sheets (SDS), if applicable
- Transport manifests and delivery records
- Environmental monitoring reports
- Audit trails for traceability
Regular Audits
- Conduct internal and third-party audits to verify compliance with environmental, safety, and logistics standards.
- Use audit results to improve processes and prevent violations.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for sand operations require proactive planning, strict adherence to regulations, and a commitment to sustainability. By following this guide, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance operational efficiency, and uphold their environmental and social responsibilities.
Conclusion on Sourcing Sands
The sourcing of sand is a critical issue that intersects environmental sustainability, economic development, and regulatory governance. As one of the most consumed natural resources after water, sand is essential for construction, infrastructure, and emerging technologies. However, the increasing global demand has led to unsustainable extraction practices, resulting in severe ecological consequences such as habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, riverbed and coastal degradation, and socio-economic conflicts in local communities.
Responsible sand sourcing requires a multifaceted approach, including stricter regulations, improved monitoring and enforcement, promotion of alternative materials (e.g., recycled aggregates and manufactured sand), and support for innovative technologies. International cooperation and transparent supply chains are crucial to curbing illegal sand mining and ensuring equitable resource management.
In conclusion, while sand remains indispensable to modern development, sustainable sourcing practices must be prioritized to balance economic needs with environmental protection and social well-being. A proactive, science-based, and collaborative strategy is essential to secure sand resources for future generations without compromising the health of our ecosystems.