The global sanding and surface preparation equipment market has experienced steady growth, driven by rising demand across woodworking, metal fabrication, and automotive industries. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial sanding equipment market size was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further amplified by advancements in automation and the integration of laser-guided precision technologies, which enhance accuracy and efficiency in material finishing processes. As manufacturers increasingly adopt smart manufacturing practices, the convergence of sanding systems with laser alignment and monitoring capabilities has positioned several innovators at the forefront of the industry. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and product scalability, the following nine companies represent the leading sanding laser manufacturers shaping the future of high-precision surface processing.
Top 9 Sanding Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
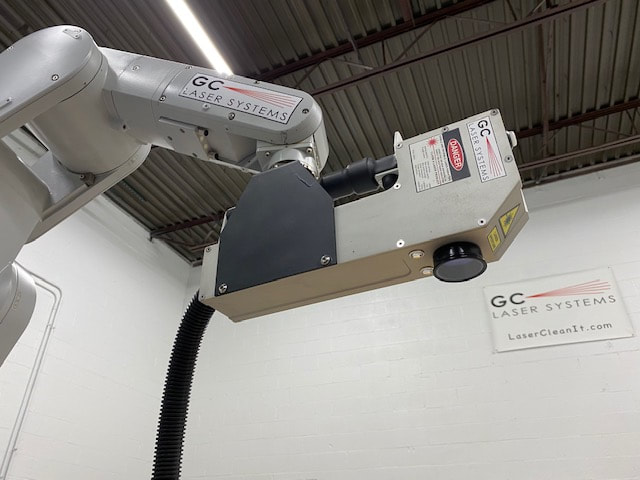
#1 G.C. Laser Systems
Website: gclasers.com
Key Highlights: G.C. Laser Systems Inc. manufactures unique laser cleaning technology that offers unmatched cleaning precision and surface prep. Our laser systems are ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#4 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics is the world leader of fiber laser technology, providing the most innovative and productive laser solutions for any industry application….
#5 Laser cleaner machine prices
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: PULSAR Laser – official logo of professional laser rust and paint removal cleaners · NEW EXCLUSIVE DISTRIBUTOR for USA and CANADA. CLICK ME ……
#6 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#7 Laserage
Website: ametekemc.com
Key Highlights: Laserage is your Premier Full-Service laser processing company for precision tube cutting, laser welding, drilling, scribing and other custom services….
#8 Fonon
Website: fonon.us
Key Highlights: Fonon specializes in creating advanced laser technologies and laser solutions for the military & defense industry. Laser cleaning, marking and defense…
#9 Nuwave Laser: Laser Cleaning Experts
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Nuwave Laser uses high-powered lasers to remove contaminants from surfaces without chemicals. Call our laser cleaning experts today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sanding Laser

H2: Market Trends for Sanding Lasers in 2026
As industrial manufacturing and precision finishing technologies evolve, sanding lasers are poised to gain significant traction in the global market by 2026. These hybrid systems—combining traditional abrasive sanding with advanced laser-assisted material removal—are emerging as a transformative force in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, woodworking, and high-end consumer goods. The 2026 market landscape for sanding lasers reflects several key trends driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and automation integration.
1. Technological Convergence and Hybrid Systems
By 2026, sanding lasers are increasingly part of intelligent, multi-functional systems that integrate laser ablation with robotic sanding arms. The laser pre-treats surfaces by removing coatings, oxides, or micro-defects, enabling mechanical sanding to proceed more efficiently and with less wear on abrasive tools. This convergence enhances surface consistency, reduces processing time, and allows for fine-tuned control in high-precision applications.
2. Rising Demand for Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
Manufacturers are adopting sanding laser systems as components of smart factories. Equipped with real-time sensors, AI-driven feedback loops, and IoT connectivity, these systems enable adaptive sanding processes that respond dynamically to material variations. In 2026, the integration with digital twins and predictive maintenance platforms is accelerating adoption in automated production lines, especially in automotive body finishing and aerospace component manufacturing.
3. Sustainability and Reduced Environmental Impact
Environmental regulations are pushing industries toward cleaner, more sustainable surface preparation methods. Sanding lasers reduce reliance on consumable abrasives and minimize dust generation, aligning with green manufacturing goals. By 2026, companies are leveraging laser-assisted sanding to lower particulate emissions, decrease waste, and comply with global environmental standards such as ISO 14001 and EU Green Deal initiatives.
4. Expansion in Wood and Composite Material Processing
The furniture, flooring, and architectural woodworking industries are increasingly deploying sanding lasers to achieve flawless finishes on engineered wood and composite materials. These systems offer precise control over texture and gloss levels, enabling customization at scale. By 2026, the growth in luxury and prefabricated wood products is fueling demand for non-contact, high-resolution surface treatment solutions.
5. Regional Market Growth and Investment Trends
Europe and North America lead in early adoption due to strong industrial automation infrastructure and high labor costs, which justify investments in advanced finishing technologies. However, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—is witnessing rapid growth, driven by expanding EV production and electronics manufacturing. Venture capital and government funding are supporting R&D in laser-material interaction, further lowering system costs and improving accessibility.
6. Cost Reduction and Scalability
Advancements in fiber laser technology and modular system design have driven down the cost of ownership for sanding laser systems. By 2026, scalable solutions are available for both large OEMs and mid-sized manufacturers, broadening market penetration. Pay-per-use and leasing models are also emerging, reducing entry barriers for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
In conclusion, the 2026 market for sanding lasers is characterized by intelligent integration, sustainability, and precision. As industries demand higher quality, lower waste, and greater automation, sanding lasers are transitioning from niche tools to essential components of modern manufacturing ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Sanding Lasers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing sanding lasers—advanced tools combining material abrasion with laser technology for precision surface finishing—introduces unique challenges, especially concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal risks, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Performance
Many suppliers, particularly those in less-regulated markets, may offer sanding lasers with substandard components or inconsistent manufacturing processes. This can result in:
- Inaccurate laser calibration, leading to uneven sanding or surface damage.
- Shorter lifespan due to inferior motors, optics, or cooling systems.
- Lack of durability under industrial workloads, increasing downtime and maintenance costs.
Without third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) or verifiable performance testing data, buyers risk acquiring unreliable equipment that fails to meet production standards.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sanding laser technology often incorporates proprietary designs, software algorithms, and patented optical systems. Sourcing from unverified suppliers increases the risk of:
- Acquiring counterfeit or cloned devices that violate existing patents or copyrights.
- Using embedded software without proper licensing, exposing the buyer to legal action.
- Becoming complicit in IP theft, especially when suppliers reverse-engineer leading brands.
Purchasers may unknowingly import infringing equipment, leading to customs seizures, lawsuits, or reputational damage.
Absence of Technical Documentation and Support
Low-cost suppliers may fail to provide comprehensive technical documentation, user manuals, or software SDKs. This creates challenges in:
- Integration with existing production systems.
- Performing maintenance or troubleshooting.
- Ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Additionally, lack of after-sales support or firmware updates can render the equipment obsolete or unsafe over time.
Misrepresentation of Capabilities and Specifications
Some vendors exaggerate the capabilities of their sanding lasers—such as beam precision, sanding speed, or material compatibility—to close sales. Buyers must verify claims through:
- Independent testing or on-site demonstrations.
- Detailed specification sheets with measurable performance metrics.
- Customer references or case studies.
Failure to validate performance can result in mismatched equipment that underperforms in real-world applications.
Inadequate Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Laser-based tools are subject to strict safety regulations (e.g., FDA/CDRH in the U.S., IEC 60825 internationally). Poorly sourced sanding lasers may lack:
- Proper laser classification labeling.
- Safety interlocks or enclosure requirements.
- EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) compliance.
Using non-compliant equipment can lead to workplace safety violations, regulatory fines, or insurance issues.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence—verifying supplier credentials, requesting IP documentation, demanding performance validation, and ensuring compliance with international standards. Partnering with reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors significantly reduces exposure to quality and IP-related pitfalls when sourcing sanding lasers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sanding Laser
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Sanding lasers, which combine abrasive surface treatment with laser technology for precision material processing, are subject to multiple international and regional regulations. These devices typically fall under industrial machinery, laser equipment, and electrical safety standards. Accurate classification is essential for compliant shipping and market access.
Harmonized System (HS) Code and Customs Classification
The appropriate HS code for sanding lasers depends on the device’s primary function and technical specifications. Common classifications include:
– 8465.95: Machines for planing, sanding, or polishing of wood, cork, bone, or similar hard materials (if primarily used for woodworking).
– 8515.21: Laser soldering, welding, or cutting machines (if the laser function is dominant).
– 9013.20: Other optical devices and instruments using lasers.
Consult local customs authorities or use binding tariff information (BTI) to confirm the correct code for your specific model.
Laser Safety Compliance (IEC & FDA)
Sanding lasers must comply with international laser safety standards:
– IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety, including classification (typically Class 1, 3B, or 4 for industrial models), labeling, and protective measures.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10/1040.11: Required for sales in the U.S. Manufacturers must file a Laser Product Report and provide compliance certification.
Ensure devices include proper warning labels, interlocks, and user manuals with safety instructions.
Electrical and EMC Regulations
Sanding lasers must meet electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility requirements:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC 2014/30/EU).
– UKCA Marking (UK): Equivalent requirements post-Brexit.
– UL/CSA Certification (North America): Required for market access; UL 61010-1 is commonly applicable.
Testing by a Notified Body or accredited lab may be required.
Packaging and Transport Requirements
Proper packaging ensures safe shipment and regulatory compliance:
– Use shock-absorbent materials and secure internal bracing to protect laser optics and moving parts.
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment” warnings.
– Include compliance labels (CE, FCC, laser class) on both device and packaging.
– For international air freight, ensure compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries (e.g., for portable units) are included.
Import/Export Controls and Documentation
Prepare the following documents for international shipments:
– Commercial invoice with detailed product description, HS code, and value.
– Packing list.
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, UKCA, UL, etc.).
– FDA Laser Product Report (for U.S. imports).
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill.
– Export license may be required for high-power lasers under dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation 2021/821).
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Ensure sanding lasers comply with environmental directives:
– RoHS (EU 2011/65/EU): Restricts hazardous substances (lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.) in electrical equipment.
– WEEE (EU 2012/19/EU): Requires registration and end-of-life take-back programs in applicable countries.
– REACH: Registration, evaluation, and authorization of chemical substances.
On-Site Installation and User Training Requirements
Many jurisdictions require certified installation and operator training:
– Provide multilingual user manuals including safety, maintenance, and laser hazard procedures.
– Offer remote or on-site training for safe operation, especially for Class 3B and 4 lasers.
– Maintain records of training for compliance audits.
Maintenance and Compliance Recordkeeping
Manufacturers and operators must maintain compliance documentation:
– Retain product test reports, certifications, and conformity declarations for at least 10 years.
– Keep logs of maintenance, repairs, and laser output calibration.
– Update compliance status when product modifications occur.
Regional Market-Specific Requirements
Adapt compliance strategy based on target market:
– United States: FDA laser compliance, FCC electromagnetic interference rules, OSHA workplace safety.
– European Union: CE marking, notified body involvement if required, Ecodesign Directive.
– China: CCC certification may apply; check GB standards for lasers and machinery.
– Australia/NZ: RCM marking under the EMC and electrical safety frameworks.
Always verify local regulations through legal counsel or compliance consultants before market entry.
In conclusion, sourcing a sanding laser requires careful consideration of various technical, operational, and financial factors. It is essential to evaluate the specific needs of your application, including material types, precision requirements, production volume, and integration capabilities with existing systems. Conducting thorough research on suppliers, assessing machine quality, support services, and long-term maintenance costs will ensure a sound investment. Additionally, choosing a reputable supplier with proven expertise in laser sanding technology can significantly enhance performance, efficiency, and return on investment. Ultimately, a well-sourced sanding laser can elevate manufacturing precision, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity in modern industrial processes.