The global saline solution for nebulization market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising prevalence of respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis. According to Grand View Research, the global respiratory care devices market was valued at USD 30.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030, with nebulization therapies playing a pivotal role in treatment protocols. As demand for safe, sterile, and effective isotonic and hypertonic saline formulations increases, manufacturers are focusing on quality compliance, scalable production, and product differentiation. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of reliable saline solution suppliers in supporting clinical and home-based respiratory care. The following overview highlights the top eight manufacturers leading innovation, scalability, and regulatory adherence in the saline solution for nebulization space.
Top 8 Saline Solution For Nebulization Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Next Generation Buffered Saline Inhalation Solution
Domain Est. 2007
Website: pharmacaribe.com
Key Highlights: Pharmacaribe is a leading manufacturer of saline solutions for inhalation and has worked collaboratively with the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and Cystic ……
#2 Sterile Sodium Chloride Inhalation Solution (0.9%) USP
Domain Est. 1997
Website: amsino.com
Key Highlights: 3 mL, 5 mL and 15 mL single-use vials with graduation for accurate dispensing · Filled with sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Inhalation Solution, USP · Easy open ……
#3 OMRON Respiratory Nebulizers & Devices for At
Domain Est. 1997
Website: omronhealthcare.com
Key Highlights: OMRON offers prescription-grade, at-home and portable nebulizer solutions to fit a variety of needs and budgets….
#4 HyperSal Sodium Chloride Solution
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pari.com
Key Highlights: PARI HyperSal Sodium Chloride Inhalation Solution is a sterile, preservative-free solution available in both 3.5% and 7% strengths….
#5 Sodium Chloride Inhalation Solution USP 3% 4 mL
Domain Est. 1998
Website: nephronpharm.com
Key Highlights: Description: Sterile individual unit dose; Preservative and additive free; Non-pyrogenic; Available in the following package configurations per box:….
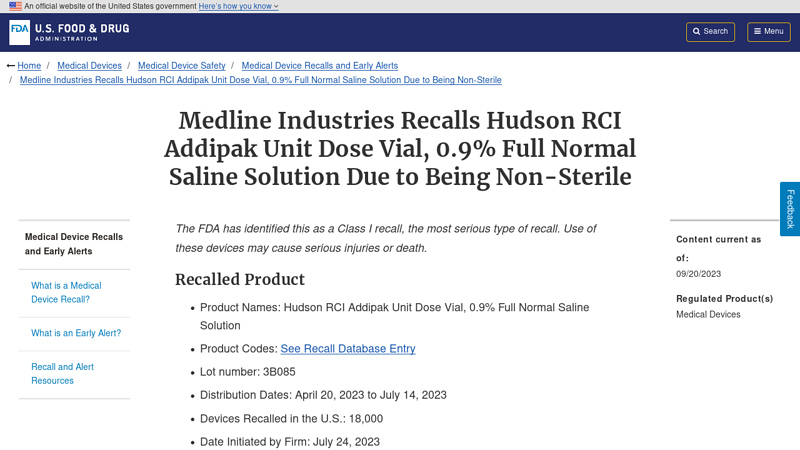
#6 Medline Industries Recalls Hudson RCI Addipak Unit Dose Vial, 0.9 …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: fda.gov
Key Highlights: The Hudson RCI Addipak Unit Dose Vials is a pack of single use 0.9% Full Normal Saline Solution used during treatments such as inhalation and ……
#7 Nebuliz 7%
Domain Est. 2003
Website: navehpharma.com
Key Highlights: Nebulize 7% is a SOLUTION indicated FOR LUNG FUNCTION IMPROVEMENT. It– combines hypertonic saline of 7% combined with hyaluronic acid….
#8 Inhaled Saline Solution
Domain Est. 2012
Expert Sourcing Insights for Saline Solution For Nebulization

H2: Market Trends for Saline Solution for Nebulization in 2026
By 2026, the global market for saline solution for nebulization is projected to experience steady growth, driven by rising respiratory disease prevalence, increased home healthcare adoption, and advancements in nebulizer technology. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Growing Prevalence of Respiratory Disorders
Chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and bronchitis continue to rise globally, particularly in aging populations and urban areas affected by air pollution. This surge is fueling demand for effective respiratory therapies, with saline solution for nebulization serving as a foundational component in airway clearance and medication delivery. -
Expansion of Home Healthcare and Self-Management
The shift toward decentralized care models is accelerating the use of nebulizers in home settings. Saline solutions, especially isotonic (0.9%) and hypertonic (3–7%) variants, are increasingly used for airway hydration and mucus clearance. Convenience, cost-effectiveness, and improved patient compliance support sustained demand for over-the-counter and prescription saline nebulization products. -
Technological Advancements in Nebulizer Devices
Innovations in nebulizer design—such as mesh, ultrasonic, and portable battery-operated devices—are enhancing the efficiency and portability of saline delivery. These improvements increase patient adherence and facilitate wider adoption across demographics, including pediatric and geriatric populations. -
Increased Focus on Hypertonic Saline in Clinical Protocols
Clinical evidence supporting the benefits of hypertonic saline (particularly 3% and 7%) in managing cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis is being integrated into treatment guidelines. This trend is driving formulation-specific demand and encouraging manufacturers to develop stabilized, preservative-free hypertonic saline products. -
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Quality Assurance
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA continue to enforce strict sterility, packaging, and labeling requirements for nebulized saline solutions. The emphasis on single-dose, preservative-free vials to reduce infection risks is influencing manufacturing practices and product designs. -
Emerging Markets Driving Growth
Regions including Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa are witnessing increased healthcare access, urbanization, and awareness of respiratory health. Rising investments in healthcare infrastructure and government initiatives for non-communicable disease management are expanding the saline nebulization market in these areas. -
Sustainability and Packaging Innovations
Environmental concerns are prompting companies to adopt eco-friendly packaging solutions. Lightweight, recyclable materials and reduced plastic usage in unit-dose packaging are becoming competitive advantages, aligning with global sustainability goals. -
Integration with Combination Therapies
Saline solutions are increasingly used as diluents for nebulized medications (e.g., bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics). The growth in combination therapies supports higher volumes of saline usage, especially in hospital and long-term care settings.
In conclusion, the saline solution for nebulization market in 2026 is characterized by clinical validation, patient-centered innovation, and geographic expansion. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, healthcare providers, and regulators—are focusing on safety, accessibility, and integration with modern respiratory care protocols to meet evolving patient needs.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Saline Solution for Nebulization (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing saline solution for nebulization requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to significant risks, including patient safety issues, regulatory non-compliance, and legal disputes. Below are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Sterility and Aseptic Manufacturing
Saline solutions for nebulization must be sterile to prevent introducing pathogens directly into the respiratory tract. A common pitfall is sourcing from manufacturers without validated aseptic processing controls or without adherence to current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). Non-sterile or contaminated solutions can lead to severe respiratory infections.
2. Incorrect Osmolality and pH
Nebulized saline must be isotonic (typically 0.9% NaCl) to minimize airway irritation. Sourcing solutions with incorrect concentrations (e.g., hypertonic without clinical indication) or improper pH can cause bronchospasm or discomfort. Ensure specifications match pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur.).
3. Presence of Impurities or Particulates
Particulate matter or endotoxins in the solution can trigger inflammatory responses or device clogging. Suppliers lacking rigorous filtration, testing (e.g., LAL for endotoxins), or cleanroom standards pose a significant risk. Always verify Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for particulate and endotoxin levels.
4. Inappropriate Packaging and Container Closure Integrity
Single-dose vials or ampoules are preferred to minimize contamination risk post-opening. Multi-dose containers increase infection risk if preservatives are absent or inappropriate. Ensure packaging is compatible with nebulizer systems and maintains sterility throughout shelf life.
5. Lack of Regulatory Compliance
Sourcing saline not approved by recognized regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, EMA) or lacking proper market authorization can result in legal and operational issues. Verify that the product has the correct regulatory status (e.g., as a medical device or pharmaceutical) in your target market.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Formulations or Delivery Systems
Some saline-based nebulization products may include proprietary additives or be part of patented delivery platforms. Sourcing generic versions without analyzing existing patents can lead to IP infringement claims. Conduct thorough freedom-to-operate (FTO) searches before commercialization.
2. Unauthorized Use of Branded Product Names or Logos
Marketing or labeling sourced saline to resemble branded products (e.g., “equivalent to Pulmopoint®”) may violate trademark laws. Avoid misleading comparisons or visual similarities that could confuse consumers or healthcare providers.
3. Breach of Confidential Manufacturing Processes
If sourcing under contract manufacturing agreements, ensure that proprietary methods (e.g., sterilization techniques or filtration processes) are protected through appropriate confidentiality agreements (NDAs). Failure to do so may expose both parties to IP theft or disputes.
4. Misuse of Regulatory Data Protection
In some jurisdictions, regulatory submissions enjoy data exclusivity. Replicating a competitor’s clinical or quality data without authorization may breach IP or regulatory exclusivity rights, especially for novel saline-based formulations with specific claims.
5. Ambiguity in Ownership of Customized Products
When working with suppliers to develop customized saline solutions (e.g., specific volume or packaging), clarify IP ownership in contracts. Without clear agreements, disputes may arise over who owns formulation improvements or design changes.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, verify compliance with pharmacopeial and regulatory standards, and engage legal counsel for IP assessments. Prioritizing quality and IP integrity ensures patient safety, regulatory approval, and long-term commercial success.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Saline Solution for Nebulization
1. Product Overview
Saline Solution for Nebulization is a sterile, isotonic (0.9%) sodium chloride (NaCl) solution intended for use in nebulizers to help deliver medication or to assist in airway hydration. It is classified as a medical device or medicinal product depending on the region and formulation (e.g., with or without active pharmaceutical ingredients). Commonly packaged in single-dose unit containers (e.g., 2 mL or 5 mL vials), it is intended for single use only.
2. Regulatory Classification
- United States (FDA):
- Regulated as a medical device (Class II) or drug, depending on labeling and claims.
- Must comply with 21 CFR parts related to sterile drug products (e.g., 21 CFR 211 for cGMP).
-
FDA Premarket Notification (510(k)) may be required; NDC listing is mandatory.
-
European Union (EU):
- Classified under the Medical Devices Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745 or as a medicinal product per Directive 2001/83/EC.
- If classified as a medical device: requires CE marking and designation under an authorized Notified Body.
- If medicinal: requires Marketing Authorization (MA) via national or centralized procedures.
-
Must comply with Annex I of MDR – General Safety and Performance Requirements.
-
Other Regions (e.g., UK, Canada, Australia):
- UK: MHRA regulations; UKCA marking post-Brexit (with CE still accepted until 2025).
- Canada: Health Canada – Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282); Class II device.
- Australia: TGA – Listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
3. Manufacturing & Quality Compliance
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
- Must be manufactured in a certified cleanroom environment (ISO Class 7 or better).
- Adherence to ISO 13485:2016 for medical devices or cGMP for pharmaceuticals.
-
Sterility assurance via terminal sterilization (e.g., autoclaving) or aseptic processing.
-
Testing & Validation:
- Sterility testing (USP <71>), bacterial endotoxins (LAL test, USP <85>), particulate matter (USP <788>).
- pH, osmolality, and NaCl concentration verification.
-
Container closure integrity testing (CCIT).
-
Labeling Requirements:
- Must include: product name, concentration (0.9% NaCl), volume, sterility statement, single-use only, lot number, expiry date, storage conditions, and regulatory identifier (e.g., CE, FDA, NDC).
- Multilingual labeling required in EU and some other regions.
4. Packaging & Cold Chain Considerations
- Primary Packaging:
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) unit-dose vials; tamper-evident seals.
-
Must maintain sterility and prevent leaching.
-
Secondary & Tertiary Packaging:
- Cartons with desiccants (if moisture-sensitive); outer shipping cases.
-
Palletized with stretch-wrapping; labeled with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Freeze”).
-
Cold Chain:
- Saline solution for nebulization is generally not refrigerated but requires controlled room temperature storage (15–25°C or as specified).
- Avoid freezing (can cause container deformation or precipitation).
- Monitor temperature during transport using data loggers if required.
5. Import/Export & Customs Compliance
- HS Code (Harmonized System):
- Typically: 3006.50 (sterile surgical or laboratory solutions) or 3824.99 (chemical preparations).
-
Country-specific variations apply; verify with local customs authority.
-
Import Requirements:
- Import permits may be required (e.g., in India, Brazil, Saudi Arabia).
- Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) or Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product (CPP) often needed.
-
Customs declaration with accurate product description, value, and origin.
-
Documentation:
- Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill.
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA), Certificate of Sterility, and GMP certificate.
- Regulatory approval evidence (e.g., CE certificate, FDA listing).
6. Storage & Distribution
- Warehousing:
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled areas (15–25°C), away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management.
-
Regular audits for compliance with GDP (Good Distribution Practices).
-
Transportation:
- Use GDP-compliant carriers with temperature monitoring if needed.
- Avoid extreme temperatures and excessive vibration.
- Secure packaging to prevent breakage.
7. Post-Market Surveillance & Compliance
- Adverse Event Reporting:
-
Establish a system for reporting incidents (e.g., contamination, device malfunction) to regulatory bodies (FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED, etc.).
-
Recall Procedures:
- Implement a field alert report (FAR) system.
-
Maintain traceability via lot numbers and serialization (where required, e.g., EU Falsified Medicines Directive).
-
Labeling Updates & Regulatory Renewals:
- Monitor expiration of certifications (e.g., CE renewal every 5 years).
- Update labeling per regulatory changes (e.g., UDI requirements in US/EU).
8. Unique Device Identification (UDI) – Where Applicable
- US FDA:
- UDI required on label and package (GUDID database submission).
-
Format per FDA guidance (e.g., GS1, HIBCC).
-
EU MDR:
- UDI mandatory; upload to EUDAMED.
- Human-readable and machine-readable (e.g., barcode or Data Matrix).
9. Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- Waste Disposal:
- Unused or expired saline is generally non-hazardous but must be disposed of per local biomedical waste regulations if opened or contaminated.
-
Intact, unused vials may be disposed of as non-hazardous waste in some regions; consult local guidelines.
-
Sustainability:
- Consider recyclable packaging materials (e.g., paperboard cartons, recyclable plastics).
10. Summary of Key Compliance Actions
| Requirement | Action Required |
|——————————-|———————————————————————————|
| Regulatory Approval | Obtain CE mark, FDA listing, or local marketing authorization |
| GMP/ISO Compliance | Maintain ISO 13485 or cGMP certification |
| Sterility & Testing | Conduct regular batch testing and validation |
| Labeling & UDI | Ensure compliant labeling and UDI implementation |
| Transport & Storage | Maintain controlled conditions; use GDP-compliant logistics |
| Export Documentation | Prepare CoA, CFS, CoA, commercial invoice, and regulatory certificates |
| Post-Market Surveillance | Establish adverse event reporting and recall systems |
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for Saline Solution for Nebulization require strict adherence to regional regulatory standards, sterility assurance, proper labeling, and secure supply chain practices. Proactive monitoring of regulatory changes and robust quality systems are essential to ensure patient safety and market access.
Conclusion: Sourcing Saline Solution for Nebulization
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate saline solution for nebulization is a critical factor in ensuring safe and effective respiratory treatment. Normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride) is the most commonly used and widely recommended solution due to its isotonic nature, which minimizes irritation to the airways. When sourcing saline, it is essential to prioritize sterile, preservative-free, single-dose vials or ampoules from reputable manufacturers to reduce the risk of contamination and adverse reactions.
Both hospital pharmacies and licensed medical suppliers can provide clinical-grade saline, while over-the-counter options should be carefully evaluated for compliance with medical standards. Home preparation of saline is strongly discouraged due to the high risk of infection or incorrect concentration.
Ultimately, healthcare providers should guide the selection and sourcing of saline solutions to ensure compatibility with the patient’s condition and nebulization equipment. Proper sourcing not only enhances treatment efficacy but also safeguards patient health, reinforcing the importance of quality, sterility, and regulatory compliance in respiratory care.