The global rust removal market is undergoing a transformative shift as industries increasingly adopt advanced, eco-friendly solutions to combat corrosion. Traditional methods such as sandblasting and chemical treatments are being phased out in favor of precision technologies, with laser rust removal emerging as a leading alternative. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning market—of which rust removal is a key application—was valued at USD 812.1 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.4% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is driven by rising demand from automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing sectors seeking non-abrasive, waste-free surface treatment solutions. As regulatory pressures mount and sustainability becomes a priority, manufacturers are investing heavily in laser-based systems that offer repeatability, reduced operational downtime, and lower environmental impact. Against this backdrop, a new cohort of innovators is shaping the future of rust remediation. Here are the top 10 laser rust removal manufacturers leading the charge through technological excellence, scalability, and proven industrial performance.
Top 10 Rust Removal By Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Our laser cleaning solutions are used to remove a range of contaminants from metal surfaces such as rust, oxide, paint, and electrolyte. As contaminants are ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: Clean smarter with laser light. Fully cleaning rust of machine parts with the help of laser cleaning. WHY LASER CLEANING? Embrace the future of sustainable ……
#3 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: “Laser Photonics technology has really simplified our work, facilitating the cleaning of rust and the removal of old paint and contaminants. The technology is ……
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#5 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#6 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: The laser rust removal machine uses a focused laser beam with high peak power and short pulse to heat the external surface (the rust) to its evaporation point….
#7 Understanding Laser Rust Removal
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Laser rust removal is a non-contact cleaning process that uses a laser beam to remove rust, oxide layers, and other contaminants from surfaces. It is an ……
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#9 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: Achieve super fast rust removal rates with out lasers. Watch this super fast rust removal from carbon steel panel with the new ultra-lightweight Vulcan handheld ……
#10 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A practical guide for professionals and entrepreneurs using PULSAR Laser systems to remove rust safely, efficiently and without abrasives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rust Removal By Laser
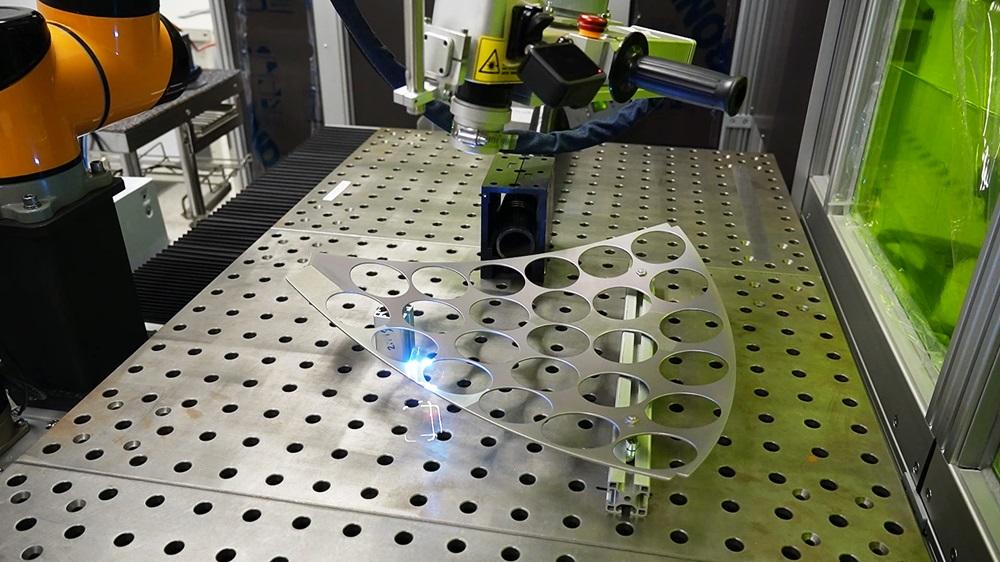

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Rust Removal by Laser
The global market for laser-based rust removal is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and growing demand for precision surface preparation across key industries. Below are the major trends shaping the Rust Removal by Laser market in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption in Industrial Maintenance and Manufacturing
By 2026, industries such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, and heavy machinery are expected to significantly expand their use of laser rust removal. The technology’s ability to selectively remove rust without damaging underlying substrates makes it ideal for high-value components. Predictive maintenance programs are increasingly integrating laser cleaning as a non-contact, repeatable method, boosting market penetration. -
Stringent Environmental Regulations Driving Shift from Chemical and Abrasive Methods
Governments worldwide are tightening regulations on chemical solvents and abrasive blasting due to environmental and worker safety concerns. Laser rust removal, being a dry, chemical-free, and low-waste process, is emerging as a sustainable alternative. By 2026, compliance with green manufacturing standards is expected to accelerate adoption, especially in Europe and North America. -
Advancements in Portable and High-Power Laser Systems
Ongoing innovations are making laser cleaning equipment more compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly. By 2026, the availability of handheld and robot-integrated laser systems will broaden accessibility for field applications, including ship hull maintenance and infrastructure rehabilitation. Improved fiber laser technology is enabling faster processing speeds and deeper rust penetration, enhancing cost-effectiveness. -
Integration with Automation and Industry 4.0
The convergence of laser cleaning with robotics, IoT, and AI is a key trend in 2026. Smart laser systems with real-time monitoring and adaptive control are being deployed in automated production lines, ensuring consistent surface quality. This integration supports digital twin technologies and data-driven maintenance strategies, increasing operational efficiency. -
Growing Investment and R&D in Laser Technology
Major players and startups are investing heavily in R&D to reduce system costs and improve performance. By 2026, economies of scale and component miniaturization are expected to lower entry barriers, making laser rust removal viable for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe lead in adoption, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and South Korea—is witnessing rapid growth due to industrial modernization and infrastructure development. Government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing are expected to fuel demand for laser cleaning solutions in these regions. -
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and ROI
End-users are increasingly evaluating laser rust removal based on long-term savings, including reduced labor, waste disposal, and rework costs. By 2026, comprehensive TCO models will support procurement decisions, further legitimizing laser technology as a cost-effective solution.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for laser-based rust removal is defined by technological maturity, regulatory tailwinds, and digital integration. As the market evolves, laser cleaning is expected to transition from a niche solution to a mainstream surface treatment method across multiple sectors.
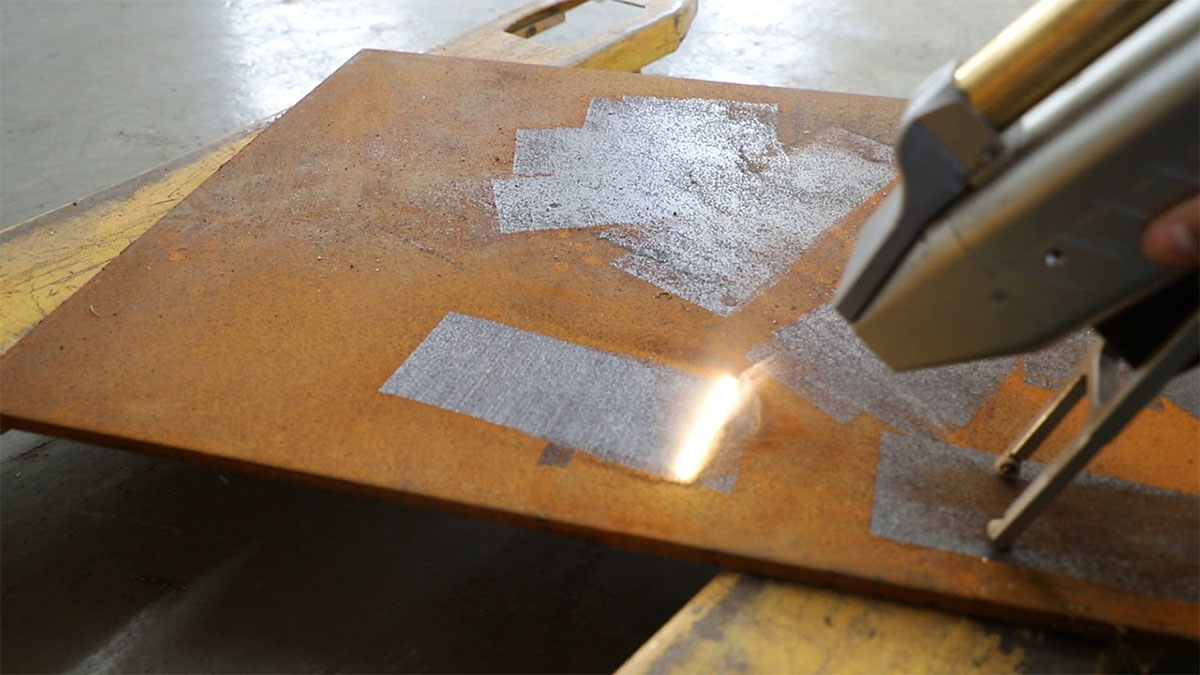

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Rust Removal by Laser (Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser-based rust removal services or equipment, businesses often encounter hidden challenges that impact quality, intellectual property (IP), and long-term operational success. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for making informed decisions.
Inadequate Laser System Quality and Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is sourcing equipment or services based on misleading or incomplete technical specifications. Some suppliers may advertise high-power lasers without clarifying pulse energy, beam quality (M²), or scanning speed—factors critical to effective rust removal. Low-quality systems may fail to remove rust uniformly, cause substrate damage, or require multiple passes, reducing efficiency. Additionally, substandard components (e.g., optics, cooling systems) can lead to frequent downtime and high maintenance costs.
Lack of Process Validation and Quality Control
Many providers lack standardized quality control procedures for laser rust removal. Without documented parameters—such as laser fluence, spot size, and scanning overlap—results can vary significantly between jobs. This inconsistency is especially problematic in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, automotive) where traceability and repeatability are mandatory. Sourcing from vendors without process validation (e.g., surface roughness testing, adhesion testing post-cleaning) increases the risk of defective outcomes.
Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure and Ownership Risks
When outsourcing laser cleaning, especially for custom applications, there is a risk of exposing proprietary designs or manufacturing processes. If the service provider is not bound by clear IP agreements, they may inadvertently (or intentionally) use your process data for competitive advantage. Moreover, custom-developed cleaning protocols or automation setups may lack defined IP ownership terms, leading to disputes over rights and usage.
Insufficient Expertise and Technical Support
Laser rust removal is not a plug-and-play solution—it requires skilled operators and deep technical knowledge. Sourcing from vendors with limited experience can result in improper parameter selection, inefficient workflows, or safety hazards. Post-sale support is often inadequate, leaving buyers to troubleshoot complex system issues without manufacturer assistance. This lack of expertise undermines the promised benefits of precision and automation.
Hidden Costs and Scalability Limitations
Initial quotes may not reflect total cost of ownership. Hidden expenses include training, maintenance, consumables (e.g., protective optics), and software updates. Furthermore, some systems are not scalable—what works for small parts may fail on large or complex geometries. Sourcing without considering future production needs can result in costly equipment upgrades or process redesigns.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Environmental Standards
Laser cleaning generates fumes and particulate matter requiring appropriate fume extraction and safety enclosures. Some low-cost suppliers omit these critical components or provide systems that do not meet OSHA, CE, or ISO safety standards. This exposes the buyer to regulatory risks and potential workplace hazards, undermining the environmental benefits often touted for laser cleaning.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence: verify technical capabilities with real-world testing, demand clear IP agreements, ensure robust support, and assess total lifecycle costs before committing to a laser rust removal solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rust Removal by Laser
Overview of Laser Rust Removal Technology
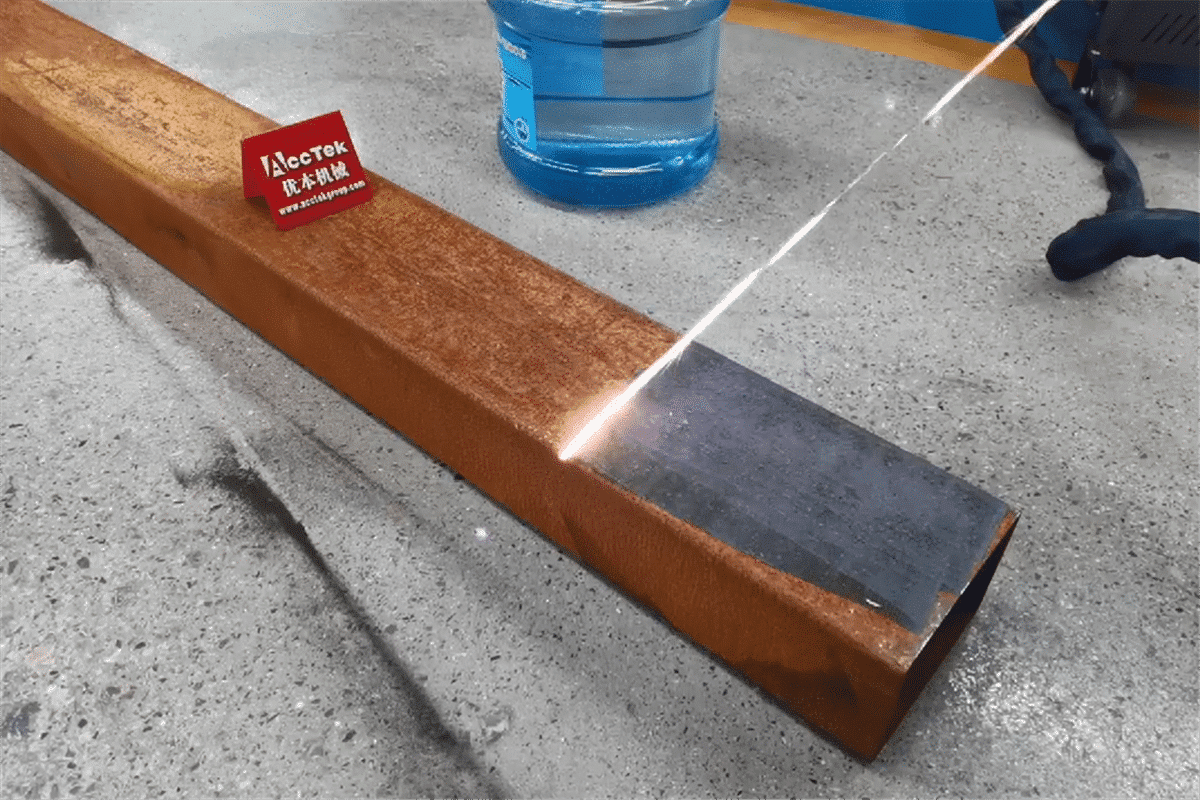
Laser rust removal is a non-contact, eco-friendly cleaning method that uses high-intensity laser beams to vaporize rust, oxides, and contaminants from metal surfaces. Unlike traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical stripping, laser cleaning produces minimal waste, requires no consumables, and preserves the underlying substrate. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for implementing laser rust removal in industrial operations.
Equipment Selection and Transportation
Choosing the appropriate laser cleaning system depends on the scale of operations, material types, and rust severity. Systems range from portable handheld units to automated robotic integrations. Ensure equipment is compatible with your facility’s power supply (typically 208–480V, 3-phase) and has adequate cooling systems. When transporting laser equipment, comply with manufacturer guidelines for shock and vibration protection. Use secure crating and climate-controlled shipping when necessary, especially for sensitive optical components.
Facility Requirements and Setup
Laser rust removal systems require a stable, clean workspace with adequate ventilation and space for operator movement. Install systems on vibration-dampened surfaces to ensure beam accuracy. Provide sufficient electrical outlets with surge protection and dedicated circuits to prevent interference. Maintain ambient temperatures between 10°C and 40°C and relative humidity below 80%. Install warning signage and physical barriers to demarcate the operational zone, especially in shared workspaces.
Safety Protocols and Operator Training
Laser cleaning involves Class 4 lasers, which pose serious risks including eye and skin injury, fire, and fume inhalation. Operators must undergo certified laser safety training covering beam hazards, emergency procedures, and equipment handling. Mandatory personal protective equipment (PPE) includes laser safety goggles with the correct optical density (OD) rating, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection if fumes are generated. Conduct regular safety drills and maintain an on-site Laser Safety Officer (LSO) as required by ANSI Z136.1 standards.
Fume and Particulate Management
Laser ablation produces metallic particulates and fumes, particularly when removing iron oxide. Install high-efficiency local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems equipped with HEPA and/or ULPA filtration to capture airborne contaminants. Conduct air quality testing to ensure compliance with OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for iron oxide and other metals. Filter systems must be inspected and maintained monthly, with records kept for regulatory audits.
Waste Handling and Environmental Compliance
Laser rust removal generates minimal waste—primarily collected particulates in filtration systems. Classified as non-hazardous unless mixed with oils or heavy metals, this waste typically requires disposal as industrial solid waste. Perform waste characterization testing per EPA regulations (e.g., TCLP) to confirm classification. Maintain documentation of disposal manifests and work with licensed waste handlers. Laser cleaning avoids hazardous solvents, supporting compliance with EPA’s Clean Air Act and reducing VOC emissions.
Regulatory Standards and Documentation
Compliance with national and international standards is essential. Key regulations include:
– ANSI Z136.1 – Safe use of lasers in industrial settings
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910.132/133 – PPE and eye/face protection
– NFPA 70 (NEC) – Electrical installation safety
– ISO 12100 – Machinery safety standards
– EU Directive 2014/35/EU (CE Marking) – For systems used in Europe
Maintain up-to-date documentation including equipment manuals, safety training records, risk assessments, maintenance logs, and compliance certifications.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular preventive maintenance ensures safety and performance. Clean optical lenses and mirrors weekly using approved methods. Inspect cooling systems, cables, and interlocks monthly. Perform annual laser power calibration by certified technicians to ensure beam accuracy and consistency. Keep a log of all maintenance activities and retain records for a minimum of five years.
Incident Reporting and Emergency Procedures
Establish a clear incident reporting protocol for laser-related accidents, near-misses, or equipment malfunctions. Post emergency contacts, eyewash station locations, and fire extinguisher types near work areas. Equip facilities with Class D fire extinguishers for metal fires. Report all incidents involving injury or exposure to relevant authorities per OSHA regulations within required timeframes (e.g., severe injuries within 8 hours).
International Shipments and Import Compliance
When shipping laser systems across borders, comply with export control regulations such as the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or EU Dual-Use Regulation. Laser cleaning equipment may be classified under ECCN 6A003.b.4. Prepare accurate documentation including commercial invoices, packing lists, and export licenses if required. Label packages with proper hazard warnings and laser classifications (IEC 60825-1).
Continuous Improvement and Audits
Conduct internal audits at least annually to assess compliance with safety, environmental, and operational standards. Use audit findings to update training programs, refine procedures, and invest in technological upgrades. Stay informed about evolving regulations and industry best practices through participation in organizations such as the Laser Institute of America (LIA) or the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can safely and effectively implement laser rust removal while meeting regulatory requirements and minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion: Sourcing Rust Removal by Laser
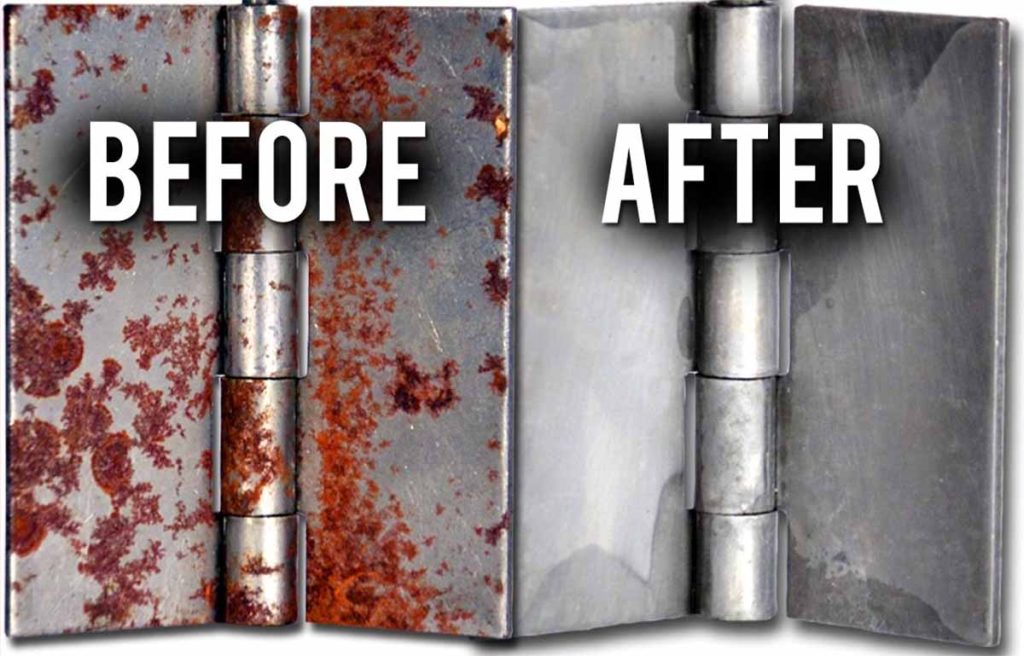
Laser rust removal presents a modern, efficient, and environmentally sustainable alternative to traditional rust removal methods such as sandblasting, chemical treatments, or mechanical abrasion. When considering sourcing laser rust removal services, the decision offers numerous advantages including precision, minimal substrate damage, no secondary waste, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
Outsourcing to specialized providers allows businesses to access state-of-the-art laser technology and technical expertise without significant upfront investment in equipment and training. This is particularly beneficial for industries requiring high standards of surface preparation, such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, and heritage restoration.
While initial service costs may be higher than conventional methods, the long-term benefits—reduced labor time, improved quality, and lower environmental impact—justify the investment. Additionally, as laser cleaning technology becomes more widespread, service availability and cost-efficiency are expected to improve further.
In conclusion, sourcing laser rust removal is a strategic choice for organizations seeking sustainable, precise, and high-quality surface treatment solutions. It aligns with modern industrial demands for cleaner production processes and sets a foundation for future-ready maintenance and restoration practices.