The global rubber spring market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial machinery, and railway applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global suspension system market—of which rubber springs are a critical component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by rising vehicle production, particularly in emerging economies, and the growing need for vibration isolation solutions in industrial equipment. Additionally, Grand View Research valued the global industrial rubber products market at USD 48.6 billion in 2022, with a CAGR of 6.1% from 2023 to 2030, underscoring robust demand for resilient elastomeric components like rubber springs. As industries prioritize noise reduction, durability, and improved ride comfort, manufacturers of rubber springs are scaling innovation in material science and application-specific designs. In this evolving landscape, the following ten companies stand out as leading rubber spring manufacturers, combining technological expertise, global reach, and a strong track record of performance.
Top 10 Rubber Spring Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rubber Springs
Domain Est. 2022
Website: santoshspring.com
Key Highlights: Supplier & Manufacturer of Rubber Springs & Rubber Air Springs. Our product range also comprises of Metal Springs, Compression Springs and Electric Switch ……
#2 Fabricated Rubber Spring Manufacturer from Kadi
Domain Est. 2013
Website: rubberspring.in
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of Rubber Spring – Fabricated Rubber Spring, Rubber Air Spring, Fabric Rubber Spring offered by Vishwaraj Rubber Industries, Kadi, Gujarat….
#3 Eibach
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eibach.com
Key Highlights: Developed and perfected on track in cooperation with race teams across the globe, Eibach Race Springs have been the choice of champions for over 35 years….
#4 Rubber Springs Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hallite.com
Key Highlights: Our range of AEON® progressive rubber springs have improved suspension performance both as a sole suspension and as a spring helper for over 40 years….
#5 Aeon Rubber Springs
Domain Est. 1999
Website: timbren.com
Key Highlights: Explore Timbren’s Aeon Rubber Springs, designed to improve vehicle suspension with unmatched durability and performance….
#6 Rubber Spring Suspension
Domain Est. 2000
Website: gmtrubber.com
Key Highlights: we have a fantastic range of rubber springs available in a range of sizes & designs, allowing for high levels of deflections for shock absorption!…
#7 Rubber Springs and Hollow Rubber Bellows
Domain Est. 2004
Website: mgmrc.com
Key Highlights: We provide Hollow Rubber Bellows in different sizes, shapes, and material to reduce sudden shocks and vibrations. Our Hollow Spring Bellows are designed to ……
#8 Specializes in the Manufacture of all kinds of
Domain Est. 2007
Website: rjspringrubber.com
Key Highlights: Coil Springs – We specialized in all kinds of springs such as compression, torsion, tension and spherical springs used for different industries such as ……
#9 Rubber
Domain Est. 2013
Website: daytonlamina.com
Key Highlights: The Lamina Marsh Mellow® Die Spring is a proven cost saver for the metal stamping industry. Marsh Mellow® Die Springs can be used as a maintenance free ……
#10 Reinforced Rubber Springs
Domain Est. 2018
Website: eganagroup.com
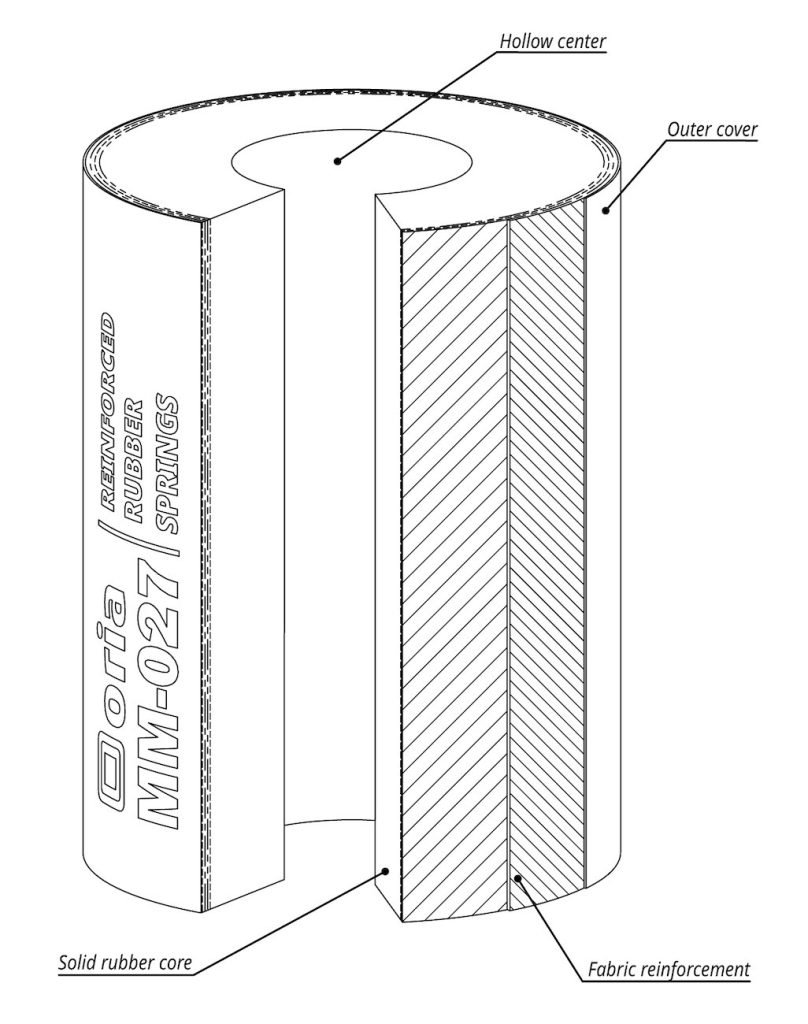
Key Highlights: Reinforced Rubber Springs. The Oria rubber fabric spring is a vibration isolator made of rubber and fabric with a hole in the centre for fixation….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rubber Spring

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Rubber Springs
The global rubber spring market is anticipated to experience steady growth and notable shifts by 2026, driven by advancements in material science, evolving industrial demands, and increasing focus on sustainability. Below are the key market trends shaping the rubber spring industry in 2026:
-
Increased Demand from Automotive and Transportation Sectors
The automotive industry remains the largest consumer of rubber springs, particularly for suspension systems, engine mounts, and vibration isolation. By 2026, rising vehicle production—especially electric vehicles (EVs)—is expected to boost demand. EVs require high-performance rubber components to manage additional battery weight and reduce noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), making rubber springs a critical component. -
Growth in Industrial Machinery and Construction Equipment
Rubber springs are widely used in heavy machinery for shock absorption and vibration control. With ongoing infrastructure development in emerging economies and the modernization of industrial equipment, demand for durable and high-load rubber springs is projected to rise significantly by 2026. -
Innovation in Material Composition and Performance
Manufacturers are investing in advanced rubber compounds, including polyurethane blends and high-damping natural/synthetic rubber composites. These materials offer improved resistance to temperature extremes, UV exposure, and chemical degradation. Customization for specific load and deflection requirements is becoming more prevalent, catering to niche applications in aerospace, rail, and renewable energy. -
Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental regulations are pushing the rubber industry toward sustainable practices. By 2026, there is an increasing shift toward using recycled rubber and bio-based materials in spring production. Companies are also adopting eco-friendly manufacturing processes to reduce carbon footprints and comply with global standards such as REACH and RoHS. -
Regional Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, is expected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and rising investments in transportation infrastructure. Local production of rubber springs is expanding to meet domestic demand and reduce reliance on imports. -
Integration with Smart and Predictive Maintenance Systems
In advanced industrial applications, rubber springs are being integrated into systems that monitor performance in real time. By 2026, smart rubber components embedded with sensors could enable predictive maintenance, improving equipment uptime and reducing operational costs. -
Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The market is witnessing strategic mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships among key players to enhance R&D capabilities and expand global reach. Companies like ContiTech (Continental AG), Bridgestone, and Freudenberg are leading innovation, while regional manufacturers are focusing on cost-effective solutions for price-sensitive markets.
In summary, the rubber spring market in 2026 will be characterized by technological innovation, sustainability, and strong demand from automotive and industrial sectors. As industries prioritize efficiency and environmental performance, rubber spring manufacturers that adapt to these trends will gain a competitive edge in the evolving global landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Rubber Springs (Quality, IP)
Sourcing rubber springs involves navigating several critical challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to performance issues, supply chain disruptions, legal risks, and increased total cost of ownership.
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Formulation
One of the most frequent issues is receiving rubber springs made from substandard or inconsistent rubber compounds. Low-quality materials may degrade prematurely due to environmental exposure (UV, ozone, temperature extremes), leading to cracking, hardening, or loss of elasticity. Suppliers may cut costs by using excessive filler content or inferior-grade synthetic rubber, which compromises load-bearing capacity and damping performance. Without stringent quality control and material traceability, batches can vary significantly, affecting reliability in end applications.
Inadequate Physical and Performance Testing
Many suppliers—especially low-cost manufacturers—do not conduct comprehensive testing to validate performance claims. Rubber springs must be tested for compression set, load-deflection characteristics, durability under cyclic loading, and resistance to environmental factors. Lack of standardized testing (e.g., ASTM or ISO standards) means buyers may unknowingly receive components that fail prematurely in service. It is essential to verify that suppliers provide test reports and maintain consistent quality assurance protocols.
Misrepresentation of Rubber Type and Specifications
Suppliers may incorrectly label rubber materials—for example, claiming EPDM when using cheaper SBR rubber. Each elastomer has distinct properties: EPDM resists weather and heat, NBR handles oils, and natural rubber offers high resilience. Misidentification can result in incompatibility with operational conditions, leading to rapid deterioration. Buyers must require material certifications (e.g., Certificates of Conformance) and, where critical, conduct third-party material analysis.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection and Risk of Copying
Rubber spring designs—especially custom geometries or proprietary bonding techniques—can be subject to IP infringement. When sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement, there is a risk that design specifications provided to suppliers may be copied or sold to competitors. This is particularly concerning for OEMs relying on differentiated performance. Failure to secure non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), clearly define ownership of tooling and designs, or register patents and design rights can expose companies to significant competitive and legal risks.
Tooling Ownership and Supplier Lock-In
Custom rubber springs often require specific molds or tooling, which can be expensive. A common pitfall is not securing clear ownership of tooling or lacking documentation for replication elsewhere. Some suppliers retain tooling rights, making it difficult and costly to switch vendors or scale production. This creates dependency and reduces negotiating power. Always clarify tooling ownership in contracts and request CAD files and mold specifications.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
Variability in curing time, temperature, and molding pressure can significantly affect the final product’s consistency and lifespan. Poor process control leads to dimensional inaccuracies, voids, or weak metal-to-rubber bonds—especially in bonded rubber-metal springs. Without process audits or supplier certification (e.g., ISO 9001), buyers risk receiving non-conforming parts that compromise assembly integrity.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Lack of traceability—batch numbers, material lot tracking, and production dates—hinders root cause analysis during field failures. In regulated industries (automotive, rail, medical), this can result in non-compliance. Reliable suppliers should provide full documentation to support quality audits and warranty claims.
Overlooking Long-Term Aging and Environmental Compatibility
Rubber properties change over time. Buyers often focus on initial performance but neglect long-term aging characteristics. Without accelerated life testing or compatibility assessments (e.g., exposure to chemicals, vibration profiles), rubber springs may fail unexpectedly in the field. Ensure specifications include expected service life and environmental resistance requirements.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through supplier vetting, clear specifications, contractual protections, and verification testing—companies can secure reliable, high-quality rubber springs while safeguarding their intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rubber Springs
Product Overview
Rubber springs are elastomeric components used in various industries—including automotive, rail, construction, and industrial machinery—for vibration isolation, shock absorption, and load support. They are typically composed of natural or synthetic rubber bonded to metal components. Understanding their specific logistics and compliance requirements ensures efficient transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence.
Classification & HS Code
Rubber springs are generally classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 8431.39.00 (Parts suitable for use with conveyors or lifting/folding machinery) or 4016.93.00 (Other articles of vulcanized rubber, with hard rubber). The exact code may vary by country and specific product design (e.g., with or without metal inserts). Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance, duty calculation, and trade compliance.
Packaging Requirements
- Protection from Contamination: Rubber springs must be packaged in moisture-resistant materials (e.g., polyethylene bags) to prevent exposure to dust, oils, and ozone.
- Cushioning and Support: Use corrugated cardboard dividers or molded trays to prevent contact between parts and reduce abrasion.
- Labeling: Each package must include product identification (part number, quantity), batch/lot number, manufacturing date, and handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Sunlight”).
- Export Packaging: For international shipping, use wooden or plastic pallets secured with strapping. Ensure compliance with ISPM 15 for wooden packaging materials.
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store between 5°C and 35°C (41°F to 95°F). Avoid extreme heat or cold to prevent hardening or softening of rubber.
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 65% to prevent mold growth and metal corrosion (if metal parts are present).
- Light Exposure: Shield from direct sunlight and UV radiation to prevent degradation and cracking.
- Ozone Protection: Keep away from electrical equipment and motors that generate ozone.
- Shelf Life: Most rubber springs have a recommended shelf life of 5–10 years; monitor expiry dates and apply FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, sea, and air freight. For air transport, ensure compliance with IATA regulations if shipping hazardous materials (e.g., certain rubber compounds).
- Loading/Unloading: Handle with care using forklifts or pallet jacks. Avoid dropping or dragging packages.
- Stacking Limit: Observe stacking limits to prevent deformation. Use tier sheets between layers when stacking on pallets.
- Container Conditions: For sea freight, ensure containers are dry and ventilated. Use desiccants if necessary to control moisture.
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Comply with Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Ensure rubber compounds do not contain SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) above threshold levels.
- RoHS (EU): Applicable if rubber springs contain electrical or electronic components; otherwise, generally not applicable.
- REPAIR (China): Confirm compliance with China’s RoHS-like regulation if exporting to China.
- TSCA (USA): Confirm that rubber materials comply with the Toxic Substances Control Act, especially regarding chemical reporting.
- Prop 65 (California): Ensure labeling if products contain chemicals listed under California Proposition 65 (e.g., certain phthalates or carbon black).
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Waste Disposal: Follow local regulations for disposal of rubber waste. Incineration should comply with emissions standards.
- Recycling: Promote recycling programs where available; rubber springs may be recyclable depending on composition.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Provide SDS for rubber compounds upon request, detailing health, safety, and environmental information.
Import/Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Material Compliance Certificates (e.g., REACH, RoHS)
- Test Reports (e.g., hardness, durability, bonding strength)
Quality Assurance & Traceability
- Maintain batch traceability from raw material to finished product.
- Conduct regular quality inspections for dimensional accuracy, bonding integrity, and visual defects.
- Keep records of compliance testing and certifications for audit readiness.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for rubber springs ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. By following this guide, manufacturers, distributors, and logistics providers can mitigate risks related to transport, storage, and international trade. Always verify country-specific regulations and update procedures as standards evolve.
Conclusion for Sourcing Rubber Springs:
In conclusion, sourcing rubber springs requires a comprehensive evaluation of material quality, manufacturing standards, application requirements, and supplier reliability. Selecting the right rubber compound—such as natural rubber, neoprene, or EPDM—is critical to ensuring performance, durability, and resistance to environmental factors like temperature, moisture, and chemicals. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards, offer consistent quality control, and can provide technical support and customization when needed.
Additionally, factors such as cost-efficiency, minimum order quantities, lead times, and long-term supply chain sustainability should be considered to ensure uninterrupted production and optimal value. By conducting thorough supplier assessments and prioritizing quality and compatibility with specific applications, organizations can secure reliable rubber spring sources that enhance product performance and reduce maintenance costs over time. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach ensures the integration of high-performing rubber springs into mechanical systems, contributing to improved vibration isolation, noise reduction, and operational efficiency.