The global market for Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) thermal sensors is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision temperature measurement across industrial automation, HVAC, oil & gas, and pharmaceutical sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the RTD market was valued at USD 850 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5.2% through 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing industrial digitization, stricter regulatory requirements for process accuracy, and the widespread adoption of smart manufacturing technologies. With North America and Asia-Pacific leading in adoption—due to advanced industrial infrastructure and growing investments in process optimization—the competitive landscape is dominated by established players focusing on sensor accuracy, durability, and integration capabilities. As demand for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance surges, the following list highlights the top 10 RTD thermal sensor manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, global reach, and technical excellence.
Top 10 Rtd Thermal Sensor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
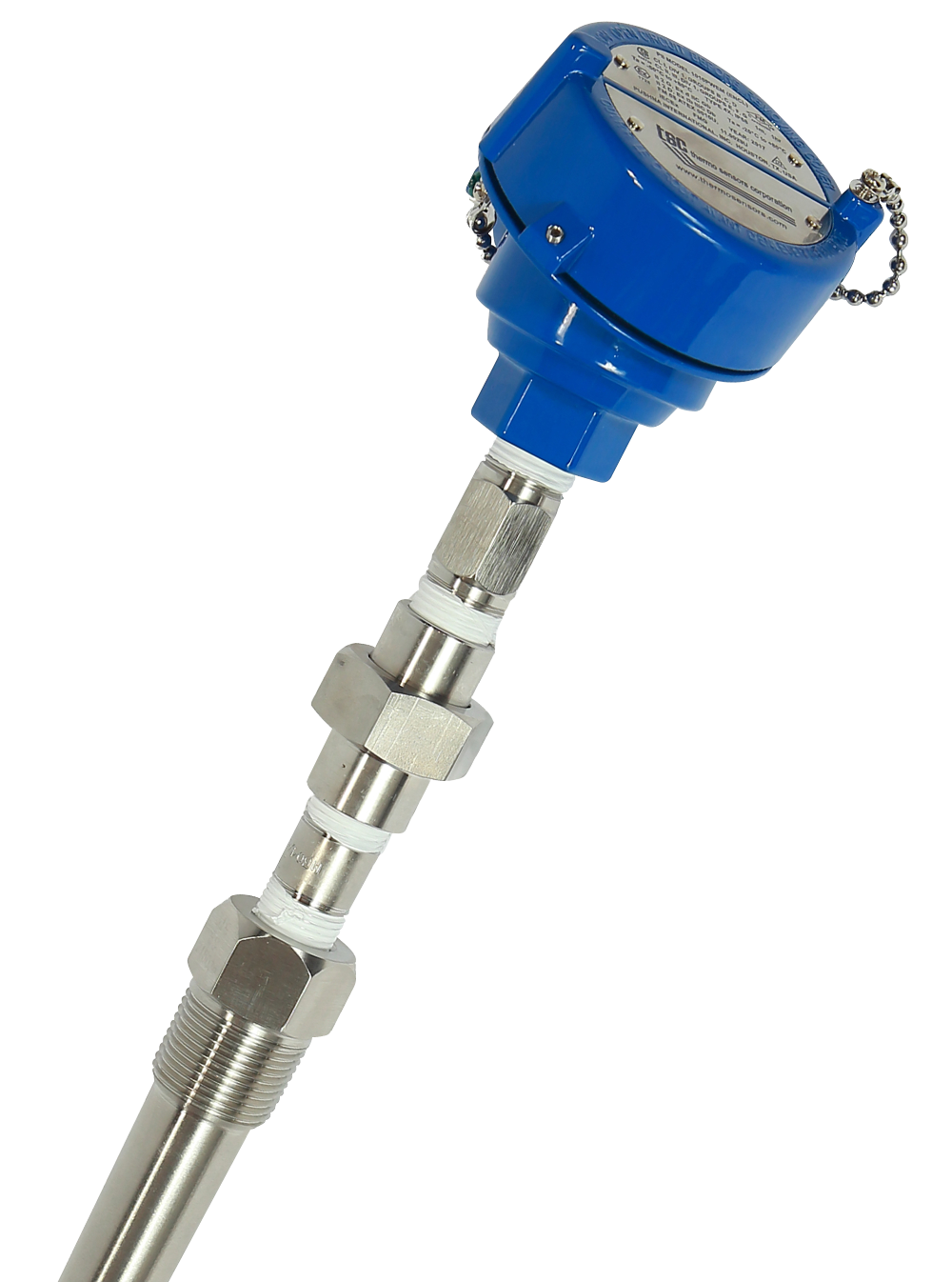
#1 MGO and Industrial Thermocouple Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1972
Website: thermosensors.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of Thermocouples and RTDs Since 1972, Thermo Sensors Corporation has been providing thermocouples, Thermowells, RTDs, Wire and Accessories….
#2 RTD Temperature Sensor Probes & Elements
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: TE offers RTD Sensors to accurately measure temperature by changing resistance. Our RTD temperature sensors are suited for OEM applications like medical and ……
#3 Pyromation
Domain Est. 1995
Website: pyromation.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Pyromation, a premier manufacturer & supplier of thermocouples, RTDs, thermowells and other temperature sensors….
#4 Resistance Temperature Detectors
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ashcroft.com
Key Highlights: Ashcroft RTD sensor assemblies monitor temperature in industrial, process and hazardous installations. Available with Pt 100 and Pt 1000 RTDs….
#5 Temperature sensors
Domain Est. 1986
Website: ti.com
Key Highlights: Our temperature sensors allow you to overcome common design challenges and continue innovating with high-accuracy, low-power consumption, and small, flexible ……
#6 Minco RTD SENSORS
Domain Est. 1994
Website: minco.com
Key Highlights: Minco supplies temperature sensors using the four main sensing element technologies: RTDs, Thermocouples, Thermistors, and Integrated Circuits….
#7 RTD elements and sensors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: omega.co.uk
Key Highlights: RTD elements come in many types conforming to different standards, capable of different temperature ranges, with various sizes and accuracies available….
#8 RTDs
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sorinc.com
Key Highlights: A resistance temperature detector (RTD) operates on the principle that a change in the temperature of a metal causes a corresponding change in that metal’s ……
#9 RTD Sensors
Domain Est. 1997
#10 RTD Sensors
Domain Est. 2018
Website: ei-sensor.com
Key Highlights: EI Sensor offers a full line of temperature sensors including thermistors, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermistor probe assemblies and RTD probe ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rtd Thermal Sensor

H2: Market Trends for RTD Thermal Sensors in 2026
As the global industrial and technological landscape evolves, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) remain a cornerstone in precision temperature measurement across various sectors. By 2026, the market for RTD thermal sensors is expected to experience steady growth driven by increasing demand for accuracy, automation, and energy efficiency. Below are the key market trends shaping the RTD thermal sensor industry in 2026:
-
Expansion in Industrial Automation and Industry 4.0
The continued adoption of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies is accelerating demand for highly reliable and precise temperature sensors. RTDs, known for their stability and repeatability, are being integrated into smart factory systems, process control loops, and predictive maintenance platforms. By 2026, the integration of RTDs with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms enables real-time monitoring and remote diagnostics, enhancing operational efficiency. -
Growth in Energy and Renewable Sectors
The global push toward clean energy is boosting RTD deployment in wind turbines, solar thermal systems, and nuclear power plants. In these applications, RTDs are critical for monitoring component temperatures to ensure safety and efficiency. The increasing investment in energy infrastructure, particularly in emerging economies, is expected to drive market growth through 2026. -
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Quality Requirements
Regulatory bodies across industries—such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and aerospace—are enforcing stricter temperature monitoring protocols. RTDs, with their high accuracy and compliance with standards like IEC 60751, are becoming the preferred choice for applications requiring traceable and calibrated temperature measurements. This regulatory push is fueling demand in highly regulated markets. -
Technological Advancements and Miniaturization
Innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques are leading to smaller, more durable RTD sensors with faster response times and improved resistance to harsh environments. Thin-film and wire-wound RTD designs are being optimized for compact applications in medical devices and electric vehicles. By 2026, enhanced signal conditioning and digital output integration (e.g., IO-Link compatibility) will further broaden RTD applicability. -
Rising Adoption in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Battery Management Systems (BMS)
RTDs are increasingly used in EV battery packs and power electronics due to their precision in monitoring thermal performance. As the EV market expands globally, demand for reliable thermal sensors to prevent overheating and ensure battery longevity is rising. RTDs offer a competitive edge over thermistors and thermocouples in high-accuracy BMS applications. -
Asia-Pacific as a Key Growth Region
Countries like China, India, and South Korea are expected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and government support for smart manufacturing and clean energy. Local production of RTDs is also increasing, reducing costs and improving supply chain resilience. -
Sustainability and Long-Term Cost Efficiency
End-users are prioritizing sensors with long service life and low maintenance. RTDs, with their durability and stable performance over time, align with sustainability goals and reduce total cost of ownership. This value proposition is influencing purchasing decisions in sectors like oil & gas and chemical processing.
In conclusion, the RTD thermal sensor market in 2026 is characterized by technological integration, regulatory compliance, and expanding applications across high-growth industries. With ongoing advancements and increased industrial digitization, RTDs are poised to maintain a strong position in the temperature sensing market, offering unmatched precision and reliability.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing RTD Thermal Sensors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) involves more than just matching specifications on paper. Overlooking key quality and IP (Intellectual Property) aspects can lead to performance issues, safety risks, and long-term liabilities. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Sensor Accuracy and Stability
One of the most frequent quality pitfalls is selecting RTDs with inadequate accuracy or long-term drift. Low-cost sensors may use impure platinum elements or lack proper annealing, leading to calibration shifts over time. Always verify that the RTD meets relevant accuracy classes (e.g., IEC 60751: Class A, B, or 1/3 DIN) and request calibration certificates. Avoid suppliers who cannot provide traceable documentation or long-term stability data.
Substandard Materials and Construction
Inferior materials—such as low-grade stainless steel sheaths, improper insulation (e.g., non-magnesium oxide fill in mineral-insulated types), or poor weld integrity—compromise sensor durability, especially in harsh environments. This can result in moisture ingress, mechanical failure, or shortened lifespan. Ensure the supplier uses appropriate materials for the intended application (e.g., 316L SS for corrosive environments) and adheres to recognized manufacturing standards.
Inadequate IP (Ingress Protection) Rating
Assuming an RTD is suitable for wet or dusty environments without verifying its actual IP rating is a critical oversight. Many low-cost sensors claim “industrial use” but lack proper sealing, leading to moisture or dust ingress, which affects accuracy and can cause short circuits. Always confirm the IP rating (e.g., IP65, IP67, IP68) matches the environmental conditions—especially for outdoor, washdown, or high-humidity applications.
Misrepresentation of Sensor Tolerance and Repeatability
Some suppliers may exaggerate performance specs or provide inconsistent tolerances across batches. Without independent testing or batch traceability, users risk receiving sensors that do not perform uniformly. Demand test reports per batch and verify that the supplier maintains strict quality control processes (e.g., ISO 9001 certification).
Lack of IP Protection and Counterfeit Risk
Purchasing from unauthorized or offshore suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or reverse-engineered RTDs that mimic well-known brands but lack performance validation. These may infringe on intellectual property and pose safety or compliance issues. Always source from authorized distributors or reputable manufacturers with verifiable designs and certifications. Beware of unusually low prices, which may indicate IP violations or substandard production.
Incomplete or Missing Documentation
Poor documentation—missing datasheets, calibration certificates, material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH), or compliance statements—hinders traceability and regulatory compliance. This is especially critical in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing. Ensure all necessary documentation is provided and conforms to industry standards.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers thoroughly, request samples for testing, and prioritize quality and compliance over upfront cost savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for RTD Thermal Sensors
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant shipment, handling, storage, and use of Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) thermal sensors. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational safety.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
RTD thermal sensors must be packaged to prevent physical damage, contamination, and environmental exposure during transit. Use anti-static materials where applicable, especially for sensors with electronic components or interfaces. Sensors should be securely immobilized within the packaging using foam inserts, bubble wrap, or molded trays to prevent movement. Outer packaging must be durable, moisture-resistant, and clearly labeled with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” and “Protect from Moisture.” Include desiccants if shipping to high-humidity environments or for extended durations. Ensure all packages meet carrier-specific requirements for dimensions, weight, and labeling.
Storage Conditions
Store RTD sensors in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment. Recommended storage temperature ranges are typically between -20°C to +70°C, unless specified otherwise by the manufacturer. Relative humidity should not exceed 80% to prevent condensation and corrosion. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, corrosive gases (e.g., H2S, SO2), and strong electromagnetic fields. Keep sensors in their original packaging until ready for use to protect from dust and mechanical stress. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize aging effects, especially on cable insulation and connection points.
Import/Export Compliance
RTD thermal sensors may be subject to international trade regulations depending on destination, technology specifications, and materials used. Verify if the product falls under export control classifications such as EAR99 under the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or similar frameworks (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation). Sensors containing certain materials or designed for high-precision industrial applications may require export licenses. Ensure Harmonized System (HS) codes are correctly classified to determine tariffs and duties. Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. For shipments to restricted regions, conduct sanctions screening and comply with OFAC (U.S.) or equivalent national regulations.
Regulatory & Safety Standards
RTD sensors must comply with relevant industry and safety standards based on application and region. Key standards include:
– IEC 60751: International standard for industrial platinum resistance thermometers.
– ASTM E1137: Standard specification for industrial platinum resistance thermometers.
– ATEX/IECEx: Required for sensors used in explosive atmospheres (hazardous locations).
– UL/CSA: For sensors used in North American markets, especially in industrial control systems.
– RoHS & REACH: Ensure compliance with restrictions on hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) and chemical registration in the EU.
Maintain documentation such as Declarations of Conformity (DoC), test reports, and material declarations to demonstrate compliance during audits or inspections.
Handling & Installation Guidelines
Handle RTD sensors with clean, dry hands or use gloves to avoid contamination of sensing elements. Avoid bending lead wires sharply or applying tension to the sensor tip. During installation, follow manufacturer torque specifications for threaded sensors and ensure proper sealing to prevent moisture ingress. Use appropriate conduit and cable glands for environmental protection. Verify electrical compatibility with measuring instruments (e.g., 2-wire, 3-wire, or 4-wire configurations). Perform calibration checks before and after installation if required by quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain complete documentation for each RTD sensor, including:
– Serial number and model information
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
– Calibration certificate (if applicable)
– Material declarations (RoHS, REACH)
– Manufacturing date and lot number
Ensure traceability throughout the supply chain by recording shipment details, storage conditions, and end-user delivery. Digital tracking systems (e.g., ERP or asset management software) are recommended for high-volume or regulated applications.
Disposal & Environmental Responsibility
Dispose of defective or end-of-life RTD sensors in accordance with local environmental regulations. While most RTDs contain inert materials like platinum and stainless steel, some may include electronic components or lead-containing solder. Recycle through certified e-waste handlers where possible. Do not incinerate or dispose of in regular landfill if hazardous materials are present. Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions.
Conclusion for Sourcing RTD Thermal Sensors
After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost implications, and long-term performance requirements, sourcing RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) thermal sensors presents a viable and advantageous solution for accurate and stable temperature measurement across industrial, commercial, and laboratory applications.
RTD sensors offer superior accuracy, excellent long-term stability, and a wide operating temperature range compared to alternative temperature sensing technologies such as thermocouples or thermistors. Their near-linear resistance-temperature relationship ensures reliable signal interpretation and minimizes calibration needs, contributing to reduced maintenance and operational costs over time.
When sourcing RTDs, key considerations such as sensor element type (commonly Pt100 or Pt1000), tolerance class (e.g., Class A or B per IEC 60751), sheath material, probe construction, and environmental protection (e.g., IP rating) must align with the specific application demands. Additionally, selecting reputable suppliers with certifications, consistent quality control, and technical support ensures product reliability and compliance with industry standards.
In conclusion, sourcing high-quality RTD thermal sensors from qualified manufacturers not only enhances measurement precision and system safety but also supports operational efficiency and longevity of temperature monitoring systems. A strategic sourcing approach, balancing performance, cost, and supplier credibility, is essential to achieving optimal outcomes in any temperature sensing application.