The global RP-SMA antenna market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for reliable wireless connectivity across industries such as telecommunications, industrial IoT, healthcare, and consumer electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global antenna market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, with compact and high-performance RF antennas like RP-SMA gaining traction due to their widespread use in Wi-Fi routers, cellular base stations, and private LTE networks. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the rising adoption of 5G infrastructure and the expansion of IoT ecosystems are key factors accelerating demand for precision antennas, particularly those offering reverse polarity to minimize interference and ensure regulatory compliance. In this expanding landscape, selecting a reliable RP-SMA antenna manufacturer has become critical for OEMs and network integrators aiming to maintain signal integrity and meet evolving technical standards. Below are the top six RP-SMA antenna manufacturers recognized for innovation, quality, and market presence.
Top 6 Rp-Sma Antenna Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 RP
Domain Est. 2020
Website: ctrfantennasinc.com
Key Highlights: C&T RF Antennas Inc is the RP-SMA Wifi Antenna 2.4 GHz rubber duck antenna Manufacturer, we provide the 2.4GHz antenna with many types….
#2 RP
Domain Est. 2002
#3 Low Loss RP
Domain Est. 2003
#4 RP
Domain Est. 2004
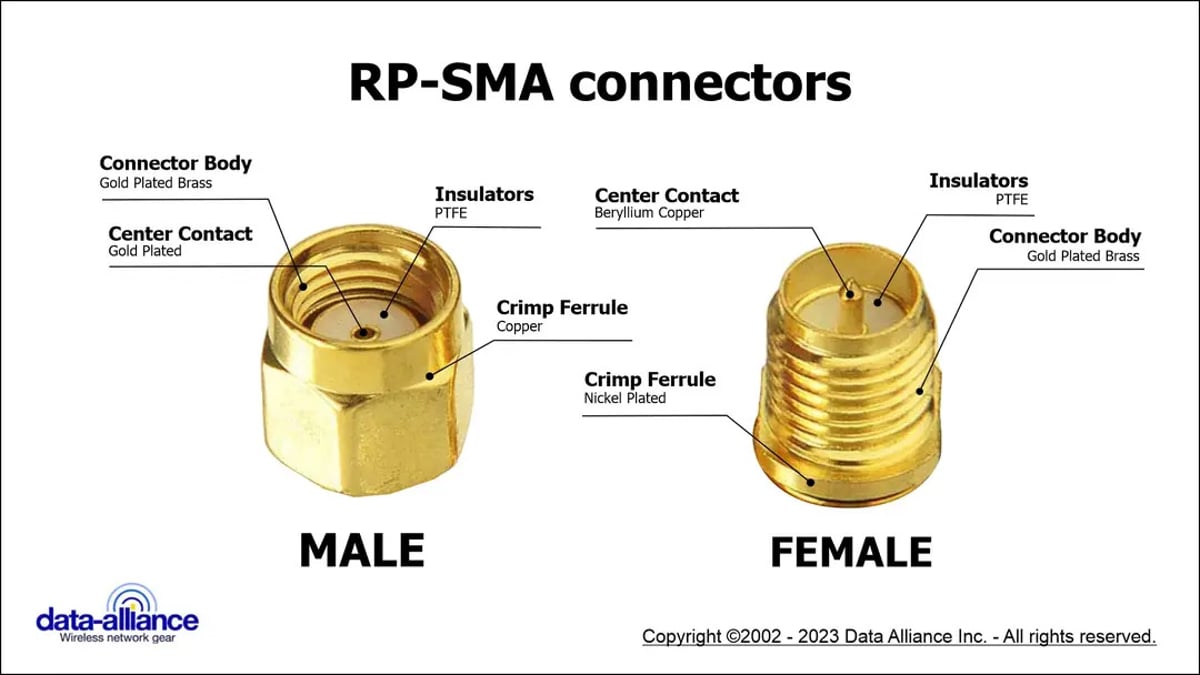
Website: data-alliance.net
Key Highlights: An RP-SMA male antenna can be attached directly to the wireless device, or extended via a coax RP-SMA cable. The connection is rated for up to 500 uses….
#5 RP
Domain Est. 2005
Website: air802.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 20-day returnsAIR802 manufactures a variety of high quality rp-sma connectors both male and female to fit a variety of cable sizes….
#6 SMA / RP
Domain Est. 2013
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rp-Sma Antenna

H2 2026 Market Trends for RP-SMA Antennas
The RP-SMA (Reverse Polarity SubMiniature version A) antenna connector, a ubiquitous component in wireless communication devices, will continue to play a critical role in H2 2026, albeit within a landscape shaped by evolving technologies, shifting demand patterns, and ongoing standardization. Here’s an analysis of key market trends expected in the second half of 2026:
1. Sustained Demand in Core Markets, Driven by IoT and WiFi 6E/7
- IoT Proliferation: The massive expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) across smart homes, industrial automation (Industry 4.0), logistics, and agriculture will remain a primary driver. Billions of new sensors, trackers, and connected devices requiring robust, cost-effective wireless connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRaWAN, cellular IoT) will utilize RP-SMA antennas, especially for external or high-gain applications.
- WiFi 6E & WiFi 7 Rollout Acceleration: H2 2026 will see significant mainstream adoption of WiFi 7 (802.11be) in consumer electronics (routers, laptops, smartphones, AR/VR headsets) and enterprise access points. While internal antennas dominate, RP-SMA remains essential for:
- High-Performance Routers & Gateways: Enthusiast and enterprise-grade equipment requiring maximum range and throughput will increasingly feature detachable RP-SMA antennas (often 2×2 or 4×4 MIMO configurations) for optimal signal placement and potential upgrades.
- External Antenna Kits: Demand will grow for aftermarket high-gain or directional RP-SMA antennas to extend WiFi 7 coverage in challenging environments (large homes, offices, industrial sites).
- Testing & Development: RP-SMA is standard in RF test equipment and development kits for WiFi 6E/7 chipsets, ensuring steady demand from the R&D sector.
2. Competition from Integrated Antennas & New Form Factors
- Internal Antenna Dominance: The trend towards sleeker, more integrated devices (thin laptops, compact IoT modules, smartphones) will continue, favoring embedded antennas (PIFA, IFA, FPC) over external RP-SMA connectors. This puts pressure on RP-SMA market share in high-volume consumer segments.
- Miniaturization Pressure: While RP-SMA is relatively small, demand for even smaller connectors (like U.FL/IPEX) in space-constrained IoT modules will persist. RP-SMA’s advantage lies in its superior RF performance and durability for external use, but miniaturization remains a competitive challenge.
3. 5G and Private Networks: A Mixed Impact
- Limited Direct Role in Consumer 5G: Consumer 5G devices (phones, hotspots) overwhelmingly use internal antennas. RP-SMA is rarely used here.
- Growth in Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) & CPE: A significant growth area. Outdoor 5G FWA Customer Premises Equipment (CPEs) and routers often feature external RP-SMA antenna ports. This allows users to connect high-gain directional antennas for improved signal reception in areas with marginal coverage, driving demand for RP-SMA connectors and compatible antennas in the fixed broadband market.
- Private 5G Networks: Industrial and enterprise private 5G networks (using CBRS in the US, similar bands elsewhere) will increasingly deploy outdoor small cells and user equipment. RP-SMA connectors are likely to be used on many of these devices for external antenna connections, representing a niche but growing application.
4. Material and Performance Optimization
- Focus on Efficiency and Reliability: Manufacturers will continue optimizing RP-SMA connector designs for lower insertion loss, higher power handling (relevant for higher WiFi 7 EIRP), and better resistance to environmental factors (moisture, UV, corrosion) – crucial for outdoor IoT and FWA applications.
- Material Choices: Stainless steel and high-grade brass with durable plating (gold, nickel) will be standard for quality connectors. Cost-effective alternatives using zinc alloy will persist in lower-tier consumer products.
5. Supply Chain Stability and Cost Pressures
- Stabilization: By H2 2026, global semiconductor and component supply chains are expected to be significantly more stable than in previous years, reducing major shortages. However, regional disruptions and geopolitical factors could still cause localized fluctuations.
- Cost Sensitivity: Intense competition, especially in the consumer WiFi and IoT markets, will maintain pressure on component costs. This favors established, high-volume RP-SMA manufacturers but challenges smaller players. Automation in manufacturing will be key to maintaining margins.
6. Standardization and Compatibility
- Universal Acceptance: RP-SMA’s status as the de facto standard for detachable Wi-Fi antennas on routers, APs, and many industrial devices is well-entrenched. This standardization reduces design friction and ensures a vast ecosystem of compatible antennas and cables.
- “Reverse Polarity” Confusion Persists: The potential for accidental mating with standard SMA connectors (which can damage equipment) remains a minor market friction point, requiring clear labeling and user education.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The RP-SMA antenna market in H2 2026 will be characterized by resilience and adaptation. While facing pressure from integrated solutions in ultra-compact devices, its core strengths – reliability, excellent RF performance, ease of replacement/upgrading, and universal standardization – ensure strong demand. Key growth drivers will be the explosion of IoT (needing robust external connectivity), the mainstream adoption of high-performance WiFi 7 in routers and CPEs, and the expansion of Fixed Wireless Access using 5G. The market will remain competitive, focusing on performance optimization, cost efficiency, and meeting the demands of outdoor and industrial applications. RP-SMA will remain a critical, albeit sometimes hidden, enabler of the expanding wireless world.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing RP-SMA Antennas (Quality and IP)
Sourcing RP-SMA antennas—especially for wireless communication devices—can be deceptively complex. While they appear simple, overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to performance issues, compliance failures, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor RF Performance Due to Substandard Components
Many low-cost RP-SMA antennas use inferior materials and manufacturing processes, resulting in poor impedance matching, reduced gain, and inconsistent radiation patterns. This can degrade signal strength, reduce range, and increase bit error rates. Always request and verify test reports for VSWR, return loss, and radiation efficiency across the intended frequency bands.
Inconsistent Connector Quality and Durability
The RP-SMA connector itself is often a weak point. Poor plating (e.g., inadequate nickel or gold layers), misaligned threads, or weak dielectric supports increase the risk of signal loss, intermittent connections, and physical damage during mating cycles. Look for connectors that meet IEC 60169-15 standards and ensure durability ratings (e.g., 500+ mating cycles) are specified.
Mislabeling or Counterfeit Antennas
Counterfeit or mislabeled antennas are common in unverified supply chains. An antenna advertised as “5dBi” may perform significantly below spec, or a connector labeled “RP-SMA” may actually be standard SMA, leading to irreversible damage when mated incorrectly. Source from reputable distributors and verify with physical inspection or third-party testing.
Lack of IP Compliance and Risk of Infringement
Using antenna designs that incorporate patented technologies (e.g., specific radiating elements, impedance matching networks, or mounting methods) without authorization can expose your product to IP litigation. Even if the antenna is purchased from a third party, OEM liability may still apply. Always confirm that the supplier holds valid rights to the design or provides indemnification.
Inadequate Environmental and Regulatory Certification
Many generic antennas lack proper certification for environmental durability (e.g., UV resistance, temperature range) or regulatory compliance (FCC, CE, RoHS). This can lead to field failures or market access denial. Ensure antennas come with full compliance documentation and are rated for the intended operating environment.
Insufficient Design Documentation and Support
Poorly documented antennas—missing radiation patterns, impedance curves, or PCB layout guidelines—hinder integration and optimization. Without proper support, system performance may suffer due to incorrect placement or grounding. Choose suppliers that provide comprehensive datasheets and engineering assistance.
Overlooking Mechanical Fit and Integration Challenges
Even with the correct electrical specs, physical dimensions, cable length, and connector orientation may not suit your enclosure or assembly process. Verify mechanical drawings and, if possible, obtain samples before full-scale procurement to avoid costly redesigns.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls early, you can ensure reliable wireless performance and mitigate legal and operational risks in your product deployment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for RP-SMA Antenna
Overview
This guide provides essential logistics and compliance information for the handling, shipping, import, and use of RP-SMA (Reverse Polarity SMA) antennas. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, product safety, and efficient supply chain operations.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC and Radio Frequency Regulations (USA)
RP-SMA antennas must comply with Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulations when used with wireless devices in the United States. Ensure that:
– The antenna is paired only with FCC-certified transmitters.
– Modifications to authorized equipment (e.g., increasing antenna gain beyond approved limits) do not void the certification.
– Devices using the antenna comply with Part 15 or Part 90 of the FCC rules, depending on application.
CE Marking and EU Compliance (Europe)
For distribution within the European Union:
– The antenna must comply with the Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU.
– Ensure integration with CE-marked radio equipment to maintain compliance.
– Documentation must include Declaration of Conformity and technical construction files.
RoHS and REACH Compliance
The RP-SMA antenna must meet:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Limits on lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials.
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals): Disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
Verify material declarations from suppliers and maintain compliance records.
Export Controls and ITAR/EAR
EAR Compliance (Export Administration Regulations)
Most RP-SMA antennas fall under the Commerce Control List (CCL) with an ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) of 5A991 (telecommunications equipment not otherwise specified).
– No license required for most destinations (NLR), but verify destination country regulations.
– Maintain export records for at least five years.
ITAR Exemption
RP-SMA antennas are generally not subject to ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) unless specifically designed for military applications. Confirm design intent and end use.
Packaging and Shipping
Packaging Standards
- Use anti-static packaging for bulk or sensitive electronic components.
- Secure antennas in rigid inner packaging to prevent damage during transit.
- Label packages with: product name, part number, quantity, and handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”).
Shipping Documentation
Include with every shipment:
– Commercial invoice (with HTS code: 8529.10 or 8517.70, depending on use)
– Packing list
– Certificate of Compliance (RoHS, REACH, FCC/CE if applicable)
– Export declaration (for international shipments)
Hazardous Materials Classification
RP-SMA antennas are typically non-hazardous. Confirm absence of batteries or restricted substances before air freight. No IATA restrictions apply under normal conditions.
Import Considerations
Customs Classification (HTS Codes)
- USA: 8529.10.00 (Parts suitable for use with radio-broadcast receivers) or 8517.70.00 (Antennas for communication equipment)
- EU: 8529.10.10 or 8517.70.00
Verify classification with local customs authority to ensure correct duty rates.
Duty and Tax Implications
- Duty rates vary by country; typical range: 0–5% for antennas.
- VAT or GST may apply upon import. Provide accurate valuation on invoices.
Handling and Storage
Environmental Conditions
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (5°C to 35°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, dust, and corrosive atmospheres.
- Keep original packaging until point of use.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Precautions
- Handle in ESD-protected areas when integrating with sensitive RF modules.
- Use grounded wrist straps and anti-static mats during assembly.
End-of-Life and Recycling
WEEE Compliance (EU)
- RP-SMA antennas are part of WEEE Category 4 (consumer equipment).
- Ensure proper take-back and recycling options are available.
- Label products with the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol if sold in the EU.
Recycling Guidelines
- Separate metal (brass, stainless steel) and plastic (housing) components.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers for environmentally responsible disposal.
Summary and Best Practices
- Always verify compliance with local regulations before shipping.
- Maintain up-to-date technical and certification documentation.
- Train logistics and procurement staff on export/import requirements.
- Audit supply chain partners for compliance with environmental and safety standards.
By following this guide, you ensure that RP-SMA antennas are handled, shipped, and used in full compliance with global regulatory and logistical standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing RP-SMA Antennas:
Sourcing RP-SMA antennas requires careful consideration of application requirements, quality standards, and supplier reliability. These antennas are commonly used in Wi-Fi devices, routers, and wireless communication systems where a secure, reverse-polarity connection helps prevent incorrect installations and ensures compatibility with specific hardware. When sourcing, it is essential to verify connector types (RP-SMA male vs. female), frequency range, gain, impedance (typically 50 ohms), and environmental durability to ensure optimal performance.
Purchasing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers with strong quality control helps avoid counterfeit or substandard products, which can degrade signal performance and system reliability. Additionally, evaluating cost versus performance, minimum order quantities, and customization options can further enhance value, especially for large-scale deployments. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that balances technical specifications, supplier credibility, and cost-efficiency will ensure reliable and effective integration of RP-SMA antennas into wireless systems.