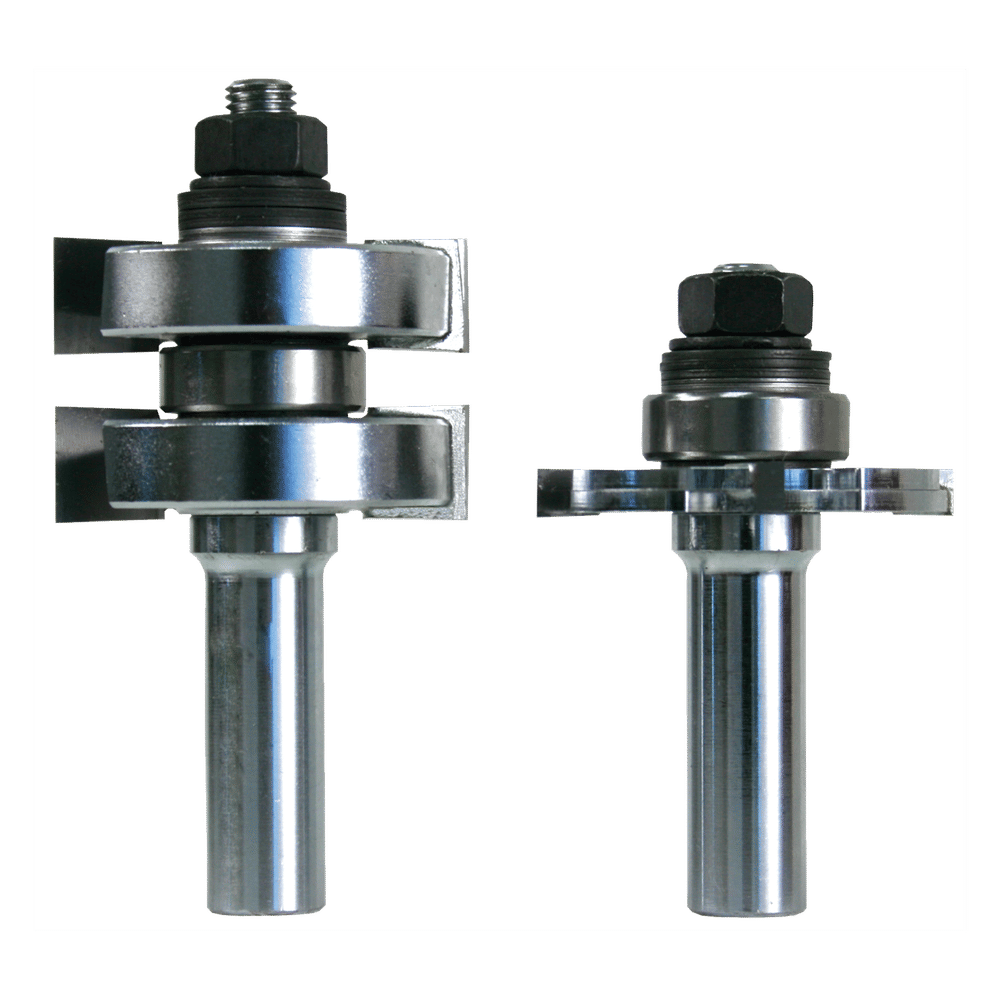
The global power tools market, driven by rising demand in construction, manufacturing, and DIY applications, is projected to expand at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. With routers ranking among the most essential drill-compatible tools, manufacturers are increasingly investing in precision, ergonomics, and smart technology integration. This growth is further amplified by advancements in cordless systems and brushless motors, boosting efficiency and user adoption across professional and home workshops. As competition intensifies, nine key manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and market share—setting the benchmark for performance in router design for drill-based applications.
Top 9 Router For Drill Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LMT Onsrud LP
Domain Est. 1996
Website: onsrud.com
Key Highlights: LMT Onsrud is a leading manufacturer of production cutting tools for the wood industry. We continue to lead the way for natural and composite wood materials….
#2 Vortex Tool, Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: vortextool.com
Key Highlights: $16.75 delivery 90-day returnsVortex Tool manufactures cutting tools for woodworking, plastics, and non-ferrous industries. We specialize in solid carbide spiral router bits and ot…
#3 Midwest Circuit Technology
Domain Est. 2004
Website: mctinfo.net
Key Highlights: Midwest proudly offers an extensive line of top quality diamond files, carbide drill bits, carbide end mills, router bits, and other cutting and etching tools….
#4 Router Bits, Saw Blades, Carbide, Drill Bits
Domain Est. 1996
Website: carbideprocessors.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 · 90-day returnsSupplier of woodworking tools including; router bits, saw blades, drill bits, Woodpecker tools, hand tools and more….
#5 Routers & Router Tables
Domain Est. 1996
Website: boschtools.com
Key Highlights: Enhance accuracy with Bosch Router Tables. Built for smooth shaping and clean cuts, with smart features like dust ports, storage, and broad compatibility….
#6 Wood Working Tools
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jessem.com
Key Highlights: JessEm Tool Company ; Router Table Packages. Full table setups for all motor types and sizes! ; Table Saw Accessories. For precision, safety and efficiency!…
#7 Whiteside Machine Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: whitesiderouterbits.com
Key Highlights: Made from high quality steel and tipped with micro-grain carbide, our years of experience provides you a full line of router bits your workshop will cherish….
#8 Freud Tools
Domain Est. 1999
Website: freudtools.com
Key Highlights: Official Website of Freud Tools. Learn about Freud’s line up of best in the world Saw Blades, Router Bits, Drilling & Boring, Cutterheads, Knives & Inserts, ……
#9 Router Bits
Domain Est. 2004
Website: diablotools.com
Key Highlights: Diablo’s complete line of routers helps woodworkers achieve the perfect finish on projects with precise cuts, excellent shaping, and unmatched durability….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Router For Drill

2026 Market Trends for Router For Drill
Rising Demand for Multi-Functional Power Tools
The global market for router for drill attachments is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing consumer preference for versatile, cost-effective power tools. As DIY (do-it-yourself) culture expands, particularly in North America and Europe, more users are seeking adaptable tools that convert existing cordless drills into routing devices. This trend reduces the need to purchase standalone routers, appealing to hobbyists and small contractors aiming to minimize tool investment.
Advancements in Ergonomic and Modular Design
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to focus heavily on ergonomic improvements and modular compatibility. Router for drill systems are being redesigned with enhanced grip stability, adjustable depth controls, and quick-connect mechanisms compatible with multiple drill brands. These design innovations aim to improve precision and user safety, making the tools more attractive to both amateur and professional users.
Growth in E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Sales
The distribution landscape is shifting, with a significant portion of router for drill sales moving to online platforms such as Amazon, Home Depot, and specialized tool retailers. Brands are leveraging social media, video tutorials, and influencer endorsements to demonstrate product utility, accelerating adoption. This digital-first approach is expected to dominate market outreach strategies by 2026.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are showing increased interest in affordable woodworking solutions. As urbanization and home improvement activities rise, demand for low-cost routing alternatives like drill-powered routers is growing. Local manufacturing partnerships and simplified product variants are likely to emerge to cater to price-sensitive consumers in these regions.
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental concerns are influencing product development. By 2026, leading manufacturers may incorporate recycled plastics and biodegradable packaging into router for drill accessories. Additionally, energy efficiency and compatibility with long-life lithium-ion batteries align with broader sustainability goals in the power tool industry.
Competitive Pressure and Price Optimization
With more entrants offering compatible router attachments, market competition is intensifying. This is expected to drive price reductions and innovation in feature sets, such as integrated dust extraction and LED guidance systems. Companies that combine affordability with reliability will likely gain significant market share by 2026.
Integration with Smart Tool Ecosystems
Though still in early stages, there is potential for router for drill systems to integrate with smart tool platforms. By 2026, some premium models could offer Bluetooth connectivity, usage tracking, or alignment assistance via smartphone apps—enhancing precision and user experience in complex woodworking tasks.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for router for drill attachments will be shaped by versatility, digital engagement, global accessibility, and sustainable innovation, positioning these tools as essential components in modern toolkits.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Router for Drill (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a router for drill operations—especially in industrial, manufacturing, or automation environments—requires careful consideration of both quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects. Overlooking these factors can lead to performance issues, legal complications, or project delays. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Durability
One of the most common issues is selecting a router with substandard materials or construction. Low-quality motors, bearings, or housings can lead to premature wear, excessive vibration, and inconsistent drilling performance. This not only affects the precision of the operation but also increases maintenance costs and downtime.
Inadequate Power and Speed Control
Not all routers are created equal when it comes to motor power and variable speed settings. Using an underpowered router or one without precise speed control can result in inefficient drilling, tool breakage, or poor finish quality—especially when working with hard materials.
Lack of IP Protection and Licensing Compliance
When sourcing routers—particularly those with embedded software or control systems—it’s crucial to ensure that intellectual property rights are respected. Using a router with unlicensed firmware or copied design elements can expose your organization to legal risks, including infringement claims or forced product recalls.
Hidden Costs from Counterfeit or Clone Products
Some suppliers offer attractively priced routers that appear to be high-end models but are actually counterfeit or reverse-engineered clones. These often lack proper quality assurance, technical support, and may use stolen IP. While initially cheaper, they can lead to higher total cost of ownership due to failures and lack of spare parts.
Insufficient Technical Support and Documentation
High-quality routers come with comprehensive documentation, calibration records, and access to technical support. Sourcing from vendors who provide minimal documentation or support can hinder integration, troubleshooting, and compliance with industry standards.
Ignoring Software and Firmware IP
Many modern drill routers include proprietary software for speed control, diagnostics, or integration with CNC systems. Using firmware that violates software licenses—or failing to verify open-source compliance—can result in legal exposure and system vulnerabilities.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Lack of visibility into the manufacturing origin and component sourcing can lead to unintentional use of blacklisted vendors or products made with forced labor, which may conflict with corporate ethics policies or regulatory requirements (e.g., Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act).
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct due diligence on suppliers, verify product certifications, review software licensing terms, and prioritize vendors with transparent supply chains and strong IP compliance practices. Investing in a high-quality, legally sound router ensures reliability, performance, and long-term operational success.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Router For Drill
Product Classification and HS Code
Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the “Router For Drill” based on its technical specifications and intended use. Typically, such tools may fall under HS Code 8467 (Machines for drilling, milling, reaming, broaching, etc.), but consult local customs authorities or a customs broker to confirm the exact classification per country. Proper classification ensures accurate duty calculation and avoids shipment delays.
Import/Export Regulations
Compliance with international trade regulations is essential. Verify export control requirements—especially if the router contains advanced electronics or dual-use technology—under frameworks such as the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) in the U.S. or the EU Dual-Use Regulation. Obtain necessary export licenses if applicable. For imports, ensure adherence to destination country regulations regarding industrial tools and machinery.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Package the router securely to prevent damage during transit, using cushioning materials and robust outer cartons. Label each package with essential shipping information, including: product name, model number, HS code, country of origin, weight, dimensions, and handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”). Include multilingual labels if shipping to non-English-speaking countries.
Safety and Technical Compliance
Ensure the router complies with safety standards in the target market. Key certifications may include:
– CE Marking (for EU markets, under Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive)
– UKCA Marking (for the UK post-Brexit)
– UL/CSA Certification (for U.S. and Canada)
– PSE Mark (for Japan)
Documentation such as Declaration of Conformity (DoC) and technical files must be available upon request.
Battery and Electrical Specifications
If the router is powered by electricity or includes a battery, confirm voltage compatibility (e.g., 110V vs. 220V) and include appropriate plug adapters or transformers. Lithium batteries, if present, must comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations for air transport, including proper packaging, labeling, and documentation (e.g., UN 3480, Class 9 label).
Shipping and Freight Considerations
Choose the appropriate shipping method (air, sea, or ground) based on urgency, cost, and product volume. Use Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) clearly in contracts to define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Work with freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial tools to ensure smooth transit.
Customs Documentation
Prepare complete customs documentation, including:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed product description, value, and HS code)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (if claiming preferential tariffs)
– Import/Export Licenses (if required)
Ensure all documents are accurate to prevent delays or penalties.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (EU) for material content. Provide information on proper end-of-life disposal or recycling, particularly for electronic components and packaging materials.
After-Sales and Warranty Logistics
Establish a logistics process for handling warranty claims, returns, and spare parts distribution. Clearly communicate warranty terms and return authorization (RMA) procedures to customers. Maintain inventory of critical components in key regions to reduce downtime.
Record Keeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintain detailed records of all compliance documentation, shipping logs, and certifications for a minimum of 5–7 years, depending on local regulations. Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing compliance with evolving trade laws and standards.
In conclusion, sourcing a router for use with a drill requires careful consideration of compatibility, functionality, and safety. Since most drills are not designed to function as routers, a dedicated routing base or adapter may be necessary to achieve accurate and stable results. While drill-powered routing can be a cost-effective and portable solution for light-duty tasks, it lacks the precision, power, and spindle stability of a dedicated router. For occasional or shallow routing jobs, a compatible drill with variable speed control and a proper guide attachment may suffice. However, for consistent, professional-grade results, investing in a purpose-built router is recommended. Ultimately, the decision should be based on the intended use, budget, and required level of accuracy.