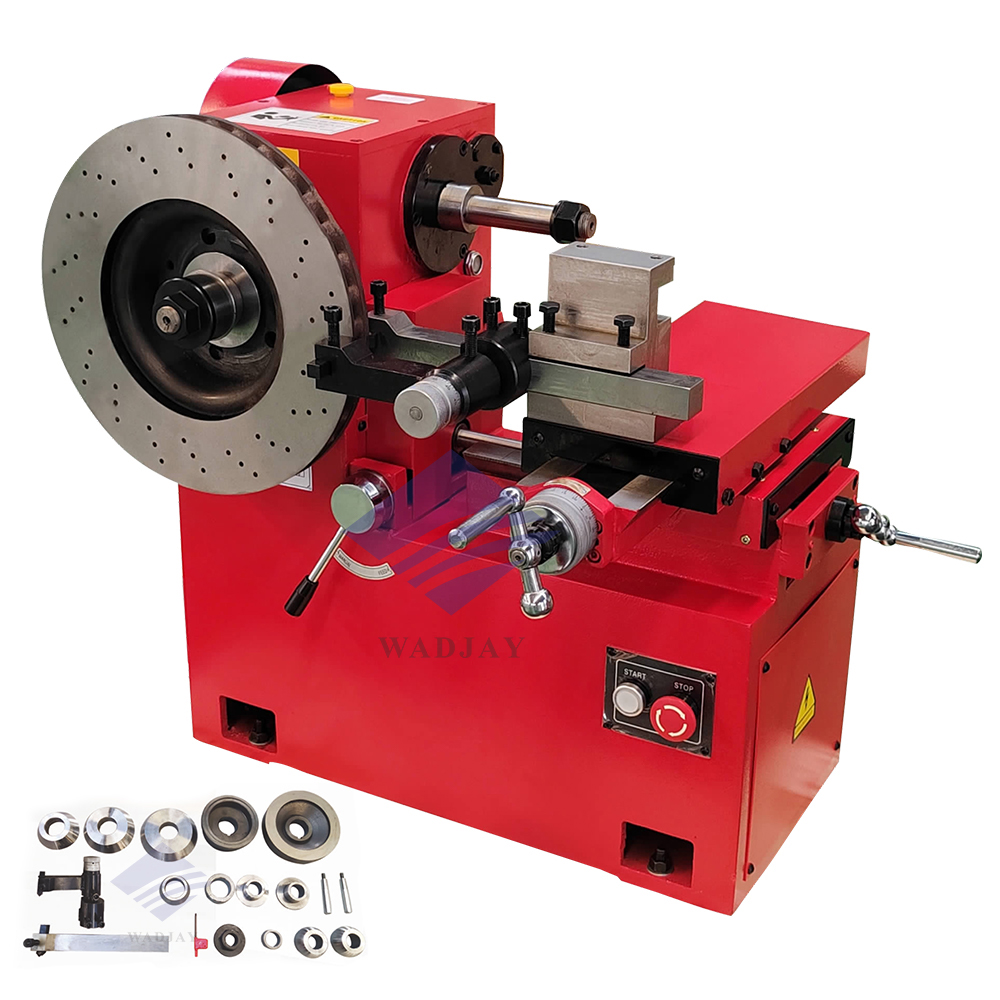
The global automotive brake component after-market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising vehicle ownership, increasing demand for vehicle safety, and growing emphasis on maintenance efficiency. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the automotive aftermarket sector—of which brake service equipment is a critical component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.8% from 2023 to 2028. Within this ecosystem, rotor resurfacing machines have become indispensable tools for automotive repair shops aiming to restore brake rotors to OEM specifications while reducing waste and part replacement costs. As demand for precision machining and cost-effective brake servicing grows, so does the need for reliable, high-performance equipment. This has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers specializing in rotor resurfacing technology. Based on market presence, product range, technological advancement, and customer reviews, the following list highlights the top 10 rotor resurfacing machine manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 10 Rotor Resurfacing Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Schaeffler Group USA Inc.
Domain Est. 2006
Website: schaeffler.us
Key Highlights: As The Motion Technology Company, we engineer innovative products and systems that power and enable the future of AI. Schaeffler is back for CES 2026 — the ……
#2 Hunter Brake Lathes
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hunter.com
Key Highlights: The AutoComp Elite® brake lathe from Hunter Engineering features a patented Variable-Speed Drive System and Anti-Chatter Technology to service rotors at the ……
#3
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parker.com
Key Highlights: Parker is the global leader in motion and control technologies, providing precision-engineered solutions for a wide variety of mobile, industrial and aerospace ……
#4 Heavy Duty Truck Rotor Resurfacing Kit
Domain Est. 1999
Website: irontite.com
Key Highlights: 2-day delivery 30-day returnsCompatible with Van Norman FG5000/FG10000 Flywheel Grinders; Resurfaces heavy-duty vehicle brake rotors; OEM-quality finish with less material removal …
#5 Heavy Equipment / Heavy Machinery
Domain Est. 1993
Website: cat.com
Key Highlights: The Cat heavy equipment line includes machines for construction, mining, agriculture, forestry, paving and more. From skid steers to excavators to mining ……
#6 Deublin
Domain Est. 1996
Website: deublin.com
Key Highlights: Deublin – Global leader in rotary unions and electrical slip rings, delivering high-performance solutions for your industry’s toughest motion and fluid ……
#7 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#8 Pro
Domain Est. 2006
Website: procutusa.com
Key Highlights: A nationwide training and certification program offering comprehensive instruction in rotor matching for Techs and Service Writers….
#9 Brake Lathes
Domain Est. 2020
Website: mechanicsuperstore.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryDeliver smooth rotor finishes with professional brake lathes. Designed for accurate disc and drum services in automotive and repair shop ……
#10 Brake Rotor Resurfacing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: blog.brushresearch.com
Key Highlights: To improve the surface finish of brake rotors, auto mechanics trust the Flex-Hone® for Rotors tool from Brush Research Manufacturing (BRM)….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rotor Resurfacing Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Rotor Resurfacing Machines
The global rotor resurfacing machine market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by evolving automotive service demands, technological advancements, and sustainability initiatives. Key trends shaping the industry include:
-
Increased Demand from Automotive Aftermarket Sector
As vehicle ownership grows globally—particularly in emerging economies—the need for cost-effective brake maintenance solutions is rising. Rotor resurfacing machines offer a viable alternative to rotor replacement, reducing repair costs and material waste. This economic advantage is expected to fuel adoption in independent repair shops and dealership service centers through 2026. -
Technological Integration and Automation
By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly incorporating automation, digital readouts, and CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology into rotor resurfacing machines. These upgrades enhance precision, reduce human error, and improve turnaround times. Smart features such as self-diagnostics and connectivity to service management software are becoming standard, especially in high-end models. -
Shift Toward On-Car Resurfacing Machines
On-car resurfacing machines—which allow rotors to be machined without removal—are gaining traction due to their ability to correct runout issues and improve brake performance. This trend is expected to accelerate as technicians prioritize alignment accuracy and minimal vehicle downtime. The convenience and performance benefits position on-car systems as a dominant segment by 2026. -
Focus on Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Environmental regulations and consumer demand for greener practices are pushing the automotive repair industry toward sustainable solutions. Resurfacing rotors instead of replacing them reduces metal waste and lowers the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing new parts. This ecological benefit is expected to influence purchasing decisions among eco-conscious fleet operators and service providers. -
Consolidation and Competitive Dynamics
The market is witnessing consolidation among equipment manufacturers, with larger players acquiring niche brands to expand product portfolios. Competition is intensifying, leading to innovation and price optimization. At the same time, e-commerce platforms are improving accessibility to resurfacing machines, especially for small garages in remote regions. -
Regional Growth Variations
North America and Europe will remain key markets due to mature automotive service infrastructures and regulatory support for vehicle maintenance. However, the Asia-Pacific region—led by China, India, and Southeast Asia—is projected to register the highest growth, driven by rising vehicle production, urbanization, and expansion of aftermarket service networks. -
Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
While regenerative braking in EVs reduces traditional brake wear, friction brakes are still essential for safety and low-speed performance. As EV adoption increases, specialized resurfacing machines that accommodate unique rotor designs and materials may emerge, creating niche opportunities by 2026.
In conclusion, the rotor resurfacing machine market in 2026 will be defined by smarter, more efficient equipment, growing environmental awareness, and regional market diversification. Companies that innovate in automation, sustainability, and service integration are likely to lead the evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Rotor Resurfacing Machine
Poor Build Quality and Durability
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing a rotor resurfacing machine is encountering units with subpar construction. Low-cost machines often use inferior materials and imprecise manufacturing, leading to premature wear, vibration during operation, and inconsistent resurfacing results. This compromises brake performance and safety, and may result in higher long-term costs due to frequent repairs or replacement.
Lack of Intellectual Property (IP) Compliance
Sourcing machines—especially from overseas suppliers—can involve risks related to intellectual property infringement. Some manufacturers may produce clones or replicas of patented designs without proper licensing. Using such equipment exposes buyers to legal liability, potential seizure of goods, and reputational damage. Always verify that the machine and its design do not violate existing patents or trademarks.
Inadequate Precision and Calibration
Rotor resurfacing demands high accuracy to ensure smooth, flat finishes. Machines with poor calibration or weak tolerance control can produce uneven surfaces, leading to brake pulsation and reduced vehicle safety. Avoid models that lack documented precision metrics or fail to include proper calibration tools and procedures.
Insufficient Technical Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many budget machines come from suppliers with limited after-sales support. This becomes a major pitfall when maintenance is needed or components fail. Lack of accessible technical assistance, user manuals in local languages, or availability of spare parts can lead to extended downtime and operational inefficiencies.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Capabilities
Some suppliers may exaggerate machine capabilities, such as maximum rotor diameter compatibility, cutting speed, or motor power. This misleading information can result in purchasing a machine that doesn’t meet your shop’s requirements. Always request verifiable test reports, customer references, or third-party certifications to confirm claimed specifications.
Ignoring Safety and Certification Standards
Machines that lack proper safety features (e.g., emergency stops, guards, CE or UL certification) pose significant risks to operators. Sourcing non-compliant equipment may violate workplace safety regulations and increase liability. Ensure the machine meets regional safety and electrical standards before purchase.
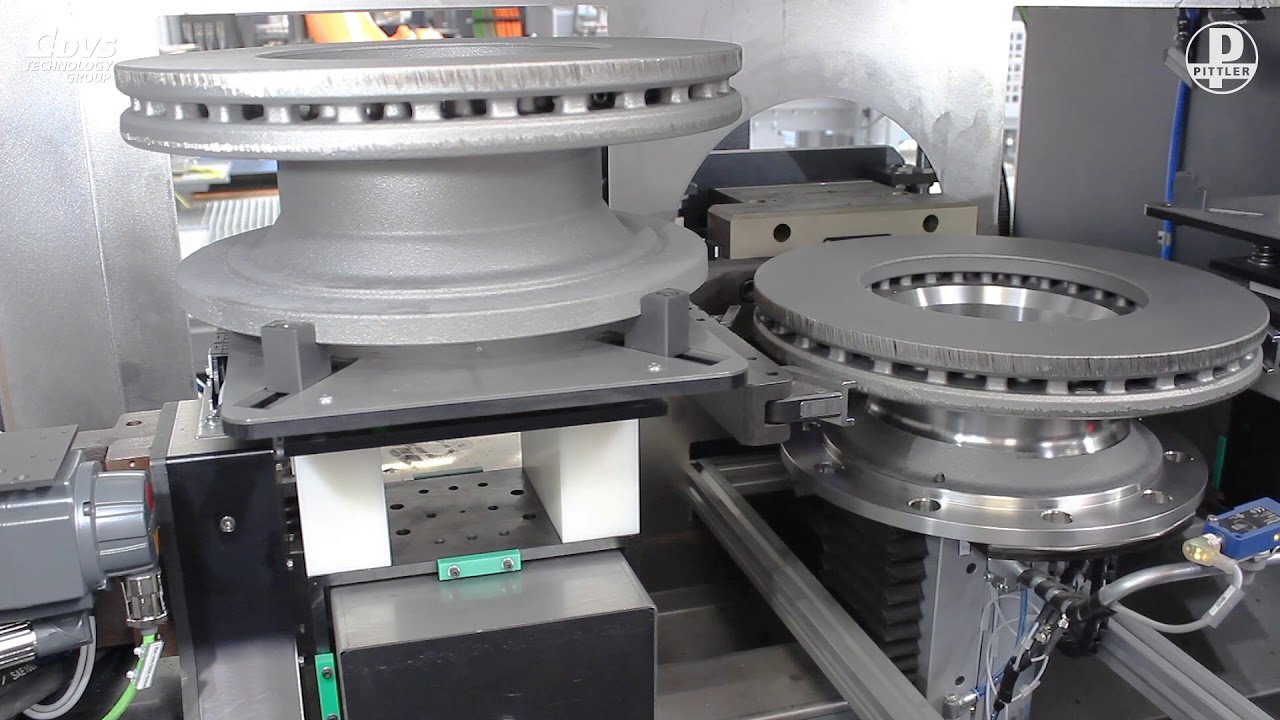

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rotor Resurfacing Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient transport, handling, and operation of a Rotor Resurfacing Machine.
Transportation & Handling
Ensure the machine is properly secured on a suitable flatbed or enclosed trailer using industrial-grade straps or chains anchored to designated lifting points. Use skid steers or forklifts with appropriate capacity to load/unload, ensuring forks are fully under the machine base. Protect hydraulic lines, electrical connections, and control panels with caps or covers during transit. Confirm route clearance (overpasses, weight limits) and obtain necessary permits for oversized loads if applicable.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify compliance with destination country regulations, including CE marking (Europe), UL/CSA certification (North America), or other regional safety standards. Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and technical specifications detailing voltage, power requirements, and dimensions. Ensure adherence to international trade controls (e.g., ECCN classification under EAR) if applicable. Retain documentation for customs clearance and potential audits.
Installation & Site Requirements
Install the machine on a level, vibration-free concrete floor with adequate load-bearing capacity. Provide proper electrical supply matching the machine’s specifications (voltage, phase, amperage) and install an appropriately rated disconnect switch within line of sight. Ensure sufficient clearance around the machine for operation, maintenance, and emergency access. Verify local building codes and facility safety standards are met.
Operational Compliance
Operate the machine only by trained personnel familiar with manufacturer procedures and safety protocols. Use required personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, hearing protection, and gloves. Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance. Maintain machine guards and emergency stop functions in working order. Follow environmental regulations for coolant and metal shavings disposal.
Maintenance & Recordkeeping
Adhere to the manufacturer’s scheduled maintenance plan, documenting all inspections, repairs, and component replacements. Keep logs of machine calibration and safety checks. Retain compliance records, training certifications, and maintenance history for minimum regulatory retention periods (typically 3–5 years). Update documentation promptly following any modifications or incidents.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Rotor Resurfacing Machine
After a thorough evaluation of available options, it is concluded that sourcing a high-quality rotor resurfacing machine is a strategic investment that significantly enhances operational efficiency, service quality, and cost-effectiveness in brake maintenance and repair operations. The selection process, which considered factors such as precision, durability, ease of use, automation features, maintenance requirements, and overall lifecycle cost, indicates that a mid-to-high-end machine offers the best long-term value.
Machines with CNC capabilities, digital controls, and robust construction not only improve machining accuracy and consistency but also reduce labor time and minimize material waste. Additionally, sourcing from reputable manufacturers with strong technical support and warranty offerings ensures reliability and minimizes downtime.
Furthermore, purchasing or leasing the machine in-house rather than relying on outsourced resurfacing can lead to faster turnaround times, better quality control, and increased customer satisfaction. While the initial investment may be substantial, the long-term savings and operational benefits justify the expenditure, particularly for medium- to high-volume service centers.
In conclusion, procuring a modern, reliable rotor resurfacing machine aligns with goals of operational excellence and service expansion. It is recommended to finalize the procurement with a supplier that balances performance, support, and cost, ensuring sustainable growth and competitiveness in the automotive service industry.