The global rotor pump market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as oil & gas, chemical processing, food & beverage, and wastewater treatment. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global rotary pump market was valued at USD 5.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by the need for energy-efficient pumping solutions and the rising adoption of precision fluid handling systems in industrial applications. With technological advancements enhancing reliability and performance, leading manufacturers are focusing on innovation, global reach, and application-specific designs. In this evolving landscape, nine rotor pump manufacturers have emerged as key players, combining engineering excellence with scalable solutions to meet complex industrial demands.
Top 9 Rotor Pump Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rotors
Domain Est. 2015
Website: rotopumpsna.com
Key Highlights: Roto Pumps North America Inc. 300 Springhill Farm Rd. – #106. Fort Mill, SC 29715 (803)547-7686 · [email protected]….
#2 About Us
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1968
Website: rotopumps.com
Key Highlights: Established in 1968, Roto Pumps is the pioneer manufacturer of Progressive Cavity Pumps in India, renowned for providing efficient and reliable pumping ……
#3 Progressive Cavity Pump Parts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: westcoastrotor.com
Key Highlights: WestCoast Rotor is the industry’s leading manufacturer of aftermarket & replacement parts for progressive cavity pumps. Contact us today to learn more….
#4 Industrial Pumps
Domain Est. 1999
Website: trirotor.com
Key Highlights: Tri-Rotor® is the inventor of the Positive displacement rotary piston pump and we’ve been manufacturing this unique pump for over 85 years….
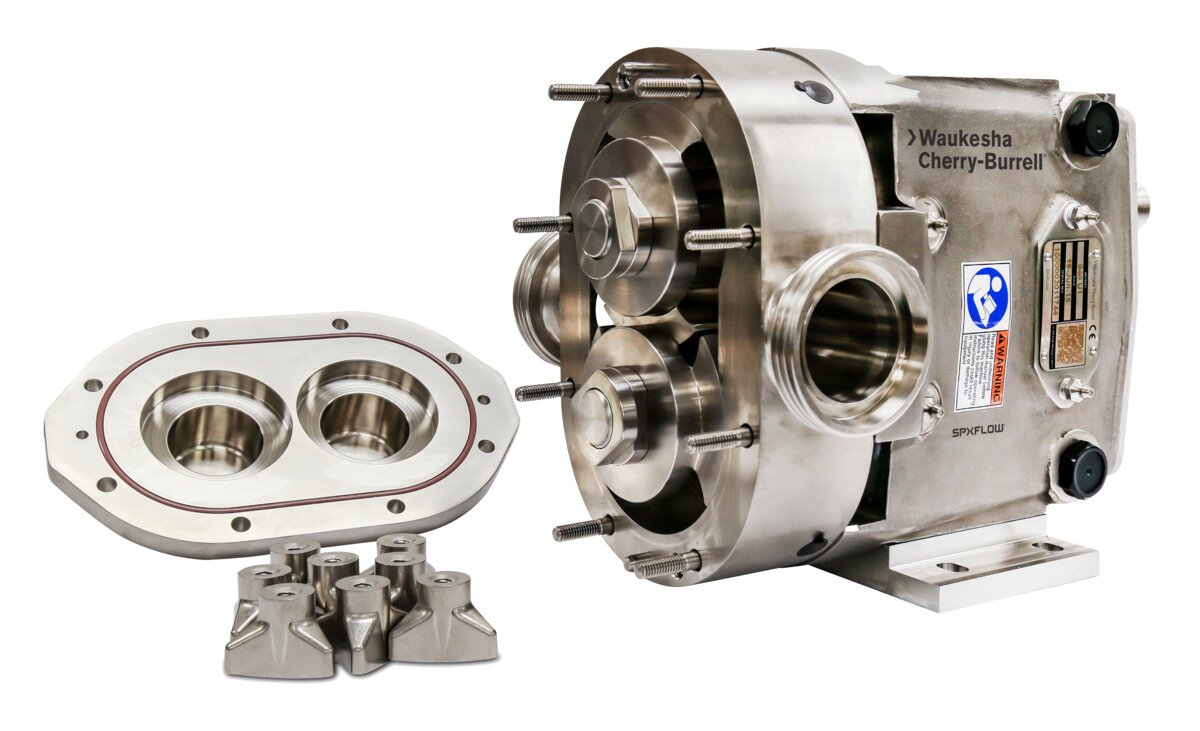
#5 Waukesha Cherry-Burrell
Domain Est. 2014
Website: spxflow.com
Key Highlights: We engineer and manufacture positive displacement and centrifugal pumps, sanitary valves, dispersion equipment, and the legendary Votator® scraped surface ……
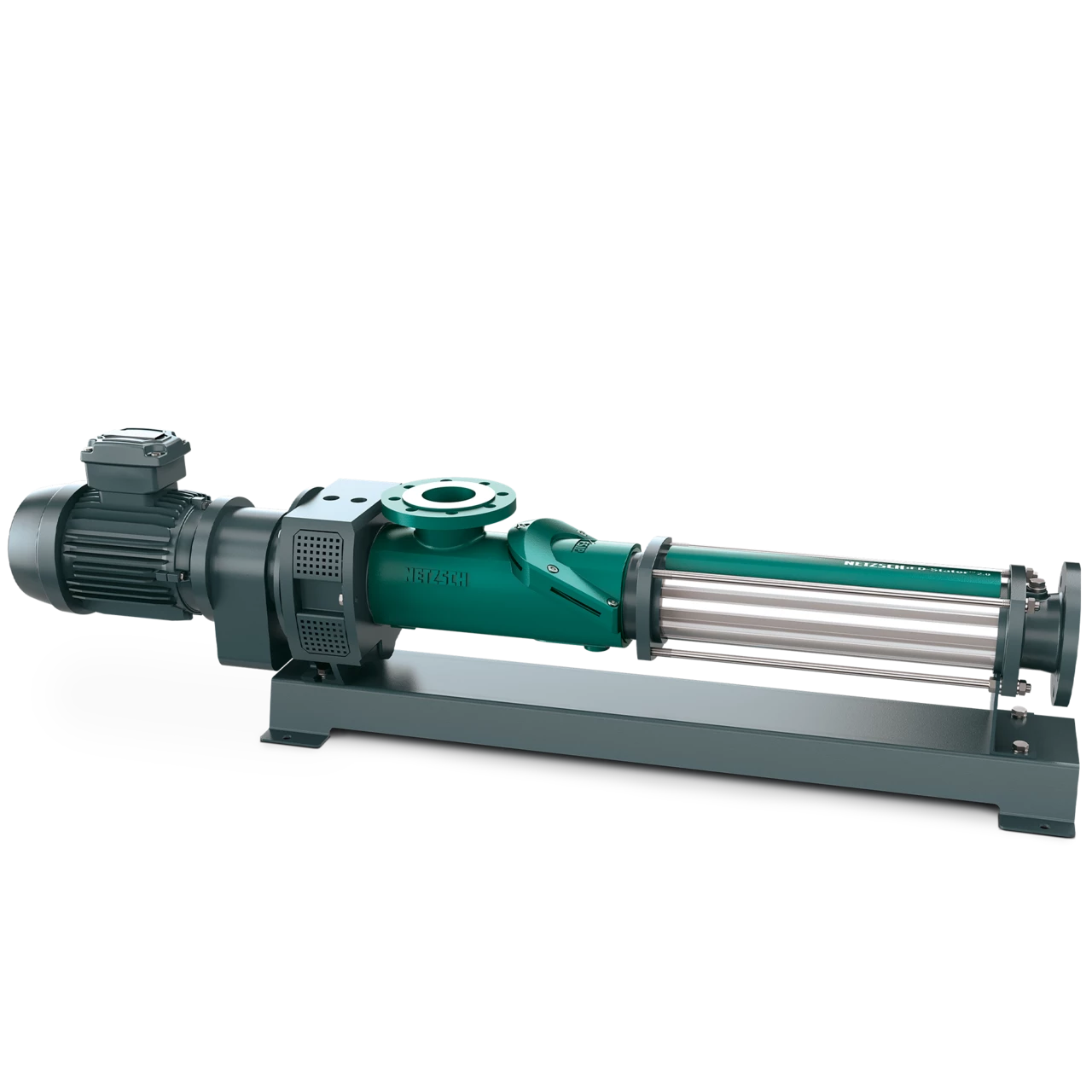
#6 NEMO® Progressing Cavity Pumps
Domain Est. 1995
Website: pumps-systems.netzsch.com
Key Highlights: Progressing cavity pumps offer you continuous, pressure-stable, gentle and low-pulsation pumping of a wide variety of media….
#7 Viking Pump
Domain Est. 1996
Website: vikingpump.com
Key Highlights: Viking Pump, a Unit of IDEX Corporation, leads the world in the design and manufacture of rotary Positive Displacement Pumps for use in some of the toughest ……
#8 Pumps & Motors: Design, Manufacturing, Service
Domain Est. 2000
Website: haywardtyler.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture, and service performance-critical electric motors and pumps to meet the most demanding of applications for the global energy and chemical ……
#9 Progressing Cavity Pumps
Domain Est. 2012
Website: novarotors.it
Key Highlights: PROGRESSIVE CAVITY PUMPS, CHARACTERISTICS. – Nova Rotors specialises in the construction of progressive cavity pumps. This type of pump is highly flexible ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rotor Pump
H2 2026 Market Trends for Rotor Pumps
The rotor pump market in H2 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and macroeconomic factors. Building on developments throughout the year, key trends emerging in the second half of 2026 point towards increased efficiency, smarter operations, and strategic shifts in key end-user sectors.
1. Accelerated Adoption of Smart & Connected Rotor Pumps:
* Trend: H2 2026 sees a significant surge in the integration of IoT sensors, predictive maintenance algorithms, and cloud-based monitoring platforms into rotor pump systems.
* Drivers: The need to minimize unplanned downtime, optimize energy consumption, and enable remote asset management in industries like food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
* Impact: Suppliers are focusing on offering “smart pump as a service” models, providing real-time performance data, leak detection, wear prediction, and automated diagnostics. This shift moves the value proposition beyond the physical pump to ongoing data-driven services.
2. Heightened Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
* Trend: Regulatory pressures (e.g., EU Ecodesign, global carbon reduction targets) and corporate ESG goals are driving demand for ultra-high-efficiency rotor pumps.
* Drivers: Rising energy costs and the need to reduce carbon footprints are paramount for end-users. Pumps are recognized as major energy consumers in fluid handling systems.
* Impact: Manufacturers are investing heavily in optimizing rotor and casing designs (e.g., tighter tolerances, advanced materials), integrating variable frequency drives (VFDs) as standard, and developing pumps specifically for low-viscosity, energy-sensitive applications. Life Cycle Cost (LCC) analysis becomes a critical purchasing criterion.
3. Material Innovation for Harsh Environments and Hygiene:
* Trend: Increased demand for rotor pumps made from advanced materials like specialized stainless steels (e.g., super duplex), high-performance polymers (e.g., PEEK, PTFE composites), and corrosion-resistant alloys.
* Drivers: Expanding applications in aggressive chemical processing, high-purity biopharma, and wastewater with high solids/abrasives. Stricter hygiene regulations (e.g., FDA, EHEDG, 3-A) in food & pharma remain critical.
* Impact: Suppliers are differentiating through proprietary material formulations and surface treatments (e.g., enhanced passivation, specialized coatings) to extend pump life and reduce contamination risks, commanding premium pricing.
4. Resilience in Key End-User Sectors with Shifting Dynamics:
* Food & Beverage (F&B): Remains a strong driver, but with increased focus on pumps handling viscous, shear-sensitive, or particulate-laden products (e.g., plant-based alternatives, sauces) and stringent cleanability. Demand for CIP/SIP compatibility is non-negotiable.
* Pharmaceuticals & Biotech: Steady growth continues, fueled by biologics manufacturing and personalized medicine. Pumps must meet highest purity standards, ensure product integrity (low shear, gentle handling), and offer full traceability.
* Chemicals & Petrochemicals: Focus shifts towards pumps for handling new bio-based feedstocks, green chemicals, and hydrogen (as a carrier or reactant), requiring compatibility with novel, often challenging, fluids. Safety and reliability are paramount.
* Wastewater & Sludge: Growing investment in advanced treatment and resource recovery (e.g., biogas, nutrient extraction) drives demand for robust, high-solids handling rotor pumps capable of handling variable, abrasive sludges efficiently.
5. Supply Chain Optimization and Regionalization:
* Trend: Lessons from prior disruptions lead to a continued push for supply chain resilience. This includes nearshoring/reshoring of some manufacturing and component sourcing, particularly in North America and Europe.
* Drivers: Geopolitical tensions, logistics volatility, and the need for faster delivery times and reduced lead times.
* Impact: Global pump manufacturers are establishing more regional production hubs or strengthening partnerships with local suppliers. This trend supports faster customization and service response but may increase initial costs.
6. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships:
* Trend: The market witnesses ongoing consolidation among pump manufacturers and increased strategic partnerships between pump OEMs, automation specialists, and material science companies.
* Drivers: Need for broader technology portfolios (pumps + controls + analytics), economies of scale, and faster innovation cycles to meet complex customer demands.
* Impact: Larger players gain market share by offering integrated fluid handling solutions. Niche players focus on specific high-value applications or materials.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The rotor pump market in the second half of 2026 is characterized by intelligence, efficiency, and resilience. Success will favor manufacturers who can deliver not just robust mechanical pumps, but integrated, data-enabled systems that optimize performance, minimize environmental impact, and ensure reliability in increasingly demanding and regulated applications. The focus is firmly on total cost of ownership, sustainability, and seamless integration into digitalized industrial processes.
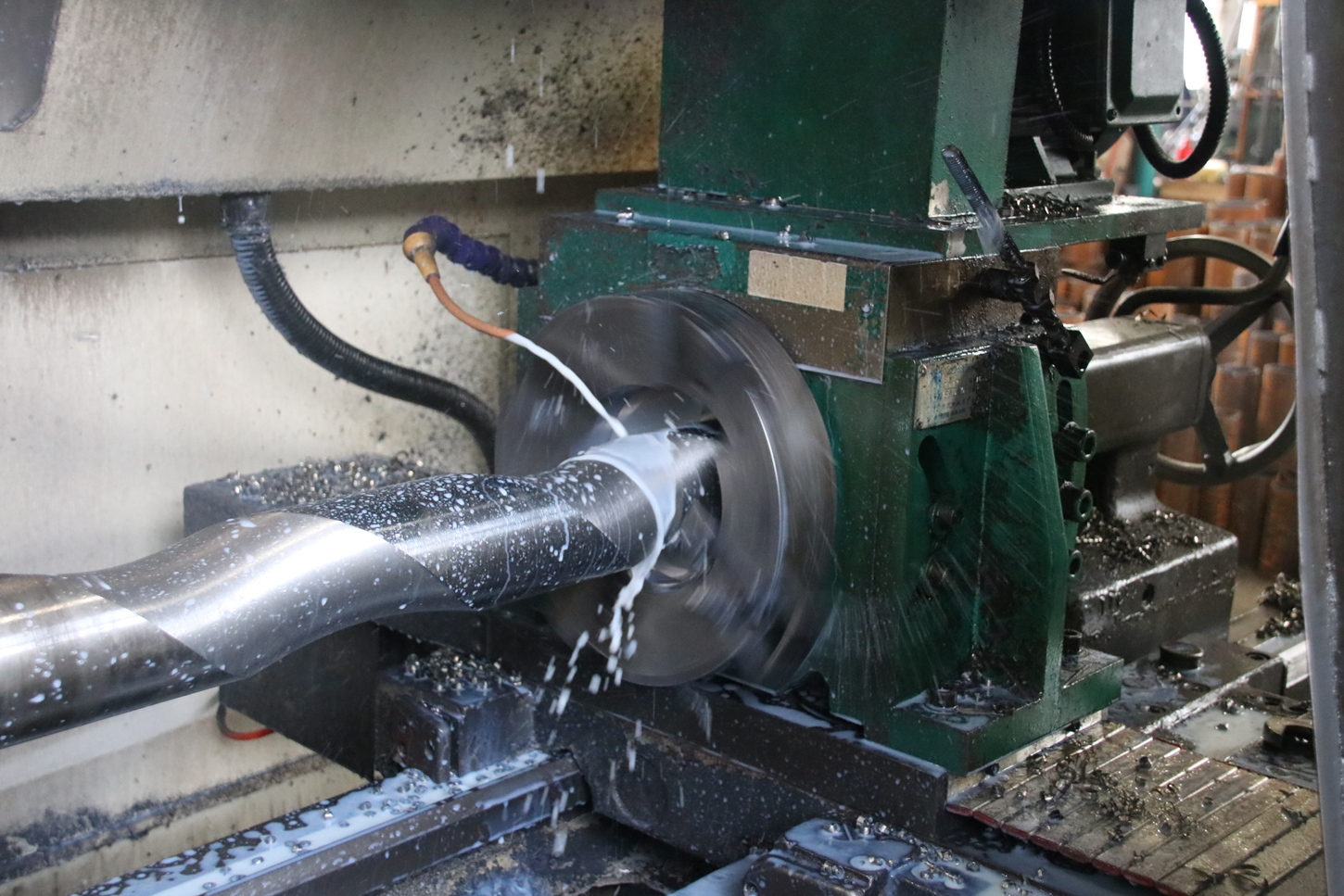

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Rotor Pumps: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing rotor pumps, especially from new or offshore suppliers, involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, legal liability, and financial loss.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Specifications and Traceability
One of the most frequent issues is receiving rotor pumps made with substandard materials. Suppliers may substitute specified alloys (e.g., 316L stainless steel) with cheaper, inferior alternatives (e.g., 304 stainless or even carbon steel with plating) without disclosure. Lack of material traceability (e.g., mill test certificates) makes it difficult to verify compliance with industry standards like ASTM or ISO. This can result in premature corrosion, contamination of sensitive processes (especially in pharmaceuticals or food & beverage), and mechanical failure under pressure or temperature.
Poor Manufacturing Tolerances and Assembly
Rotor pumps rely on precise clearances between rotors, casing, and drive components to maintain efficiency and prevent leakage. Suppliers with outdated machinery or lax quality control may produce components with inconsistent tolerances. This leads to reduced pump performance, increased wear, excessive noise, and shortened service life. Poor assembly practices—such as incorrect rotor alignment or improper sealing—further compound these issues and are often not detectable during initial inspection.
Lack of Performance Validation and Testing
Many suppliers, particularly low-cost manufacturers, do not conduct or provide documented performance testing (e.g., flow rate, pressure, NPSH, efficiency). Without certified test reports under real-world conditions, buyers risk receiving pumps that fail to meet specified operational requirements. This can disrupt entire systems, especially in critical applications like chemical transfer or hygienic processing.
Insufficient Quality Assurance Processes
Suppliers lacking certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) often have inconsistent production standards. This increases the risk of batch-to-batch variability and makes it harder to enforce corrective actions when defects are discovered. Without robust incoming inspection, in-process checks, and final validation, defects may go undetected until the pump is installed.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Replication of Patented Designs
Rotor pump designs—particularly those involving proprietary rotor profiles, timing gear configurations, or sealing mechanisms—are often protected by patents. Unethical suppliers may reverse-engineer and copy these designs without licensing, offering “compatible” or “equivalent” pumps at lower prices. Purchasing such products can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially if the IP owner pursues enforcement actions against downstream users.
Misrepresentation of Brand and Origin
Some suppliers falsely label their products as being from well-known brands or originating from reputable manufacturing countries. This includes affixing counterfeit nameplates or falsifying documentation. Buyers may unknowingly purchase counterfeit pumps that lack design integrity, safety certifications, or warranty support, mistaking them for genuine OEM products.
Lack of Transparency in Design Ownership
Suppliers may be unable or unwilling to clarify whether their rotor pump designs are original or licensed. This ambiguity increases the risk of infringing third-party IP. In regulated industries, using unlicensed or cloned technology can invalidate compliance certifications and lead to audit failures.
Weak Contractual IP Protections
Purchase agreements that fail to include clear IP indemnification clauses leave buyers vulnerable. If a supplier’s product infringes on another party’s patent, the buyer—not the supplier—may be held responsible for damages, recalls, or legal costs. Contracts should require suppliers to warrant original design ownership and assume liability for IP violations.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Require full material traceability and third-party test certifications.
– Conduct factory audits to assess manufacturing capabilities and QA processes.
– Perform independent performance testing upon delivery.
– Verify patent status and licensing for critical pump designs.
– Include strong IP indemnification clauses in supply contracts.
– Source from reputable suppliers with transparent design and manufacturing practices.
Proactive due diligence is essential to ensure both the quality and legal safety of sourced rotor pumps.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rotor Pump
Product Overview
Rotor pumps are positive displacement pumps used across industries such as oil & gas, chemical processing, food & beverage, and wastewater management. Due to their mechanical complexity and sensitivity to handling, proper logistics and compliance protocols are essential to ensure safe transport, regulatory adherence, and operational reliability upon delivery.
Packaging Requirements
Use robust, custom-fitted packaging to protect the rotor pump during transit. The pump must be securely mounted on a wooden pallet with corner protectors and enclosed in a moisture-resistant, corrugated cardboard or wooden crate. Internal components, especially the rotor and stator, should be coated with anti-corrosion compound and sealed to prevent contamination. Include desiccants inside the packaging to mitigate moisture damage in humid environments.
Transportation Guidelines
Transport rotor pumps in a horizontal position unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer. Avoid tilting or inverting the unit to prevent internal damage or fluid leakage. Use climate-controlled vehicles when shipping through extreme temperatures. Secure the package to prevent shifting during transit. For international shipments, adhere to IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations if the pump contains lubricants or hazardous residues.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify applicable Harmonized System (HS) codes for rotor pumps—typically classified under 8413.70 or similar subheadings—depending on design and application. Obtain required export licenses if shipping to restricted regions. Comply with International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR) if the pump contains controlled technology. Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. For EU destinations, ensure alignment with CE marking requirements and relevant Machinery Directive standards.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Rotor pumps must meet industry-specific compliance standards depending on their application:
– ATEX/IECEx: Required for pumps used in explosive atmospheres (oil & gas, chemical plants).
– FDA/USDA: Necessary for pumps in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical applications.
– PED (Pressure Equipment Directive): Mandatory for pumps operating above specified pressure thresholds in the EU.
– API 676: Common standard for rotary pumps in the petroleum industry.
Ensure all certifications are documented and available for inspection during customs clearance or customer audit.
Handling and Storage Instructions
Upon receipt, inspect packaging for damage before acceptance. Store rotor pumps in a dry, indoor environment with stable temperatures (10°C–30°C). Keep protective caps on ports and avoid exposure to dust, moisture, or corrosive agents. Rotate stored pumps periodically per manufacturer guidelines to prevent bearing deformation. Do not remove anti-rust coatings until installation.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain a complete compliance dossier including: Material Test Reports (MTRs), conformity certificates, test reports (e.g., performance and leakage tests), and calibration records. Assign a unique serial number to each unit for full traceability throughout the supply chain. Provide multilingual instruction manuals where required by destination country regulations.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Dispose of packaging materials in accordance with local waste management regulations. If the pump contains hazardous substances (e.g., lead seals, specific lubricants), comply with REACH (EU) or TSCA (USA) requirements. Report any spills or damages during transport immediately and follow established environmental response protocols.
Final Inspection and Delivery Confirmation
Conduct a pre-shipment inspection to verify packaging integrity, labeling accuracy, and documentation completeness. Upon delivery, require recipient signature and encourage immediate inspection. Provide a digital compliance passport or QR code linking to product certifications and operating manuals for enhanced transparency.
Conclusion on Sourcing Rotor Pumps
In conclusion, sourcing rotor pumps requires a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors including application requirements, fluid characteristics, flow rate and pressure demands, material compatibility, and operational environment. Rotor pumps offer significant advantages such as high efficiency, excellent suction capability, and reliable performance with viscous or shear-sensitive fluids, making them ideal for industries such as food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and wastewater treatment.
When selecting a supplier, it is essential to consider their technical expertise, customization capabilities, quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards), after-sales support, and proven track record. Opting for reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors ensures product reliability, adherence to industry standards, and access to technical assistance and spare parts.
Moreover, a total cost of ownership approach—factoring in initial cost, maintenance, energy efficiency, and service life—often reveals that investing in a high-quality rotor pump from a trusted source leads to long-term savings and operational reliability.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of rotor pumps hinges on aligning technical specifications with application needs while partnering with reliable suppliers who can deliver performance, durability, and support throughout the pump’s lifecycle.