The global rotary broaching tools market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision machining across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global broaching machine market—closely tied to tooling—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights increasing industrial automation and the need for high-efficiency cutting tools as key catalysts, with the global cutting tools market expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. Amid this growth, rotary broaching tools have gained favor for their ability to produce precise internal and external forms in a single rotation, reducing cycle times and improving part consistency. As demand for accuracy, speed, and cost-effective machining rises, manufacturers are turning to leading rotary broaching tool suppliers that combine innovation, durability, and technical support. In this evolving landscape, the following seven companies stand out for their market presence, technological advancements, and customer-driven solutions.
Top 7 Rotary Broaching Tool Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rotary Broaching Tools
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sommatool.com
Key Highlights: Somma Tool is the leading manufacturer of Rotary Broaching Tools for Screw machine, Multi Spindle, CNC Lathe, Mill, and Swiss Machines….
#2 Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: slatertools.com
Key Highlights: Slater Tools Inc. manufactures the largest variety of internal/ ID and external/OD precision rotary broaches, also known as wobble broaches….
#3 Colonial Tool Group
Domain Est. 1996
Website: colonialtool.com
Key Highlights: Colonial Tool Group designs and manufactures precision spindles, broaching tools, machines, and indexable cutting tool systems for demanding industries….
#4 Broach Tools
Domain Est. 2002
Website: genswiss.com
Key Highlights: Precision manufactured in-house, GenSwiss’ Signature Series line of premium hexagonal rotary broach tools deliver high-performance cutting for industries ……
#5 Performance Rotary Broaching Tools for CNC Swiss, Lathes …
Domain Est. 2004
Website: rotarybroaching.net
Key Highlights: Genevieve Swiss Industries is a reliable source of high quality rotary/wobble broaching tools and rotary broach holders. Used for years on automatic lathes, ……
#6 Rotary Broach Tools
Domain Est. 2008
Website: polygonsolutions.com
Key Highlights: Polygon Solutions specializes in rotary broaches also known as wobble broach tools for CNC lathes, mills and screw machines….
#7 Hassay Savage
Domain Est. 2017
Website: pilotprecision.com
Key Highlights: Our Swiss Style Rotary Punch Broaches offer consistent high-tolerance forms for long production runs. The broach has superb surface finishes as well as an ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rotary Broaching Tool

2026 Market Trends for Rotary Broaching Tools
The rotary broaching tool market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving manufacturing demands, and global industrial shifts. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the market, focusing on innovation, regional dynamics, industry adoption, and competitive landscape.
Technological Advancements and Automation Integration
One of the most significant drivers of the rotary broaching tool market in 2026 is the integration of advanced materials and smart manufacturing technologies. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting carbide and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) inserts in rotary broaching tools to enhance durability and precision, especially for high-volume production environments. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 has led to the development of smart broaching systems that feature real-time monitoring, IoT-enabled diagnostics, and CNC compatibility. These innovations improve tool life, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent part quality, making rotary broaching a more attractive solution for precision machining applications.
Growth in Aerospace and Medical Device Manufacturing
The aerospace and medical device sectors are expected to be primary growth engines for rotary broaching tools by 2026. These industries demand complex geometries, tight tolerances, and high repeatability—capabilities that rotary broaching delivers efficiently. In aerospace, the need for lightweight, high-strength components made from titanium and Inconel alloys is increasing the use of advanced broaching tools. Similarly, in the medical sector, rotary broaching is critical for creating hexagonal and splined features in orthopedic implants and surgical instruments. As both industries expand globally, so too will demand for high-performance rotary broaching solutions.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to lead global market growth in 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization, rising investments in manufacturing infrastructure, and strong demand from automotive and electronics industries—particularly in China, India, and South Korea. North America and Europe will maintain steady growth, supported by mature aerospace and medical sectors and a strong focus on automation and precision engineering. However, supply chain localization trends may encourage regional production of rotary broaching tools, reducing dependency on imports and fostering local innovation.
Sustainability and Cost Efficiency Pressures
Environmental regulations and cost optimization are pushing manufacturers to adopt more sustainable and efficient machining processes. Rotary broaching, known for its single-setup operation and minimal material waste, aligns well with these goals. By 2026, tool producers are likely to emphasize recyclable tool bodies, energy-efficient designs, and longer tool life to appeal to eco-conscious buyers. Furthermore, the ability of rotary broaching to reduce cycle times and eliminate secondary operations enhances its cost-effectiveness, making it a preferred choice in competitive manufacturing environments.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The rotary broaching tool market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established players and niche manufacturers investing in R&D. Companies are focusing on modular tooling systems, customizable broach forms, and enhanced coatings to differentiate their offerings. Strategic partnerships with CNC machine manufacturers and digital tool management platforms are also emerging as key growth strategies. By 2026, market leaders will likely offer integrated broaching solutions that combine hardware, software, and predictive maintenance services.
Conclusion
By 2026, the rotary broaching tool market will be shaped by technological innovation, sector-specific demand, and regional manufacturing trends. With growing emphasis on precision, efficiency, and sustainability, rotary broaching is set to expand beyond traditional applications into advanced manufacturing domains. Companies that invest in smart, adaptable, and eco-friendly tooling solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving opportunities.
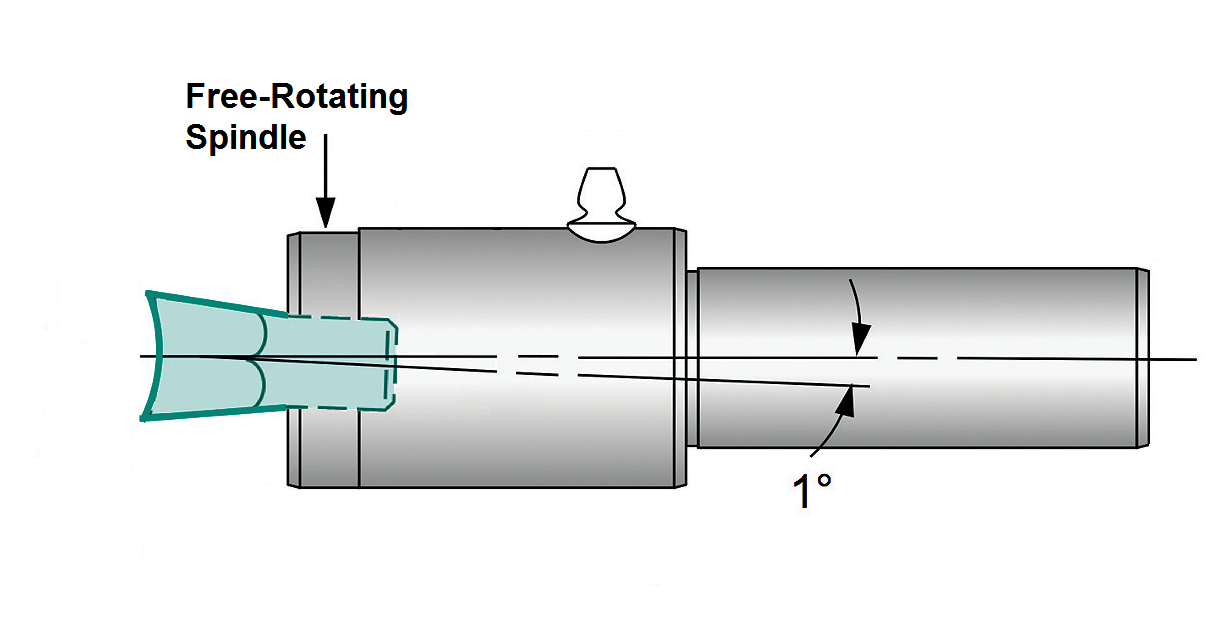
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Rotary Broaching Tools (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing rotary broaching tools from overseas, particularly from regions with less stringent IP enforcement, can lead to significant quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for protecting your operations, reputation, and bottom line.
Poor Material Quality and Heat Treatment
Many low-cost rotary broaching tools use substandard materials or improper heat treatment processes. This results in tools that wear out quickly, fail prematurely under load, or cannot maintain sharp cutting edges. Inferior steel lacks the hardness and toughness required for precision broaching, leading to increased downtime and higher long-term costs despite the lower initial price.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
High-precision rotary broaching relies on tight geometric tolerances. Offshore manufacturers may lack the necessary quality control systems, leading to inconsistencies in tool geometry, cutting edge alignment, and runout. These variations cause poor surface finishes, inaccurate part dimensions, and increased tool breakage — all undermining the reliability and repeatability you expect from your machining process.
Copying Branded Tools Without Authorization
A major IP concern is the unauthorized replication of patented or trademarked rotary broaching tool designs. Some suppliers copy well-known brands (such as Star SU, NTK, or other proprietary tooling) and sell counterfeit versions at lower prices. Purchasing these tools exposes your company to legal liability, including claims of contributory infringement, and can damage your reputation as a compliant and ethical business.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable manufacturers provide documentation such as material certifications, heat treatment records, and quality inspection reports. Many low-cost suppliers offer no traceability, making it difficult to verify tool origin, materials used, or compliance with industry standards. This absence of documentation increases risk, especially in regulated industries where audit trails are mandatory.
Hidden IP Infringement Risks
Even if a tool appears generic, it may still incorporate patented design features — such as specific flute geometry, mounting mechanisms, or indexing systems — without a license. Unwittingly using such tools can lead to IP disputes, product seizures, or costly litigation. The burden of due diligence falls on the buyer, and sourcing from non-transparent suppliers increases exposure.
Limited Technical Support and Warranty
Low-cost suppliers often lack the technical expertise to support complex broaching applications. If a tool fails, resolving the issue can be slow or impossible due to communication barriers, lack of local support, or refusal of warranty claims. This contrasts sharply with established brands that offer engineering support, troubleshooting, and reliable warranties.
Short-Term Savings vs. Long-Term Costs
While counterfeit or low-quality tools may appear cost-effective upfront, their poor performance leads to higher total cost of ownership. Frequent replacements, scrapped parts, machine downtime, and potential legal fees far outweigh initial savings. Investing in genuine, high-quality tools from authorized distributors ensures reliability, consistency, and IP compliance.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, always source rotary broaching tools from reputable suppliers with verifiable quality systems and clear IP licensing. Conduct supplier audits, request certification documentation, and consult legal or technical experts when unsure about a tool’s legitimacy. Protecting your operation from poor quality and IP exposure starts with informed, responsible sourcing decisions.
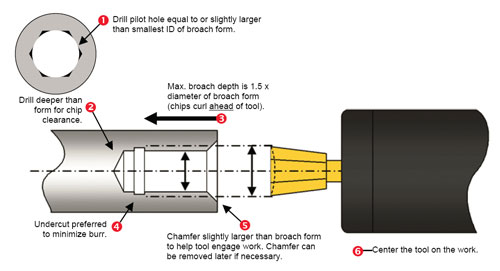
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rotary Broaching Tools
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling, transportation, and use of rotary broaching tools, ensuring adherence to international standards and regulatory requirements.
Product Classification & HS Code
Rotary broaching tools are precision cutting tools used in machining operations to create non-round shapes (e.g., hex, square, splines) in a single rotation. For international trade purposes, these tools are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code:
- HS Code: 8207.50 – “Parts and accessories suitable for use solely or principally with machine tools of heading 84.61, 84.66 or 84.79, for working metal: for tools for working metal: broaches, reamers, taps and dies.”
Note: Always verify the correct HS code with local customs authorities, as classification may vary slightly by country and specific tool composition.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit and ensure tool integrity.
- Internal Packaging: Each rotary broaching tool should be individually wrapped in anti-corrosion paper or placed in sealed plastic sleeves to prevent moisture and oxidation.
- Cushioning: Use foam inserts, molded trays, or bubble wrap within sturdy cardboard or plastic cases to minimize movement and impact.
- Outer Packaging: Ship in durable, corrugated cardboard boxes clearly labeled with contents, part numbers, and handling instructions.
- Labeling: Include:
- Product name and model number
- Net weight and dimensions
- “Fragile – Handle with Care”
- “Keep Dry” and “Do Not Stack Excessively” if applicable
- Export Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill. For regulated destinations, a Certificate of Origin may be required.
Import & Customs Compliance
Ensure compliance with destination country regulations:
- Duty & Tax Assessment: Provide accurate HS code, value, and country of manufacture (usually indicated on tool or packaging) for tariff calculation.
- Import Permits: Generally not required for rotary broaching tools, but verify with local customs if intended for restricted industries (e.g., defense).
- Restricted Materials: Confirm the tool does not contain controlled substances (e.g., certain cobalt or tungsten alloys) that may require export licenses under regulations like ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations). Standard HSS or carbide tools typically do not fall under these controls.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Verify that tool materials comply with EU regulations:
- REACH (EC 1907/2006): No SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) above threshold levels.
- RoHS (2011/65/EU): Applies primarily to electrical equipment; rotary broaches are generally exempt unless part of an electronic assembly.
Safety & Operational Compliance
Adhere to workplace safety standards when using rotary broaching tools:
- Machine Compatibility: Use only with compatible tool holders and CNC/manual lathes equipped with live tooling. Follow manufacturer torque and speed specifications.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators must wear safety glasses, hearing protection, and gloves during installation and operation.
- ISO Standards: Tools should comply with relevant ISO standards for dimensional tolerances and performance (e.g., ISO 13399 for cutting tool data representation).
- CE Marking: For tools sold in the European Economic Area, ensure CE marking indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards (Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC if part of a machine system).
Storage & Handling
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent rust and dimensional instability.
- Orientation: Keep tools in upright or horizontal positions using racks to avoid tip damage.
- Inventory Management: Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) rotation to maintain tool performance and coating integrity.
Disposal & Environmental Considerations
- End-of-Life Handling: Rotary broaching tools contain recyclable materials (steel, carbide). Dispose of through certified metal recycling facilities.
- Hazardous Waste: Tungsten carbide inserts may require special disposal in some jurisdictions due to cobalt content. Consult local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S.).
- Waste Oil/Coolant: Chips and coolant generated during use must be managed per local environmental laws (e.g., proper filtration and recycling).
Regulatory Documentation & Certifications
Maintain and provide upon request:
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS) for tool materials
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for ISO or CE compliance
- Calibration and inspection reports (if applicable)
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) – typically EAR99 for standard broaching tools
By following this guide, businesses can ensure the compliant and efficient global distribution and use of rotary broaching tools while minimizing risk and maximizing operational safety.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sourcing a rotary broaching tool requires careful evaluation of several key factors including tool quality, material compatibility, precision requirements, supplier reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness. High-quality rotary broaching tools from reputable manufacturers ensure better performance, longer tool life, and improved accuracy in machining operations. It is essential to partner with trusted suppliers who offer technical support, consistent product quality, and timely delivery. Additionally, considering in-house capabilities versus outsourcing, as well as total cost of ownership—factoring in maintenance and replacement frequency—can significantly impact long-term efficiency and productivity. By conducting thorough research and supplier assessments, organizations can make informed sourcing decisions that enhance manufacturing capabilities and maintain competitive advantage.