The global rolling rubber market has seen steady expansion, driven by rising demand across automotive, industrial, and consumer sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the rubber market was valued at approximately USD 43.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing applications in tires, conveyor systems, seals, and industrial rollers, particularly in emerging economies. As manufacturing processes become more precise and durability requirements intensify, leading rolling rubber manufacturers are investing in advanced compounding technologies and sustainable materials to maintain competitive edges. In this evolving landscape, the top nine rolling rubber manufacturers stand out for their innovation, global reach, and consistent quality—shaping the future of rubber-based motion and load-bearing solutions.
Top 9 Rolling Rubber Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
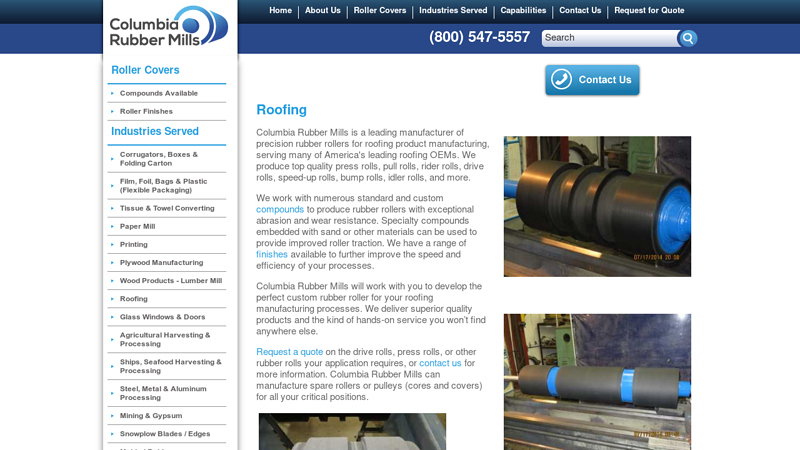
#1 Rubber Rollers for Roofing Product Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: columbiarubbermills.com
Key Highlights: Columbia Rubber Mills is a leading manufacturer of precision rubber rollers for roofing product manufacturing, serving many of America’s leading roofing OEMs….
#2 Arvind Rubber
Domain Est. 1998
Website: arvindrubber.com
Key Highlights: Arvind Rubber is a top rubber roller manufacturer, supplier, and exporter in India, delivering high-quality industrial rubber rollers. As a trusted company ……
#3 Roller Manufacturers
Website: rollermanufacturer.com
Key Highlights: You can find and buy direct from the top roller manufacturers and suppliers that are producing excellent, efficient, unique industrial roller designs….
#4
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1919
Website: passaic.com
Key Highlights: Family owned and operated since 1919, Passaic Rubber always supplies the best results for all your rubber manufacturing needs….
#5 Specialized in industrial roller rubber coating
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1998
Website: silgum.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to our official website! SILGUM S.r.l. has been operating since 1998 in the specialized field of rubber roller coating, gaining consolidated ……
#6 Custom Rubber Roller Products & Industrial Rubber Rolls
Domain Est. 2004
Website: harwoodrubber.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture top-quality industrial rubber rollers and customized rubber products, and offer rubber roller resurfacing and recovering services….
#7 Rubber Roller Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ctsindustries.com
Key Highlights: We are the only Rubber Roller Facility that manufactures our product from start to finish in 10 days or less AND with 10+ years employment per employee here!…
#8 Custom Molded Rubber Rollers & Molded Precision Parts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rol-tec.com
Key Highlights: Rol-Tec has the most complete product line to manufacture every aspect of your custom molded rubber roller or molded part. Contact us for more information ……
#9 Rubber Rollers / Chrome Rollers Manufacturing and Reconditioning
Domain Est. 2010 | Founded: 1959
Website: abbaroller.com
Key Highlights: Since 1959, ABBA Roller has been the world-leading provider of Critical-To-Function, (CTF) high-precision, rotary components….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rolling Rubber

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Rolling Rubber
Based on current industry trajectories, technological advancements, and macroeconomic factors, the second half of 2026 presents a dynamic and evolving landscape for Rolling Rubber, a leading specialty rubber compounding company. This analysis focuses on key trends shaping the market and their implications.
1. Accelerating Demand in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Advanced Mobility
- Trend: The global EV market continues its rapid expansion, driven by stricter emissions regulations (e.g., Euro 7, US CAFE standards), falling battery costs, and expanding charging infrastructure. This directly impacts Rolling Rubber’s core markets.
- Impact on Rolling Rubber: Demand for specialized rubber compounds is surging, particularly for:
- High-Performance Seals & Hoses: Requiring enhanced thermal stability, chemical resistance (for coolants, battery electrolytes), and long-term durability under demanding under-hood conditions in EVs (inverter cooling, battery thermal management).
- NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) Solutions: EVs are quieter, making component noise more noticeable. Advanced elastomers for bushings, mounts, and damping components are critical for premium ride quality.
- Battery Encapsulation & Protection: Developing compounds for gaskets, seals, and protective layers within battery packs that resist moisture, thermal runaway, and potential chemical exposure.
- Opportunity: Position Rolling Rubber as a solutions provider for EV-specific challenges. Invest in R&D for next-gen EV compounds and form strategic partnerships with tier-1 suppliers serving major EV OEMs.
2. Intensified Focus on Sustainability and Circularity
- Trend: Regulatory pressure (Extended Producer Responsibility, carbon taxes) and consumer/investor ESG demands are forcing the automotive and manufacturing sectors towards circularity. Bio-based materials, recyclability, and reduced carbon footprint are paramount.
- Impact on Rolling Rubber:
- Material Sourcing: Increased demand for high-performance rubber compounds incorporating bio-based feedstocks (e.g., bio-oils, natural rubber derivatives) and recycled rubber content without compromising performance.
- End-of-Life Management: Growing focus on designing for disassembly and recyclability. Rolling Rubber may face pressure to develop compounds that are easier to separate or recycle, or to offer take-back/recycling programs.
- Carbon Accounting: Customers (OEMs, Tier 1s) will demand detailed carbon footprint data for supplied materials. Transparency in the supply chain is crucial.
- Opportunity: Invest in R&D for sustainable compound formulations (bio-based, higher recycled content). Develop robust carbon accounting systems. Market “green” compound lines as a competitive differentiator. Explore partnerships with recycling technology firms.
3. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
- Trend: Geopolitical instability and lessons from past disruptions continue to drive efforts towards supply chain diversification and regionalization (“friend-shoring,” “near-shoring”).
- Impact on Rolling Rubber:
- Raw Material Sourcing: Potential for volatility in key raw materials (synthetic rubber, specialty chemicals, fillers). Need for diversified supplier base and strategic inventory management.
- Manufacturing Footprint: Customers may prefer suppliers with regional production capabilities to reduce logistics risks and costs. Rolling Rubber may need to evaluate capacity in key markets (North America, Europe, potentially Southeast Asia).
- Logistics: Focus on optimizing logistics networks for efficiency and resilience, potentially leveraging near-term regional hubs.
- Opportunity: Strengthen relationships with diverse raw material suppliers. Evaluate strategic investments in regional manufacturing or partnerships. Enhance supply chain visibility and risk management tools.
4. Advanced Materials and Digital Integration
- Trend: Integration of Industry 4.0 and the development of “smart” materials are gaining traction.
- Impact on Rolling Rubber:
- Material Innovation: Development of compounds with enhanced properties (e.g., self-healing elastomers, conductive rubbers for sensors, materials with embedded functionality) remains a key differentiator.
- Digitalization: Increased use of AI/ML in compound formulation optimization, predictive maintenance in manufacturing, and digital twins for process simulation. Customers may demand digital product passports.
- Precision Manufacturing: Demand for tighter tolerances and consistency, driven by automated assembly lines and quality requirements.
- Opportunity: Increase R&D investment in next-generation functional materials. Implement advanced digital tools (AI, IoT) across R&D, production, and quality control to improve efficiency, consistency, and speed to market.
5. Competitive Landscape Evolution
- Trend: The specialty rubber market remains competitive, with large global players and agile niche innovators. Competition is shifting beyond price to include technology, sustainability credentials, and supply chain reliability.
- Impact on Rolling Rubber: Need to continuously differentiate through superior technical service, innovative solutions (especially for EVs and sustainability), and strong customer partnerships. Price pressure may persist in commoditized segments.
- Opportunity: Leverage technical expertise as a key selling point. Focus on high-value, application-specific solutions. Build long-term partnerships based on co-development and reliability.
Conclusion for Rolling Rubber (H2 2026 Outlook):
The H2 2026 market presents significant growth opportunities for Rolling Rubber, primarily driven by the unstoppable shift towards electrification and the imperative of sustainability. Success will hinge on the company’s ability to:
- Lead in EV Solutions: Become the go-to partner for high-performance, durable rubber components critical to next-generation EVs.
- Embed Sustainability: Make sustainability core to its product portfolio, operations, and reporting, moving beyond compliance to innovation.
- Enhance Resilience: Build a robust, transparent, and responsive supply chain capable of navigating global uncertainties.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize digital tools and advanced materials science to drive innovation, efficiency, and quality.
- Differentiate Strategically: Compete on value, innovation, and partnership, not just cost.
By proactively addressing these converging trends, Rolling Rubber can strengthen its market position and achieve sustainable growth in the dynamic second half of 2026 and beyond.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Rolling Rubber (Quality, IP)
Sourcing rolling rubber—commonly used in conveyor belts, seals, rollers, and industrial wheels—presents several challenges related to material quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to performance failures, safety risks, and legal complications.
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is receiving rubber that does not meet required physical or chemical specifications. Suppliers may provide inconsistent hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation, or resistance to abrasion, heat, or chemicals. This variability often stems from substandard raw materials, poor manufacturing processes, or lack of quality control. Using low-grade rubber can result in premature wear, cracking, or failure under operational stress.
Misrepresentation of Rubber Compound Formulation
Some suppliers may misrepresent the type or grade of rubber compound (e.g., claiming EPDM when supplying inferior synthetic blends). This mislabeling not only compromises performance but may also violate industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Without proper material certification or third-party testing, buyers risk sourcing materials unsuitable for their specific application environment.
Lack of Traceability and Certifications
Reputable rolling rubber should come with full traceability, including batch numbers, material safety data sheets (MSDS), and compliance certifications (e.g., FDA, REACH, RoHS). Sourcing from vendors who cannot provide these documents increases the risk of regulatory non-compliance and makes it difficult to address quality issues post-delivery.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Using or sourcing rubber components based on proprietary formulations or patented designs without authorization can lead to IP violations. Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” products that closely mimic patented compounds or roller designs. While marketed as cost-effective alternatives, these may infringe on existing patents, exposing the buyer to legal liability, product recalls, or import bans.
Inadequate Testing and Validation
Failing to conduct in-house or third-party testing—such as durometer checks, aging tests, or dynamic performance evaluations—can result in undetected defects. Relying solely on supplier claims without independent validation increases the risk of field failures, especially in high-stress or safety-critical applications.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Opaque supply chains, particularly with offshore or secondary suppliers, increase the risk of counterfeit or recycled rubber being passed off as virgin material. Without direct oversight or audits, buyers may unknowingly source from unauthorized subcontractors using unapproved processes.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should prioritize suppliers with transparent processes, verifiable certifications, and a history of IP compliance. Conducting due diligence, requiring material test reports, and consulting legal experts on IP matters are essential steps in securing reliable, high-quality rolling rubber.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rolling Rubber
This comprehensive guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, storing, and disposing of rolling rubber products—such as rubber wheels, casters, tires, and related components—throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance Framework
Ensure all operations adhere to relevant international, national, and regional regulations, including:
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals—verify that rubber formulations do not contain substances of very high concern (SVHC).
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances—applicable if rolling rubber components are used in electrical or electronic equipment.
– TSCA (USA): Toxic Substances Control Act—ensure compliance with chemical reporting and restrictions.
– DOT & FMVSS (USA): Department of Transportation and Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards—critical for rubber tires used in transportation.
– IMO & IMDG Code: For international maritime transport of rubber goods, especially if classified as hazardous due to flammability or chemical additives.
– Local Environmental Regulations: Compliance with waste disposal, recycling, and emissions standards in each operational region.
Transportation & Shipping Requirements
Rolling rubber must be transported safely and efficiently, considering its physical properties and potential hazards:
– Packaging Standards: Use durable, weather-resistant packaging to prevent deformation, moisture damage, or contamination. Secure individual units to avoid shifting during transit.
– Load Securing: When shipping palletized rubber goods, ensure proper strapping and corner protection to prevent movement in trucks, containers, or railcars.
– Hazard Classification: Natural and synthetic rubber may be classified as flammable solids (UN 2956, Class 4.1) under certain conditions. Verify classification and label shipments accordingly.
– Temperature Control: Avoid exposure to extreme heat or cold during transit, which may degrade rubber compounds or affect performance.
– Documentation: Provide accurate shipping manifests, safety data sheets (SDS), and compliance certificates (e.g., ISO, ASTM) with each shipment.
Storage & Handling Procedures
Proper storage is essential to maintain product integrity and ensure workplace safety:
– Storage Environment: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight, ozone sources (e.g., electric motors), and heat-generating equipment.
– Shelf Life Management: Monitor expiration dates; most rubber products have a recommended shelf life of 3–5 years. Practice FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory rotation.
– Stacking Guidelines: Do not exceed manufacturer-recommended stacking heights to prevent deformation. Use pallets and avoid direct floor contact to reduce moisture absorption.
– Segregation: Keep rubber materials separate from oils, solvents, acids, and other chemicals that may cause degradation or contamination.
Import/Export Considerations
Cross-border movement of rolling rubber requires attention to trade regulations:
– Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Harmonized System (HS) codes for rubber wheels or tires (e.g., 8708.29 or 4011) must be correctly applied.
– Duty & Tariff Classification: Verify tariff rates and preferential treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU trade deals).
– Sanitary & Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures: While typically not applicable to synthetic rubber, natural rubber products may require inspection or certification depending on country of origin and destination.
– Export Controls: Confirm that no rolling rubber components contain controlled materials or technologies subject to export restrictions.
Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS) Guidelines
Prioritize worker safety and environmental protection:
– Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide gloves, eye protection, and respiratory equipment when handling powdered rubber or during cutting/machining processes.
– Fire Safety: Rubber is combustible. Maintain fire suppression systems (e.g., sprinklers) and prohibit open flames in storage areas.
– Waste Management: Recycle scrap rubber where possible. Dispose of non-recyclable waste in accordance with local hazardous or solid waste regulations.
– Spill & Leak Response: Establish procedures for cleaning up rubber dust or chemical residues from processing; use HEPA vacuums for fine particulates.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain compliance and customer trust through robust quality systems:
– Batch Tracking: Implement a system to trace raw materials and finished goods by lot number to support recalls or compliance audits.
– Testing & Certification: Conduct regular quality checks per ASTM, ISO, or customer-specific standards (e.g., load capacity, durometer hardness, abrasion resistance).
– Supplier Compliance: Require suppliers of raw rubber and additives to provide SDS and compliance documentation.
Sustainability & End-of-Life Management
Support circular economy principles:
– Recycling Programs: Partner with certified rubber recyclers for end-of-life products. Promote take-back programs where feasible.
– Eco-Design: Encourage the use of recyclable or bio-based rubber compounds in product development.
– Carbon Footprint Reduction: Optimize logistics routes, use sustainable packaging, and report environmental metrics in line with ESG goals.
By adhering to this Logistics & Compliance Guide, Rolling Rubber operations can ensure regulatory adherence, operational efficiency, and environmental responsibility across the product lifecycle.
Conclusion for Sourcing Rolling Rubber:
In conclusion, sourcing rolling rubber requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, supplier reliability, and sustainability. Selecting the right type of rubber—whether natural, synthetic, or a specialized compound—depends on the specific application requirements such as durability, elasticity, temperature resistance, and load-bearing capacity. Establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers, conducting thorough due diligence, and considering factors like material certifications, production standards, and logistics is essential to ensure consistent supply and performance.
Additionally, with increasing emphasis on environmental responsibility, evaluating the sustainability of rubber sources—including ethical sourcing practices and recyclability—can enhance long-term value and brand reputation. By implementing a well-structured sourcing strategy, businesses can secure high-performing rolling rubber materials that support operational efficiency, product reliability, and competitive advantage in the market.