The global demand for RoHS-compliant batteries has surged in recent years, driven by tightening environmental regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainable electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global RoHS compliance market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.5% from 2023 to 2028, with the electronics and energy storage sectors being key contributors. This growth is further amplified by the expansion of electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems—all of which require environmentally safe, lead-free, and hazardous-substance-compliant battery solutions. As regulatory frameworks like the European Union’s RoHS directive continue to influence global manufacturing standards, battery producers are increasingly prioritizing compliance to access international markets. With over 50% of manufacturers in key regions now aligning with RoHS standards, identifying leading suppliers who combine regulatory adherence with innovation and scale has become critical for OEMs and procurement teams. Based on market presence, compliance consistency, and technological capabilities, the following eight manufacturers stand out as top producers of RoHS-certified batteries.
Top 8 Rohs Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Rohs Bluetooth Manufacturers and Factory, Suppliers
Domain Est. 2004
Website: anbotek.com
Key Highlights: Rohs Bluetooth Manufacturers, Factory, Suppliers From China, Welcome to make contact with us if you’re fascinated inside our product, we are going to ……
#2 Discover Battery
Domain Est. 2007
Website: discoverbattery.com
Key Highlights: An international manufacturing and engineering company that provides leading-edge battery technology for transportation, motive power, and energy storage ……
#3 RoHs
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: It is a page about RoHs | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd … Official Social Media. LinkedIn. Products · Solutions · Applications · Support · FAQs · PDF Catalog ……
#4 RHY Battery
Domain Est. 2017
Website: rhybattery.com
Key Highlights: RHY Battery is a professional manufacturer focus on designing and producing battery packs and chargers. Our custom battery packs and chargers are widely ……
#5 Grand Teton Energy Systems
Website: grandteton.energy
Key Highlights: We specialize in custom battery systems and bulk orders for demanding applications like marine, RV, UPS systems, golf carts, industrial, and medical equipment….
#6 2026 RoHS, REACH, WEEE, Battery Compliance, Hazmat …
Domain Est. 2005
Website: rohsguide.com
Key Highlights: RoHSGuide is the authoritative resource on RoHS, REACH, WEEE, Battery, and hazardous process materials. RoHSGuide explains how compliance, ……
#7 What’s the RoHS Certification of Li Polymer Battery?
Domain Est. 2019
Website: li-polymer-battery.com
Key Highlights: RoHS Certification of Li Polymer Battery RoHS is a mandatory standard established by EU legislation. Its full name is “Restriction of Hazardous Substances”….
#8 China Taiwan Lithium Battery Devices Must Comply with RoHS …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: chemradar.com
Key Highlights: These devices will be managed according to the standards related to the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) in electrical and electronic ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rohs Battery

H2: 2026 Market Trends for RoHS-Compliant Batteries
By 2026, the market for RoHS (Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment) compliant batteries is expected to experience robust growth, driven by stringent regulations, technological advancements, and shifting consumer and industrial demands. Here’s a detailed analysis of the key trends shaping this market:
1. Regulatory Pressure Intensifies Globally
RoHS regulations, particularly EU RoHS 3 (2015/863), already restrict the use of substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain phthalates in batteries. By 2026:
– Expanded compliance requirements are expected, with more countries adopting or tightening RoHS-like standards (e.g., China RoHS, UK REACH, and similar frameworks in Southeast Asia and Latin America).
– Stricter enforcement will increase the demand for certified, traceable RoHS-compliant battery components.
– Upcoming EU Battery Regulation (2023) will mandate carbon footprint declarations, recycled content targets, and enhanced chemical safety, reinforcing RoHS principles and pushing manufacturers toward cleaner chemistries.
2. Shift Toward Safer, Sustainable Chemistries
The phase-out of hazardous substances is accelerating innovation:
– Lithium-ion dominance continues, with cobalt reduction and increased use of LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries, which are inherently safer, longer-lasting, and more RoHS-friendly due to lower toxicity.
– Solid-state batteries are expected to enter early commercialization, offering higher energy density and eliminating liquid electrolytes containing hazardous substances.
– Sodium-ion batteries gain traction as a sustainable alternative, especially for stationary storage, due to abundant materials and non-toxic components.
3. Growth in High-Demand Sectors
RoHS-compliant batteries are critical in industries with strict environmental and safety standards:
– Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, wearables, and laptops continue to demand compact, safe, and recyclable batteries.
– Electric Vehicles (EVs): The global EV boom drives demand for RoHS-compliant traction batteries. By 2026, over 40% of new EVs sold are expected to use LFP batteries—ideal for RoHS compliance.
– Renewable Energy Storage: Grid-scale and home energy storage systems require large volumes of compliant batteries, favoring non-toxic and recyclable options.
4. Circular Economy and Recycling Imperatives
RoHS compliance is increasingly linked with end-of-life management:
– Battery passport initiatives (mandated under EU regulations) will require full material disclosure, traceability, and recycling instructions—enhancing RoHS accountability.
– Closed-loop recycling systems are expected to grow, with >50% of cobalt and >70% of lithium targeted for recovery by 2026, reducing reliance on virgin, potentially hazardous materials.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Compliance Costs
Manufacturers face rising pressure to:
– Audit supply chains for RoHS compliance, especially for raw materials like graphite, electrolytes, and cathode components.
– Invest in testing and certification, increasing short-term costs but reducing regulatory and reputational risks.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
- Europe and North America remain strictest enforcers, setting global benchmarks.
- Asia-Pacific (especially China, South Korea, Japan) dominates production and innovation, with local RoHS alignment becoming a competitive advantage.
- Emerging markets adopt RoHS standards gradually, creating both challenges and opportunities for compliant exporters.
Conclusion
By 2026, the RoHS-compliant battery market will be defined by regulatory rigor, technological innovation, and sustainability imperatives. Companies that proactively invest in cleaner chemistries, supply chain transparency, and recycling infrastructure will lead the market. The convergence of RoHS with broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals will make compliance not just a legal requirement, but a strategic differentiator in the global battery economy.
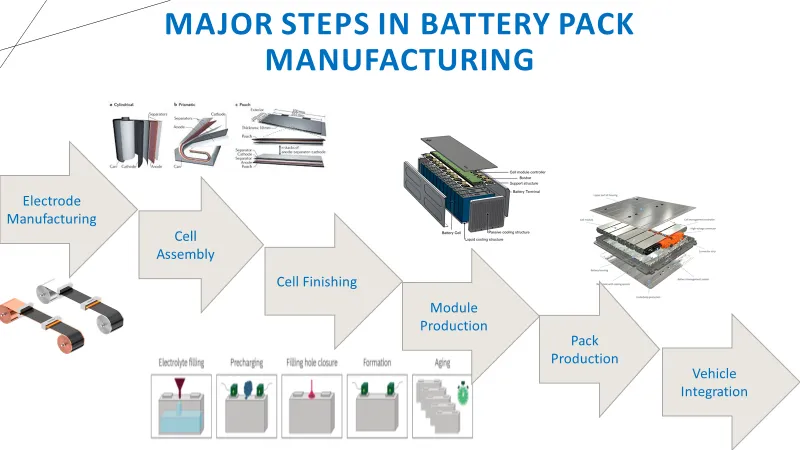
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing RoHS-Compliant Batteries (Quality & IP)
Sourcing RoHS-compliant batteries involves more than just checking a certification box. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to significant risks, including product failures, regulatory non-compliance, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Misunderstanding RoHS Scope: Assuming RoHS compliance automatically guarantees overall battery quality or safety. RoHS restricts hazardous substances (like lead, cadmium, mercury) but does not cover performance, lifespan, safety (e.g., thermal runaway), or reliability. A battery can be RoHS-compliant yet still be poorly manufactured or unsafe.
- Inadequate Supplier Vetting: Relying solely on supplier claims or generic RoHS certificates without verifying the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), and traceability processes. Unreliable suppliers may provide inconsistent quality or falsify documentation.
- Lack of Material Traceability: Failing to ensure the supplier can provide full material declarations (e.g., via IPC-1752 standard) and traceability back to raw materials. This is crucial for verifying RoHS compliance throughout the supply chain and identifying contamination risks.
- Insufficient Testing and Validation: Not conducting independent testing (e.g., IEC 62133 for safety, performance testing) or batch verification to confirm both RoHS compliance (via XRF screening or lab testing) and functional quality. Certificates can become outdated or inaccurate.
- Counterfeit or Substandard Components: Sourcing from unauthorized distributors or the grey market, increasing the risk of receiving counterfeit batteries that may not meet RoHS requirements or safety standards, posing serious safety hazards.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
- Infringing on Patented Technology: Unknowingly sourcing batteries that incorporate patented cell designs, chemistries (e.g., specific lithium-ion formulations), or manufacturing processes without proper licensing. This can lead to costly lawsuits, import bans, and product recalls.
- Using Counterfeit Branded Batteries: Purchasing batteries that falsely bear the logos or part numbers of reputable brands (e.g., Samsung, LG, Panasonic). This not only violates trademark laws but also guarantees poor quality and non-compliance.
- Lack of IP Due Diligence: Failing to require suppliers to warrant that their batteries do not infringe third-party IP rights or to provide evidence of freedom-to-operate (FTO). Contracts often lack strong IP indemnification clauses.
- Design Copying Risks: Sourcing generic batteries that are too closely modeled on a competitor’s patented product design or packaging, potentially leading to design patent or trade dress infringement claims.
- Unclear Ownership of Custom Designs: If working with a supplier on a custom battery solution, not having clear contractual agreements defining IP ownership of the resulting design, specifications, or tooling, leading to disputes or loss of control.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier audits (on-site or virtual) focusing on quality systems and compliance processes.
- Require detailed, up-to-date RoHS compliance documentation (including full material declarations and test reports) for each batch.
- Implement a robust testing program for both compliance and performance.
- Source from authorized distributors or directly from reputable manufacturers.
- Perform IP landscape searches or consult legal counsel to assess infringement risks for critical components.
- Include strong contractual clauses covering IP warranties, indemnification, and compliance obligations.
- Maintain clear records of sourcing decisions, certifications, and testing results for audit purposes.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can ensure they source reliable, compliant, and legally sound RoHS batteries, minimizing risk and protecting their brand.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for RoHS-Compliant Batteries
Ensuring the safe and compliant transportation, storage, and handling of batteries while adhering to the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive is critical. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for RoHS-compliant batteries.
H2: Regulatory Compliance & Documentation
- RoHS Declaration of Conformity (DoC): Maintain a valid and up-to-date DoC for every battery type, explicitly stating compliance with Directive 2011/65/EU (RoHS 2) and its amendments. This is the primary compliance document.
- Substance Declarations: Obtain and retain detailed substance concentration declarations from battery manufacturers/suppliers, confirming lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted substances are below RoHS limits.
- Battery Directive (2006/66/EC): Comply with relevant aspects of the EU Battery Directive, including labeling requirements (crossed-out wheeled bin symbol, chemical symbols for Pb, Cd, Hg if applicable), collection, and recycling obligations. Note: RoHS restricts substances within the battery; the Battery Directive governs lifecycle management.
- REACH & Other Regulations: Be aware of overlapping regulations like REACH (SVHCs) and national battery labeling/recycling laws (e.g., WEEE in the EU, state laws in the US).
- Transport Documentation: Ensure Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are RoHS-compliant and readily available. Include RoHS compliance status in shipping manifests and commercial invoices where required by customers or regulations.
H2: Packaging & Labeling
- RoHS Marking: While RoHS itself doesn’t mandate a specific mark on the battery, the CE marking on the final product (or sometimes the battery pack) signifies conformity, including RoHS. Ensure packaging reflects the compliance status as per internal or customer requirements.
- Hazard Communication: Use appropriate transport hazard labels (e.g., UN numbers, Class 9 hazard labels for lithium batteries – UN 3090, UN 3480, etc.) as per IATA DGR, IMDG Code, or ADR regulations. Crucially, RoHS compliance does not eliminate transport hazards.
- Battery Directive Labeling: Apply the mandatory crossed-out wheeled bin symbol (⌀ ≥ 3% of surface area, min 1cm²) and chemical symbols (Pb, Cd, Hg) on the battery itself or its smallest packaging unit if the battery contains above threshold levels of these substances (though RoHS aims to minimize this).
- Secure Packaging: Use robust, non-conductive packaging designed to prevent short circuits (e.g., individual pouches, terminal protection, rigid outer boxes). Packaging must withstand transport conditions (stacking, vibration, moisture).
H2: Storage & Handling
- Environment: Store batteries in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and flammable materials. Temperature control is vital for safety and longevity, especially for Li-ion.
- Separation: Store different battery chemistries (e.g., Li-ion, NiMH, Lead-acid) separately. Keep charged and discharged batteries apart if possible. Isolate damaged or recalled batteries immediately.
- Short Circuit Prevention: Never allow loose batteries to contact conductive materials (metal, keys, coins). Keep terminals protected. Use non-conductive dividers in storage containers.
- Stock Rotation: Implement a strict First-In, First-Out (FIFO) system to minimize the risk of shipping outdated or degraded batteries.
- Handling Procedures: Train personnel on safe handling, emphasizing avoiding physical damage (punctures, crushing), preventing short circuits, and recognizing signs of damage (bulging, leakage, heat). Use appropriate PPE if handling damaged batteries.
H2: Transportation
- Regulatory Adherence: Strictly follow the latest editions of IATA DGR (air), IMDG Code (sea), or ADR (road) regulations based on battery type (lithium content, state of charge), packaging, and quantity. RoHS compliance is separate from these safety regulations.
- State of Charge (SoC): For air transport of lithium batteries, adhere to SoC limits (typically ≤30% for standalone batteries shipped with equipment, ≤30% for spares). Document SoC testing if required.
- Packaging Certification: Use packaging that meets the performance standards (e.g., UN 38.3 testing for lithium batteries) and is properly marked.
- Documentation: Provide accurate shipping papers, including proper shipping name, UN number, hazard class, packing group, and emergency contact information. Include RoHS DoC upon request.
- Carrier Notification: Inform carriers in advance about shipping batteries, especially lithium types, to ensure they accept the shipment and apply correct handling procedures.
H2: End-of-Life & Returns
- Collection & Recycling: Establish clear procedures for collecting end-of-life batteries from customers or within operations. Partner with certified battery recyclers compliant with WEEE/Battery Directive requirements.
- RoHS in EoL: Ensure recyclers have processes to handle RoHS-compliant materials appropriately, even though restricted substances are minimized.
- Return Handling: Treat returned batteries (especially damaged ones) as potentially hazardous. Inspect carefully, store securely in designated areas, and follow specific protocols for disposal or recycling. Document returns.
- Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive records of RoHS DoCs, substance declarations, shipping manifests (including transport compliance), recycling certificates, and return logs for the legally required period (often 10+ years).
Key Takeaway: RoHS compliance focuses on the composition of the battery. Logistics must simultaneously manage the inherent safety hazards of batteries during transport and storage (governed by IATA/IMDG/ADR) and the environmental lifecycle obligations (governed by the Battery Directive/WEEE). Robust documentation, proper packaging, trained personnel, and adherence to all relevant regulations are essential.
Conclusion for Sourcing RoHS-Compliant Batteries
In conclusion, sourcing RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliant batteries is a critical step in ensuring environmental responsibility, regulatory compliance, and product safety. As global regulations continue to tighten around hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium, selecting RoHS-certified batteries helps manufacturers meet legal requirements and avoid penalties, especially in markets like the European Union.
RoHS-compliant batteries not only reduce environmental impact and support sustainable practices but also enhance brand reputation by demonstrating a commitment to health and safety standards. When sourcing, it is essential to verify supplier certifications, obtain accurate Declarations of Conformity (DoC), and conduct regular audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
Moreover, advancements in battery technology have made RoHS-compliant options—such as lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride—readily available without compromising performance. Therefore, integrating RoHS-compliant batteries into product designs supports innovation while aligning with environmental directives and global market demands.
Ultimately, prioritizing RoHS-compliant battery sourcing is not just a regulatory necessity but a strategic advantage in today’s environmentally conscious and highly regulated electronics industry.