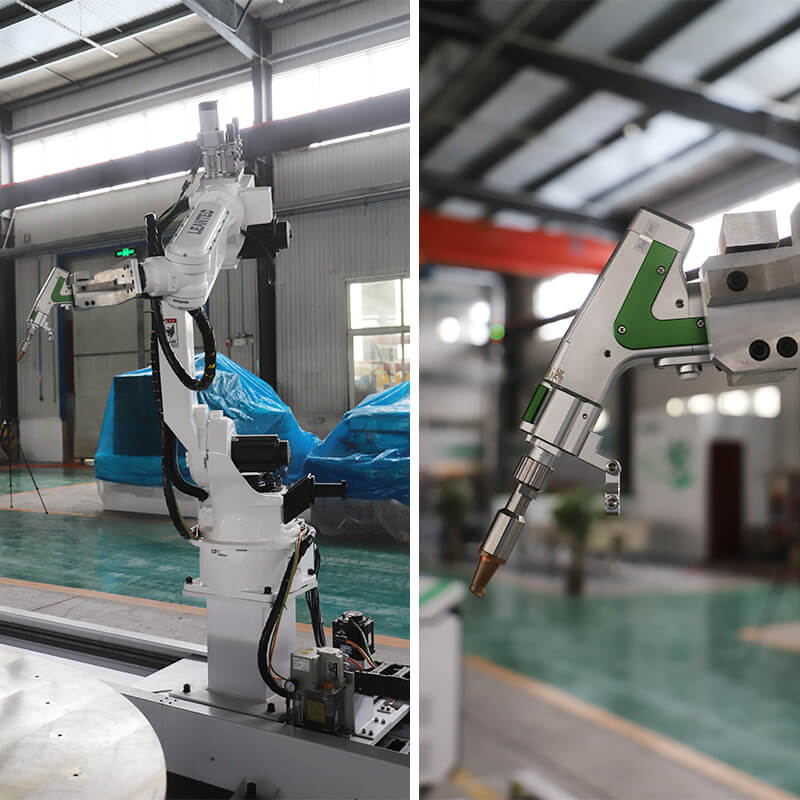
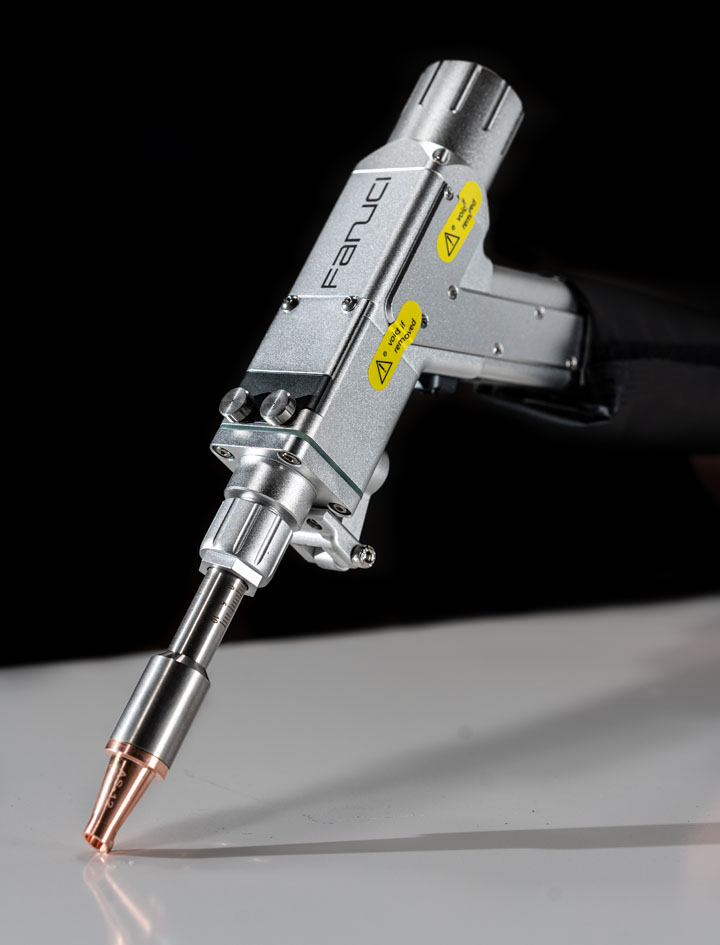
The global robotic laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision, efficiency, and automation in manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the industrial robotics market—which includes robotic laser welding systems—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in laser technology and the integration of AI-driven automation. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.4% through 2030, with robotic integration being a key growth driver. As manufacturers seek to enhance weld quality, reduce cycle times, and lower operational costs, the adoption of robotic laser welding systems has become a strategic imperative. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and scalable solutions to meet the demands of modern production environments. Here are the top 8 robotic laser welder manufacturers shaping the future of industrial automation.
Top 8 Robotic Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
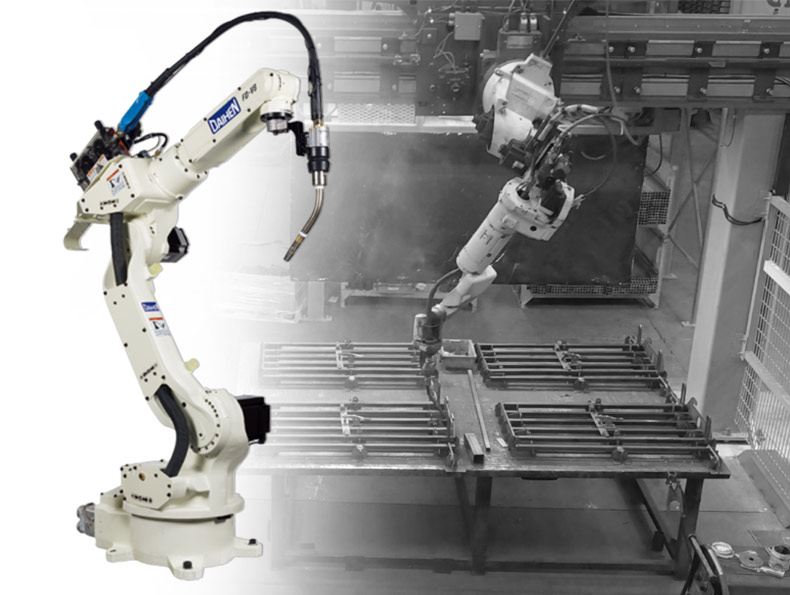
#1 OTC DAIHEN, Inc. USA Robotic Welding Solutions
Website: daihen-usa.com
Key Highlights: OTC DAIHEN is the world’s No. 1 manufacturer of arc welding robots. At OTC DAIHEN USA, we are a true single-source solution provider….
#2 IPG Genesis
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: As part of IPG Photonics, we combine Genesis’ proven integration expertise with IPG’s world-leading laser technology to provide complete, reliable robotic ……
#3 Robotic Laser Welding
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: First, visit the manufacturer’s or supplier’s official website, such as laser-welder.net, and navigate to the product category or shop page ……
#4 MIG, TIG, Robotic, & Laser Welding Solutions
Website: binzel-abicor.com
Key Highlights: Explore ABICOR BINZEL USA for advanced welding solutions. We offer MIG, TIG robotic, and laser welding technologies, along with MIG guns and robotic torches ……
#5 Welding Machines / Robots / Lasers
Website: connect.panasonic.com
Key Highlights: Introduction of various automation, demonstration and solution cases and products using Panasonic welding machines, robot systems, etc….
#6 Robotic Welding Equipment and Automation Solutions
Website: lincolnelectric.com
Key Highlights: Lincoln Electric provides a wide range of robotic welding equipment and automation solutions to help you improve your welding productivity and quality….
#7 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#8 LW
Website: blmgroup.com
Key Highlights: Highly automated robotic laser welding system. Welding in 4 modes. Up to 10 degrees of freedom. Layout configurable according to your needs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Robotic Laser Welder
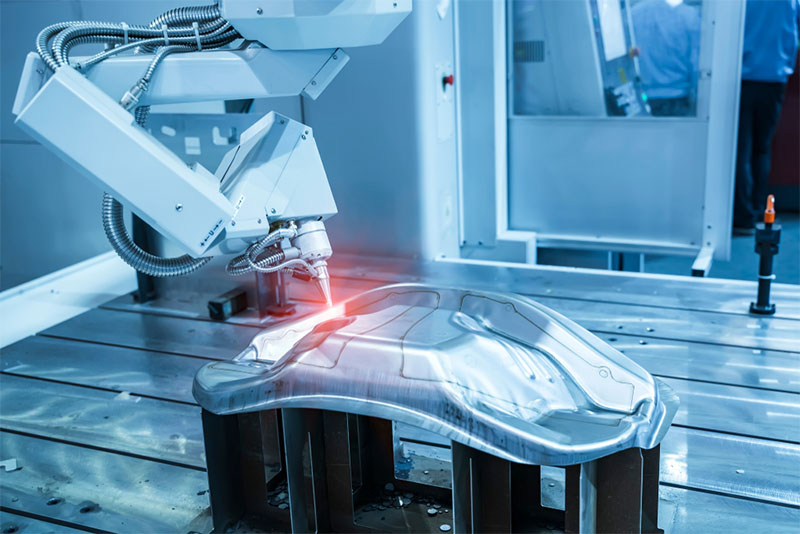

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Robotic Laser Welding
The robotic laser welding market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and macroeconomic shifts. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
-
Accelerated Adoption in EV and Battery Manufacturing: The explosive growth of the electric vehicle (EV) industry will be the primary driver. Robotic laser welding is essential for high-speed, precision welding of battery cells (especially tab welding), busbars, and lightweight aluminum chassis components. Demand for improved battery safety, energy density, and production throughput will push manufacturers to invest heavily in automated laser welding cells, making this sector the fastest-growing application segment.
-
Integration of Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Beyond basic automation, robotic laser welders will increasingly incorporate sophisticated AI for real-time process optimization and predictive maintenance. AI algorithms will analyze sensor data (e.g., from cameras, spectrometers, force sensors) to dynamically adjust parameters (power, speed, focus) during welding, compensating for minor fit-up variations and ensuring consistent, high-quality welds. ML will predict component wear and schedule maintenance, minimizing unplanned downtime.
-
Rise of Hybrid and Multi-Process Systems: To maximize flexibility and efficiency on complex parts, robotic cells will increasingly integrate laser welding with other processes like arc welding (MIG/MAG, TIG), laser brazing, or even additive manufacturing. This “multi-tool” approach allows a single robot to perform various joining operations in one setup, reducing cycle times and capital expenditure for manufacturers dealing with diverse component geometries and material combinations.
-
Focus on Process Monitoring and Closed-Loop Control: Ensuring weld quality and traceability will be paramount, especially in regulated industries (automotive, aerospace). Advanced in-process monitoring systems (coaxial cameras, plasma monitoring, seam tracking) will become standard. True closed-loop control systems, where sensor feedback instantly corrects the welding process, will move from niche applications to broader industrial use, guaranteeing defect-free welds and enabling full traceability for quality assurance.
-
Increased Emphasis on Flexibility and Ease of Programming: As production volumes for individual models fluctuate and customization increases, manufacturers demand faster changeovers. Trends include:
- Enhanced Offline Programming (OLP) & Simulation: More intuitive, physics-based simulation software allowing virtual commissioning and rapid program generation.
- Improved Path Planning & Collision Avoidance: Smarter software for complex 3D paths and automatic collision checking.
- Simplified User Interfaces (HMI): More intuitive touchscreens and programming interfaces, reducing the skill barrier for operators and technicians.
-
Growth of High-Power and Blue/Green Wavelength Lasers: Adoption of higher-power fiber lasers (>10 kW) will enable faster welding speeds and deeper penetration, boosting productivity. Crucially, blue (450nm) and green (515nm) wavelength lasers will gain significant traction, particularly in EV battery manufacturing. These wavelengths are absorbed much more efficiently by highly reflective materials like copper and aluminum (ubiquitous in batteries and electronics), enabling stable, high-quality welding that traditional infrared lasers struggle with.
-
Expansion into New Materials and Industries: While automotive remains dominant, applications will broaden. This includes:
- Aerospace: Welding lightweight titanium and advanced alloys for structural components.
- Medical Devices: Precision welding of intricate, miniaturized components requiring high cleanliness and strength.
- Consumer Electronics: Joining housings and internal components for smartphones, wearables, and laptops.
- Heavy Industry & Energy: Welding thick-section steels for pipelines, pressure vessels, and renewable energy infrastructure (e.g., wind turbine components).
-
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus: Manufacturers will increasingly prioritize the energy efficiency of laser sources (fiber lasers are inherently more efficient than CO2 or arc processes) and the overall reduced material waste (due to precision and narrow heat-affected zones) offered by robotic laser welding. This aligns with corporate sustainability goals and reduces operational costs.
-
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization: Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions will drive efforts to localize production, particularly in North America and Europe. This will create opportunities for regional manufacturing of robotic laser welding systems and components, potentially increasing investment in domestic automation capabilities.
-
Workforce Evolution: The increased complexity will shift the workforce needs. Demand will grow for technicians and engineers skilled in robotics, laser physics, AI/ML integration, and data analysis, rather than just traditional welding skills. Upskilling programs will be crucial.
Conclusion for H2 2026: The robotic laser welding market in 2026 will be characterized by smarter, faster, more flexible, and more integrated systems. Driven overwhelmingly by the EV revolution and powered by AI, advanced sensing, and new laser technologies (especially blue/green), the focus will be on achieving unprecedented levels of quality, productivity, and traceability. Success will depend on vendors offering holistic solutions combining robust hardware, intelligent software, and deep application expertise, while users adapt their operations and workforce to leverage this advanced automation effectively.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Robotic Laser Welder: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing a robotic laser welding system is a significant investment that demands careful due diligence. While these systems offer precision, speed, and repeatability, overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly failures, production delays, and legal exposure. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Underestimating the Importance of Laser Source Quality and Reliability
The laser source is the heart of the system. Choosing a lower-cost, unproven, or poorly maintained laser source is a major quality pitfall. Low-quality lasers often suffer from inconsistent beam quality, unstable power output, shorter lifespans, and higher maintenance requirements. This directly impacts weld quality (porosity, spatter, lack of fusion) and increases downtime. Always verify the laser manufacturer, model specifications (wavelength, power stability, beam parameter product – BPP), warranty, and service support. Avoid systems using refurbished or undocumented laser sources.
2. Ignoring System Integration and Process Validation
A robotic laser welder is a complex integration of laser, robot, optics, safety systems, and software. A critical pitfall is assuming the supplier will deliver a “plug-and-play” solution that works perfectly out of the box. Poor integration can lead to calibration errors, collision risks, inconsistent weld paths, and software incompatibilities. Insist on a detailed integration plan, witness a validation test run with your specific parts and materials, and verify the supplier provides comprehensive process documentation and training. Never skip the Factory Acceptance Test (FAT).
3. Overlooking Safety Certification and Compliance
Laser welding involves Class 4 lasers, posing severe eye and skin hazards, fire risks, and fume generation. Sourcing a system without proper safety certifications (e.g., ISO 13849, IEC 60825-1, local regulations like OSHA/ANSI Z136 in the US) is a dangerous pitfall. Non-compliant systems lack adequate interlocks, enclosures, emergency stops, and labeling, creating liability and potential shutdowns. Ensure the entire system, including the robot cell enclosure, fume extraction, and laser safety barriers, meets all relevant safety standards and has documented certification.
4. Failing to Secure Clear Ownership and Licensing of Software and IP
This is a critical IP pitfall. The control software, robot path programs, laser parameter recipes, and potentially the mechanical design of custom tooling contain valuable IP. Sourcing agreements often fail to explicitly state who owns what. Key questions must be answered:
* Who owns the source code for the control software?
* Who owns the custom robot welding programs developed for your parts?
* Who owns the optimized laser parameter sets?
* Are you granted a perpetual, transferable license to use and modify the software?
* Are there restrictions on using the system if you switch suppliers?
Avoid agreements where the supplier retains broad IP rights, charges exorbitant fees for software updates or program transfers, or prohibits reverse engineering for maintenance. Ensure your contract grants you full ownership or a robust, unrestricted license to all IP directly related to your processes and data.
5. Neglecting Long-Term Support, Spare Parts, and Technology Lock-in
A poor quality system might be impossible to support long-term. A major pitfall is sourcing from suppliers with limited local support, unreasonably priced or unavailable spare parts (especially for the laser source or specialized optics), or proprietary interfaces. This leads to extended downtime and high operating costs. Furthermore, relying on a supplier with closed, proprietary software creates technology lock-in, making future upgrades, integration with other systems, or switching support providers difficult and expensive. Prioritize suppliers with proven global support networks, transparent spare parts pricing, and open or well-documented communication protocols (like OPC UA).
6. Not Addressing Data Security and Cybersecurity Risks
Modern robotic laser welders are connected industrial IoT devices. A significant, often overlooked, IP and operational risk is cybersecurity. Systems with weak network security, unpatched software, or lack of access controls are vulnerable to hacking, data theft (stealing your proprietary welding recipes), or ransomware attacks that halt production. Ensure the supplier provides systems with robust cybersecurity features (firewalls, user authentication, secure remote access) and a clear patch/update policy. Understand how your process data is stored, accessed, and protected.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls during the sourcing process – through rigorous technical evaluation, thorough contract negotiation, and demanding validation – you can secure a reliable, safe, and legally sound robotic laser welding solution that protects your investment and intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Robotic Laser Welder
Shipping and Handling
Ensure the robotic laser welder is securely crated using industrial-grade packaging materials to prevent damage during transit. Use shock-absorbing padding and secure all moving parts with transit locks. Label crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Heavy Equipment” warnings. Ship via freight carrier experienced in handling precision industrial machinery, and confirm insurance coverage for the full replacement value. Coordinate delivery scheduling with site availability and ensure unloading equipment (e.g., forklift) is on-site.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify that the robotic laser welder complies with export control regulations such as the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), if applicable. Obtain required export licenses based on the destination country and technical specifications (e.g., laser power, control software). For imports, ensure compliance with local customs authorities, including proper Harmonized System (HS) code classification, duty assessment, and documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin).
Safety Standards and Certifications
Confirm the robotic laser welder meets relevant international safety standards prior to deployment. Required certifications typically include CE marking (for EU markets) indicating compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive. In North America, ensure compliance with ANSI Z535 for safety signage and adherence to OSHA and NFPA 79 electrical standards. IEC 60825-1 certification for laser safety is mandatory to classify the laser and define appropriate protective measures.
Installation Site Requirements
Prepare the installation site to meet electrical, ventilation, and spatial requirements. Provide stable power supply matching the voltage and phase specified by the manufacturer (e.g., 480V 3-phase), with proper grounding and surge protection. Ensure adequate clearance around the unit for maintenance and robotic arm movement. Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) if fumes are generated during welding. Designate a controlled access area with safety interlocks, light curtains, and emergency stop buttons compliant with ISO 13849-1 for functional safety.
Laser Safety Compliance
Implement a Laser Safety Program in accordance with ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825 standards. Appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) to oversee compliance. Use appropriate engineering controls, including fully enclosed beam paths, interlocked access panels, and beam shutters. Provide Class-specific laser protective eyewear for personnel and post warning signs at all entry points to the laser operation zone. Conduct regular safety audits and maintain records of laser safety training for operators and maintenance staff.
Environmental and Waste Management
Address environmental compliance related to operational byproducts. Capture and filter welding fumes using certified filtration systems to meet local air quality regulations (e.g., EPA or EU Industrial Emissions Directive). Properly dispose of consumables, such as nozzles and lenses, according to hazardous waste guidelines if contaminated. Minimize noise emissions by enclosing the workstation if necessary, ensuring compliance with occupational noise exposure limits (e.g., OSHA PEL or EU Directive 2003/10/EC).
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive documentation for compliance audits and operational traceability. This includes the machine’s technical file, CE or UL certification documents, risk assessment reports, installation manuals, and safety training records. Keep logs of maintenance, laser output checks, safety system tests, and incident reports. Ensure all documentation is accessible to authorized personnel and updated per regulatory or manufacturer recommendations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Robotic Laser Welder
After thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, and supplier capabilities, sourcing a robotic laser welding system represents a strategic investment in advancing manufacturing precision, consistency, and efficiency. The integration of robotic automation with high-precision laser technology enables superior weld quality, reduced material distortion, and increased throughput—key advantages for high-mix or high-volume production environments.
Careful consideration of factors such as laser power, automation compatibility, safety requirements, and total cost of ownership—including initial investment, maintenance, and operator training—ensures long-term operational success. Engaging with reputable suppliers offering proven technology, comprehensive support, and service networks minimizes downtime and enhances system reliability.
Ultimately, the implementation of a robotic laser welder aligns with goals of improving product quality, optimizing labor resources, and strengthening competitive advantage in advanced manufacturing. With proper planning and vendor selection, this technology will deliver a strong return on investment and position the organization for future growth and innovation.