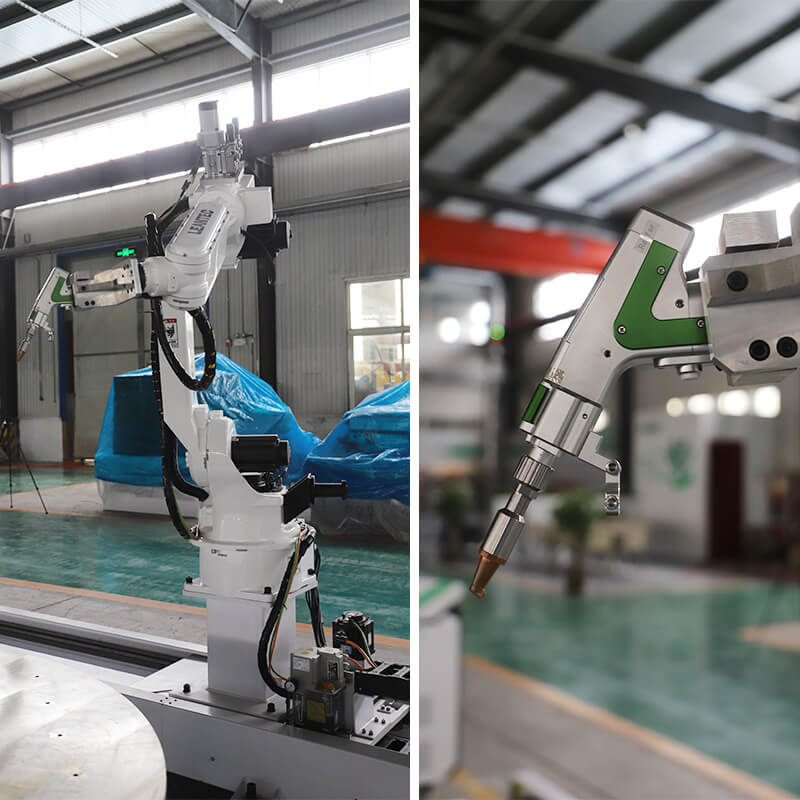
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision, automation, and high-speed manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 7% during the forecast period 2024–2029, citing rising adoption of industrial robotics and advancements in fiber laser technology as key growth drivers. As automation becomes integral to modern production lines, robot laser welding systems are emerging as a critical solution, combining the accuracy of lasers with the flexibility of robotic arms. This surge in demand has led to a competitive landscape of manufacturers pioneering innovations in efficiency, integration, and process control. Below, we spotlight the top 9 robot laser welding manufacturers shaping the future of industrial manufacturing.
Top 9 Robot Laser Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 3D ROBOT
Website: servo-robot.com
Key Highlights: SERVO-ROBOT is the leading manufacturer of 3D Robot-Vision systems and software dedicated to real-time intelligent control and monitoring of industrial robots….
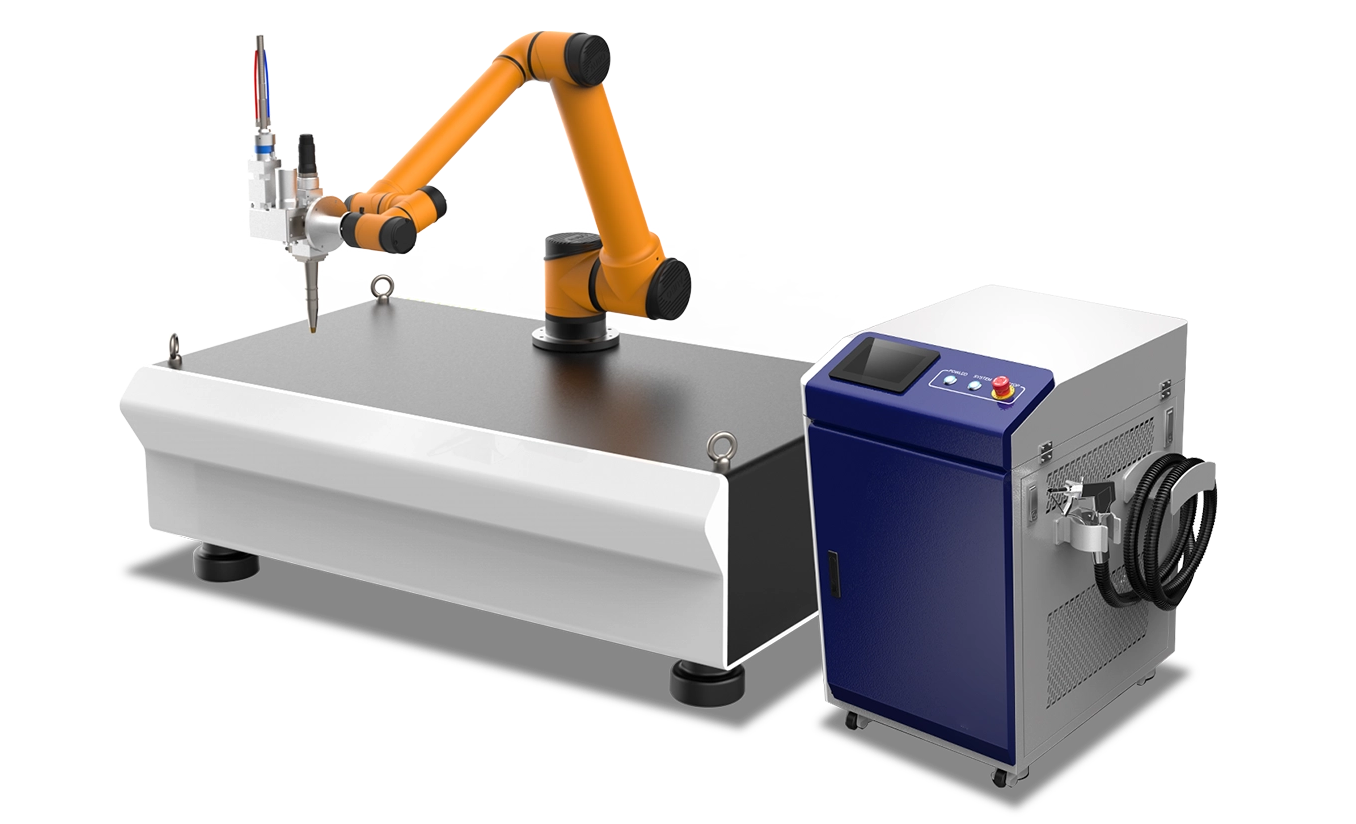
#2 IPG Genesis
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: … robotic solutions manufacturers have trusted for decades with a focus on laser welding, laser cleaning, laser surface modification and MIG welding automation….
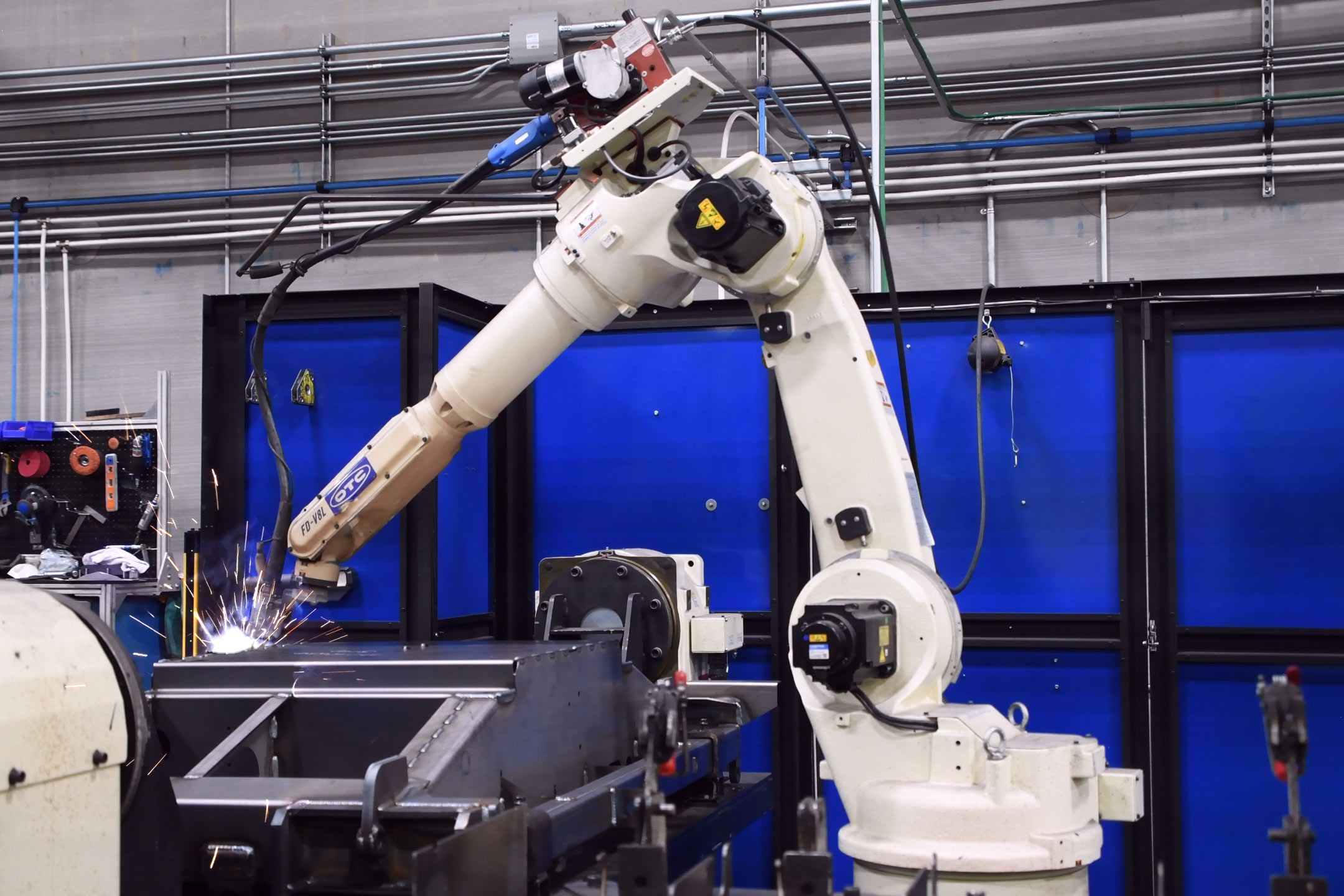
#3 OTC DAIHEN, Inc. USA Robotic Welding Solutions
Website: daihen-usa.com
Key Highlights: OTC DAIHEN, Inc. is a one-stop shop for innovative robotic and manual welding solutions. It is the American subsidiary of DAIHEN Corporation….
#4 Robotic Laser Welding Collaborative Systems
Website: thgautomation.com
Key Highlights: Discover robotic laser welding systems designed for extreme speed, low heat input, precision, & productivity, without any industrial-use compromise….
#5 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Engineered for precision and power, Denaliweld delivers up to 300W of reliable laser rust cleaning machine and laser welder with one-click operation, compact ……
#6 MIG, TIG, Robotic, & Laser Welding Solutions
Website: binzel-abicor.com
Key Highlights: Explore ABICOR BINZEL USA for advanced welding solutions. We offer MIG, TIG robotic, and laser welding technologies, along with MIG guns and robotic torches ……
#7 Daihen Robotic Site
Website: daihen-robot.com
Key Highlights: Collaborative Robot. Search by Application. Arc welding · Handling and transportation · Laser welding/cutting · Plasma welding/cutting · Spot welding · Spraying….
#8 Laser Welding Cobot System
Website: cobot.systems
Key Highlights: A laser welding robot is designed to achieve high precision and consistency in welding tasks, which makes it ideal for jobs requiring high quality and accuracy….
#9 Welding Machines / Robots / Lasers
Website: connect.panasonic.com
Key Highlights: Introduction of various automation, demonstration and solution cases and products using Panasonic welding machines, robot systems, etc….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Robot Laser Welding

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Robot Laser Welding
The global robot laser welding market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing automation across industries, and a growing emphasis on precision manufacturing. This analysis explores key trends shaping the market landscape in 2026 under the H2 (second half) projection, highlighting growth drivers, competitive dynamics, regional developments, and emerging applications.
1. Accelerated Adoption in Automotive and Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The automotive industry remains the largest end-user of robot laser welding systems, and this dominance will continue into 2026. With the rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production, manufacturers are increasingly relying on robot laser welding for its high-speed, precision joining of lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel. Battery pack assembly, structural components, and electric motor manufacturing are key applications driving demand. By H2 2026, integration of laser welding robots in EV production lines is expected to grow at a CAGR exceeding 12%, particularly in North America, Europe, and China.
2. Advancements in Laser and Robotic Integration Technologies
By 2026, robot laser welding systems will benefit from tighter integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and advanced sensor technologies. Real-time monitoring, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance features will enhance process reliability and reduce downtime. High-power fiber lasers with improved beam quality and efficiency will become standard, enabling faster welding speeds and deeper penetration. Collaborative robots (cobots) equipped with laser welding heads are expected to gain traction in small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), offering flexibility and ease of deployment.
3. Expansion in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors are increasingly adopting robot laser welding for critical components such as turbine blades, fuselage sections, and engine parts. The technology’s ability to produce high-integrity, low-distortion welds in exotic alloys like titanium and Inconel aligns with the industry’s performance and safety requirements. By H2 2026, defense modernization programs in the U.S., Europe, and Asia-Pacific will drive investment in automated laser welding solutions, with a focus on certification and traceability.
4. Growth in Asia-Pacific, Led by China and India
Asia-Pacific is expected to remain the fastest-growing regional market for robot laser welding by 2026. China’s continued push for smart manufacturing under its “Made in China 2025” initiative, coupled with India’s expanding industrial base, will fuel demand for automated welding systems. Local robotics manufacturers and laser technology providers are enhancing their capabilities, reducing dependency on Western imports. Government incentives for automation and rising labor costs further support market growth in the region.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency as Market Drivers
As industries prioritize sustainability, robot laser welding offers environmental advantages over traditional arc welding, including reduced energy consumption, minimal material waste, and lower emissions. By H2 2026, manufacturers will increasingly adopt laser welding as part of their green manufacturing strategies. Additionally, developments in energy-efficient lasers and recyclable material processing will enhance the technology’s eco-credentials.
6. Competitive Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
The robot laser welding market will see intensified competition among key players such as Fanuc, KUKA, ABB, Trumpf, and Mitsubishi Electric. Strategic partnerships between robotics companies and laser source providers (e.g., IPG Photonics) will accelerate innovation and expand application reach. By 2026, system integrators will play a crucial role in customizing turnkey solutions for specific industry needs, particularly in high-mix, low-volume production environments.
7. Challenges: High Initial Costs and Skilled Labor Shortage
Despite strong growth, the market faces challenges related to high capital investment and the need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain advanced systems. However, by H2 2026, cloud-based remote monitoring, modular system designs, and expanded training programs are expected to mitigate these barriers, especially in emerging markets.
Conclusion
By H2 2026, the robot laser welding market will be characterized by deeper industry integration, technological convergence, and geographic diversification. As industries pursue higher productivity, quality, and sustainability, robot laser welding will transition from a niche technology to a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing. Companies that invest in innovation, application-specific solutions, and workforce development will be best positioned to capture value in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Robot Laser Welding (Quality, IP)
When sourcing robotic laser welding systems, companies often encounter significant challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, legal disputes, and compromised competitiveness.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate System Validation and Process Certification
A frequent oversight is failing to validate the complete robotic laser welding process under real production conditions. Buyers may focus solely on component specifications—such as laser power or robot accuracy—without verifying how the integrated system performs on actual parts. Without proper process validation (e.g., weld penetration testing, bead consistency, and repeatability studies), the system may underperform, leading to high scrap rates and rework.
Insufficient Supplier Qualification
Choosing a supplier based only on cost or delivery time, without assessing their technical expertise and track record in laser welding applications, increases risk. Unqualified suppliers may lack the engineering support needed for integration, troubleshooting, and maintenance. This often results in prolonged commissioning times and unstable weld quality.
Lack of Defined Quality Metrics and Acceptance Criteria
Ambiguous or missing acceptance criteria in procurement agreements can lead to disputes over system performance. Without clear KPIs—such as weld strength, defect rates, cycle time, and system uptime—it becomes difficult to hold suppliers accountable. This ambiguity often surfaces only after installation, when expectations and reality diverge.
Overlooking Consumables and Maintenance Support
The quality of welding depends heavily on consistent performance of optics, nozzles, and shielding gas delivery. Sourcing from vendors who do not provide reliable access to consumables or technical support can degrade weld quality over time. Additionally, poor maintenance guidance or lack of training can shorten system lifespan and affect output consistency.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unclear Ownership of Customized Solutions
When robots and laser systems are customized for a specific application, IP rights to the programming, end-effectors, or process parameters may not be explicitly assigned. Suppliers may retain rights to software or methods developed during integration, limiting a buyer’s ability to replicate, modify, or transfer the process without permission or additional cost.
Inadequate Protection of Proprietary Processes
Sharing sensitive product designs or welding parameters with external integrators without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) exposes companies to IP theft or unauthorized use. Some suppliers may reuse process data across clients, potentially compromising competitive advantage.
Dependency on Proprietary Software Platforms
Many robotic laser systems rely on vendor-specific programming environments or control software. Without contractual rights to access source code, modify programs, or integrate with other systems, companies risk vendor lock-in. This restricts flexibility and increases long-term costs for updates or scaling.
Failure to Secure IP in Joint Development Projects
In co-development scenarios, the absence of clear IP clauses in contracts can lead to disputes over ownership of innovations. Without predefined agreements, both parties may claim rights to improvements, delaying deployment or requiring costly legal resolution.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, define quality and IP terms upfront in contracts, and engage legal and technical experts during the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Robot Laser Welding
Equipment Transportation and Handling
Ensure robot laser welding systems are transported using secure, climate-controlled vehicles to prevent moisture damage and physical shock. Use custom crating with shock-absorbing materials during shipping. Upon arrival, inspect all components for damage before installation. Only trained personnel should handle the robotic arms, laser sources, and optical components to avoid misalignment or contamination.
Installation and Facility Requirements
Install the robot laser welding system on a stable, vibration-free foundation with proper leveling. Ensure adequate space for robotic movement, maintenance access, and safety interlocks. Provide clean, dry compressed air, stable power supply (per manufacturer specifications), and proper cooling systems (chillers for laser sources). Verify that exhaust and fume extraction systems are in place and compliant with local air quality regulations.
Safety Compliance and Risk Management
Adhere to OSHA, ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers), and IEC 60825 standards for laser safety. Implement Class 1 enclosure requirements or use appropriate interlocks, beam shutters, and emergency stops. Install certified laser safety curtains or enclosures with door interlocks. All personnel must undergo laser safety training and wear appropriate PPE, including laser safety eyewear rated for the specific laser wavelength and power.
Regulatory Documentation and Certification
Maintain up-to-date documentation including CE/UKCA marking, Factory Mutual (FM) approval (if applicable), and compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) or equivalent. Keep records of risk assessments, safety validation reports, and laser classification certificates. Ensure the system’s control panel displays required safety labels and warning signs in local languages.
Operational Permits and Environmental Compliance
Obtain necessary permits for laser operation, particularly in industrial zones with strict emission controls. Comply with local regulations regarding noise levels, electrical installations, and hazardous emissions from welding fumes. Implement a fume management system that meets EPA or equivalent air quality standards. Regularly monitor and document air quality and filter performance.
Maintenance and Service Logistics
Schedule preventive maintenance per manufacturer guidelines, including optical alignment checks, cooling system servicing, and robotic calibration. Use only OEM or certified replacement parts to maintain compliance. Keep a log of all maintenance activities and component replacements. Establish a service agreement with certified technicians for emergency repairs and annual safety audits.
Training and Personnel Certification
Ensure all operators, programmers, and maintenance staff are certified in robotic laser welding systems. Training must cover operational procedures, emergency response, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and laser hazard awareness. Maintain training records and conduct periodic refresher courses. Assign a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) to oversee compliance and safety protocols.
International Shipping and Import Compliance
When shipping robot laser welding systems across borders, classify equipment under the correct HS codes (e.g., 8456.30 for laser cutting/welding machines). Comply with export control regulations such as ITAR or EAR if applicable, particularly for high-power lasers. Provide technical documentation, conformity certificates (CE, UL, etc.), and bilingual labeling as required by destination countries.
End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
Dispose of laser components, especially laser diodes, optical fibers, and batteries, in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and RoHS directives. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to ensure environmentally sound disposal. Document all decommissioning and recycling activities for audit purposes.
Conclusion for Sourcing Robot Laser Welding Systems
Sourcing a robot laser welding system represents a strategic investment in advanced manufacturing capabilities, offering significant improvements in precision, speed, consistency, and overall weld quality. As industries continue to demand higher production efficiency and tighter tolerances, integrating robotic laser welding enhances competitiveness by reducing cycle times, minimizing material waste, and lowering long-term operational costs through automation.
When sourcing such systems, it is essential to evaluate not only the technical specifications—such as laser power, robot reach, precision, and compatibility with existing production lines—but also the vendor’s support services, training programs, and system scalability. Factors like integration complexity, maintenance requirements, and total cost of ownership must be carefully assessed to ensure a seamless transition and maximum return on investment.
Furthermore, choosing a reputable supplier with proven industry experience and strong after-sales support ensures long-term reliability and adaptability to future manufacturing needs. In conclusion, sourcing robot laser welding technology is a forward-thinking move toward smart manufacturing, enabling companies to achieve superior product quality, operational efficiency, and agility in an increasingly automated industrial landscape.