The global rigid galvanized steel conduit market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across commercial, industrial, and infrastructure sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the Electrical Conduit and Fittings Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, with rigid steel conduits maintaining a dominant share due to their durability, fire resistance, and compliance with electrical safety codes. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights that the increasing focus on safe electrical installations in developing regions, along with infrastructure modernization in North America and Europe, continues to fuel demand for high-performance conduit solutions. Against this backdrop, manufacturers specializing in rigid galvanized steel conduit are scaling production and innovation to meet stringent regulatory standards and evolving project requirements. Below, we identify the top 7 manufacturers leading this segment through proven quality, global reach, and technological advancement.
Top 7 Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
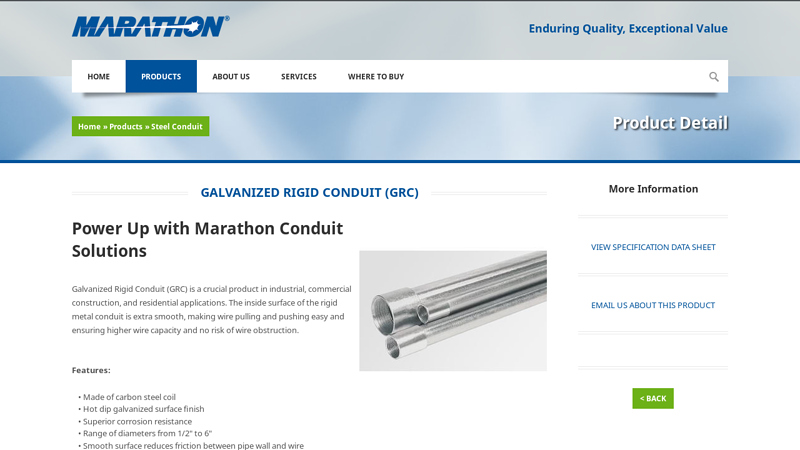
#1 Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC)
Domain Est. 2009
Website: marathonbroadband.com
Key Highlights: Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC) is a crucial product in industrial, commercial construction, and residential applications….
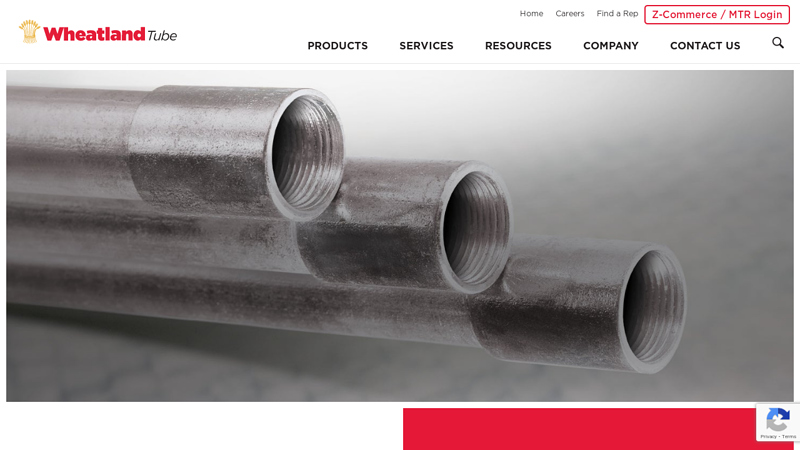
#2 Steel Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)
Domain Est. 1995
Website: wheatland.com
Key Highlights: Wheatland’s steel rigid metal conduit (RMC) is made and melted in America and hot-dipped galvanized for use in tough environments….
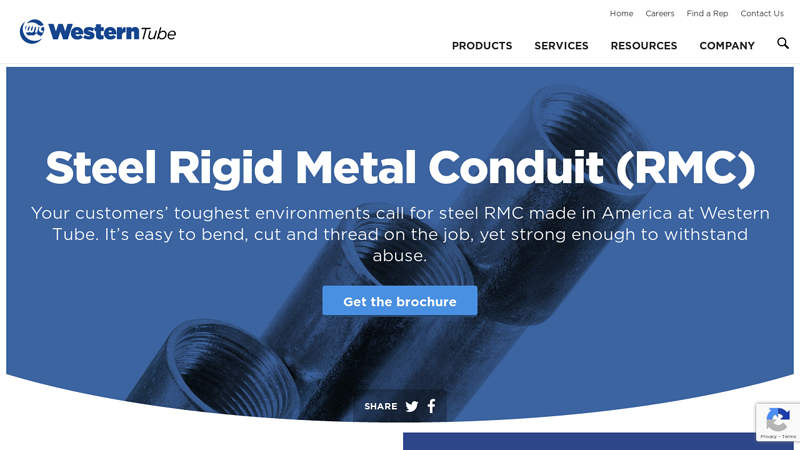
#3 Steel Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: westerntube.com
Key Highlights: Our steel rigid metal conduit (RMC) is made in the USA. It’s easy to bend, cut and thread on the job, yet strong enough to withstand abuse….
#4 Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC)
Domain Est. 1999
Website: reynoldsonline.com
Key Highlights: Ocal® COND11/4-G Rigid Conduit, 1-1/4 in Trade, 1.394 in ID x 1.74 in OD, 9.91 ft L, Steel. MFG Part #:COND11/4-G. Call for Pricing. Compare. Add to List….
#5 Galvanized Rigid Steel Conduit (GRC, RMC)
Domain Est. 2010
Website: atkore.com
Key Highlights: Manufactured from mild steel, rigid conduit is highly resistant to damage from impact yet ductile to facilitate bending….
#6 Galvanized Rigid Steel/Metallic Conduit Pipe (GRC)
Domain Est. 2016
Website: octalsteel.com
Key Highlights: Galvanized rigid steel conduit is the heaviest weight and thickest wall of electrical conduits. It is made of low carbon steel pipe with accurate round section….
#7 Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)
Domain Est. 2023
Website: qualitytubeusa.com
Key Highlights: RMC is the heavy wall option for excellent corrosion and damage prevention. This high strength conduit may be bent, cut, & threaded on jobsites to meet ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit (RMC)
The Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit (RMC) market in 2026 is expected to experience steady growth, driven by enduring demand in key infrastructure and industrial sectors, while facing competitive pressures from alternative materials and evolving construction practices. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Resilient Demand in Core Sectors:
- Industrial & Manufacturing: Continued investment in industrial automation, factory upgrades, and new manufacturing facilities (especially in sectors like semiconductors, electric vehicles, and advanced materials) will sustain strong demand for RMC. Its superior mechanical protection against impact, crushing, and abrasion remains critical in harsh industrial environments.
- Commercial Construction: New office buildings, data centers (requiring robust grounding and EMI shielding), retail complexes, and healthcare facilities will continue to specify RMC, particularly in areas requiring high physical protection (e.g., parking garages, mechanical rooms, exposed runs).
- Infrastructure Renewal & Expansion: Government spending on infrastructure modernization (power grids, transportation hubs, water treatment plants) and new energy projects (including grid interconnections for renewables) will provide a significant boost. RMC’s durability and long service life make it ideal for these long-term investments.
-
Competition from Alternative Conduit Systems:
- EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing): EMT will maintain its dominance in standard commercial and residential applications due to its lower cost, lighter weight, and easier installation. RMC’s market share will remain concentrated in applications where its higher strength and protection justify the premium.
- PVC Conduit: PVC will continue to gain ground, especially in corrosive environments (chemical plants, coastal areas, wastewater) and direct burial applications, due to its excellent corrosion resistance and lower material cost. RMC’s galvanized coating provides good corrosion resistance, but PVC is inherently superior in highly corrosive settings.
- Flexible Conduit (LFMC, FMC): Increased use in complex routing and vibration-prone areas will limit RMC’s application in specific scenarios, though RMC remains the standard for rigid, straight runs.
-
Focus on Sustainability and Long-Term Value:
- Lifecycle Cost Advantage: The industry will increasingly emphasize RMC’s longevity (50+ years) and minimal maintenance compared to alternatives, positioning it as a sustainable choice despite higher initial cost. Its high recyclability (steel) aligns with green building certifications (LEED, etc.).
- Circular Economy: Demand for recycled steel in RMC production may increase due to ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) pressures and potential regulations, potentially impacting raw material sourcing and costs.
-
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Factors:
- Steel Price Volatility: RMC prices will remain sensitive to global steel market fluctuations, influenced by raw material costs (iron ore, scrap), energy prices, and trade policies (tariffs, quotas). Supply chain resilience will be a key concern for manufacturers and distributors.
- Regional Growth Disparities: Growth will be strongest in developing economies (Asia-Pacific, Middle East, parts of Latin America) experiencing rapid urbanization and industrialization. Mature markets (North America, Western Europe) will see more modest growth, focused on renovation and infrastructure replacement.
-
Technological and Installation Trends:
- Prefabrication & BIM: Increased use of prefabrication and Building Information Modeling (BIM) in construction may favor standardized RMC lengths and fittings, potentially improving efficiency but requiring closer coordination.
- Labor Costs & Skill: The relative labor intensity of installing threaded RMC (vs. EMT’s set-screw or compression fittings) will remain a factor. However, the demand for highly skilled electricians capable of proper RMC installation will persist, especially in complex projects.
Conclusion for 2026:
The RMC market in 2026 will be characterized by stable, niche-oriented growth. It will maintain a vital role in applications demanding maximum physical protection, durability, and grounding performance, particularly within industrial, heavy commercial, and critical infrastructure sectors. While facing persistent competition from lighter and cheaper alternatives like EMT and PVC, RMC’s inherent advantages in strength, safety, and longevity will ensure its continued relevance. Success for manufacturers and distributors will depend on emphasizing total cost of ownership, navigating steel price volatility, targeting high-value applications, and adapting to sustainable sourcing demands.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit (Quality and IP)
Sourcing Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit (RGS) requires careful attention to both material quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, and costly rework. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Galvanization Quality
One of the most frequent issues is poor or inconsistent galvanization. Substandard zinc coating results in insufficient corrosion protection, especially in harsh or humid environments. Watch for thin, patchy, or non-uniform zinc layers, which can lead to rust and structural degradation over time. Ensure the conduit meets recognized standards such as ASTM A53 or EN 10255, and request mill test certificates verifying coating thickness (typically ≥ 50–70 µm depending on specification).
Non-Compliance with IP Ratings
RGS conduit is often used in environments requiring specific Ingress Protection, such as outdoor installations or wet locations. A common mistake is assuming that the conduit alone provides the required IP rating. In reality, the entire system—including couplings, fittings, and terminations—must be properly sealed. Using unsealed joints or incompatible accessories can compromise the IP rating, allowing water or dust ingress that damages internal wiring. Always verify that the full assembly (conduit + fittings) is rated for the intended IP level (e.g., IP66, IP68).
Use of Substandard or Non-Standard Materials
Some suppliers may offer conduit made from inferior steel or with incorrect wall thicknesses, deviating from industrial standards. This can compromise mechanical strength and fire resistance. Avoid products lacking traceability or proper certification. Confirm dimensional accuracy (diameter, wall thickness) and material grade to ensure compatibility with installation requirements and local electrical codes.
Poor Thread Quality and Dimensional Inaccuracy
Improperly cut or damaged threads hinder secure connections, leading to leaks and reduced mechanical integrity. Poor thread quality also increases the risk of cross-threading during installation. Inspect samples for burrs, incomplete threading, or mismatched thread standards (e.g., NPT vs. BSPT). Dimensional inaccuracies can cause misalignment and difficulties in fitting accessories, increasing labor costs and installation time.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable suppliers should provide full product traceability, including heat numbers and compliance documentation (e.g., ISO, CE, UL). Sourcing from vendors without proper certification increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant products. Always request and verify compliance with regional and project-specific standards to ensure safety and regulatory approval.
Ignoring Environmental and Installation Conditions
Selecting conduit without considering the operating environment—such as coastal areas with high salt exposure or industrial zones with chemical vapors—can lead to rapid deterioration. Similarly, failing to account for installation stresses (e.g., bending, pulling cables) may result in damage during or after installation. Choose conduit with appropriate corrosion resistance and mechanical strength for the specific application.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, buyers can ensure they source high-quality, compliant Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit that delivers long-term performance and safety.
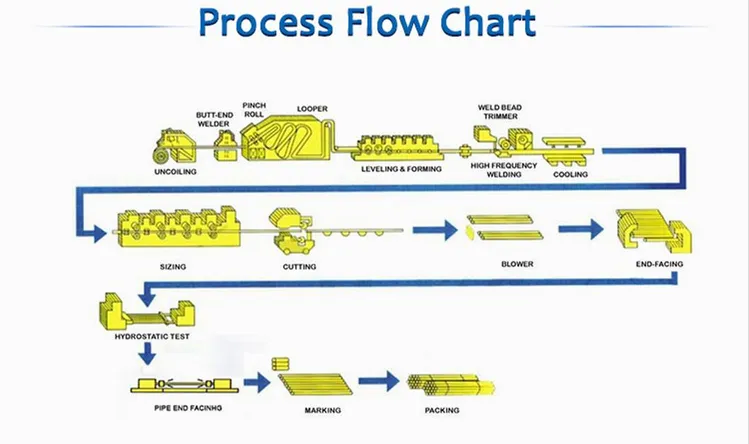
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit (RGS)
Overview
Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit (RGS) is a durable, heavy-wall steel tubing used in electrical installations to protect and route wiring in commercial, industrial, and hazardous environments. Due to its weight, material composition, and application, proper logistics and compliance procedures are critical for safe handling, transportation, and regulatory adherence.
Material Specifications & Standards
RGS conduit must comply with recognized industry standards to ensure quality and safety. Key specifications include:
– ASTM A53/A53M: Standard specification for pipe, steel, black and hot-dipped, zinc-coated, welded and seamless.
– UL 6: Underwriters Laboratories standard for rigid metal conduit.
– NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code – NEC): Article 344 governs the installation requirements for RGS.
– CSA C22.2 No. 45: Canadian standard for rigid steel conduit.
Ensure all RGS products are certified and labeled accordingly (e.g., UL Listed, CSA Certified).
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging and handling minimize damage and ensure product integrity:
– Bundle Configuration: Conduit sections are typically bundled in standard lengths (10 ft or 3.05 m) and secured with steel or nylon strapping.
– End Protection: Use plastic caps or protective sleeves on conduit ends to prevent deformation and protect workers.
– Lifting & Stacking: Use forklifts or cranes with appropriate slings; avoid dragging. Do not stack bundles more than 3–4 high on pallets to prevent collapse.
– Weather Protection: Store indoors or under cover; prolonged exposure to moisture can compromise galvanized coating.
Transportation Requirements
Transporting RGS requires attention to weight, length, and load security:
– Weight Considerations: RGS is heavy; a 10 ft section of 2-inch conduit weighs approximately 5.8 lbs/ft (8.7 kg/m). Plan vehicle capacity accordingly.
– Load Securing: Use tie-down straps, load bars, or dunnage to prevent shifting during transit. Comply with FMCSA (U.S.) or CVSA (Canada) cargo securement rules.
– Length Restrictions: Confirm compliance with local regulations for oversize loads if transporting long sections or large quantities.
– Labeling: Mark bundles clearly with product details, length, diameter, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile Ends,” “Do Not Drop”).
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage prevents corrosion and physical damage:
– Indoor Storage: Preferred to avoid moisture exposure and UV degradation.
– Elevation: Store on flat, level surfaces using wooden skids or pallets to prevent ground moisture absorption.
– Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow to reduce condensation under cover.
– Separation: Keep away from corrosive chemicals or salt-laden environments, especially in coastal areas.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to safety and environmental regulations is mandatory:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Follow guidelines for material handling, fall protection, and worker safety during loading/unloading.
– DOT (Department of Transportation): Comply with hazardous materials regulations if transporting in bulk or with coatings containing regulated substances (typically not applicable for standard RGS).
– REACH & RoHS (if exported to EU): Confirm that zinc coating and any associated materials comply with substance restrictions.
– Customs Documentation (International Shipments): Provide accurate HS Code (e.g., 7306.30 for threaded steel pipe) and certificates of origin, conformity, and compliance.
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Recyclability: RGS is 100% recyclable; coordinate with certified metal recyclers for scrap.
- Galvanized Coating: Avoid burning or grinding without proper ventilation and PPE, as zinc fumes can be hazardous.
- Site Safety: Train personnel on safe handling techniques to prevent cuts, pinching, or back injuries.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain comprehensive records for compliance and quality assurance:
– Mill Test Reports (MTRs): Provide material certification for steel grade and galvanization.
– Certificates of Compliance (CoC): Confirm adherence to ASTM, UL, or CSA standards.
– Bill of Lading & Packing Lists: Include quantity, dimensions, weight, and handling instructions.
– Traceability: Assign batch/lot numbers to facilitate recalls or audits if needed.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for Rigid Galvanized Steel Conduit ensure product integrity, regulatory adherence, and worker safety. By following established handling, transportation, storage, and documentation practices, stakeholders can mitigate risk and support reliable electrical system installations. Always consult local codes and standards for region-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing rigid galvanized steel conduit (RGS) requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, availability, and compliance with industry standards. By selecting reputable suppliers who provide certified materials meeting ASTM A53 or UL 6 standards, stakeholders can ensure durability, corrosion resistance, and long-term performance in electrical installations. Evaluating factors such as pricing, lead times, logistics, and technical support helps optimize the procurement process. Additionally, considering sustainability and total cost of ownership—rather than initial price alone—contributes to more informed and responsible sourcing decisions. Overall, a well-structured sourcing strategy for rigid galvanized steel conduit supports safe, reliable, and cost-effective electrical system installations across commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects.