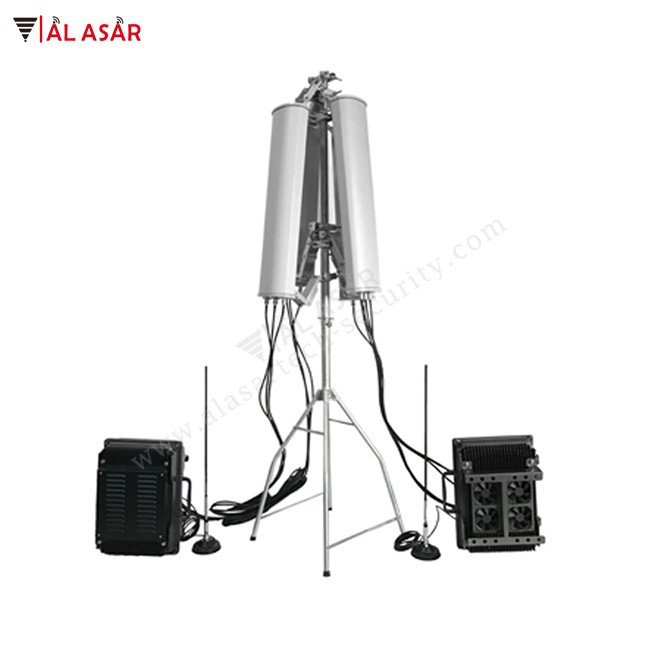
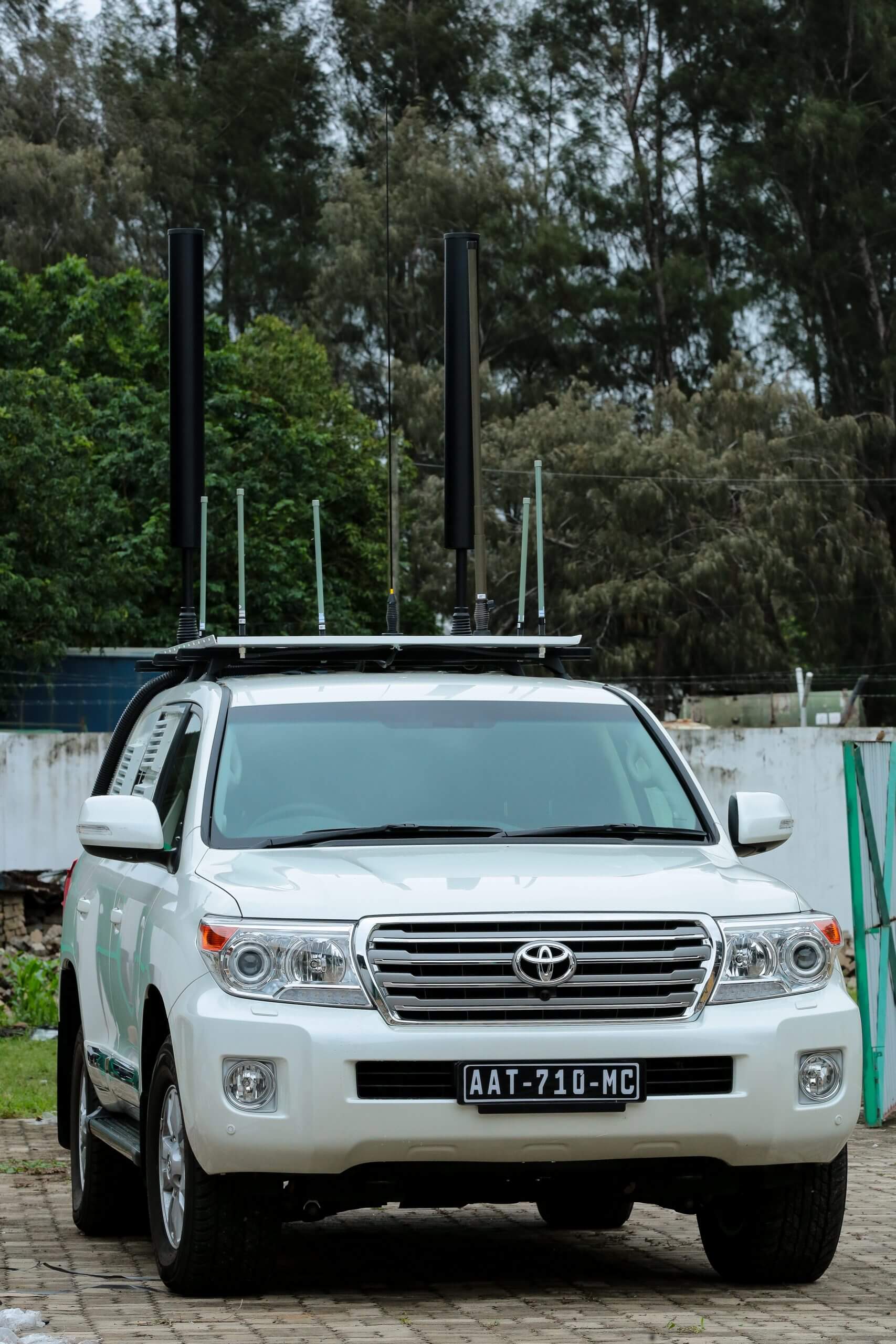
The global RF jammer market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for secure communications in defense, public safety, and critical infrastructure sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global signal jammer market size was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising cybersecurity threats, geopolitical tensions, and the proliferation of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) that necessitate reliable RF jamming solutions. Directional RF jammers, in particular, are gaining prominence due to their precision, reduced collateral interference, and effectiveness in targeted signal disruption. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, product performance, and global deployment. Below are the top 10 directional RF jammer manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Rf Jammer Directional Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 OEM Powerful Pro Jammer Jammers Brouilleur Inhibidor Störsenders
Domain Est. 2014
Website: jammers4u.com
Key Highlights: Jammers4u is OEM Manufacturer that make customized Jammers and directly helps you to design your Jamming systems per your project needs. Jammers are used in ……
#2 NovoQuad Group
Domain Est. 1996
Website: army-technology.com
Key Highlights: ND-BU003 Basic Anti-drone System consists of RF detector, directional jammer and central control laptop, with obvious price advantage. With 3D linear frequency ……
#3 ACASOM
Domain Est. 2021
Website: acasom.com
Key Highlights: ACASOM specializes in high-power amplifiers, signal jammers, and jammer modules, helping customers achieve optimal signal control and clarity….
#4 High
Domain Est. 2024
Website: marsrf.com
Key Highlights: Looking for a reliable directional jammer? Mars RF Microwave offers high-quality directional jammers for all your needs. Contact us today!…
#5 Regulus
Domain Est. 1994
Website: regulus.com
Key Highlights: A cybersecurity software solution to protect against GNSS spoofing & jamming attacks. GNSS Spoofing and Jamming attacks pose an ongoing threat to ……
#6 RF Jamming
Domain Est. 1994
Website: tcibr.com
Key Highlights: RF Jamming – Jam every drone signal – GNSS, command, control, and telemetry. Upgrade your defense now!…
#7 Drone RF Jammers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: unmannedsystemstechnology.com
Key Highlights: Drone RF (radio frequency) jammers are a form of counter-UAS (unmanned aerial systems) device that are designed to disrupt drone threats….
#8 RF Jammer
Domain Est. 2012
Website: bstarcom.co.kr
Key Highlights: Products: Hybrid Anti-Drone System, RF Scanner, Drone Dome, RF Jammer, Drone Gun Solutions, Ground-Based Solution, Vehicle-Based Solution….
#9 Directional Jammers – Targeted High
Domain Est. 2022
Website: jammermfg.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryExplore our range of directional signal jammers, including portable units, tripod-mounted systems, and custom-built precision RF drone jamming devices—all ……
#10 VIP Car Type Jammer
Website: atel.com.tr
Key Highlights: RF Output Power: Typical 40 Watts, Max 50 Watts Antenna Suitable for use with 1 directional antenna on the rifle or 1 co-directional antenna on the back…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rf Jammer Directional

H2: Market Trends for RF Jammer Directional Devices in 2026
The global market for directional RF (Radio Frequency) jammer devices is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving security demands, technological advancements, and shifting regulatory landscapes. As governments, military organizations, and private entities increasingly prioritize secure communications and counter-drone operations, directional RF jammers — known for their targeted signal disruption capabilities — are emerging as critical tools in electronic warfare and security infrastructure.
1. Rising Demand in Defense and Homeland Security
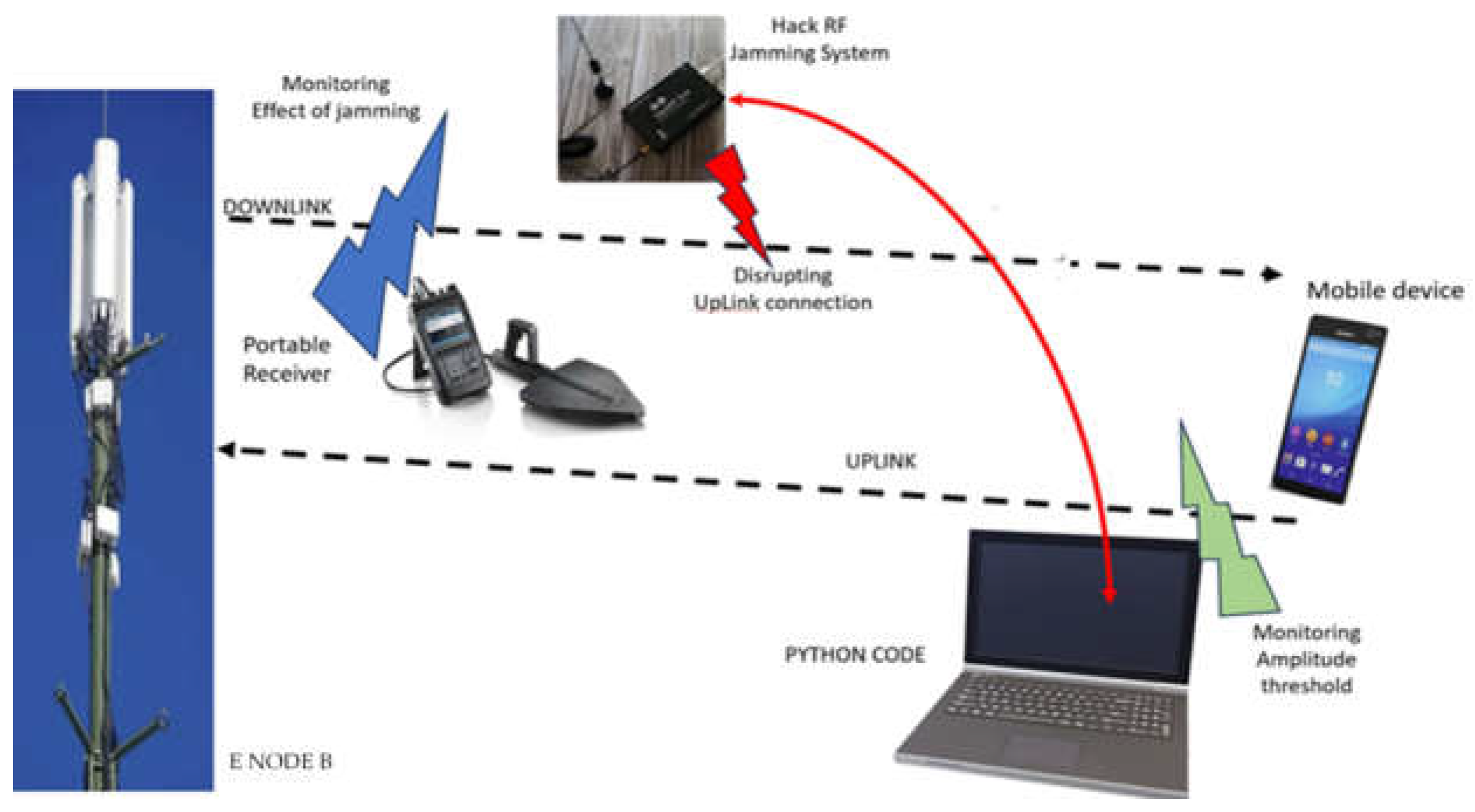
By 2026, defense and homeland security sectors are expected to remain the primary drivers of the directional RF jammer market. Escalating geopolitical tensions and the proliferation of unmanned aerial systems (UAS), including drones used for surveillance or attacks, have heightened the need for precision electronic countermeasures. Directional RF jammers offer the advantage of localized interference, minimizing collateral disruption to friendly communication systems — a key requirement in modern battlefield and urban security operations.
2. Growth in Counter-Drone Technology Integration
The integration of directional RF jammers into counter-drone (C-UAS) systems is accelerating. As commercial and hostile drone usage grows, so does the demand for effective, scalable countermeasures. By 2026, many C-UAS platforms are expected to feature modular, directional jamming components capable of targeting specific frequency bands used by drones (e.g., GPS, Wi-Fi, and RC control links). This trend is particularly strong in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, where governments are investing heavily in airspace protection.
3. Technological Advancements: Miniaturization and AI Integration
Advances in semiconductor technology and antenna design are enabling smaller, lighter, and more energy-efficient directional RF jammers. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of compact, portable units suitable for tactical deployment by special forces or law enforcement. Additionally, artificial intelligence and machine learning are being leveraged to enable adaptive jamming — systems that can automatically detect, classify, and respond to RF threats in real time, enhancing operational effectiveness.
4. Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Despite growth, the directional RF jammer market faces significant regulatory hurdles. In many countries, including the United States, civilian use of jammers is strictly prohibited due to potential interference with emergency and public communication services. However, licensed use in defense, law enforcement, and secure facilities continues to expand. By 2026, clearer regulatory frameworks may emerge, especially for controlled environments such as prisons, government campuses, and critical infrastructure sites.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
North America, led by the U.S. Department of Defense and DHS initiatives, will likely dominate the market in 2026. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, India, and South Korea, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to rising military modernization and border security concerns. Europe is also investing in electronic warfare capabilities, with NATO members enhancing defense electronics procurement.
6. Commercial and Critical Infrastructure Applications
Beyond military use, interest in directional RF jammers is growing in commercial sectors. High-security facilities such as data centers, executive transport, and VIP protection details are exploring directional jamming to prevent remote detonation of explosives or eavesdropping via wireless devices. These niche applications are expected to create new revenue streams by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the directional RF jammer market will be shaped by technological innovation, increased defense spending, and expanding use cases in both public and private sectors. While regulatory restrictions will continue to limit broad commercial adoption, the demand for precision, low-collateral electronic countermeasures will fuel sustained growth — particularly in defense, counter-drone systems, and high-security applications. Companies investing in smart, agile, and compliant jamming solutions are likely to lead the market in the coming years.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing RF Jammer Directional Devices: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns

Logistics & Compliance Guide for RF Jammer Directional
Overview
RF Jammer Directional devices are specialized electronic tools designed to block or disrupt wireless communication signals within a specific direction and range. Due to their potential impact on public safety, telecommunications, and national security, these devices are highly regulated worldwide. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, and operating directional RF jammers.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Strict Legal Restrictions
The use, sale, import, and operation of RF jammers are prohibited or heavily restricted in most countries. In the United States, for example, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) bans the marketing, sale, and use of jammers by private individuals and organizations under the Communications Act of 1934. Similar regulations exist in the European Union, Canada, Australia, and many other jurisdictions.
Authorized Use Only
RF jammers may only be legally operated by authorized government agencies (e.g., military, law enforcement, intelligence) under specific circumstances and with proper licensing. Unauthorized possession or deployment can result in severe penalties, including fines, equipment confiscation, and criminal charges.
Export Controls
Directional RF jammers may be classified as dual-use items under international export control regimes such as the Wassenaar Arrangement. Exporting these devices requires compliance with national regulations (e.g., U.S. Department of Commerce Bureau of Industry and Security – BIS) and may require an export license.
Import and Customs Procedures
Documentation Requirements
Importing RF jammers requires detailed documentation, including technical specifications, end-user certificates, and proof of authorization from relevant regulatory bodies. Failure to provide complete documentation may result in shipment delays or seizure.
Customs Classification
Proper Harmonized System (HS) code classification is essential. Jammers may fall under categories related to radio-frequency equipment or electronic warfare systems (e.g., HS 8517.62 or 8543.70, depending on design). Misclassification can lead to legal and financial consequences.
Prohibited Imports
Many countries explicitly prohibit the import of jamming devices for civilian use. Importers must verify local laws and obtain any required governmental clearances prior to shipment.
Transportation and Handling
Secure Packaging
RF jammers should be transported in anti-static, shock-resistant packaging to prevent damage. Devices should be powered off and stored in shielded containers to avoid unintended signal emission.
Air, Sea, and Ground Transport
Transport via commercial carriers (e.g., FedEx, DHL, UPS) is typically prohibited due to the illegal nature of jammers in most jurisdictions. Government or military logistics channels must be used for authorized movements. If transport is permitted, it must comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations or national equivalents, even if the device is not classified as hazardous.
Chain of Custody
Maintain a documented chain of custody for accountability. Access should be restricted to authorized personnel only, with tracking logs for movement, storage, and usage.
Storage and Security
Controlled Access Facilities
RF jammers must be stored in secure, access-controlled environments, such as locked cabinets or restricted facilities with surveillance. Access logs should be maintained.
Electromagnetic Shielding
Storage areas should ideally include RF-shielded enclosures (e.g., Faraday cages) to prevent accidental signal leakage or detection.
Inventory Management
Conduct regular audits to ensure all units are accounted for and comply with organizational or governmental inventory reporting requirements.
Operational Compliance
Authorization and Oversight
Operation must be conducted only under explicit legal authority, with oversight from qualified command or regulatory personnel. Mission-specific permissions may be required.
Frequency and Power Limits
Ensure jamming parameters (frequency bands, power output, directionality) are strictly limited to authorized scopes to avoid interference with emergency services, aviation, or civilian communications.
Monitoring and Reporting
Real-time monitoring of jamming activity and detailed operational logs (time, location, frequencies used, duration) must be maintained and reported as required by law or agency policy.
Training and Personnel Requirements
Certified Operators
Only personnel with proper training and certification should handle or operate RF jamming systems. Training should include legal limitations, technical operation, and safety protocols.
Compliance Education
All personnel involved in logistics or handling must be educated on applicable laws, export controls, and organizational policies.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Violations of RF jammer regulations can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Heavy fines (e.g., up to $112,500 per violation under FCC rules)
- Imprisonment
- Loss of operating licenses
- Asset forfeiture
- International sanctions (for unauthorized exports)
Conclusion
The logistics and compliance framework for directional RF jammers is complex and strictly enforced. Strict adherence to national and international laws, secure handling practices, and proper authorization are imperative. Always consult legal and regulatory experts before acquiring, transporting, or operating such equipment. Unauthorized use not only violates the law but also poses significant risks to public safety and critical communications infrastructure.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Directional RF Jammer
Sourcing a directional RF (Radio Frequency) jammer involves significant technical, legal, and ethical considerations. While directional RF jammers can be valuable in specific authorized applications—such as military operations, law enforcement, or secure facility protection—their possession and use are strictly regulated or outright banned in many countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, and most of the European Union.
From a technical standpoint, directional jammers offer focused interference, minimizing collateral disruption compared to omnidirectional models. This makes them potentially useful in scenarios requiring precision signal blocking, such as counter-drone operations or protecting sensitive perimeters. However, sourcing such devices requires vetting reputable manufacturers, ensuring compliance with electromagnetic safety standards, and confirming intended use aligns with authorized applications.
Legally, unauthorized use of RF jammers—regardless of directionality—can result in severe penalties, including fines and criminal charges, due to the risk of disrupting critical communications (e.g., emergency services, aviation, or public safety networks).
Therefore, while sourcing a directional RF jammer may be technically feasible, it should only be pursued by authorized entities with proper licensing and a clear operational need. For most organizations and individuals, legal alternatives—such as RF detection systems, signal monitoring, or managed access systems—are recommended to address security concerns without violating telecommunications regulations.
In summary: Proceed with caution, prioritize legality, and consult regulatory authorities before attempting to source or deploy any RF jamming technology.