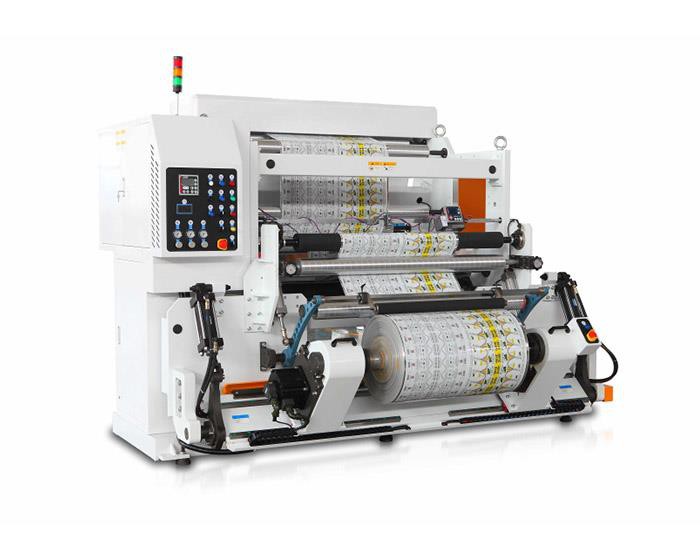
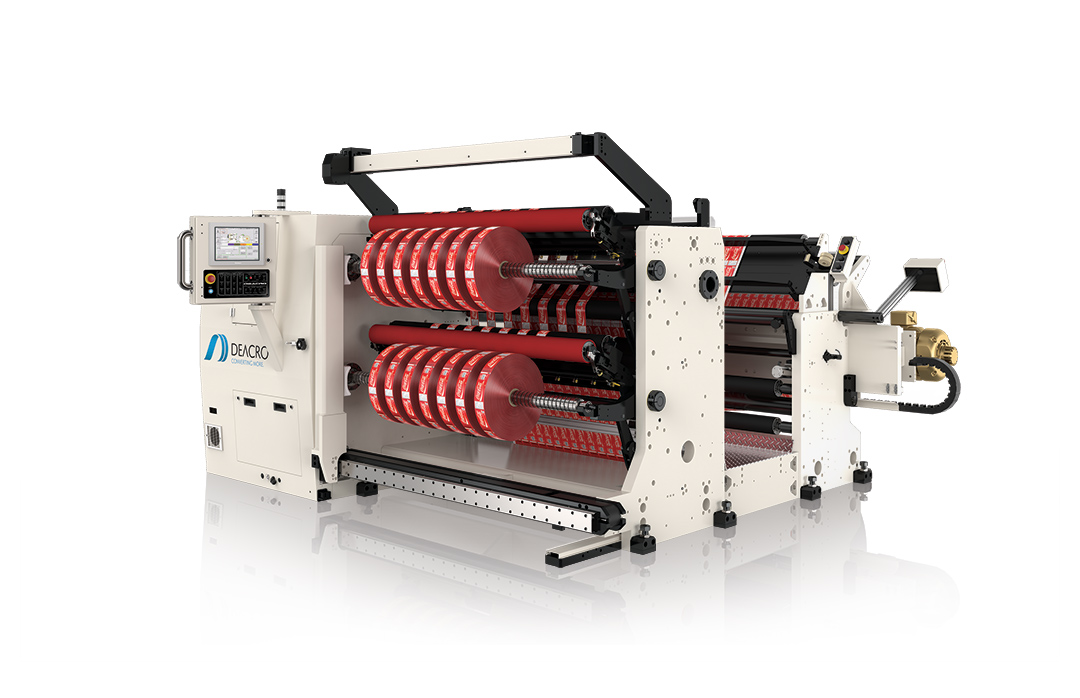
The global rewind machine market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for automated material handling across industries such as packaging, printing, wire and cable, and textiles. According to Grand View Research, the global slitting and rewinding machines market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing production efficiency requirements, advancements in precision engineering, and the adoption of smart manufacturing technologies. As manufacturers seek higher throughput and reduced downtime, demand for reliable, high-performance rewind machinery continues to rise. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders, combining innovation, durability, and automation expertise. Based on market presence, technological advancements, and customer performance data, the following nine companies represent the forefront of rewind machine manufacturing worldwide.
Top 9 Rewind Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
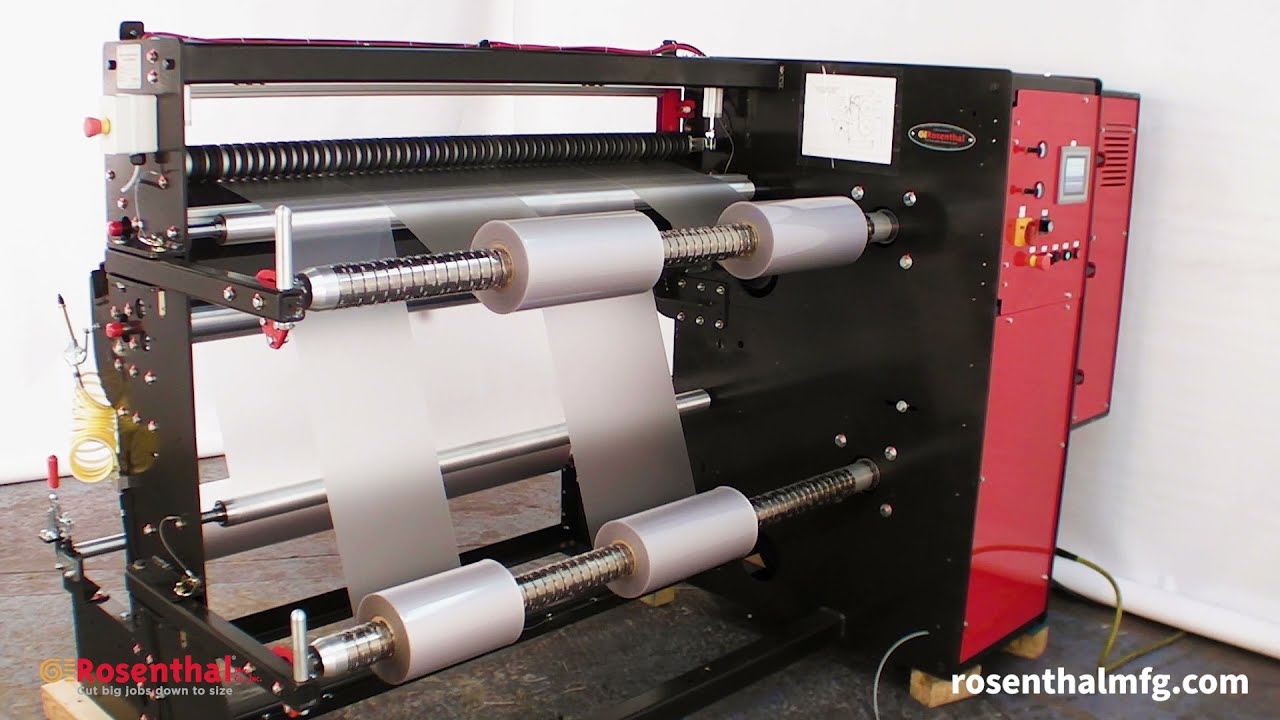
#1 Slitter Rewinder Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ashe.co.uk
Key Highlights: With over 45 years of experience, ASHE US is a slitter rewinder manufacturer, providing high-tech slitting machinery, rewinders & converting equipment….
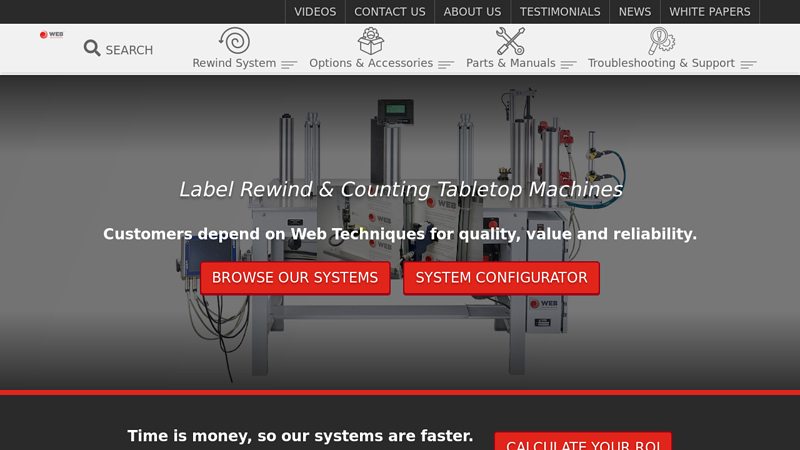
#2 Label Counter & Rewinding Machines
Domain Est. 2001
Website: webtechniquesinc.com
Key Highlights: Label Rewind & Counting Tabletop Machines. Customers depend on Web Techniques for quality, value and reliability. Browse Our Systems….
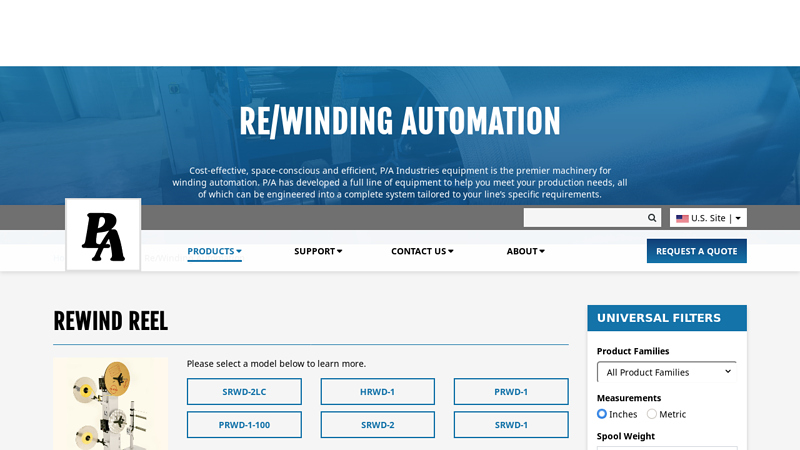
#3 Re/Winding Automation
Domain Est. 1994
Website: pa.com
Key Highlights: P/A Industries offers high speed winding and rewind equipment for delicate electronic components and parts through a secondary molding or plating process….
#4 Inspection Rewinding Machine
Domain Est. 1997
Website: welead.com
Key Highlights: Welead’s Inspection Rewinding Machine ensures precise defect detection, high-speed tension-controlled rewinding, and easy operation, with a versatile design for ……
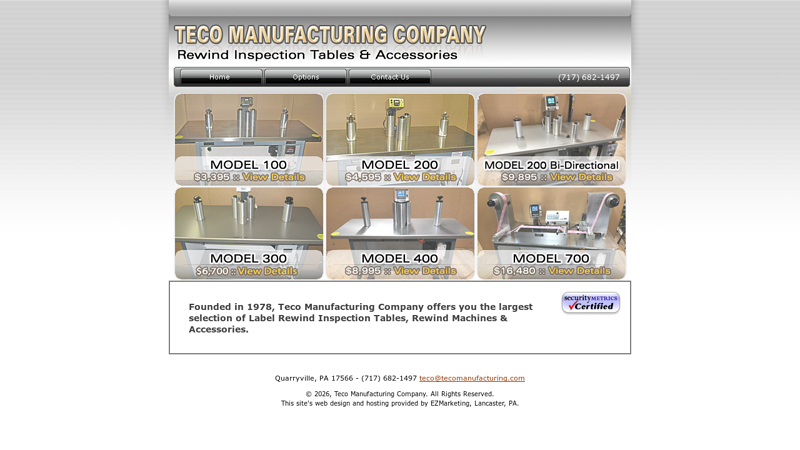
#5 Teco Manufacturing: Rewind Inspection Tables
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1978
Website: tecomanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1978, Teco Manufacturing Company offers you the largest selection of Label Rewind Inspection Tables, Rewind Machines & Accessories….
#6 Slitting & Rewinding
Domain Est. 1999
Website: kymc.com
Key Highlights: The Smart series slitter rewinder is the most cost-effective machine, is able to provide the most reliable and efficient operation for variety of materials….
#7 High
Domain Est. 1999
Website: practix-usa.com
Key Highlights: Discover reliable roll rewinding equipment and printing rewind machines at Practix USA. Enhance efficiency with precision-engineered solutions….
#8 SP Ultraflex Systems Pvt Ltd
Domain Est. 2006
Website: spultraflex.com
Key Highlights: To complement its range of world class slitter rewinders, SP Ultraflex also specialises in the manufacture of rewinding machines, including reversible Web ……
#9 Rewinding Machine / Product Guide
Domain Est. 2006
Website: fae.jp
Key Highlights: Our Rewinding Machines support high speed rewinding of ultra-thin materials under constant and low tension. They can be used as rectangular wire/ bonding ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rewind Machine

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Rewind Machine
As we approach the second half of 2026, the market landscape for Rewind Machine — a hypothetical or emerging tech solution likely centered around data recovery, digital preservation, time-based data access, or AI-driven content reconstruction — is being shaped by several converging macro and sector-specific trends. While public data on a specific “Rewind Machine” may be limited, the following analysis projects key developments based on broader technology, regulatory, and consumer behavior trends.
1. Surge in Demand for Data Resilience and Digital Legacy Management
By H2 2026, individuals and enterprises are increasingly concerned with digital continuity and personal data sovereignty. High-profile data breaches, accidental deletions, and AI-generated content floods have intensified the need for reliable data rollback mechanisms. Rewind Machine could benefit from this trend by positioning itself as a digital time capsule or recovery layer, especially in sectors like personal cloud storage, creative industries, and decentralized social platforms. Integration with Web3 wallets and NFT archives may expand its relevance.
2. AI-Driven Content Reconstruction Gains Traction
Generative AI tools dominate digital content creation, but they also introduce challenges around authenticity and version control. Rewind Machine may leverage advanced AI to reconstruct prior states of digital assets (e.g., reverting AI-edited images, documents, or code). In H2 2026, demand for “AI rollback” features is expected to rise, particularly among professionals in design, software development, and journalism who need audit trails and version fidelity.
3. Regulatory Pressure on Data Transparency and Right to Remember
Global regulations are evolving beyond GDPR-style “right to be forgotten” toward a “right to remember” — enabling individuals to preserve and retrieve their digital history. New EU digital legacy directives and U.S. state-level data portability laws may require platforms to offer rewind-like capabilities. Rewind Machine could emerge as a compliance enabler, providing certified timestamped archives and verifiable data recovery logs for regulated industries.
4. Growth of Edge Computing and On-Device Rollback
With increasing concerns over cloud dependency and latency, H2 2026 sees a shift toward edge-based data processing. Rewind Machine may capitalize on this by offering lightweight, on-device rollback solutions for smartphones, IoT devices, and local servers. This reduces reliance on centralized infrastructure and appeals to privacy-conscious users and enterprise IT departments.
5. Integration with Digital Twin and Metaverse Platforms
As digital twins and persistent metaverse environments mature, the ability to “rewind” virtual experiences becomes essential for debugging, training, and user safety. Rewind Machine could serve as a temporal layer in industrial simulations, virtual events, or gaming ecosystems, enabling stakeholders to review and analyze past interactions in immersive environments.
6. Consumerization of Enterprise-Grade Recovery Tools
Once limited to IT departments, data rollback tools are becoming consumer-friendly. In H2 2026, user expectations for seamless, one-click recovery across apps and devices are rising. Rewind Machine could differentiate through intuitive UI, cross-platform synchronization, and AI-powered smart recovery suggestions (e.g., “Restore the version from before the AI rewrite”).
7. Cybersecurity Convergence: Rollback as a Ransomware Defense
Ransomware attacks remain prevalent, and backup solutions are no longer sufficient — rapid rollback is critical. Rewind Machine may integrate with endpoint protection platforms to offer automated rollback to pre-attack states, reducing downtime. This positions the product as a core component of zero-trust and cyber resilience frameworks.
Conclusion:
In H2 2026, Rewind Machine operates in a favorable environment shaped by rising digital complexity, regulatory evolution, and AI proliferation. Success will depend on its ability to position itself not just as a recovery tool, but as an essential layer of digital trust, continuity, and control. Strategic partnerships with cloud providers, AI platforms, and cybersecurity firms will be key to scaling. Companies that embrace temporal data intelligence — the ability to navigate across digital timelines — will lead the next wave of innovation in personal and enterprise software.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Rewind Machine (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a rewind machine—especially from international suppliers or lesser-known manufacturers—can present several challenges related to both equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure a reliable, legally sound investment.
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Many low-cost rewind machines are constructed with substandard materials or imprecise engineering, leading to frequent mechanical failures, inconsistent tension control, and premature wear. This compromises production efficiency and increases long-term maintenance costs.
Inadequate Precision and Tension Control
A high-quality rewind machine must maintain precise tension and alignment during operation. Sourcing from unqualified suppliers often results in machines with poor control systems, leading to material defects such as wrinkles, telescoping, or edge damage—especially critical in industries like film, foil, or paper converting.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Overseas or unknown suppliers may offer attractive upfront pricing but lack reliable technical support, training, or access to spare parts. This can result in extended downtime and increased operational risk when maintenance or repairs are needed.
Hidden Costs from Non-Compliance or Reconfiguration
Machines sourced without adherence to regional safety or electrical standards (e.g., CE, UL) may require costly modifications before deployment. Additionally, integration with existing production lines may be hindered by incompatible interfaces or outdated control systems.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Some suppliers replicate patented designs or use proprietary technology without authorization. Purchasing such equipment can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially if the machine incorporates copied control systems, mechanical designs, or software protected under IP law.
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Software
Rewind machines with PLCs or HMI systems may run on pirated or unlicensed software. This not only violates copyright laws but can also lead to system instability, lack of updates, and potential security vulnerabilities.
Limited Warranty and Ambiguous Contracts
Suppliers may offer vague or limited warranties that exclude critical components or fail to specify performance guarantees. Without clear contractual terms, buyers have little recourse if the machine underperforms or fails to meet specifications.
Insufficient Documentation and Training
Poor documentation—including missing operation manuals, schematics, or maintenance guides—hampers safe and efficient use. Inadequate training from the supplier further increases the risk of operator error and machine misuse.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, request references, inspect machines in person or via third-party audits, and ensure all technical and legal aspects—including IP rights and compliance—are clearly addressed in procurement agreements.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rewind Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance requirements for operating and distributing Rewind Machine, ensuring smooth operations, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction.
Shipping and Fulfillment
Rewind Machine must be shipped in accordance with carrier regulations and international shipping standards. All units should be securely packaged using manufacturer-approved materials to prevent damage during transit. Use tracked and insured shipping methods for all orders, both domestic and international. Coordinate with fulfillment partners to ensure accurate order processing, timely dispatch, and real-time inventory management.
Import and Export Compliance
When shipping across international borders, ensure compliance with local customs regulations. Prepare and maintain accurate documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Classify Rewind Machine under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code to determine applicable tariffs and duties. Verify export control requirements—especially if the device contains software or components subject to ITAR or EAR regulations.
Product Safety and Certification
Rewind Machine must meet all relevant product safety standards in target markets. Ensure the device carries required certifications such as CE (Europe), FCC (USA), UKCA (United Kingdom), and other local marks as applicable. Maintain up-to-date test reports and technical documentation to demonstrate compliance with electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental standards.
Data Privacy and Software Compliance
If Rewind Machine collects, processes, or stores user data, it must comply with data protection regulations including GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), and other applicable privacy laws. Implement data encryption, user consent mechanisms, and clear privacy notices. Ensure software components, including open-source libraries, are properly licensed and attributed in accordance with their terms.
Environmental and Sustainability Requirements
Adhere to environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives. Provide end-of-life disposal information to customers and support recycling initiatives. Minimize packaging waste by using recyclable or biodegradable materials wherever possible.
Warranty and Returns Management
Establish a clear warranty policy that complies with local consumer protection laws (e.g., 2-year warranty in the EU). Set up a compliant returns process for defective or unwanted units, including reverse logistics and inspection procedures. Document all returns and repairs for quality tracking and compliance audits.
Regulatory Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records including bills of materials, compliance certificates, shipping documents, and customer communications. Store records securely and ensure they are accessible for audits or regulatory inquiries. Assign responsibility for compliance oversight to a designated team member or officer.
Training and Internal Compliance
Train logistics, customer support, and sales teams on compliance requirements related to shipping, data privacy, and product handling. Conduct periodic reviews of logistics partners to ensure they meet your compliance standards. Update policies regularly to reflect changes in regulations or business operations.
By following this guide, Rewind Machine operations will remain legally compliant, reduce risk, and support reliable, trustworthy service delivery across all markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Rewind Machine:
After careful evaluation of technical specifications, production requirements, supplier credibility, and cost considerations, sourcing a rewind machine is a strategic investment that will enhance operational efficiency, improve product quality, and support scalability in production. Selecting the right rewind machine—aligned with material type, speed requirements, automation level, and integration capabilities—ensures long-term reliability and return on investment. It is recommended to finalize procurement with a reputable supplier offering strong after-sales support, warranties, and technical training to maximize machine performance and minimize downtime. Proper sourcing not only meets current operational needs but also positions the organization for future growth and competitiveness.