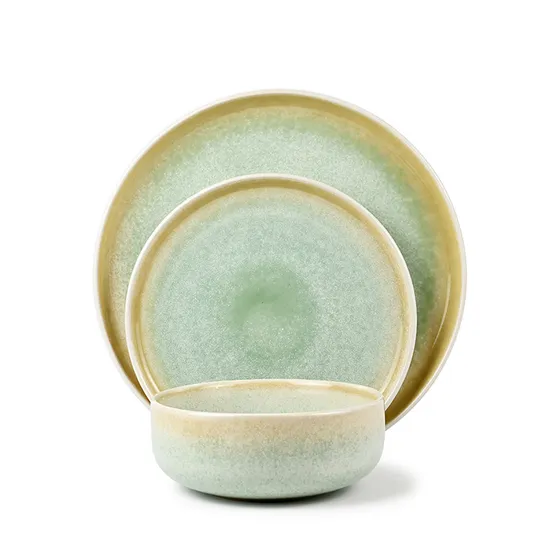
The global restaurant dining ware market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising foodservice demand, expanding hospitality infrastructure, and increasing consumer preference for aesthetically pleasing and durable tableware. According to Grand View Research, the global tableware market size was valued at USD 46.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence reports steady expansion in the sector, citing urbanization, the proliferation of restaurants and cafes, and growing investments in commercial dining as key growth catalysts. As operators prioritize efficiency, sustainability, and brand presentation, demand for high-performance, innovative dining ware has surged—placing manufacturers at the forefront of industry transformation. In this evolving landscape, the top 10 restaurant dining ware manufacturers have distinguished themselves through product innovation, scalable production, and a deep understanding of commercial kitchen needs.
Top 10 Restaurant Dining Ware Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 BIA Cordon Bleu
Domain Est. 1996
Website: biacordonblu.com
Key Highlights: BIA Cordon Bleu is pleased to present its 72nd collection of bakeware, dinnerware and kitchenware for home and restaurant use….
#2 Buy fine dinnerware online now
Domain Est. 1997
Website: villeroy-boch.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $75 30-day returnsFrom timeless classics to innovative designs, you’ll find the perfect dinnerware for every occasion at Villeroy & Boch. Dive in and be inspired…
#3 TableCraft
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tablecraft.com
Key Highlights: For over 73 years, TableCraft Products Company has brought innovative and quality products to the foodservice industry….
#4 Chefs’ Warehouse
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chefswarehouse.com
Key Highlights: We deliver the finest specialty foods, fresh produce, and premium proteins with expert service for chefs who demand exceptional quality and creativity….
#5 Zwiesel Fortessa
Domain Est. 1999
Website: fortessa.com
Key Highlights: Create your own five-star dining experience at home with Zwiesel Fortessa dinnerware, flatware, and drinkware collections. Mix and match collections for a ……
#6 Front of the House®
Domain Est. 2002
Website: frontofthehouse.com
Key Highlights: Front of The House® designs and manufactures distinctive tableware and serveware for the hospitality industry….
#7 Porcelain for hotels and restaurants
Domain Est. 2003
Website: bernardaud.com
Key Highlights: Its broad selection includes white or decorated plates, compartmented serving dishes and small rectangular trays with slightly rounded corners as well as ……
#8 Dinnerware
Domain Est. 2018
#9 Tableware Collections, Foodservice Dinnerware & Buffetware …
Domain Est. 2019
Website: libbeyfoodservice.com
Key Highlights: Libbey Foodservice provides an array of fine tableware collections, foodservice dinnerware, glassware, flatware, buffetware and other tabletop solutions….
#10 Fiesta Tableware
Domain Est. 2020
Website: fiestatableware.com
Key Highlights: An American icon crafted in West Virginia. Fiesta was founded along the banks of the Ohio River, in a region known for rich deposits of clay….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Restaurant Dining Ware

2026 Market Trends for Restaurant Dining Ware
The restaurant dining ware market in 2026 is poised for dynamic evolution, driven by sustainability imperatives, shifting consumer preferences, technological integration, and economic factors. As the industry recovers from global disruptions and adapts to new dining behaviors, key trends are reshaping the types of plates, glassware, cutlery, and serving ware used in commercial kitchens and dining spaces.
Sustainability and Eco-Conscious Materials Dominate
Environmental responsibility will be the cornerstone of dining ware innovation in 2026. Restaurants are under increasing pressure—from consumers, regulators, and investors—to reduce their environmental footprint. As a result:
– Plant-based and compostable materials like bamboo, bagasse (sugarcane fiber), and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) are expected to capture a growing share of the disposable segment.
– Recycled content in ceramics, glass, and melamine will become a standard expectation, with brands emphasizing closed-loop production and recyclability.
– Full-service restaurants will increasingly adopt reusable systems, including third-party dishwashing services and modular ware designed for high durability and low waste.
– Certifications such as B Corp, Cradle to Cradle, and compostability labels will be prominently displayed to build consumer trust.
Design Innovation Meets Functionality
Aesthetic appeal and practical performance will converge in 2026 dining ware:
– Restaurant-branded tableware will rise, with custom-designed plates, cups, and utensils that reinforce brand identity and enhance the guest experience.
– Ergonomic and modular designs will cater to both staff efficiency and guest comfort—lightweight yet durable materials, stackable configurations, and heat-retaining properties will be prioritized.
– Color and texture experimentation will grow, with matte finishes, artisan-inspired glazes, and biophilic designs creating immersive dining atmospheres.
Technology Integration and Smart Ware
While still emerging, smart dining ware will gain early adoption in high-end and tech-forward restaurants:
– RFID-enabled plates or trays may be used for inventory tracking, portion control, or interactive dining experiences (e.g., pairing with digital menus).
– Temperature-sensitive coatings could indicate optimal serving temperature, reducing food waste and improving consistency.
– Integration with kitchen management systems allows real-time monitoring of ware usage, breakage rates, and supply needs, improving operational efficiency.
Resilience and Cost Optimization Post-Pandemic
Economic pressures will continue to influence purchasing decisions:
– Durability and lifecycle cost will outweigh initial price, with operators favoring premium melamine, reinforced porcelain, and tempered glass that withstand high-volume use.
– Supply chain localization will increase, reducing dependency on overseas manufacturing and minimizing delays—this will boost regional production in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
– Multi-use ware that transitions seamlessly from kitchen to table (e.g., oven-to-table ceramics) will be favored for space and cost savings.
Rise of Hybrid Dining Models
As takeout, delivery, and ghost kitchens remain significant, dining ware must serve dual purposes:
– Dual-format packaging—containers that double as serving dishes—will grow in popularity, reducing the need for additional ware.
– Premium disposable lines made from sustainable materials will be used even in upscale delivery models, maintaining brand image beyond the dine-in experience.
– Ware designed for easy stacking and storage will support space-constrained urban kitchens and delivery hubs.
In conclusion, the 2026 restaurant dining ware market will be defined by a fusion of sustainability, smart design, and operational intelligence. Operators who align their ware choices with environmental goals, guest expectations, and cost efficiency will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Restaurant Dining Ware (Quality, IP)
Sourcing restaurant dining ware—such as plates, bowls, glassware, cutlery, and serving items—requires careful consideration to ensure both quality and compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to customer dissatisfaction, increased costs, and even legal issues. Below are common pitfalls, particularly related to quality and intellectual property (IP), that businesses should avoid.
Overlooking Material Quality and Durability
Many buyers focus on aesthetics or initial cost while neglecting the functional durability of dining ware. Low-quality ceramics may chip easily, melamine can warp under heat, and thin glassware may break frequently. This leads to higher replacement costs and inconsistent guest experiences. Always verify material specifications (e.g., vitrified ceramic, tempered glass) and request samples for real-world testing under restaurant conditions.
Ignoring Heat, Chemical, and Impact Resistance
Restaurant environments involve dishwashers, ovens, acidic foods, and frequent handling. Sourcing items not rated for commercial use—such as non-dishwasher-safe plastics or non-tempered glass—can result in rapid degradation. Confirm industry certifications (e.g., NSF, ISO) and ensure the ware meets thermal shock and mechanical stress standards.
Assuming Aesthetic Appeal Equals Performance
Glossy catalogs and online images can be misleading. Items may look elegant but fail under real dining conditions—plates may stain, colors fade, or textures trap grime. Always conduct side-by-side performance testing with shortlisted options before large-scale procurement.
Falling for Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Designs
Some suppliers offer “inspired by” or duplicate versions of premium branded or designer tableware (e.g., mimicking high-end porcelain patterns or glassware shapes). These may infringe on trademarks, copyrights, or design patents. Using such items exposes restaurants to legal liability, brand damage, and forced discontinuation. Always verify design ownership and request documentation from suppliers.
Failing to Audit Supplier IP Compliance
Suppliers in certain regions may unknowingly—or knowingly—distribute products with stolen designs. Conduct due diligence: ask for proof of design licenses, original design documentation, and ensure contracts include IP indemnification clauses. Avoid vendors reluctant to provide transparency.
Inconsistent Sizing and Compatibility
Mixing manufacturers or poorly controlled production can lead to mismatched plate diameters, non-standard glass heights, or cutlery that doesn’t fit trays. This disrupts kitchen workflows and presentation. Stick to consistent lines from reliable suppliers and verify dimensions across batches.
Underestimating Total Cost of Ownership
Cheaper upfront pricing often hides long-term costs due to breakage, replacement frequency, or poor ergonomics leading to staff fatigue. Evaluate total cost per use, including durability, maintenance, and labor efficiency, rather than unit price alone.
Neglecting Brand Alignment and Customer Experience
Dining ware reflects a restaurant’s brand identity. Poorly sourced items may clash with the desired ambiance—e.g., flimsy flatware in a fine dining setting. Ensure the look, weight, and feel of the ware support the intended guest experience.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, restaurant owners and operators can ensure their dining ware enhances both operational efficiency and brand integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Restaurant Dining Ware
Overview
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for sourcing, transporting, storing, and using dining ware in a restaurant setting. Proper management ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and food safety.
Regulatory Compliance
Food Contact Safety
All dining ware—plates, bowls, cutlery, glassware, and disposable items—must comply with food safety regulations. In the U.S., the FDA enforces 21 CFR Part 170-189, which governs materials that come into contact with food. Ensure all ware is labeled as “food-grade” and free from harmful substances such as lead, cadmium, and BPA.
Certification Requirements
Verify that suppliers provide documentation proving compliance with standards such as:
– FDA (U.S.)
– EU Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 (Europe)
– NSF International certification (especially for reusable ware)
Single-Use and Disposable Ware
If using disposable dining ware (e.g., paper plates, compostable cutlery), confirm that materials are certified compostable or recyclable per local waste management regulations. Avoid misleading environmental claims; labeling must comply with FTC Green Guides.
Sourcing & Procurement
Supplier Vetting
Choose suppliers with proven compliance records and transparent sourcing. Request certificates of conformance (CoC) and material safety data sheets (MSDS) for all products. Prioritize vendors audited for ethical labor and sustainable practices when possible.
Sustainable Sourcing
Comply with local and state mandates on single-use plastics. Many jurisdictions restrict polystyrene foam and non-recyclable plastics. Opt for biodegradable, recycled, or reusable alternatives to meet sustainability goals and regulations.
Transportation & Receiving
Packaging and Protection
Ensure dining ware is transported in sealed, clean, and pest-free packaging to prevent contamination. Fragile items (e.g., glassware) should be appropriately cushioned to minimize breakage.
Temperature and Environmental Controls
While most dining ware does not require temperature control, avoid exposure to extreme heat or moisture during transit (e.g., don’t transport compostable ware in a hot delivery vehicle for extended periods, as it may degrade).
Receiving Procedures
Upon delivery:
– Inspect packaging for damage or contamination
– Verify quantities and compliance labels
– Reject non-compliant or damaged goods immediately
– Record lot numbers and expiration dates (if applicable) for traceability
Storage & Inventory Management
Clean, Dry, and Pest-Free Environment
Store dining ware in enclosed, clean areas off the floor, away from chemicals, and protected from dust, pests, and moisture. Maintain proper ventilation to prevent mold or degradation—especially critical for paper or compostable items.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
Implement FIFO inventory rotation to prevent expired or degraded stock (particularly relevant for biodegradable/disposable ware with shelf life limits).
Segregation of Clean and Used Ware
Keep clean dining ware separate from soiled items. Use covered racks or cabinets to protect clean stock in busy kitchen environments.
Usage & Handling
Hygiene and Sanitation
Reusable dining ware must be washed, rinsed, and sanitized using commercial dishwashers at appropriate temperatures (typically 160°F/71°C final rinse) per local health codes. Follow manufacturer cleaning guidelines to avoid damage.
Staff Training
Train staff on proper handling, storage, and inspection of dining ware. Discard chipped, cracked, or excessively worn items to prevent injury and contamination.
Allergen and Cross-Contamination Control
Avoid using wood or unsealed materials that can harbor allergens or bacteria. Ensure thorough cleaning between allergen-containing meals.
Disposal & Waste Management
Recycling and Composting
Comply with local waste regulations. Separate recyclable or compostable dining ware and dispose of them in designated bins. Maintain records if required for sustainability reporting.
Hazardous Waste
Broken glass or ceramic must be disposed of in puncture-resistant containers labeled appropriately to protect staff.
Recordkeeping & Audits
Documentation
Maintain records of:
– Supplier certifications
– Delivery logs
– Inventory rotation
– Training sessions
– Equipment maintenance (e.g., dishwasher logs)
Health Inspections
Be prepared for routine health department inspections. Dining ware storage, cleanliness, and condition are common audit points.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for restaurant dining ware safeguard public health, support sustainability, and ensure regulatory adherence. Regular review of policies, staff training, and supplier relationships are key to maintaining a safe and efficient operation.
In conclusion, sourcing restaurant dining ware requires a careful balance between quality, durability, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness. The choice of materials—such as porcelain, stoneware, melamine, or glass—should align with the restaurant’s concept, service style, and target clientele. It is essential to consider factors like chip resistance, heat retention, ease of cleaning, and environmental impact when selecting products. Building relationships with reliable suppliers, comparing quotes, and ordering samples can help ensure consistency and long-term satisfaction. Ultimately, investing in well-sourced dining ware not only enhances the overall guest experience but also supports operational efficiency and brand identity, contributing to the restaurant’s success and reputation in a competitive industry.