The global rebound hammer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising infrastructure development and increasing demand for non-destructive testing (NDT) methods in construction and civil engineering. According to Mordor Intelligence, the non-destructive testing equipment market—of which rebound hammers are a key component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028. With concrete quality assessment becoming critical in ensuring structural safety, rebound hammers remain a go-to tool for on-site compressive strength estimation. As urbanization accelerates across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, the demand for reliable and portable testing instruments has intensified, spurring innovation among manufacturers. In this evolving landscape, seven companies have emerged as leaders, combining engineering precision, global reach, and technological advancement to dominate the rebound hammer segment.
Top 7 Rebound Hammer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Original Schmidt Digital Rebound Hammer, Type N
Domain Est. 1995
#2 rebound
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ndtjames.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsDigital Test Hammers for the quick and easy determination of the strength of concrete, and hardness of construction materials….
#3 Concrete Rebound Hammers, Schmidt Hammers
Domain Est. 1999
#4 Rebound Concrete Test Hammers
Domain Est. 2000
Website: matest.com
Key Highlights: Designed to perform non-destructive tests on concrete structures, it gives an immediate indication of the compressive strength of the concrete….
#5 Rebound (Schmidt) Hammer
Domain Est. 2007
Website: gbg-us.com
Key Highlights: Rebound (Schmidt) Hammer assesses hardness in concrete, rock, and masonry, estimates compressive strength, and locates surface defects in concrete….
#6 The Original Schmidt Rebound Hammer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: screeningeagle.com
Key Highlights: The original rebound test hammers for compressive strength and homogeneity assessment. The Original Schmidt was invented and introduced into the market by ……
#7 Rebound Hammer Testers for Concrete Strength Testing
Domain Est. 2023
Website: langryndt.com
Key Highlights: LANGRY’s rebound hammers are mainly designed for testing concrete. But they can also be used to assess the hardness of other materials such as rock and masonry….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Rebound Hammer
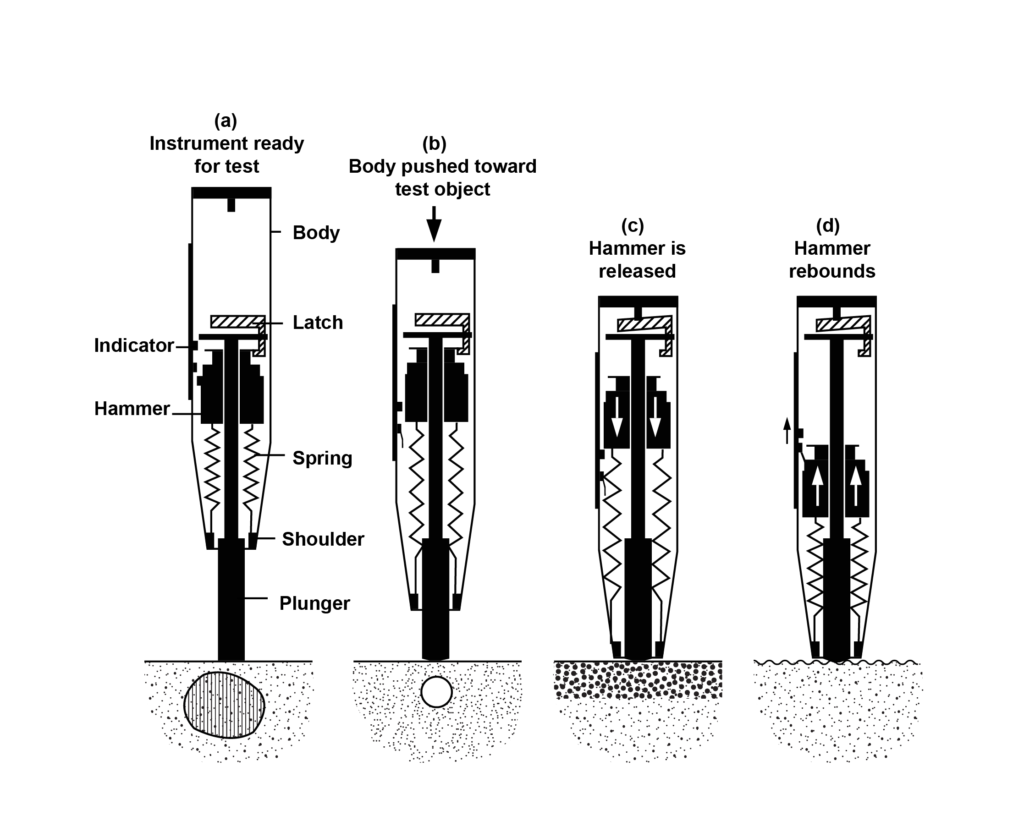
H2 2026 Market Trends for Rebound Hammer
The rebound hammer market in the second half of 2026 is poised for significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving construction demands, and a growing emphasis on infrastructure quality and sustainability. Here are the key trends shaping the market:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Digital and Smart Rebound Hammers
By H2 2026, digital rebound hammers will dominate new equipment sales, largely replacing traditional analog models. Integrated Bluetooth connectivity, real-time data logging, GPS tagging, and compatibility with construction management software (e.g., BIM platforms) will become standard. Operators will rely on mobile apps for instant analysis, automated report generation, and cloud-based data storage—improving efficiency and auditability. This shift is fueled by demand for accurate, traceable data in compliance-heavy projects and smart city developments.
2. Integration with AI and Predictive Analytics
Advanced rebound hammers will incorporate AI-powered software that correlates rebound number (RN) data with other non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV). Machine learning models will offer predictive assessments of concrete strength and degradation, enabling proactive maintenance. This trend supports asset lifecycle management in aging infrastructure, particularly in North America and Europe.
3. Focus on Infrastructure Resilience and Retrofitting
With global governments investing heavily in resilient infrastructure post-pandemic and in response to climate challenges, H2 2026 will see increased demand for NDT tools in bridge, road, and building inspections. Rebound hammers will play a critical role in assessing the structural integrity of existing concrete structures, especially in emerging economies modernizing transport networks and developed nations upgrading aging assets.
4. Rise in Green Construction and Sustainability Compliance
Sustainability standards (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) will drive demand for tools that support material efficiency and longevity assessments. Rebound hammers will be used not only for quality control during construction but also to validate the performance of low-carbon concrete mixes (e.g., those with fly ash or slag). Accurate in-situ strength verification reduces over-design and material waste, aligning with green building goals.
5. Expansion in Emerging Markets and Urbanization Hubs
Asia-Pacific (especially India and Southeast Asia) and parts of Africa will experience strong market growth due to rapid urbanization and public infrastructure programs. Affordable, durable rebound hammers with localized technical support will be in high demand. Local manufacturing and partnerships with global brands will expand distribution networks and reduce costs.
6. Enhanced Calibration and Standardization Efforts
Regulatory bodies and industry consortia will push for stricter calibration protocols and international standardization (beyond ASTM C805 and EN 12504-2). H2 2026 may see wider adoption of automated calibration systems and blockchain-based certification to ensure measurement integrity, particularly in high-stakes projects.
7. Training and Certification Gains Importance
As reliance on rebound hammer data grows, so will the need for certified operators. Online training platforms and VR-based simulations will emerge as key tools for upskilling technicians, ensuring consistent and reliable test results across global projects.
Conclusion:
By H2 2026, the rebound hammer market will transition from a basic testing tool to a critical component of smart construction ecosystems. Innovation, digitization, and sustainability will be the main drivers, with leaders in the space offering integrated hardware-software solutions that deliver actionable insights. Companies that invest in AI, connectivity, and user training will gain competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven construction landscape.
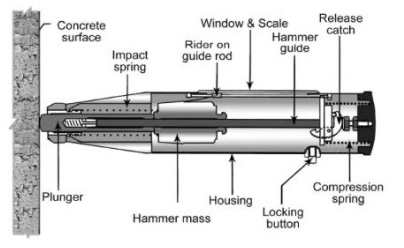
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Rebound Hammer (Quality and Intellectual Property)
When procuring a rebound hammer—also known as a Schmidt hammer—for assessing concrete strength, buyers often encounter critical challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to inaccurate test results, compliance issues, and even legal risks. Below are key areas to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Inaccurate Calibration
One of the most common issues is sourcing rebound hammers made with substandard materials or imprecise manufacturing. Low-quality hammers may feature inconsistent spring tension, worn plunger mechanisms, or poorly aligned impact components, all of which compromise measurement accuracy. Devices lacking proper factory calibration or traceable certification (e.g., to ASTM C805 or EN 12504-2) can yield unreliable data, undermining structural assessments.
Lack of Compliance with International Standards
Many inexpensive or generic rebound hammers do not meet recognized international standards. Sourcing non-compliant devices risks invalidating test reports, especially in regulated construction or infrastructure projects. Always verify that the equipment adheres to ASTM, ISO, or other applicable standards to ensure data credibility and project compliance.
Counterfeit or Clone Instruments Infringing IP
Rebound hammers, especially those modeled after the original Schmidt hammer by Proceq, are frequently counterfeited. These clones often replicate design features, logos, and packaging, infringing on intellectual property rights. Purchasing counterfeit devices not only exposes organizations to legal liability but also results in inferior performance and unreliable diagnostics.
Absence of Manufacturer Support and Warranty
Generic or unbranded rebound hammers may lack technical support, repair services, or valid warranties. If the device malfunctions, users may face long downtimes or high costs for third-party servicing. Genuine manufacturers typically offer calibration verification, spare parts, and software updates—critical for long-term usability.
Misleading Marketing and False Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate product capabilities, claiming compliance or precision that isn’t verified. For example, a device may be labeled as “ISO-certified” without providing documentation. Always request test certificates, calibration reports, and proof of conformity before purchase.
No Traceability or Serial Number Verification
Authentic rebound hammers come with unique serial numbers and traceable manufacturing records. Counterfeit or low-quality models often omit these details, making it impossible to verify authenticity or service history. This lack of traceability can be problematic during audits or quality inspections.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, source rebound hammers only from authorized distributors or reputable manufacturers with clear IP rights, verifiable compliance, and robust quality assurance. Investing in genuine, standards-compliant equipment ensures accurate, defensible test results and protects your organization from legal and operational risks.
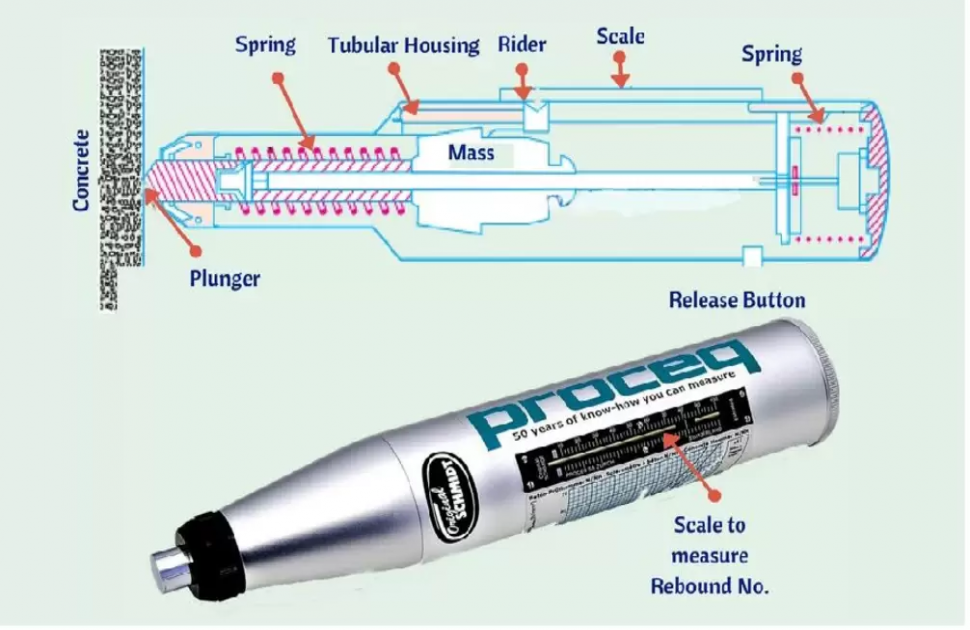
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Rebound Hammer
Overview
The Rebound Hammer, also known as a Schmidt Hammer, is a non-destructive testing (NDT) device used to assess the surface hardness and approximate compressive strength of concrete. Due to its precision and use in construction and engineering, its transportation, import/export, and usage are subject to logistics and compliance regulations depending on the region and application.
Regulatory Classification
Rebound Hammers are typically classified as industrial measuring instruments or testing equipment. Under international trade systems:
– HS Code: Generally falls under 9024.80 (instruments and appliances for testing mechanical properties of materials).
– ECCN: In the U.S., it may be classified under EAR99, meaning it is not specifically controlled but still subject to export regulations. However, verify based on technical specifications.
Export and Import Compliance
- Export Controls: Confirm whether the device incorporates any technology subject to ITAR or dual-use regulations (e.g., integrated GPS or data transmission features). Most standard rebound hammers are EAR99 and can be exported without a license to most countries, except embargoed destinations.
- Import Duties and Taxes: Duties vary by country. For example:
- EU: Typically 0% duty for scientific instruments under certain conditions (check TARIC code).
- India: Subject to Basic Customs Duty (BCD) and IGST; exemptions may apply under project imports or research use.
- Documentation Required: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, certificate of origin, and technical specifications.
Packaging and Shipping
- Packaging: The device must be securely packed in a shock-resistant case with cushioning to prevent damage during transit. Include all accessories (e.g., calibration anvil, user manual).
- Labeling: Clearly mark as “Fragile” and “This Side Up.” Include handling icons per ISTA or ISO standards.
- Shipping Modes: Suitable for air, sea, or ground freight. Use insured, trackable services. For air freight, ensure compliance with IATA packaging directives for instruments.
Calibration and Certification
- Rebound hammers should be delivered with a valid calibration certificate traceable to national standards (e.g., NIST, UKAS, DAkkS).
- Periodic recalibration is required (typically annually) to maintain compliance with standards such as ASTM C805 or EN 12504-2.
- Include calibration records with shipment for quality assurance and customs verification if required.
Safety and Handling
- Although not hazardous, the hammer mechanism can pose a pinching risk. Include safety warnings in user documentation.
- No special handling required for transport under IATA/IMDG/ADR regulations, unless battery-powered components are included (check lithium battery rules if applicable).
End-Use and Compliance with Standards
- Ensure the device is used in compliance with local building codes and testing standards.
- For projects under international contracts (e.g., World Bank-funded), test equipment may need third-party certification or approval from the overseeing body.
Record Keeping and Traceability
- Maintain records of serial numbers, calibration dates, shipping documents, and end-user information for at least 5 years (or as required by local law).
- Essential for audit trails, warranty claims, and anti-diversion compliance.
Regional Variations
- USA: Complies with ASTM C805; no special import license for EAR99 items.
- EU: Must comply with CE marking directives if sold as a complete instrument (may fall under Measuring Instruments Directive 2014/32/EU).
- GCC Countries: May require SASO certification or G-Mark conformity for market access.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and compliance verification are essential when shipping Rebound Hammers internationally. Always consult with customs brokers and regulatory experts to ensure adherence to local laws, especially regarding certification, duties, and end-use restrictions.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Rebound Hammer:
Sourcing a rebound hammer requires careful consideration of quality, accuracy, reliability, and compliance with international standards such as ASTM C805 or EN 12504-2. It is essential to select a reputable supplier or manufacturer known for producing durable and calibrated equipment to ensure consistent and dependable test results. Factors such as ease of use, availability of technical support, calibration services, and warranty should also influence the sourcing decision. Investing in a high-quality rebound hammer from a trusted source not only enhances the efficiency of non-destructive concrete strength assessment but also contributes to the overall safety and integrity of construction projects. Therefore, a strategic and well-researched procurement approach is crucial to obtaining a rebound hammer that meets both technical requirements and long-term operational needs.