The global natural stone market, driven by rising demand for luxury finishes in residential and commercial construction, is experiencing steady growth. According to Grand View Research, the global natural stone market size was valued at USD 38.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030. Marble, as one of the most sought-after natural stones due to its elegance, durability, and timeless appeal, represents a significant share of this expansion. Factors such as urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing preference for premium building materials in regions like Asia-Pacific, North America, and the Middle East are fueling demand for high-quality marble. As supply chains evolve and sustainability gains importance, leading manufacturers are investing in advanced quarrying techniques, eco-friendly processing, and global distribution networks. In this competitive landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as top real marble manufacturers, combining heritage, scale, and innovation to dominate the international market.
Top 9 Real Marble Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Georgia Marble Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: polycor.com
Key Highlights: It wouldn’t be until 1884 that the Georgia Marble Company was officially founded, gaining control of 7,000 acres on Samuel Tate’s land. The Georgia Marble ……
#2 Blanc Carrare, the marble manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: blanc-carrare.com
Key Highlights: Blanc Carrare has over the years established itself as the benchmark marble manufacturer for the architectural and interior design sectors….
#3 Vermont Quarries Corp.
Domain Est. 2019
Website: vermontdanbymarble.com
Key Highlights: Vermont Quarries Corp. We Are The Largest Underground Marble Quarry in The World. There is no Substitute for Danby Marble!Missing: manufacturer official…
#4 Marble of the World: Top Tile and Stone Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: marbleoftheworld.com
Key Highlights: Explore luxury surfaces, exotic stone slabs & gallery-style showrooms. Walk in or schedule a visit in Pompano Beach, Miami or Stuart….
#5 House of Marbles
Domain Est. 1999
Website: houseofmarbles.com
Key Highlights: We are makers & purveyors of a world famous range of glass marbles, board games, classic toys, puzzles, pastimes & decorative accessories for the home and ……
#6 Official Web Site of International Marble Company LLC
Domain Est. 2003 | Founded: 1999
Website: intmarbleco.com
Key Highlights: International Marble Co. LLC (IMC) , an ISO 9001certified company, was established in 1999 with the objective of producing and supplying top quality marble….
#7 Phillipsburg Marble Company
Domain Est. 2004
Website: pburgmarble.com
Key Highlights: In Phillipsburg, NJ surrounding areas we specialize in the sales and installation of marble, granite, quartz and limestone for beautiful kitchens and baths….
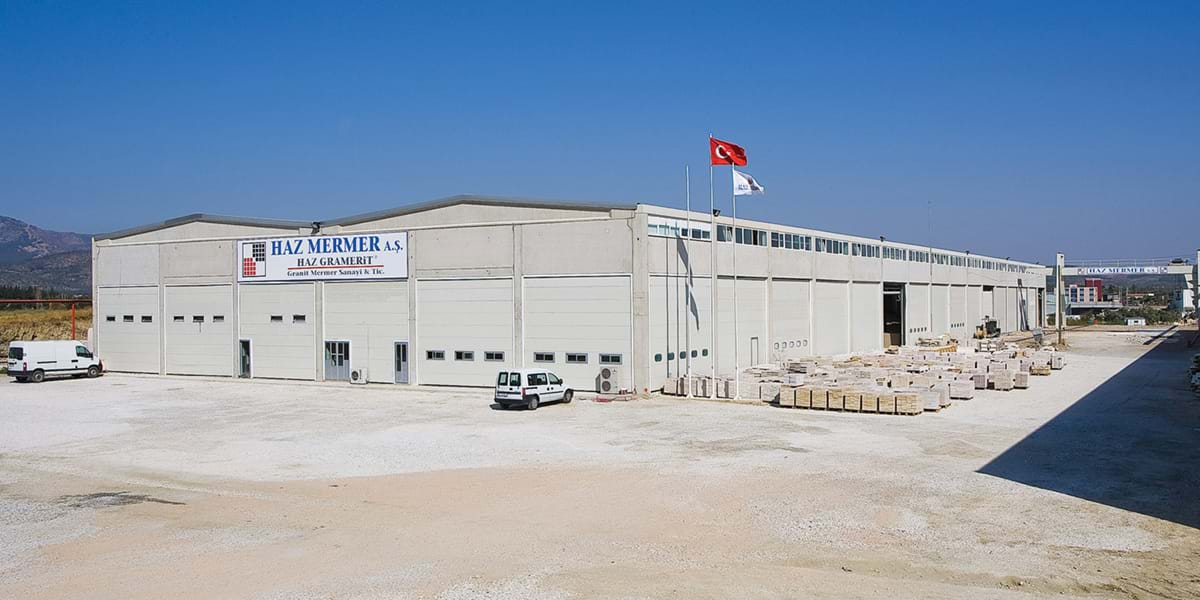
#8 HAZ MARBLE
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 1978
Website: hazmarble.com
Key Highlights: HAZ Marble was established in 1978 and have now successfully completed over 6000000 m2 of natural stone installation work….
#9 Marble King
Domain Est. 2007
Website: marblekingusa.com
Key Highlights: Established in the late 1940’s, Marble King Marbles are highly recognized and respected worldwide. Discover for yourself why we are known for our tradition, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Real Marble

H2 2026 Market Trends for Real Marble
The real marble market in the second half of 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and macroeconomic factors. While demand for luxury and natural aesthetics remains strong, the sector faces significant headwinds related to sustainability, cost, and competition. Here’s a detailed analysis of the key trends anticipated for H2 2026:
1. Sustainability as a Primary Differentiator
Environmental concerns will be central to the marble market. Consumers and commercial developers increasingly prioritize low-carbon materials. As a result:
* Traceability & Certification: Demand will surge for marble with verifiable sustainability credentials (e.g., EPD – Environmental Product Declarations, quarries with ISO 14001 certification). Blockchain-based traceability from quarry to installation will gain traction.
* Local Sourcing Preference: Regional marble (e.g., U.S. marble in North America, Italian Carrara with local distribution) will be favored over imports to reduce transportation emissions, though premium international varieties will retain their niche.
* Water & Energy Efficiency in Quarries: Investment in modern, energy-efficient extraction and processing technologies will be a competitive necessity.
2. Premiumization and Experiential Design
Despite economic fluctuations, the high-end residential and luxury hospitality sectors will drive demand for unique, high-quality marble:
* Rare Varieties & Custom Finishes: Increased demand for exotic or less common marble types (e.g., deep green, dramatic veining) and custom finishes (e.g., honed, brushed, flamed) to create distinctive, personalized spaces.
* Integration with Wellness & Biophilic Design: Marble’s natural beauty and cool thermal properties will make it a key material in wellness spaces (spas, bathrooms) and biophilic interiors aiming to connect occupants with nature.
* Architectural Statement Pieces: Use of large-format slabs and book-matched installations for dramatic walls, islands, and feature elements will grow in premium projects.
3. Technology Driving Efficiency and Customization
Technology will play a crucial role in mitigating costs and enhancing value:
* Advanced Fabrication: Wider adoption of CNC waterjet cutting and robotic polishing will improve precision, reduce waste, and enable complex, custom designs more efficiently.
* Digital Showrooms & AR/VR: Virtual and augmented reality tools will allow designers and clients to visualize marble applications in real spaces remotely, accelerating decision-making and reducing sample waste.
* AI for Resource Management: AI algorithms will optimize quarry planning and logistics to minimize environmental impact and operational costs.
4. Persistent Cost Pressures and Competitive Landscape
Economic factors and competition will challenge the market:
* High Energy & Transport Costs: Volatile energy prices and ongoing logistics complexities (especially for imported marble) will keep prices elevated, limiting mass-market appeal.
* Strong Competition from Alternatives: Engineered stone (quartz) and high-quality porcelain slabs (offering marble-like aesthetics with greater durability and lower maintenance) will continue to capture significant market share, particularly in mid-tier residential and commercial projects.
* Labor Shortages: Skilled stoneworkers remain in short supply, impacting installation timelines and costs, potentially slowing project completions.
5. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Resilience
Supply chains will remain a focus:
* Diversification of Sources: Buyers and fabricators will seek to diversify quarry sources beyond traditional hubs (Italy, Turkey, Greece) to mitigate geopolitical risks and ensure supply stability (e.g., increased focus on India, Brazil, China with improved quality control).
* Inventory Buffering: Strategic stockpiling of key popular slabs by distributors and large fabricators may become more common to hedge against supply disruptions.
Conclusion
H2 2026 will see the real marble market firmly entrenched in the premium segment, driven by its unparalleled natural beauty and status appeal, particularly in luxury applications. Success will hinge on the industry’s ability to address sustainability concerns transparently, leverage technology to improve efficiency and customization, and clearly articulate its unique value proposition against high-performing alternatives. While cost and competition remain significant challenges, the enduring demand for authenticity and luxury ensures a resilient, albeit specialized, market for genuine marble.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Real Marble (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing real marble for architectural, design, or construction projects can be rewarding, but it comes with several challenges—particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Being aware of these pitfalls can help buyers, designers, and contractors make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
1. Misrepresentation of Marble Quality
One of the most common issues in marble sourcing is the misrepresentation of quality. Suppliers may label lower-grade stone as premium marble, leading to dissatisfaction upon installation.
- Vein Variation and Consistency: Natural marble varies significantly between slabs. Buyers expecting uniformity may be disappointed if variations in color, veining, or texture are not disclosed upfront.
- Fillers and Resins: Some marble slabs are heavily filled with epoxy or resin to mask natural fissures. While common, excessive filling can compromise durability and aesthetics.
- Thickness and Dimensional Accuracy: Inconsistent slab thickness or inaccurate dimensions can cause installation problems and increased waste.
Tip: Always request samples, inspect full slabs in person when possible, and specify quality grades in contracts.
2. Confusion Between Natural Marble and Alternatives
Buyers may inadvertently purchase marble-look porcelain tiles, engineered stone, or cultured marble instead of genuine natural marble.
- Marketing Terminology: Terms like “marble effect” or “marble-style” may be used loosely, misleading clients into believing they are purchasing real stone.
- Origin Mislabeling: Some stones are marketed as “Italian marble” but are actually sourced elsewhere and only finished in Italy.
Tip: Verify the stone’s geological classification and origin with certification (e.g., certificate of authenticity, quarry documentation).
3. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Without proper documentation, it can be difficult to confirm the marble’s origin, treatment history, or compliance with sustainability standards.
- Unethical Sourcing: Marble from conflict zones or quarries with poor labor practices may enter the supply chain without traceability.
- Import Regulations: Missing or falsified documentation can lead to customs delays or legal issues, especially in regions with strict import controls.
Tip: Work with suppliers who provide full traceability, including quarry location, extraction date, and treatment records.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) and Design Rights Violations
In high-end design, unique marble patterns or custom finishes may be protected under IP laws—especially when used in signature architectural elements.
- Patented Finishes or Cuts: Some companies develop proprietary cutting techniques or surface treatments (e.g., honed, brushed, or 3D textured finishes) that are trademarked or patented.
- Copycat Projects: Using a distinctive marble layout or combination from a famous building without permission may lead to legal disputes, especially if it’s part of a registered design.
Tip: When replicating a design, consult legal counsel to ensure compliance with design rights and avoid infringement claims.
5. Inadequate Supplier Vetting
Choosing suppliers based solely on price or convenience can result in poor-quality materials and unreliable delivery.
- Fake Certifications: Some suppliers present forged quality or sustainability certifications (e.g., ISO, LEED-compliant).
- Middlemen Without Transparency: Importers or resellers may not disclose the original quarry, increasing the risk of receiving inconsistent or misrepresented material.
Tip: Audit suppliers, visit quarries if possible, and require third-party lab testing for material composition and performance.
6. Ignoring Environmental and Ethical Concerns
Sustainability is increasingly important, and overlooking ethical sourcing can damage brand reputation.
- Carbon Footprint: Transporting heavy marble over long distances contributes significantly to emissions.
- Quarrying Impact: Unsustainable extraction can lead to environmental degradation and community disputes.
Tip: Source regionally when possible, and look for suppliers with environmental management certifications.
Conclusion
Sourcing real marble requires due diligence to avoid pitfalls related to quality misrepresentation and IP issues. By verifying authenticity, demanding transparency, and respecting design rights, stakeholders can ensure a successful and legally sound procurement process.
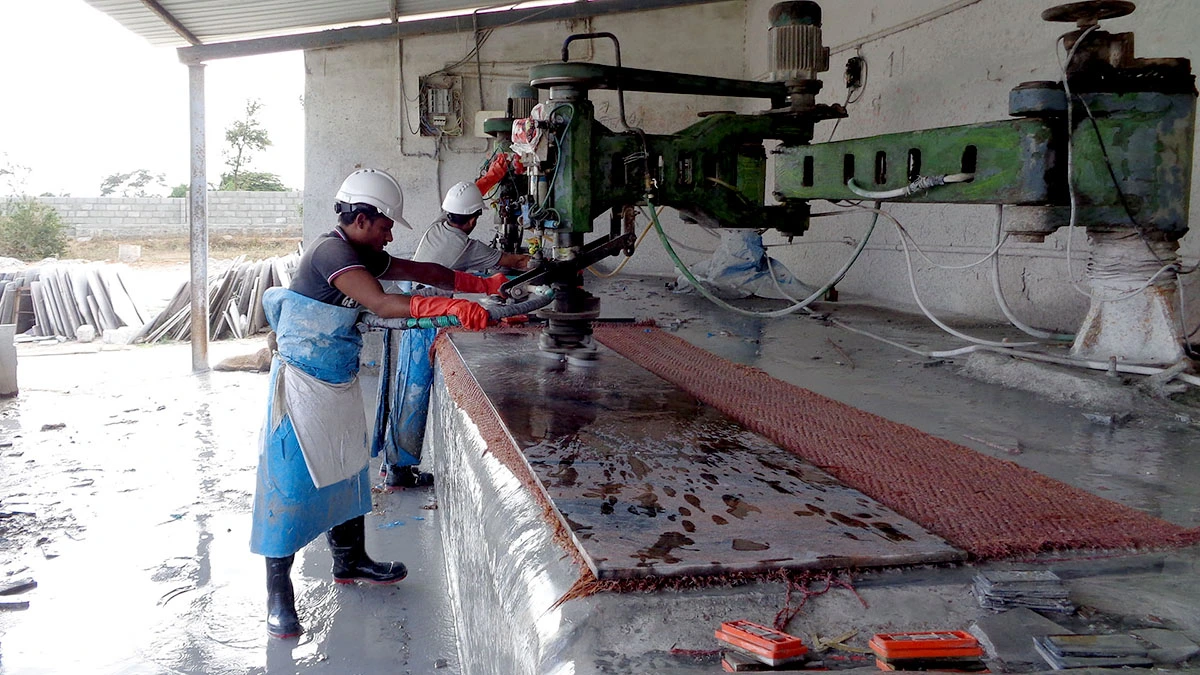

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Real Marble
Transporting and handling real marble requires meticulous planning due to its weight, fragility, and natural variability. Adhering to proper logistics and compliance protocols ensures product integrity, on-time delivery, and adherence to international trade regulations.
Product Handling and Packaging Standards
Real marble must be packaged to withstand shocks, moisture, and pressure. Use wooden crates with internal foam or cardboard dividers to prevent surface scratching and edge chipping. Each slab or block should be individually separated and secured. Vertical storage during transport is recommended to reduce stress on edges. Label all packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and handling instructions.
Transportation Requirements
Due to the high density of marble (typically 160–180 lbs per cubic foot), only heavy-duty vehicles with proper load distribution and securing mechanisms should be used. Flatbed trucks with side rails and tie-down straps are ideal for slabs. Blocks must be secured with chains and dunnage to prevent shifting. Temperature and humidity should be monitored, especially for long-haul or overseas shipments, to avoid condensation that can lead to staining or mold.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify all applicable international trade regulations, including export controls from the country of origin and import requirements in the destination country. Required documentation typically includes a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and sometimes a phytosanitary certificate if wooden packaging is used (ISPM 15 compliance). Ensure all documentation accurately describes the stone type, quantity, weight, and value.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Classify marble under the correct Harmonized System (HS) code—common codes include 2515.11 (unworked marble) or 6802.91 (worked marble). Duty rates vary by country; consult local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker. Be prepared for potential anti-dumping or countervailing duties, particularly when importing from regions with subsidized production. Provide all supporting documents promptly to avoid delays.
Environmental and Sustainability Regulations
Source marble from quarries compliant with local environmental laws and sustainability standards. Some markets (e.g., EU, California) may require disclosure of environmental impact or adherence to green building certifications (e.g., LEED). Maintain records of quarry origin and extraction practices to support claims of responsible sourcing.
Safety and Worker Compliance
Ensure all warehouse and loading personnel are trained in safe marble handling techniques, including the use of mechanical aids (e.g., forklifts with slab clamps). Comply with OSHA (or local equivalent) regulations for workplace safety, including personal protective equipment (PPE), lifting procedures, and hazard communication. Conduct regular risk assessments at handling and storage sites.
Quality Inspection and Documentation
Perform pre-shipment inspections to verify dimensions, surface finish, color consistency, and absence of defects. Document each batch with photographs and quality reports. Provide clients with certificates of conformance and material test reports when applicable. Retain records for traceability and dispute resolution.
Risk Management and Insurance
Procure comprehensive cargo insurance covering damage, breakage, theft, and delays. Clearly define liability terms in transport contracts. Include contingency plans for rerouting, storage, or replacement in case of unforeseen disruptions (e.g., port delays, natural disasters).
Adhering to this guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient movement of real marble across global supply chains while maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, sourcing real marble requires careful consideration of quality, origin, authenticity, and ethical practices. It is essential to establish relationships with reputable suppliers and verify the marble’s natural characteristics through physical inspection or certification. Factors such as color variation, veining, durability, and suitability for the intended application must be evaluated to ensure the material meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. Additionally, considering sustainability and responsible quarrying practices contributes to a more ethical sourcing process. With thorough research, due diligence, and attention to detail, sourcing real marble can result in a timeless, luxurious material that adds lasting value to any project.