The global ratchet wheel market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global hand tools market—which includes ratchet-based tools—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, with ratchet wrenches and components like ratchet wheels forming a significant segment. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global hand tools market at USD 17.8 billion in 2022 and forecasts continued expansion, fueled by advancements in tool durability, ergonomics, and the rising need for precision in mechanical applications. As industrial automation and vehicle production increase worldwide, the demand for high-performance ratchet wheels—known for their reliability in torque transmission and motion control—has intensified. This growing market landscape has elevated the role of specialized manufacturers who combine engineering precision with scalable production. Below are the top 10 ratchet wheel manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and global supply in this evolving industry.
Top 10 Ratchet Wheel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 RATCHET WHEEL ASSEMBLY 0.75 T (42587) TOR
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1932
Website: aceindustries.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $499.99 30-day returnsEstablished in 1932, Ace industries have supplied replacement, maintenance, and repair parts from original equipment manufacturers (OEM) fo…
#2 The Ratchet Depot, Inc.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ratchetdepot.com
Key Highlights: The Ratchet Depot, Inc. is an American made cargo-containment manufacturing company….
#3 TOR
Domain Est. 2003
Website: hoosiercrane.com
Key Highlights: In stock 3-day deliveryTOR-0041 – RATCHET WHEEL ASSEMBLY 3T. Manufacturer Part Number TOR-0041. Availability Available For Order. Special Price $43.01 Regular Price $47.52….
#4 Ratchet Wheel
Domain Est. 2005
Website: pearlengineers.com
Key Highlights: Any kind of Ratchet Wheel of 15 deg; 30deg; 45 deg; 60 deg; angle of any number of Teeth can be cut. We are leading manufacturer of Ratchet Wheel, supplier of ……
#5 Ratchet Wheel
Domain Est. 2012
Website: hewittrad.com
Key Highlights: In stock $27.43 deliveryRatchet Wheel-Hewitt Winch. Hewitt is a leading USA manufacturer of docks, lifts, pontoon legs, & much more. Buy online or find a dealer near you!…
#6 Ratchet Wheel Manufacturers, Exporters & Suppliers in India
Domain Est. 2015
Website: rminingtools.com
Key Highlights: Rama Mining Tools is a leading manufacturer, exporter and supplier of Ratchet Wheel in India, exports to USA, Spain, Colombia, Peru, Australia, UK, Russia, ……
#7 Ratchet Wheel [AC
Domain Est. 2000
Website: crowdersupply.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsRatchet Wheel. $329.40. Weight: 1.7 lbs. Add to Cart: Add to ……
#8 American Power Pull 27166
Domain Est. 2008
Website: autotoolworld.com
Key Highlights: 1–2 day delivery 90-day returnsWe carry brand name manufactures from KD Tools, Mityvac, Robinair, and Zinko Jacks just to name a few. Shop By Categories. Categories. Abrasives & Ad…
#9 Ratchet Wheels
Domain Est. 2009
#10 HAZET 6401
Domain Est. 2017
Website: misterworker.com
Key Highlights: 8-day delivery 14-day returnsRatchet wheel with quick-release press-button, pawl, shift lever, screws, ball and compression spring for insert reversible ratchet square….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ratchet Wheel

H2: Ratchet Wheel Market Trends Forecast for 2026
As the global industrial and automotive sectors continue to evolve, the ratchet wheel market is poised for notable shifts by 2026. Driven by automation, sustainability mandates, and technological innovation, key trends are expected to shape demand, material usage, and application diversification. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of the anticipated market dynamics:
1. Increased Demand in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive sector—particularly electric vehicle (EV) production—is expected to be a major growth driver for ratchet wheels by 2026. Ratchet mechanisms are essential in seat adjusters, handbrakes, and transmission systems. With the global push toward electrification and smart vehicle features, demand for precision-engineered, lightweight ratchet components will rise. Growth in EV assembly lines will require high-reliability ratchet systems for automated torque tools and assembly jigs.
2. Rise of Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 and the expansion of smart factories will boost the use of ratchet wheels in robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and precision tooling. In 2026, expect increased integration of ratchet systems in modular automation equipment, where controlled, incremental motion is critical. Smart ratchets with embedded sensors (for torque monitoring and wear detection) may begin to enter niche markets, enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities.
3. Material Innovation and Lightweighting
To meet efficiency and emissions standards, manufacturers are prioritizing lightweight materials. By 2026, advanced engineering plastics (e.g., PEEK, nylon composites) and high-strength alloys will gain market share over traditional steel in ratchet wheel production—especially in aerospace and automotive applications. These materials offer corrosion resistance, reduced weight, and quieter operation, aligning with sustainability goals.
4. Growth in Renewable Energy and Infrastructure
The expansion of wind and solar energy projects will increase demand for ratchet wheels in maintenance tools, turbine assembly rigs, and tensioning systems. Offshore wind installations, in particular, require durable, corrosion-resistant ratcheting tools for high-torque applications. Similarly, infrastructure development in emerging economies will drive demand for manual and powered ratcheting tools in construction and pipeline industries.
5. Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific—led by China, India, and Southeast Asia—will remain the dominant market for ratchet wheels due to robust manufacturing, automotive growth, and infrastructure investment. However, North America and Europe will see steady growth driven by automation adoption and EV production. Localized production and supply chain resilience will become strategic priorities, reducing dependency on single-source suppliers.
6. Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will push manufacturers toward recyclable materials and longer-lasting ratchet components. By 2026, expect increased focus on designing ratchet systems for disassembly, repair, and reuse. Companies may adopt closed-loop manufacturing processes, particularly in Europe, where circular economy principles are being institutionalized.
7. Consolidation and Technological Differentiation
The ratchet wheel market may see further consolidation as larger industrial component suppliers acquire niche players to expand product portfolios. Competitive advantage will shift from cost leadership to innovation—such as noise reduction, anti-backlash designs, and integration with digital tool control systems.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the ratchet wheel market will be shaped by the convergence of digitalization, sustainability, and sector-specific demands. While traditional applications will persist, growth will be fueled by advanced manufacturing, EVs, and renewable energy. Companies that invest in material science, smart integration, and regional agility will be best positioned to capture emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ratchet Wheels: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing ratchet wheels—critical components in mechanisms requiring controlled motion and torque transmission—can introduce significant challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failure, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Material and Manufacturing Quality
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing ratchet wheels is substandard material selection and inconsistent manufacturing processes. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior-grade metals or plastics that lack the necessary strength, wear resistance, or dimensional stability. This can result in premature tooth wear, deformation under load, or complete mechanical failure. Additionally, imprecise machining or poor heat treatment compromises tooth profile accuracy and surface hardness, undermining the ratchet’s functional reliability.
Inadequate Quality Control and Testing
Many suppliers—especially those in regions with lax regulatory oversight—may lack rigorous in-house quality assurance systems. Without proper inspection protocols such as geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) verification, hardness testing, and functional performance checks, defective units can pass undetected. This increases the risk of field failures and costly warranty claims downstream.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Sourcing ratchet wheels without proper documentation—such as material certifications (e.g., mill test reports), process validation records, or ISO compliance—limits traceability. In regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, medical devices), this absence can result in non-compliance and audit failures. Without traceability, identifying the root cause of a defect becomes nearly impossible.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Ratchet wheel designs, especially proprietary tooth profiles or integrated features, may be protected by patents, trade secrets, or design rights. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers or copying OEM designs—even unintentionally—can lead to IP infringement claims. This is particularly risky when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement, where suppliers may freely replicate patented components without legal repercussions.
Unprotected Design Disclosure
When engaging suppliers for custom ratchet wheels, companies often share detailed engineering drawings or CAD models. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear contractual terms, these designs may be reverse-engineered or sold to competitors. Suppliers in some markets may leverage disclosed designs to produce and market identical parts independently, undermining the original buyer’s market advantage.
Supply Chain Transparency Gaps
Many sourced ratchet wheels pass through multiple tiers of subcontractors, obscuring the actual point of manufacture. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to verify claims about quality standards, labor practices, or IP compliance. Hidden subcontracting increases exposure to counterfeit parts and unauthorized production.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits, including on-site inspections of manufacturing facilities.
– Require material and process certifications and perform incoming quality inspections.
– Use legally binding agreements that protect IP and define ownership of custom designs.
– Work with suppliers in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement when possible.
– Specify performance and dimensional requirements clearly in technical documentation.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, companies can ensure reliable performance, legal compliance, and long-term supply chain integrity when sourcing ratchet wheels.
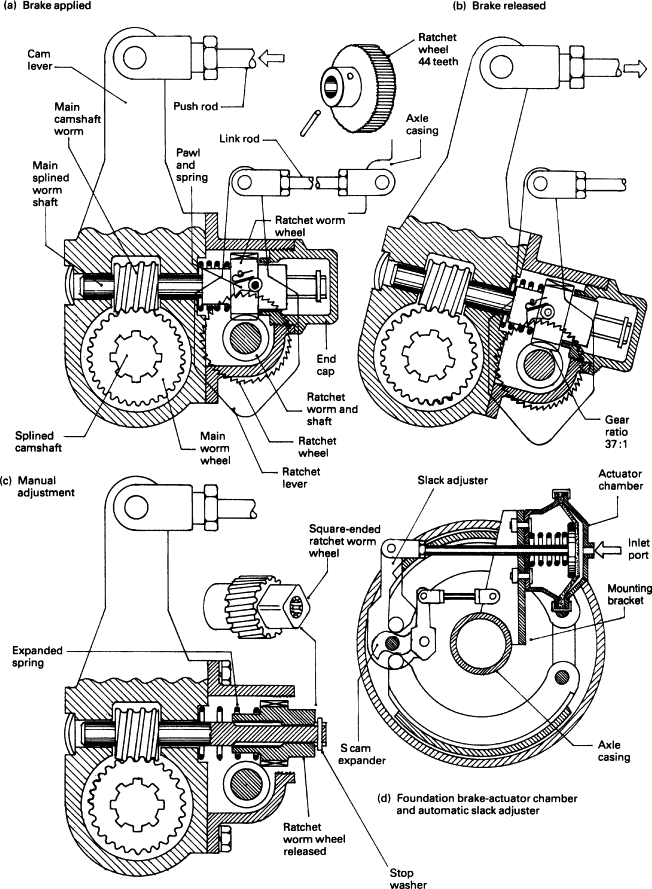
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ratchet Wheel
Overview of Ratchet Wheel Classification
Ratchet wheels are mechanical components commonly used in tensioning devices, such as tie-down straps, winches, and lifting equipment. They are typically made from metal (e.g., steel, aluminum) or high-strength polymers. For logistics and compliance purposes, accurate classification under international trade codes (e.g., HS Code) is essential. Ratchet wheels generally fall under HS Code 8483.60 (Transmission shafts, cranks, bearing housings, plain shaft bearings, gearing, and driving elements). However, classification may vary based on material, function, and whether the ratchet wheel is imported as a standalone part or as part of an assembly.
Export Documentation Requirements
When shipping ratchet wheels internationally, the following documentation is typically required:
– Commercial Invoice: Must include product description, quantity, value, country of origin, and HS code.
– Packing List: Details packaging type, gross/net weight, and dimensions.
– Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries for tariff determination; may be preferential (e.g., Form A for GSP) or non-preferential.
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): Essential for freight movement and customs clearance.
Ensure all documents clearly describe the item as “Ratchet Wheel – Mechanical Component for Tensioning Devices” to avoid misclassification.
Import Regulations and Duties
Import regulations for ratchet wheels depend on the destination country. Common considerations include:
– Tariff rates based on the HS code classification.
– Anti-dumping or safeguard measures (e.g., on certain steel products in the EU or US).
– Compliance with local product standards (e.g., ISO, ANSI, or regional mechanical safety requirements).
Importers should verify whether ratchet wheels are subject to any import licensing, quotas, or additional fees. For example, the U.S. may impose Section 232 tariffs on steel-derived components.
Packaging and Shipping Best Practices
To ensure safe and efficient transport:
– Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., corrugated cardboard with internal dividers or wooden crates for bulk shipments).
– Securely fasten components to prevent movement during transit.
– Label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”) and proper UN/DOT markings if applicable.
– Optimize packaging size to reduce volumetric weight charges, especially for air freight.
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
Ratchet wheels may be subject to industry-specific regulations depending on their end use:
– If used in automotive or aerospace applications, compliance with ISO/TS 16949 or AS9100 standards may be required.
– In lifting or rigging equipment, adherence to OSHA (U.S.), LOLER (UK), or similar safety regulations is critical.
– Ensure materials meet REACH (EU) or RoHS requirements if applicable, particularly for metal alloys or coated finishes.
Restricted Destinations and Embargoes
Be aware of international trade restrictions. Ratchet wheels could be controlled under dual-use regulations if designed for military or strategic applications (e.g., under the Wassenaar Arrangement). Always screen customers and end-users against denied party lists (e.g., U.S. BIS, EU Consolidated List) to ensure compliance with sanctions programs.
Customs Clearance Tips
- Provide a detailed technical specification sheet with your shipment, including material composition, dimensions, and intended use.
- Pre-classify the product with customs authorities if uncertainty exists (e.g., via U.S. CBP Binding Rulings).
- Work with a licensed customs broker in the destination country to expedite clearance and avoid delays.
Environmental and Sustainability Standards
Consider environmental compliance when manufacturing and shipping:
– Recyclable packaging materials are encouraged to meet green logistics goals.
– Comply with local waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) directives if ratchet wheels are part of larger electromechanical systems.
– Reduce carbon footprint by optimizing transport routes and choosing sea freight over air when possible.
By following this guide, manufacturers and distributors can ensure efficient, compliant global logistics for ratchet wheel components.
Conclusion for Sourcing Ratchet Wheel:
After a comprehensive evaluation of suppliers, cost, quality, lead times, and technical specifications, it is concluded that sourcing the ratchet wheel from [Supplier Name/Region] presents the most favorable balance of reliability, performance, and cost-efficiency. The selected supplier demonstrates consistent quality control, adherence to required materials and manufacturing standards (e.g., precision machining, durability testing), and the capability to meet projected demand volumes. Additionally, logistics and communication channels are viable, ensuring smooth order fulfillment and timely delivery.
Long-term benefits such as potential volume discounts, scalability, and technical support further strengthen this sourcing decision. However, it is recommended to maintain supply chain resilience through periodic performance reviews and identifying alternate suppliers as a risk mitigation strategy. Overall, the chosen sourcing approach supports operational efficiency, product integrity, and cost objectives for the ratchet wheel component.