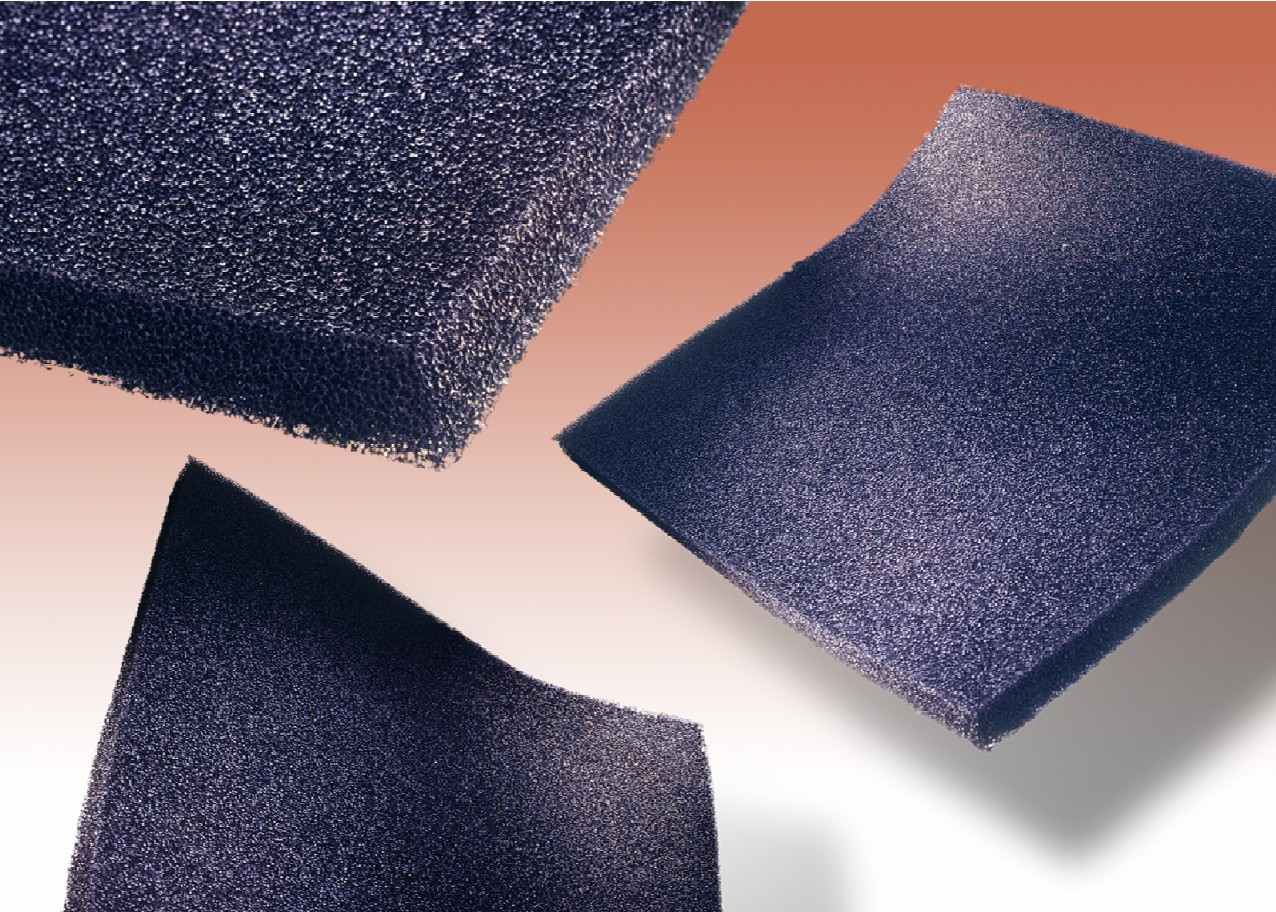
The global radar absorbent materials (RAM) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing defense spending, advancements in stealth technology, and rising demand for electromagnetic interference shielding in aerospace and military applications. According to Grand View Research, the global radar absorbent materials market was valued at USD 1.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued expansion, attributing growth to heightened investments in next-generation defense systems and the proliferation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) requiring low-observable characteristics. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and performance, shaping the future of stealth and electromagnetic absorption technologies. The following list highlights the top eight radar absorbent materials manufacturers leading this transformation.
Top 8 Radar Absorbent Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Cuming Microwave Custom Radar Absorbing Structures
Domain Est. 1990
Website: ppg.com
Key Highlights: Cuming Microwave Corporation offers a variety of Radomes and Radar Absorbing Structures designed to meet specific customer requirements….
#2 ARC Technologies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rf.cdiweb.com
Key Highlights: ARC Technologies, a Hexcel Company, is the leading supplier of microwave and RF absorbing materials for commercial and defense applications….
#3 Radar Absorbent Coatings For Stealth Protection
Domain Est. 1997
Website: armorthane.com
Key Highlights: Polyurea can serve as effective radar-absorbent materials (RAMs) while also providing additional protection from harsh environments, and even enemy fire….
#4 Radar Absorbent Materials
Domain Est. 1999
Website: solianiemc.com
Key Highlights: RADAR Absorbent Material: Broadband, Conical, Weather proof, suitable for sea applications. Contact us for more information!…
#5 MAST from RFMW
Domain Est. 2003
Website: rfmw.com
Key Highlights: MAST Technologies designs, develops and manufactures innovative RF, microwave and EMI absorbing materials for integration into military and electronics ……
#6 MagRAM (Magnetic Radar Absorbing Materials) RF Absorbers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: mwtmaterials.com
Key Highlights: MWT Materials is a full service RF Control Business. We manufacture MagRAM sheets that can be die cut and MagRAM coatings for irregular surfaces….
#7 Top Radar Absorbing Material Suppliers
Website: aft.systems
Key Highlights: Discover top-quality radar absorbing materials by MAST at AFT Systems. Your reliable radar absorbing material suppliers for advanced engineering solutions….
#8 Radar Absorbent Material
Website: micromag.es
Key Highlights: For over 10 years, Micromag has been working with defence industry customers which sole focus is on Radar Absorbing Materials for stealth applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Radar Absorbent
H2: Market Trends for Radar Absorbent Materials in 2026
The radar absorbent materials (RAM) market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising global defense expenditures, advancements in stealth technology, and increasing demand from aerospace, defense, and commercial sectors. The market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.8% from 2021 to 2026, reaching an estimated value of USD 2.3–2.5 billion by 2026, according to industry analyses.
Below are the key market trends shaping the radar absorbent materials landscape in 2026:
-
Heightened Defense Modernization Programs
Geopolitical tensions and strategic defense initiatives in regions such as North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe are accelerating investments in stealth platforms. Countries including the U.S., China, India, and Russia are modernizing their military fleets—especially stealth aircraft, naval vessels, and ground vehicles—fueling demand for advanced RAM. The integration of RAM in next-generation platforms like sixth-generation fighter jets and unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs) is a major growth catalyst. -
Advancements in Material Science and Nanotechnology
By 2026, innovations in nanomaterials—such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), graphene-based composites, and metamaterials—are enhancing the performance of RAM. These materials offer superior electromagnetic wave absorption, broader frequency bandwidths, and reduced weight. Lightweight, flexible, and multifunctional coatings that combine radar absorption with thermal management or structural integrity are gaining traction, especially in aerospace applications. -
Shift Toward Multispectral and Broadband Absorption
There is a growing demand for RAM that can absorb not only radar waves (RF) but also infrared (IR) and terahertz signatures. By 2026, multispectral RAM solutions are becoming critical to ensure full-spectrum stealth, particularly in counter-surveillance and electronic warfare. Broadband RAM capable of attenuating signals across multiple radar bands (L-band to Ka-band) is increasingly preferred for versatile threat environments. -
Expansion in Commercial and Civil Applications
Beyond defense, RAM is finding new applications in commercial sectors. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding in 5G infrastructure, data centers, and autonomous vehicles is driving demand. Additionally, anechoic chambers used for testing and calibrating radar and communication systems are adopting advanced RAM to ensure accuracy, contributing to market diversification. -
Regional Growth Dynamics
- North America remains the largest market due to robust defense R&D and procurement by the U.S. Department of Defense.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by China’s military modernization and India’s indigenous defense production push.
- Europe is focusing on collaborative defense programs (e.g., FCAS, Tempest) that incorporate stealth technologies.
-
The Middle East is increasing defense imports, including stealth-capable systems, which indirectly boosts RAM demand.
-
Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Environmental regulations are influencing the development of eco-friendly RAM formulations. By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly adopting water-based coatings and recyclable composites to meet REACH and RoHS standards, particularly in Europe. -
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Innovations
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) of RAM structures allows for complex geometries and customized absorption profiles. This trend is enabling rapid prototyping and integration of RAM into curved or irregular surfaces, improving stealth performance without compromising aerodynamics.
In conclusion, the 2026 radar absorbent materials market reflects a convergence of technological innovation, strategic defense needs, and expanding commercial applications. With continued R&D investment and a focus on multifunctional, lightweight, and environmentally sustainable solutions, the RAM market is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of stealth and electromagnetic management technologies.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Radar Absorbent Materials (RAM): Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing radar absorbent materials (RAM) is a highly specialized process fraught with technical and legal challenges. Buyers, particularly in defense, aerospace, and advanced electronics sectors, must navigate significant pitfalls related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Performance Verification
Radar absorption performance is highly dependent on frequency range, angle of incidence, environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), and substrate compatibility. A common mistake is accepting vendor-supplied data without independent verification under real-world or application-specific conditions. Lab results under ideal conditions may not translate to field performance.
Material Inconsistency and Batch Variability
RAM formulations—especially coatings, foams, or composite sheets—can suffer from batch-to-batch inconsistencies due to variations in raw materials, mixing processes, or curing conditions. Without strict quality control (QC) and traceability, this leads to unpredictable RF performance and potential system failures.
Poor Environmental Durability
Many RAMs degrade under UV exposure, moisture, thermal cycling, or mechanical stress. Sourcing materials without thorough environmental testing (e.g., MIL-STD-810 compliance) can result in delamination, cracking, or loss of absorptive properties in operational environments.
Insufficient Substrate Adhesion and Integration
RAM must bond reliably to the host structure. Poor adhesion leads to peeling or vibration-induced failure. Buyers often overlook the need for compatibility testing with the intended substrate and surface preparation requirements.
Lack of Standardized Testing and Documentation
Unlike some commercial materials, RAM performance testing lacks universal standards. Vendors may use proprietary methods or selective data presentation. Absence of traceable, third-party test reports (e.g., from anechoic chamber testing) increases risk.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Formulations
Many high-performance RAMs are protected by patents, trade secrets, or technical data rights. Sourcing from unauthorized suppliers or reverse-engineered products can expose the buyer to infringement claims, especially in regulated industries.
Ambiguous Licensing Terms
Even when licensing RAM technology, agreements may lack clarity on field of use, resale rights, or modification permissions. This can restrict integration into new systems or future upgrades, creating legal and operational constraints.
Loss of Design Control and Customization Rights
Suppliers may retain full IP ownership, preventing the buyer from modifying, reproducing, or qualifying alternative sources. This leads to vendor lock-in, supply chain vulnerability, and increased lifecycle costs.
Insufficient IP Due Diligence
Failing to verify the supplier’s IP ownership or freedom-to-operate can result in downstream liability. This is especially critical in international sourcing, where patent landscapes vary significantly by region.
Export Control and ITAR Compliance Risks
Many RAMs are subject to export controls (e.g., ITAR in the US). Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers—or using materials without proper authorization—can lead to severe regulatory penalties and project delays.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires thorough technical evaluation, third-party validation, robust supplier vetting, and clear contractual agreements that address both performance specifications and IP rights.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Radar Absorbent Materials (RAM)
Overview of Radar Absorbent Materials
Radar Absorbent Materials (RAM) are specialized composites or coatings designed to reduce the radar cross-section (RCS) of objects, making them less detectable by radar systems. These materials are commonly used in defense, aerospace, and stealth technology applications. Due to their strategic importance, the handling, transport, and use of RAM are subject to strict national and international regulations.
Regulatory Classification and Export Controls
Radar absorbent materials are typically classified under dual-use regulations due to their potential military applications. In the United States, RAM may fall under the jurisdiction of the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), administered by the Department of State’s Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC), or the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), managed by the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).
– ITAR-Controlled Items: If RAM is specifically designed or modified for military use, it is likely listed on the U.S. Munitions List (USML), Category XI (Military Electronics) or XII (Fire Control, Laser, Imaging, and Guidance Equipment).
– EAR-Controlled Items: Civilian or commercial-grade RAM may be subject to EAR and listed on the Commerce Control List (CCL) under ECCN 1C995 or similar.
Prior to shipment, verify the correct classification through a commodity jurisdiction (CJ) determination or a commodity classification automated tracking system (CCATS) request.
Licensing Requirements
Export, re-export, or transfer of RAM generally requires a license or license exception, depending on the destination country, end user, and end use.
– ITAR-controlled RAM typically requires a DSP-5 license for export.
– EAR-controlled RAM may be eligible for license exceptions such as LVS (Low-Value Shipments) or TMP (Temporary Exports), provided all criteria are met.
– Destinations under embargo (e.g., Iran, North Korea, Syria, and Crimea) generally require denial of export privileges.
Always conduct end-user and end-use screening using tools such as the Denied Persons List (DPL), Entity List, and Specially Designated Nationals (SDN) List.
Transportation and Packaging Standards
- Domestic Transport: Follow Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations for hazardous materials if RAM contains volatile or toxic components (e.g., solvents in spray-on coatings). Use appropriate packaging to prevent degradation and ensure material integrity.
- International Shipping: Comply with International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations or International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code as applicable. Include proper labeling, documentation, and hazard communication.
- Climate-Controlled Transport: Some RAM formulations are sensitive to temperature and humidity. Use climate-controlled containers or packaging with desiccants to maintain performance characteristics.
Handling and Storage Protocols
- Store RAM in secure, access-controlled facilities compliant with ITAR or EAR physical security requirements.
- Maintain environmental controls (temperature, humidity) per manufacturer specifications to prevent material degradation.
- Implement inventory tracking systems to monitor usage, movement, and storage of RAM.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling RAM, especially powdered or liquid forms, to avoid exposure to potentially hazardous constituents.
Recordkeeping and Auditing
- Maintain detailed records of all transactions involving RAM for a minimum of five years, including:
- Export licenses and authorizations
- Technical data transfers
- End-user documentation
- Shipping manifests and customs declarations
- Conduct regular internal audits to ensure compliance with export control laws and company policies.
- Prepare for potential government audits by maintaining an up-to-date compliance program, including employee training records.
Compliance Training and Personnel Clearance
- Ensure all personnel involved in the handling, shipping, or management of RAM complete regular export control training (e.g., annual ITAR/EAR compliance training).
- For ITAR-controlled materials, only U.S. persons (U.S. citizens, lawful permanent residents, or protected individuals) may access technical data without a license. Foreign nationals require a Technical Assistance Agreement (TAA) or other authorization.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of radar absorbent materials are critical to avoiding regulatory violations, penalties, and national security risks. Organizations must implement robust export control programs, conduct accurate classifications, maintain secure handling procedures, and stay current with evolving regulations. Consult legal counsel or export compliance experts when uncertainty arises.
In conclusion, sourcing radar absorbent materials (RAM) requires a careful evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, cost, availability, and supplier reliability. The selection process should align with the intended use—whether for defense, aerospace, or electromagnetic interference reduction—ensuring optimal performance in terms of absorption efficiency, bandwidth, weight, durability, and environmental resistance. Engaging with reputable suppliers, considering both domestic and international options, and staying informed about advancements in metamaterials and nanotechnology can enhance sourcing strategies. Long-term success depends on balancing performance needs with logistical and financial constraints, while maintaining flexibility for future technology integration. Effective collaboration with research institutions and material experts can further support informed decision-making and innovation in radar-absorbing solutions.