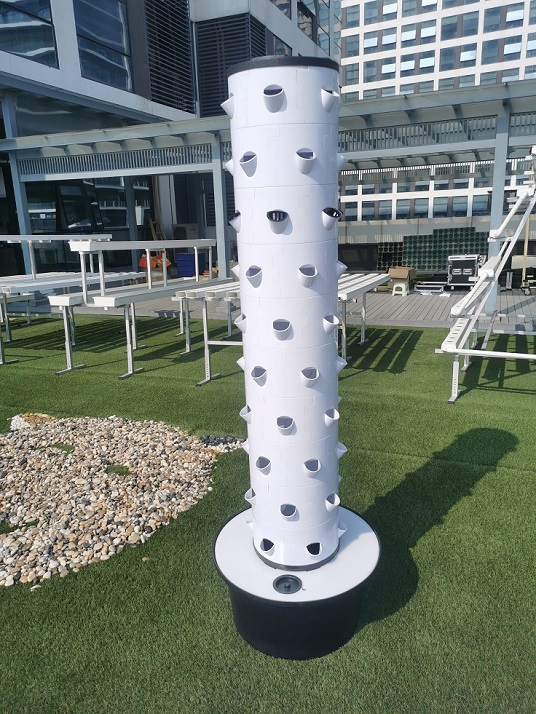
The global hydroponics market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for sustainable agriculture, increasing urbanization, and advancements in controlled environment farming. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the hydroponics market was valued at USD 19.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2024 to 2029. A key enabler of this expansion is the widespread adoption of durable and cost-effective materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in hydroponic system construction. PVC’s resistance to moisture, ease of installation, and structural reliability make it a preferred choice among commercial and hobbyist growers alike. As the industry scales, manufacturers specializing in PVC-based hydroponic components are playing a pivotal role in standardizing systems, improving efficiency, and driving down costs. This growing demand has given rise to a competitive landscape of innovative manufacturers focused on quality, scalability, and technological integration—making it essential to identify the top performers shaping the future of soilless cultivation.
Top 10 Pvc Hydroponics Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Custom Pvc Hydroponics Factory, Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2023
Website: m.sinabeacon.com
Key Highlights: Looking for PVC hydroponic systems? Shandong Hualiang Greenhouse Engineering Co., Ltd. offers high-quality solutions for your hydroponic needs….
#2 PVC Profile for the hydroponic sector
Domain Est. 1997
Website: quadraplast.com
Key Highlights: PVC profiles are becoming the preferred material for transporting and treating the water necessary for greenhouse cultivation….
#3 CropKing Inc
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cropking.com
Key Highlights: For over 35 years, CropKing has been the leader in controlled environment agriculture. We’ve manufactured and sold greenhouse structures, hydroponic growing ……
#4 ZipGrow™ Towers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: zipgrow.com
Key Highlights: They are a specially designed and scientifically proven vertical hydroponic Tower that helps growers maximize production….
#5 FloraFlex
Domain Est. 2010
Website: floraflex.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsFloraFlex offers an extensive selection of hydroponic growing supplies, such as nutrients, drip irrigation kits, coconut coir, light shields, and more….
#6 GrowersHouse
Domain Est. 2011
Website: growershouse.com
Key Highlights: Complete hydroponic kits, individual products, and accessories for a better grow. Free shipping on qualified orders. Expert advice….
#7 Hydroponic Growing Systems
Domain Est. 2016
Website: growrillahydroponics.com
Key Highlights: 14-day returnsGrowrilla Hydroponics is a 100% Italian brand of hydroponic growing systems, designed and manufactured in Italy by growers for growers….
#8 The Bucket Company
Domain Est. 2016
Website: thebucketcompany.com
Key Highlights: The Bucket Company offers a wide selection of hydroponic supplies for all growing applications. From home gardens to commercial facilities, our range of ……
#9 NFT PVC hydroponic system Company
Domain Est. 2018
Website: wellgaingreenhouse.com
Key Highlights: We provide all kinds of planting design, flat cultivation, multi-layer cultivation and A-frame cultivation. We provide technical solutions for Gutter ……
#10 Garden Tower Farming
Domain Est. 2021
Website: hydroponicschina.com
Key Highlights: We have complete hydroponics, or aeroponic tower for sale, easy to assemble and complete with accessories, and also provide hydroponics project design, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pvc Hydroponics
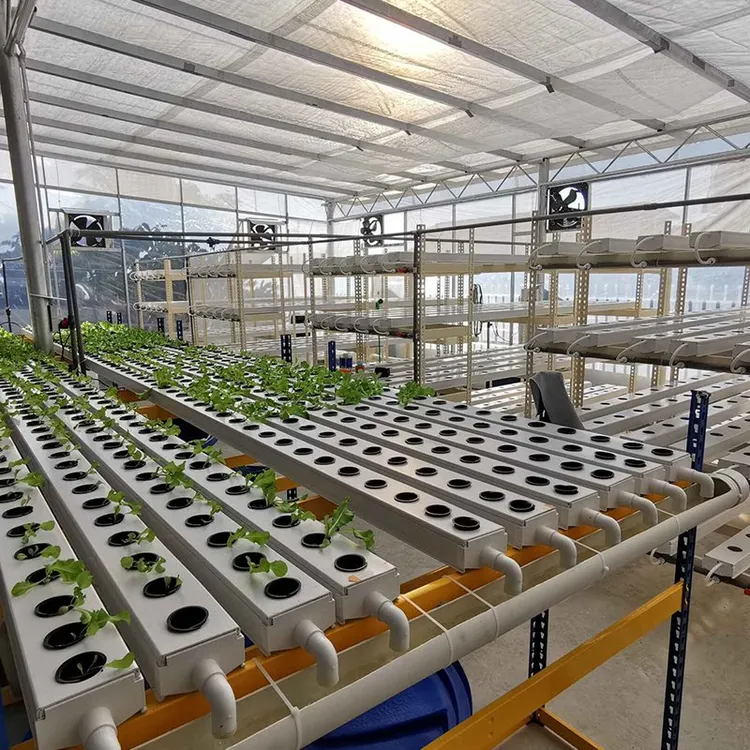

H2: 2026 Market Trends for PVC Hydroponics
The global PVC hydroponics market is poised for notable growth and transformation by 2026, driven by increasing demand for sustainable agriculture, urban farming, and cost-effective cultivation solutions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) remains a preferred material in hydroponic system construction due to its durability, affordability, and ease of assembly. As urbanization accelerates and arable land diminishes, hydroponic systems using PVC piping offer scalable and space-efficient alternatives for food production. The following key trends are expected to shape the PVC hydroponics market through 2026:
-
Rise in Urban and Indoor Farming
With over 60% of the global population projected to live in urban areas by 2030, space-efficient farming technologies are gaining traction. PVC-based hydroponic systems are increasingly adopted in vertical farms, rooftop gardens, and home setups due to their modular design and compatibility with limited spaces. Municipalities and private developers are investing in urban agriculture initiatives, further boosting demand for PVC hydroponics. -
Cost-Effectiveness and DIY Adoption
PVC materials are significantly cheaper than alternatives like metal or food-grade polymers, making them ideal for do-it-yourself (DIY) hydroponic kits. The growing popularity of home gardening and educational projects has led to a surge in online tutorials and pre-fabricated PVC hydroponic kits. This trend is expected to expand the consumer base beyond commercial growers to include hobbyists and schools. -
Sustainability and Material Innovations
Environmental concerns around traditional PVC—particularly its chlorine content and non-biodegradability—are prompting manufacturers to develop eco-friendlier, UV-stabilized, and recyclable PVC blends. By 2026, an increasing number of suppliers are expected to offer lead-free, phthalate-free PVC pipes certified for food-safe applications, aligning with global green building and organic farming standards. -
Integration with Smart Agriculture Technologies
The convergence of hydroponics with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, automated nutrient dosing, and climate control systems is transforming PVC setups into smart farming units. While PVC serves as the structural backbone, integration with digital monitoring tools enhances yield precision and resource efficiency. This hybrid approach is gaining favor among commercial growers seeking scalability and data-driven crop management. -
Regional Market Expansion
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific (e.g., India, Indonesia), Africa, and Latin America are witnessing rapid adoption of PVC hydroponics due to water scarcity, climate volatility, and food security concerns. Government subsidies and NGO-led agricultural programs are promoting low-cost PVC systems as tools for rural development and climate-resilient farming. -
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
As awareness grows about potential leaching of harmful additives from low-grade PVC under heat or UV exposure, regulatory scrutiny is increasing. By 2026, stricter standards are expected in key markets like the EU and North America, favoring certified food-grade PVC materials and driving innovation in safer alternatives.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for PVC hydroponics is characterized by strong demand, technological integration, and a shift toward sustainability. While challenges related to environmental impact and material safety persist, ongoing innovation and policy support are expected to solidify PVC’s role as a foundational component in the future of controlled-environment agriculture.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing PVC for Hydroponics (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing PVC components for hydroponic systems involves navigating several potential pitfalls related to material quality and intellectual property. Overlooking these can lead to system failures, health risks, or legal complications.
Poor Material Quality and Chemical Leaching
One of the most critical risks is sourcing low-grade PVC that can degrade or leach harmful substances into the nutrient solution. Many industrial or construction-grade PVC pipes contain additives like phthalates, lead-based stabilizers, or BPA, which can leach into water—especially under UV exposure or temperature fluctuations. These contaminants can harm plant health and pose risks if crops are consumed. Always verify that PVC is NSF/ANSI 61 certified for potable water use, as this ensures it’s safe for contact with drinking water and, by extension, hydroponic solutions.
UV Degradation and Structural Failure
Standard PVC is highly susceptible to UV radiation from sunlight or grow lights. Prolonged exposure causes the material to become brittle, discolor, and crack—leading to leaks and system breakdowns. While some suppliers may offer “UV-resistant” PVC, it’s essential to verify third-party testing or opt for PVC specifically designed for outdoor or agricultural use. Alternatively, consider using UV-stabilized CPVC or schedule 80 PVC with protective coatings.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Sizing
Suppliers may misrepresent pipe dimensions, wall thickness (schedule), or pressure ratings. Using undersized or thin-walled PVC can lead to structural failure under water pressure or during system expansion. Always cross-check product specifications with industry standards (e.g., ASTM D1785) and request material test reports when sourcing in bulk.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Hydroponic systems often incorporate proprietary designs, patented fittings, or branded components (e.g., specific manifold configurations or drip irrigation manifolds). Sourcing generic or unlicensed copies of patented designs—especially from overseas suppliers—can expose buyers to intellectual property (IP) infringement claims. This is particularly common with “knock-off” versions of popular systems like NFT channels or ebb-and-flow trays. Always confirm whether components are protected by patents or trademarks and obtain appropriate licensing if required.
Lack of Traceability and Compliance Documentation
Many low-cost suppliers, especially in international markets, fail to provide adequate documentation such as compliance certificates, material safety data sheets (MSDS), or country of origin details. This lack of traceability increases the risk of receiving substandard or non-compliant materials. Insist on full documentation and consider third-party inspection services for large orders.
Supply Chain and Long-Term Availability Issues
Relying on a single or obscure supplier for custom PVC parts can create vulnerability if the supplier discontinues a product or faces production delays. This is especially problematic for commercial operations needing long-term consistency. Evaluate the supplier’s reliability, minimum order quantities, and scalability before committing.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers rigorously, demand certifications, test materials when possible, and consult legal counsel when replicating or sourcing branded components.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for PVC Hydroponics
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for businesses involved in the manufacturing, distribution, or use of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) in hydroponic systems. Ensuring regulatory adherence and efficient supply chain operations is essential for safety, environmental responsibility, and market access.
Material Sourcing & Supply Chain Management
PVC Resin Procurement
Source food-grade or potable-water-rated PVC materials from certified suppliers. Confirm that resins comply with standards such as NSF/ANSI 61 for components in contact with water or nutrients. Maintain supplier documentation, including certifications and material safety data sheets (MSDS).
Component Manufacturing
Ensure manufacturing processes adhere to ISO 9001 quality management standards. Monitor for regulated additives (e.g., phthalates, lead stabilizers) and use compliant alternatives (e.g., calcium-zinc stabilizers). Implement traceability systems for batch tracking.
Regulatory Compliance
Food Safety & Material Contact Regulations
PVC components in hydroponic systems that contact water or nutrient solutions must comply with food-safe material standards, including:
– NSF/ANSI 61: Ensures drinking water system components do not leach harmful contaminants.
– FDA 21 CFR §177.2500: Regulates PVC resins for repeated use in food-contact applications.
– EU REACH & RoHS: Restrict hazardous substances in plastics; ensure compliance for international distribution.
Environmental & Chemical Regulations
- TSCA (USA): Comply with Toxic Substances Control Act requirements for chemical substances, including vinyl chloride monomer limits.
- Proposition 65 (California): Provide warnings if products contain chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm (e.g., certain plasticizers).
- WEEE & Packaging Waste Directives (EU): Follow end-of-life management and packaging recycling obligations.
Product Labeling & Documentation
Required Labeling
Clearly label products with:
– Material type (e.g., “PVC – NSF/ANSI 61 Certified”)
– Intended use (e.g., “For Hydroponic Systems – Not for Potable Water Consumption”)
– Compliance marks (NSF, CE, RoHS, etc.)
– Manufacturer name, batch number, and date of production
Technical Documentation
Maintain technical files including:
– Compliance test reports
– Risk assessments
– Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
Transportation & Storage
Domestic & International Shipping
- Classify PVC hydroponic components correctly under HTS codes (e.g., 3917.33 for tubes/pipes of PVC).
- Follow IATA/IMDG regulations if shipping internationally, particularly when additives are classified as hazardous.
- Use weather-resistant packaging to prevent moisture damage during transit.
Storage Conditions
Store PVC components in dry, shaded environments with temperatures between 5°C and 35°C. Avoid direct sunlight to prevent UV degradation and warping. Stack materials properly to prevent deformation.
Quality Control & Testing
In-Process & Final Product Testing
Conduct routine testing for:
– Leachability (using simulated nutrient solutions)
– Dimensional accuracy and structural integrity
– Compliance with pressure and flow rate specifications
Use accredited third-party labs for certification testing to ensure impartiality and acceptance.
End-of-Life & Sustainability
Recycling & Disposal
Design products for disassembly and recyclability. Label with resin identification code (♳). Partner with certified PVC recyclers and provide end-user guidance on proper disposal.
Sustainability Reporting
Track and report on:
– Use of recycled PVC content
– Carbon footprint of manufacturing and logistics
– Waste reduction initiatives
Recordkeeping & Audits
Maintain logs of supplier audits, compliance certifications, test results, and customer complaints for a minimum of 5 years. Prepare for unannounced audits by regulatory bodies or certification agencies.
Conclusion
Adhering to logistics best practices and compliance standards ensures the safety, reliability, and marketability of PVC hydroponic systems. Regular review of evolving regulations and investment in sustainable processes will support long-term business success.
Conclusion for Sourcing PVC in Hydroponics
Sourcing PVC for hydroponic systems offers a practical, cost-effective, and durable solution for building efficient growing structures. Its widespread availability, ease of customization, and resistance to water and corrosion make PVC a popular choice among hobbyists and commercial growers alike. However, careful consideration must be given to the type of PVC used—specifically, selecting food-safe, UV-stabilized, and non-toxic materials such as NSF-approved PVC or alternatives like CPVC or food-grade polyethylene to avoid potential leaching of harmful chemicals into the nutrient solution.
Additionally, sustainable sourcing practices and proper disposal or recycling methods should be considered to minimize environmental impact. While PVC remains a reliable material for hydroponic infrastructure, ongoing evaluation of safer and more eco-friendly alternatives is recommended as the industry evolves toward greater sustainability.
In conclusion, when responsibly sourced and properly applied, PVC continues to be a valuable material in the development of robust, scalable, and affordable hydroponic systems.