The global industrial grinding equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across sectors such as metal fabrication, automotive, and construction. According to Grand View Research, the global grinding machines market size was valued at USD 7.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing automation, precision manufacturing requirements, and technological advancements in CNC-driven grinding systems. Within this landscape, punch grinders—specialized machines used for sharpening and maintaining stamping dies and punch tools—have become critical for maintaining operational efficiency in high-volume production environments. As industries prioritize tool longevity and accuracy, the demand for reliable, high-performance punch grinder manufacturers has surged. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and global reach, here are the top 8 punch grinder manufacturers leading the space today.
Top 8 Punch Grinder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kingsland
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kingsland.com
Key Highlights: Kingsland has been established for over 60 years as an innovative designer and manufacturer of top quality Universal Steelworkers, punching machines, ……
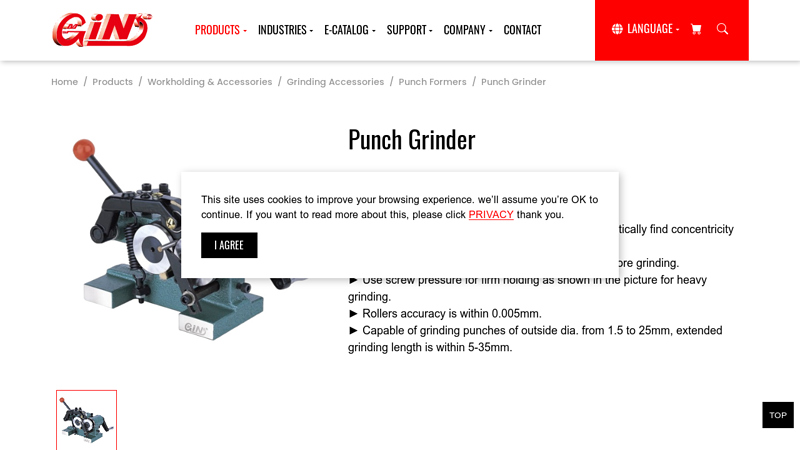
#2 Punch Grinder
Domain Est. 2017
Website: gin-chan.com
Key Highlights: Punch Grinder. Model & Order No. 51450 PGA. ▻ PGA can be applied on surface grinder and automatically find concentricity for cylindrical grinding ……
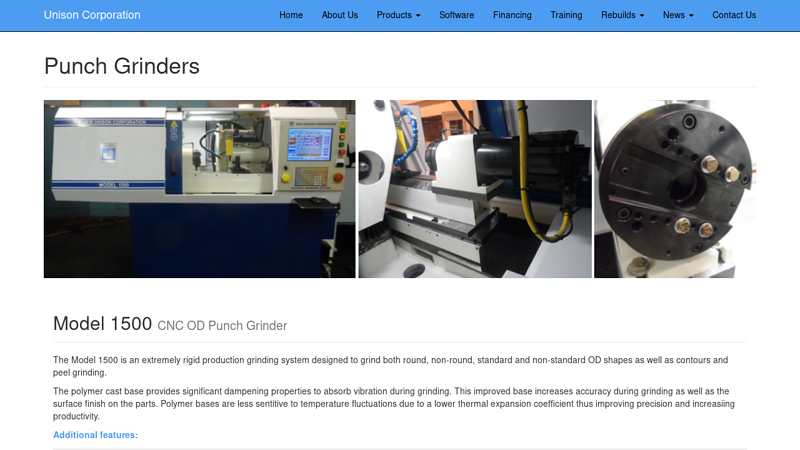
#3 Model 1500 CNC OD Punch Grinder
Domain Est. 1996
Website: unisoncorp.com
Key Highlights: The Model 1500 is an extremely rigid production grinding system designed to grind both round, non-round, standard and non-standard OD shapes as well as ……
#4 A Punch Grinder with JVL Controller is specially constructed
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jvl.dk
Key Highlights: Punch Grinder controlled by JVL Controller. The company Sorenco produces advanced machinery for grinding punches and dies. A Punch Grinder is ……
#5 Cutting Tool Grinding
Domain Est. 2000
Website: rollomaticusa.com
Key Highlights: Rollomatic specializes in designing high-precision CNC machines that are used for manufacturing rotary dental cutting tools and for dental blank preparation….
#6 JAGULAR
Domain Est. 2006
Website: en.jaguraweb.com
Key Highlights: In the beginning, we manufactured punch grinder and various internal and external grinding machines. After over 30 years’ continuous effort, based on the ……
#7 Punch Grinders and Formers
Domain Est. 2016
Website: matchling-tooling.com
Key Highlights: MATCHLING TOOLING’s punch grinders enable high-precision grinding when mounted on a standard surface grinder, making them ideal for mold manufacturing….
#8 CNC high
Website: waida.co.jp
Key Highlights: WAIDA MFG. is a world leader in special grinding machines specializing in precision machining of hard and brittle materials….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Punch Grinder
H2: 2026 Market Trends Forecast for the Punch Grinder Industry
Based on current technological trajectories, industrial demands, and economic indicators, the punch grinder market in 2026 is expected to be shaped by several key converging trends, emphasizing automation, precision, sustainability, and digital integration. Here’s a breakdown of the anticipated landscape:
1. Accelerated Automation and Smart Integration (Industry 4.0):
* Dominant Trend: Punch grinders will increasingly feature advanced automation, moving beyond basic CNC controls towards full integration within smart factories.
* Key Drivers: Labor shortages, demand for consistent 24/7 production, and the need for seamless data flow across manufacturing systems (MES, ERP).
* 2026 Expectations: Widespread adoption of:
* Automated Loading/Unloading: Integration with robotic arms for lights-out operation.
* In-Process Gauging & Closed-Loop Control: Real-time measurement of grind dimensions and automatic wheel dressing/spindle adjustments to maintain micron-level tolerances.
* Predictive Maintenance: Sensors monitoring vibration, temperature, and wheel wear, feeding data to AI algorithms to predict failures and optimize maintenance schedules, minimizing downtime.
* IIoT Connectivity: Machines acting as data nodes, providing real-time performance analytics, OEE tracking, and remote monitoring/support capabilities.
2. Uncompromising Demand for Ultra-High Precision and Consistency:
* Dominant Trend: As end-products (especially in aerospace, medical, and advanced electronics) require ever-tighter tolerances and finer surface finishes, punch grinder performance will be paramount.
* Key Drivers: Miniaturization of components, use of harder/tougher materials (e.g., advanced tool steels, carbides, ceramics), and zero-defect manufacturing philosophies.
* 2026 Expectations:
* Sub-Micron Accuracy: Machines designed and built to achieve and maintain repeatability in the sub-micron range (<1µm).
* Enhanced Thermal Stability: Advanced cooling systems, thermally symmetric machine designs, and real-time thermal compensation software to counteract heat-induced errors.
* Superior Vibration Damping: Use of advanced materials (granite, polymer concrete) and active/passive damping systems for flawless surface finishes.
* Advanced Wheel Technology Integration: Grinders optimized for the latest ultra-precise, high-performance grinding wheels (e.g., CBN, diamond, electroplated, metal-bonded).
3. Focus on Sustainability and Efficiency:
* Dominant Trend: Environmental regulations and cost pressures will push manufacturers towards more sustainable and resource-efficient grinding processes.
* Key Drivers: Energy costs, environmental compliance (coolant disposal, emissions), and corporate sustainability goals.
* 2026 Expectations:
* Reduced Energy Consumption: More efficient motors (e.g., direct-drive spindles), optimized grinding cycles, and regenerative braking systems.
* Advanced Coolant Management: Closed-loop filtration systems, minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) adoption for suitable applications, and development of more eco-friendly, biodegradable coolants.
* Reduced Waste: Optimized wheel life through better dressing strategies and monitoring, reduced scrap rates due to improved process control, and recycling of grinding swarf.
4. Software-Driven Intelligence and User Experience:
* Dominant Trend: The “smarts” of the machine will reside increasingly in sophisticated software, simplifying operation and maximizing output.
* Key Drivers: Need to reduce programming time, minimize operator errors, and leverage data for optimization.
* 2026 Expectations:
* AI-Powered Process Optimization: AI algorithms suggesting optimal grinding parameters (speeds, feeds, depths of cut) based on material, geometry, and desired finish, adapting in real-time.
* Intuitive, Adaptive HMI: Touchscreen interfaces with augmented reality (AR) guidance for setup, diagnostics, and training. Voice control potential.
* Advanced Simulation & Virtual Commissioning: Highly accurate digital twins allowing offline programming, collision checking, and process validation before machine time is used.
* Cloud-Based Analytics: Secure cloud platforms for aggregating performance data across fleets of grinders for benchmarking, predictive analytics, and remote expert support.
5. Material-Specific and Application-Optimized Solutions:
* Dominant Trend: One-size-fits-all grinders will be less common; machines will be increasingly tailored for specific material challenges (hard alloys, carbides, ceramics) or applications (micro-punches, complex geometries).
* Key Drivers: Specialized requirements of key industries and the need for maximum performance in niche areas.
* 2026 Expectations:
* Dedicated Machine Configurations: Grinders optimized for carbide tooling, medical component sharpening, or micro-feature grinding with specialized spindles, fixtures, and controls.
* Enhanced Flexibility: While specialized, machines will still need some flexibility. Quick-change systems for spindles, chucks, and wheel heads will be standard.
* Focus on Complex Geometries: Improved software and hardware (e.g., multi-axis capabilities, sophisticated dressing) to handle intricate punch profiles with high precision.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the punch grinder market will be defined by “Smart, Sustainable Precision.” Success will belong to manufacturers and users who leverage integrated, data-driven, and automated grinding systems capable of delivering unmatched consistency and quality while minimizing environmental impact and total cost of ownership. The machine itself becomes less of a standalone tool and more of an intelligent node within a connected, optimized manufacturing ecosystem. Investment in these advanced capabilities will be essential for competitiveness, particularly in high-value sectors.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Punch Grinder (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a punch grinder—especially for precision tooling, stamping, or mold-making—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly downtime, subpar tool performance, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Inadequate Quality Standards and Verification
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing punch grinders is assuming all machines deliver the same precision. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners on materials, components, or calibration, resulting in inconsistent grinding accuracy and shorter machine life.
- Poor Spindle Accuracy: Inferior spindles lead to vibration and reduced surface finish quality, impacting punch longevity and performance.
- Substandard Construction Materials: Machines built with lower-grade cast iron or inadequate thermal stability warp over time, affecting dimensional accuracy.
- Lack of Calibration Documentation: Reputable manufacturers provide traceable calibration reports (e.g., laser interferometer data); missing documentation is a red flag.
- Insufficient After-Sales Support: Remote suppliers may lack local service technicians or spare parts, increasing downtime.
Always request performance test reports, conduct factory audits, or require sample workpieces before finalizing a purchase.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Infringement
Sourcing from certain regions—particularly where IP enforcement is weak—raises the risk of acquiring machines that infringe on patented technologies or contain copied software and control systems.
- Counterfeit CNC Systems or Software: Some machines use unlicensed versions of popular control software (e.g., Mitsubishi, Siemens, or proprietary grinding software), exposing the buyer to legal liability.
- Cloned Machine Designs: Entire machines may be reverse-engineered from well-known brands, violating design and utility patents.
- No IP Warranty or Indemnification: Suppliers in high-risk regions often refuse to provide contractual guarantees that the equipment is free from IP claims.
To mitigate these risks:
– Require written IP indemnification in contracts.
– Verify the originality of control systems and software licenses.
– Work with suppliers who have a transparent design and manufacturing process.
Overlooking Application-Specific Requirements
A punch grinder must match the specific needs of the operation—whether for high-volume production, micro-punch grinding, or hardened tool steel.
- Wrong Grinding Wheel Options: Not all grinders support the necessary diamond or CBN wheels for hard materials.
- Insufficient Automation Integration: Lack of compatibility with robotic loaders or in-process gauging limits productivity.
- Inadequate Precision for Tolerances: Punches for fine-blanking or micro-stamping require sub-micron accuracy—standard models may not suffice.
Ensure the supplier understands your application and can demonstrate capability with actual workpieces.
Hidden Costs from Poor Build Quality
Low initial pricing can be misleading. Inferior build quality often leads to:
– Frequent breakdowns and maintenance.
– Higher consumable usage (e.g., wheels, coolant).
– Increased operator training and scrap rates.
Factor in total cost of ownership (TCO), including service, downtime, and consumables, rather than focusing solely on purchase price.
Conclusion
Sourcing a punch grinder demands due diligence beyond price and delivery. Prioritize suppliers with verifiable quality controls, transparent IP practices, and proven application expertise. Investing in a reputable, IP-compliant machine ensures long-term reliability, legal safety, and optimal tool performance.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Punch Grinder
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, transportation, and use of a Punch Grinder. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational integrity, regulatory compliance, and personnel safety.
Product Description and Specifications
The Punch Grinder is a precision industrial tool designed for sharpening, shaping, and maintaining punch tools used in stamping, forming, and die-making operations. Key specifications typically include motor power (e.g., 1–3 HP), wheel diameter (e.g., 6–10 inches), spindle speed (e.g., 1,750–3,450 RPM), and compatibility with various grinding wheels (e.g., aluminum oxide, silicon carbide). Confirm exact model specifications before shipping or installation.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
All Punch Grinders must comply with applicable national and international standards. Key regulations include:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) – 29 CFR 1910.215 (Occupational Safety and Health Standards for Abrasive Wheel and Tools)
– ANSI B7.1 – Safety Requirements for the Use, Care, and Protection of Abrasive Wheels
– CE Marking (Europe) – Compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EN standards (e.g., EN 60204-1 for electrical safety)
– UL/CSA (North America) – Electrical safety certification for equipment
Ensure the unit bears required certifications and includes a Declaration of Conformity.
Packaging and Handling Instructions
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit:
– Use manufacturer-recommended packaging with sturdy outer casing, internal foam supports, and corner protectors.
– Secure the grinding wheel separately in protective wrapping; do not ship installed unless specified.
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
– Use lift trucks or dollies for handling; never drag the machine.
– Retain all packaging materials until equipment is commissioned, in case of return or re-shipment.
Shipping and Transportation
Coordinate shipping with certified freight carriers experienced in industrial machinery:
– Confirm dimensional weight and freight class with the carrier.
– Use enclosed, climate-controlled trucks where possible to avoid exposure to moisture and extreme temperatures.
– Secure the grinder with straps or braces inside the transport vehicle to prevent shifting.
– Provide proper documentation, including bill of lading, commercial invoice (for international), and packing list.
– For international shipments, ensure compliance with export controls (e.g., EAR or ITAR, if applicable) and customs declarations.
Import and Export Documentation
For cross-border movement of the Punch Grinder:
– Prepare accurate commercial invoice detailing product description, value, country of origin, and HS Code (e.g., 8461.30 for grinding machines).
– Include packing list, certificate of origin, and bill of lading/air waybill.
– Verify export licensing requirements based on destination country and technology specifications.
– Comply with import regulations such as customs duties, VAT, and local safety standards (e.g., UKCA marking in the UK).
Installation and Site Preparation
Prior to installation:
– Ensure the facility has adequate floor strength, ventilation, and power supply (voltage, phase, frequency per nameplate).
– Install in a clean, dry, and vibration-free environment away from excessive dust or coolant spray.
– Provide local exhaust ventilation (LEV) if grinding operations generate airborne particulates.
– Ground the machine properly per electrical codes (e.g., NEC Article 250).
– Follow the manufacturer’s installation manual and involve qualified personnel.
Operational Safety and Training
Only trained personnel may operate the Punch Grinder:
– Conduct site-specific safety training covering emergency stops, wheel inspection, guarding, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
– PPE includes safety glasses with side shields, face shield, hearing protection, and protective gloves.
– Inspect grinding wheels for cracks or damage before mounting; perform ring test as per ANSI B7.1.
– Ensure all machine guards are in place and functional prior to operation.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Implement a preventive maintenance schedule:
– Lubricate spindles and moving parts as specified in the manual.
– Check electrical connections, wheel flanges, and mounting bolts regularly.
– Replace worn or damaged components immediately using OEM or approved parts.
– Maintain logs for inspections, repairs, wheel changes, and operator training to demonstrate compliance during audits.
Environmental and Waste Management
Address environmental compliance:
– Collect grinding dust using a dust extraction system; dispose of metal fines as hazardous or non-hazardous waste per local regulations (e.g., EPA, local environmental agency).
– Do not discharge coolant or lubricants into drains; recycle or dispose through licensed waste handlers.
– Recycle packaging materials (cardboard, plastic, wood) where possible.
Incident Reporting and Recalls
In the event of malfunction, injury, or non-compliance:
– Immediately cease use and report the incident to management and safety officers.
– Document details including date, time, personnel involved, and nature of the issue.
– Follow internal procedures for equipment lockout/tagout (LOTO).
– Monitor manufacturer communications for product recalls or safety notices; respond promptly to any recall action.
Contact Information and Support
For compliance or technical assistance:
– Manufacturer: [Insert Manufacturer Name, Address, Phone, Website]
– Technical Support: [Insert Support Email/Phone]
– Regulatory Compliance Officer: [Insert Name and Contact]
– Local Safety Authority: [Insert OSHA/Equivalent Agency Contact]
Always refer to the latest product manual and regulatory updates to ensure continued compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Punch Grinder
In conclusion, sourcing a punch grinder requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, supplier reliability, and long-term cost-effectiveness. The chosen punch grinder must align precisely with the operational demands of the manufacturing or tool maintenance process, ensuring high precision, durability, and minimal downtime. Evaluating reputable suppliers, considering after-sales service, spare parts availability, and compliance with safety and quality standards further strengthens the sourcing decision. By prioritizing performance, reliability, and total cost of ownership, the selected punch grinder will enhance tool maintenance efficiency, extend tool life, and contribute to overall production excellence. A strategic sourcing approach ultimately ensures a reliable, efficient, and future-ready solution for precision grinding needs.