The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision cleaning solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 425.8 million in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.3% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the shift away from abrasive and chemical cleaning methods toward sustainable alternatives, with pulsed laser cleaning emerging as a preferred technology due to its non-contact operation, minimal substrate damage, and high efficiency. As industrial players prioritize automation and environmental compliance, investment in advanced laser systems has intensified. Against this backdrop, several manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, reliability, and scalable solutions. The following analysis highlights the top seven pulsed laser cleaning manufacturers shaping the future of industrial surface treatment.
Top 7 Pulsed Laser Cleaning Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: The PULSAR Laser product portfolio covers a wide range of laser cleaning applications, from precision pulsed cleaning to high-power industrial surface treatment ……
#3 Pulse Wave Laser Machines
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Explore our cutting-edge technology of pulse laser cleaning machines, delivering efficient removal of oil, weld seams, and gear rust….
#4 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: Narran is a direct Czech manufacturer of laser cleaning systems. Depending on the needs of the application, we can design and integrate the laser into ……
#5 Pulsed laser cleaning Machine
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: The laser cleaning machine is a state-of-the-art equipment that uses laser as a stripping system for the removal of impurities, leaving the substrate intact….
#6 Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: triumphlaser.com
Key Highlights: A pulse laser cleaning machine is an advanced, highly efficient tool designed for precision cleaning and removal of contaminants such as rust, paint, oil, and ……
#7 Fortune Laser pulse Laser cleaning Machine
Website: fortunelaser.com
Key Highlights: Fortune Laser portable handheld laser cleaning machine has many advantages such as portability, lightness, flexible parameter adjustment, etc….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pulsed Laser Cleaning

H2: Projected Market Trends for Pulsed Laser Cleaning in 2026
By 2026, the pulsed laser cleaning market is poised for significant expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, non-abrasive cleaning technologies across key industrial sectors. Several interrelated trends are expected to shape the market landscape:
-
Growing Adoption in Manufacturing and Automotive Industries: Pulsed laser cleaning is gaining traction in precision manufacturing, especially in automotive and aerospace sectors, where surface integrity and material preservation are critical. The technology’s ability to remove rust, oxides, paints, and contaminants without damaging the underlying substrate makes it ideal for component refurbishment and pre-welding surface preparation. By 2026, OEMs and tier suppliers are anticipated to increasingly integrate pulsed laser systems into production lines to improve quality control and reduce rework.
-
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers: With tightening global regulations on chemical usage and abrasive blasting (e.g., VOC emissions, silica dust), industries are turning to green alternatives. Pulsed laser cleaning produces no secondary waste and eliminates the need for chemical solvents, aligning with sustainability goals and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria. This regulatory tailwind is expected to accelerate adoption, particularly in Europe and North America.
-
Technological Advancements and Cost Reductions: Continuous improvements in fiber laser efficiency, pulse control, and portability are making pulsed laser systems more accessible. By 2026, advancements in automation and integration with robotics (e.g., collaborative robots or cobots) will enhance precision and throughput, lowering operational costs and expanding usability in SMEs. Additionally, falling prices of key components like high-power laser diodes and improved cooling systems are contributing to better ROI.
-
Expansion in Niche Applications: Beyond traditional industrial cleaning, pulsed laser cleaning is finding new applications in heritage conservation, nuclear decontamination, and electronics manufacturing. For example, art restorers are using low-energy pulsed lasers to clean delicate historical artifacts without surface damage. In the semiconductor sector, ultra-short pulse lasers are being employed for micron-level contaminant removal. These niche markets are expected to grow steadily, diversifying revenue streams for laser cleaning providers.
-
Regional Growth Dynamics: Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to be the fastest-growing region due to rapid industrialization, strong government support for advanced manufacturing, and rising investments in automation. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will maintain strong market positions, supported by mature industrial infrastructure and early adoption of clean technologies.
-
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation: The market is witnessing increased competition among laser system manufacturers, with key players focusing on R&D and strategic partnerships. By 2026, consolidation is expected through mergers and acquisitions, as companies aim to broaden their product portfolios and global reach. New entrants offering compact, user-friendly systems may disrupt the mid-range market segment.
In summary, by 2026, the pulsed laser cleaning market will be characterized by robust growth fueled by technological innovation, environmental compliance, and expanding industrial applications. Companies that invest in scalable, intelligent, and sustainable laser solutions will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.
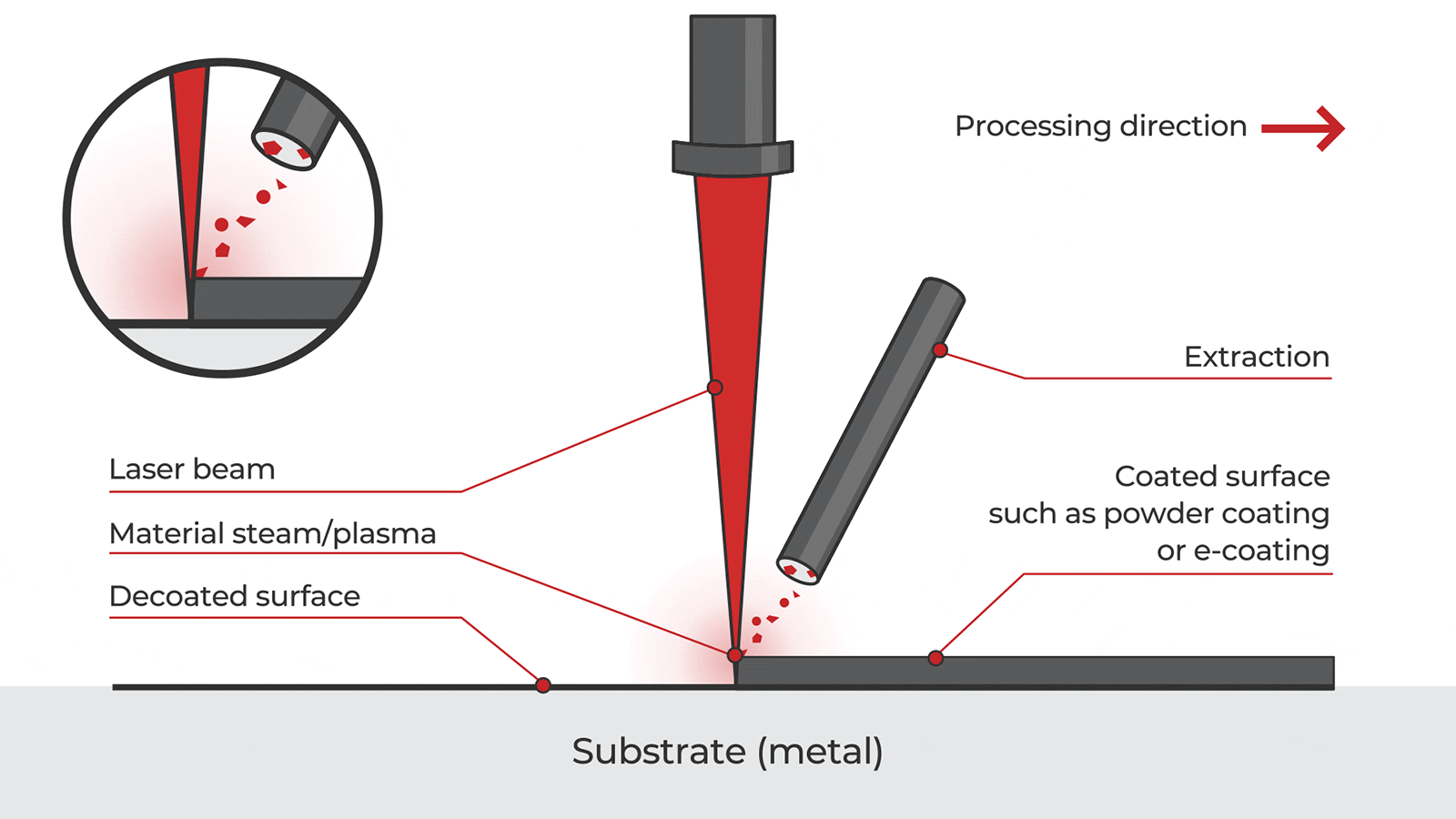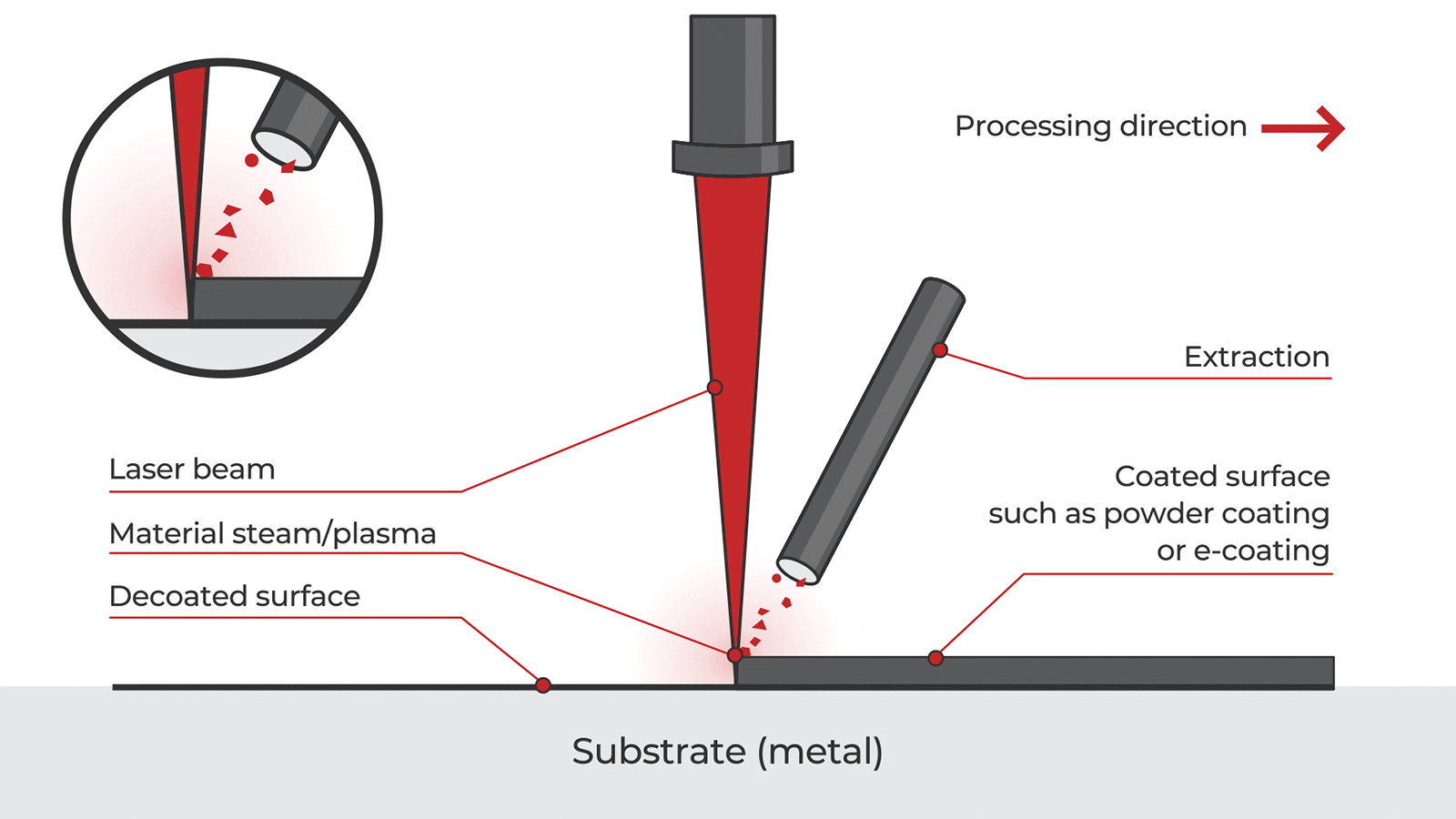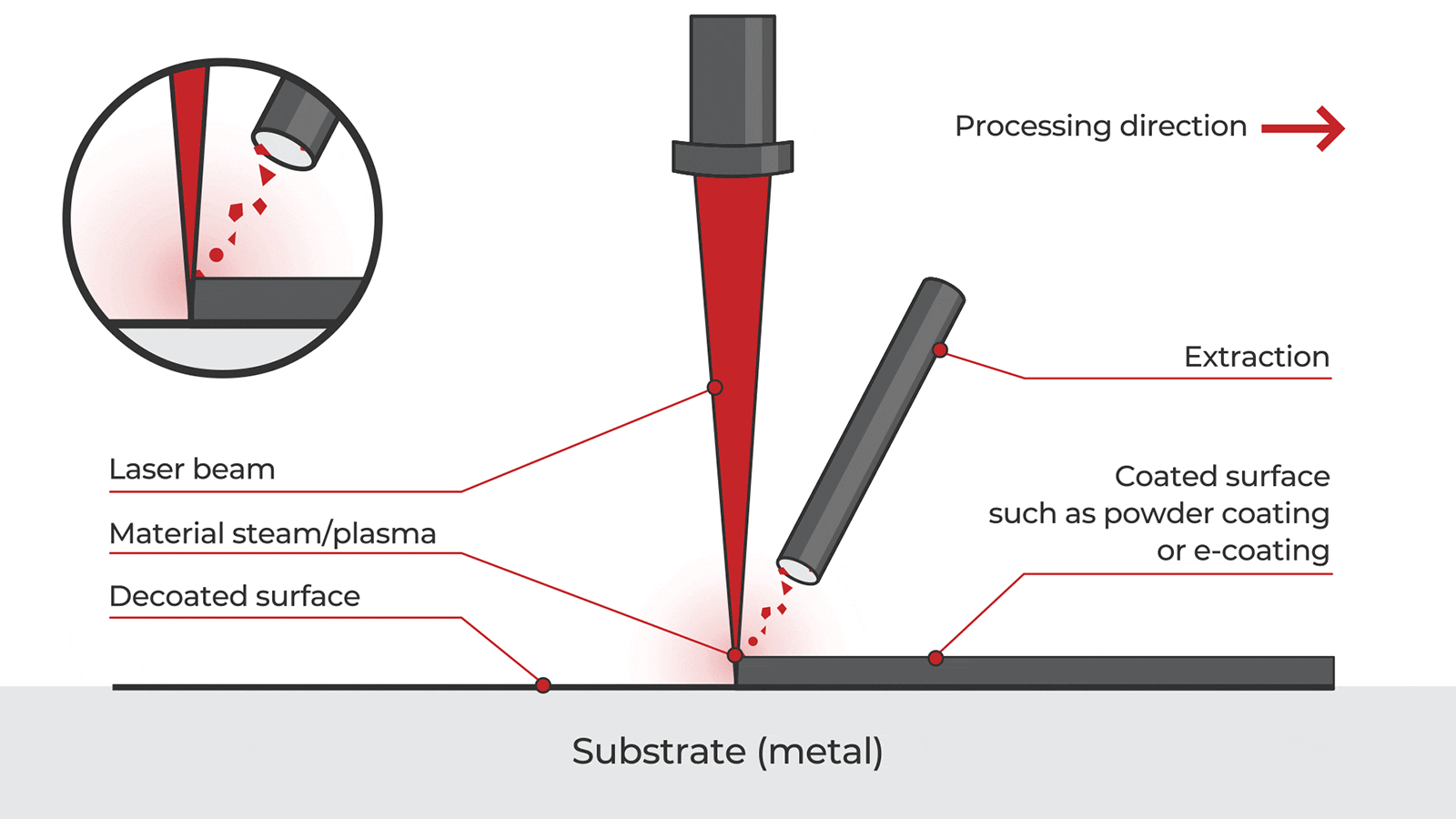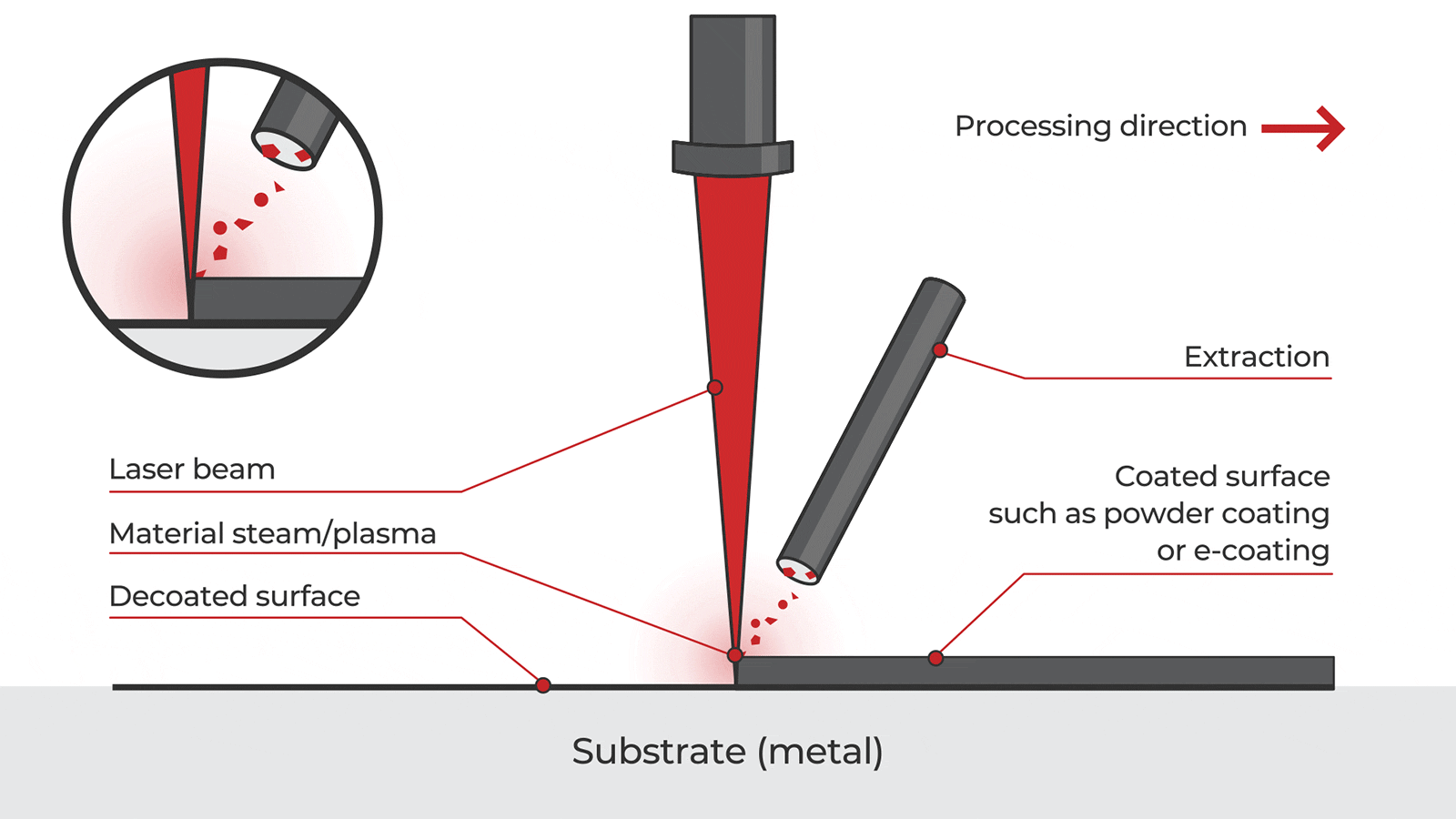
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Pulsed Laser Cleaning Systems: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
When sourcing pulsed laser cleaning systems, organizations often focus on performance specifications and cost, overlooking critical risks related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and compromised competitive advantage.
H2: Quality Consistency and Reliability Risks
One of the most significant challenges in sourcing pulsed laser cleaning technology is ensuring consistent build quality and long-term reliability across suppliers—particularly when comparing established OEMs with emerging or offshore manufacturers.
-
Inconsistent Component Sourcing: Many lower-cost suppliers use variable-grade optical components, diodes, or cooling systems to reduce prices. This results in unpredictable beam quality, fluctuating pulse energy, and shortened system lifespan. Without strict quality control, units from the same batch may perform differently.
-
Lack of Standardized Testing and Certification: Reputable suppliers adhere to international standards (e.g., ISO 13849 for functional safety, IEC 60825 for laser safety). However, some vendors provide systems without third-party validation or comprehensive test reports, increasing the risk of safety hazards or non-compliance in regulated industries.
-
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Calibration: High-power pulsed lasers require regular calibration and maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers without local service networks or technical expertise can lead to prolonged downtime and increased cost of ownership.
-
Overstated Performance Claims: Some vendors exaggerate cleaning speed, depth, or material compatibility based on ideal lab conditions. Buyers may discover that real-world performance falls short, especially on complex substrates or contaminated surfaces.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: request sample testing under your operational conditions, audit manufacturing processes, and verify compliance with relevant safety and performance standards.
H2: Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure and Infringement
Sourcing pulsed laser cleaning systems also introduces substantial IP-related risks, both in terms of protecting your own innovations and avoiding liability from using infringing technology.
-
Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components: Lower-cost systems, particularly from certain regions, may incorporate cloned control boards, firmware, or laser sources that infringe on patented technologies. Purchasing such systems can expose your organization to legal action, especially in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement.
-
Lack of IP Warranty or Indemnification: Many suppliers, especially smaller ones, do not offer warranties that their systems do not infringe on third-party IP. Without contractual protection, buyers may be held liable for IP violations even if unintentional.
-
Proprietary Process Vulnerability: Integrating a laser cleaning system into a proprietary manufacturing process may require sharing sensitive operational data with the supplier for customization. If proper non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and data security measures are not in place, your trade secrets could be exposed.
-
Firmware and Software Lock-in: Some vendors use proprietary software with restrictive licensing, limiting your ability to modify, integrate, or repair the system. This can hinder process optimization and create dependency on the supplier—potentially compromising long-term IP strategy.
To safeguard IP, ensure suppliers provide written IP indemnification, conduct patent landscape analysis before procurement, and implement robust contractual safeguards covering data use, reverse engineering, and post-contract obligations.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns during sourcing, organizations can deploy pulsed laser cleaning systems that are not only effective and reliable but also legally secure and aligned with long-term innovation goals.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pulsed Laser Cleaning
Pulsed laser cleaning is an advanced, eco-friendly technology used to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, oil, and oxides from surfaces without damaging the underlying material. While highly effective, the deployment of this technology requires careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance to ensure safety, efficiency, and legal adherence. This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and compliance aspects of pulsed laser cleaning operations.
H2: Equipment Transportation and Handling
- Packaging and Protection: Pulsed laser cleaning systems are sensitive electronic and optical instruments. Transport in shock-resistant, moisture-proof packaging with proper cushioning to prevent damage during transit.
- Climate Control: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and condensation during storage and transport. Maintain ambient conditions per manufacturer’s specifications.
- Power Requirements: Verify voltage, phase, and frequency compatibility at the destination site. Use voltage regulators or transformers if necessary.
- Mobility and Setup: For portable systems, ensure ease of movement using carts or carrying cases. Confirm adequate space and ventilation at the operational site.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825 / ANSI Z136.1):
- Classify the laser system according to international standards (typically Class 4 for high-power pulsed lasers).
- Implement engineering controls (e.g., interlocks, enclosures) and administrative controls (e.g., restricted access zones).
-
Provide laser safety training for all operators and maintain a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) if required.
-
Workplace Safety (OSHA / Local Regulations):
- Ensure compliance with local occupational health and safety regulations.
- Conduct risk assessments for exposure to laser radiation, fumes, and noise.
-
Install appropriate ventilation or fume extraction systems to capture particulates generated during cleaning.
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
-
Confirm equipment meets EMC standards (e.g., FCC Part 15 in the U.S., CE marking in the EU) to avoid interference with other electronic devices.
-
Environmental Regulations:
- Pulsed laser cleaning produces no chemical waste, but ablated particles must be collected and disposed of properly.
- Follow local regulations for handling and disposing of hazardous materials (e.g., lead-based paint residues).
- Use HEPA-filtered vacuum systems to capture airborne particulates and prevent environmental contamination.
H2: Operational Logistics
- Site Assessment: Conduct a pre-deployment survey to evaluate access, power availability, ventilation, and potential hazards.
- Operator Training: Ensure personnel are certified in laser operation, safety protocols, and emergency procedures.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance intervals for optics, cooling systems, and power modules.
- Spare Parts and Support: Maintain a supply of critical spare parts and ensure access to technical support for troubleshooting.
H2: Documentation and Certification
- Maintain records of:
- Equipment serial numbers, calibration, and maintenance logs.
- Operator training and certification.
- Safety audits and incident reports.
- Obtain and carry all required certifications (e.g., CE, FCC, ISO 9001) when transporting or operating across jurisdictions.
H2: International Considerations
- Import/Export Controls: Check if laser equipment is subject to export restrictions (e.g., under the Wassenaar Arrangement or national export control lists).
- Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate technical descriptions, Harmonized System (HS) codes, and certificates of origin.
- Local Approvals: Verify compliance with national laser safety and electrical standards in the destination country.
H2: Emergency Preparedness
- Establish emergency shutdown procedures.
- Provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles with correct wavelength filtering.
- Post warning signs in laser operation areas and enforce controlled access.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can safely and legally deploy pulsed laser cleaning technology while minimizing operational risks and ensuring regulatory conformity.
Conclusion for Sourcing Pulsed Laser Cleaning Systems
Sourcing pulsed laser cleaning technology represents a forward-thinking investment in precision, efficiency, and sustainability. As industries increasingly prioritize non-abrasive, environmentally friendly cleaning methods, pulsed laser systems offer a compelling alternative to traditional techniques such as sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or dry ice blasting. These systems provide high precision, minimal substrate damage, and the ability to remove contaminants without media or secondary waste, significantly reducing operational downtime and long-term costs.
When sourcing pulsed laser cleaning equipment, key considerations include laser pulse energy, repetition rate, wavelength, beam quality, portability, and ease of integration into existing production or maintenance workflows. It is also essential to evaluate vendor reliability, technical support, training availability, and compliance with safety standards.
While the initial investment may be higher compared to conventional methods, the long-term benefits—such as reduced environmental impact, lower consumable costs, and extended equipment lifespan—justify the cost. Additionally, automation compatibility and advancements in fiber laser technology continue to enhance the versatility and accessibility of these systems across aerospace, automotive, heritage conservation, and precision manufacturing sectors.
In conclusion, sourcing pulsed laser cleaning systems is a strategic move toward modernizing maintenance and manufacturing processes. With careful vendor selection and proper implementation, organizations can achieve superior cleaning performance, regulatory compliance, and operational sustainability, positioning themselves at the forefront of industrial innovation.