The global solar charge controller market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising solar energy adoption and advancements in photovoltaic system efficiency. According to Mordor Intelligence, the solar charge controller market was valued at USD 1.68 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029. A key technology fueling this expansion is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which remains a cost-effective and reliable method for regulating voltage and current from solar panels to batteries, particularly in small to medium-scale off-grid applications. Despite the emergence of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers, PWM charge controllers continue to hold significant market share due to their simplicity, durability, and lower upfront costs, especially in developing regions and rural electrification projects.
As demand grows, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in PWM charge controller innovation, quality, and global reach. Based on market presence, product performance, distribution networks, and technological consistency, the following nine companies represent the top players shaping the PWM charge controller segment worldwide.
Top 9 Pulse Width Modulation Charge Controller Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MPPT vs PWM
Domain Est. 1997
Website: morningstarcorp.com
Key Highlights: PWM controllers tend to be smaller and they operate at battery voltage, whereas MPPT controllers use newer technology to operate at the maximum power voltage….
#2 Xantrex PWM Charge Controller
Domain Est. 1995
Website: xantrex.com
Key Highlights: The Xantrex Solar PWM Charge Controller 30 features a highly-efficient PWM charging mode, designed specifically for an aesthetically clean and integrated look ……
#3 Working Principle of PWM and MPPT Solar Charge Controllers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: anern.com
Key Highlights: This article will provide a detailed introduction to the working principles and differences of PWM and MPPT solar charge controllers. Working ……
#4 MPPT and PWM Meaning Explained
Domain Est. 2010
Website: renogy.com
Key Highlights: Get to know the meaning of MPPT and PWM and how the MPPT and PWM charge controller work now. All you want to know is included here….
#5 Solar Charge Controllers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: epever.com
Key Highlights: The two main categories are pulse width modulation (PWM) and maximum power point tracking (MPPT) charge controllers. While PWM controllers are cheaper, they ……
#6 Solar Charge Controller
Domain Est. 2017
Website: carspa.cc
Key Highlights: A PWM (pulse width modulation) controller canbe thought of as an (electronic) switch betweenthe solar panels and the battery: The switch isON when the charger ……
#7 Solar Charge Controller
Domain Est. 2021
Website: anerngroup.com
Key Highlights: Anern solar controllers manage battery charging safely and efficiently. MPPT & PWM options available for off-grid, hybrid, and solar storage systems….
#8 Charge Controllers
Domain Est. 2021
Website: solinved.com
Key Highlights: Types of Charge Controllers. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Charge Controllers: These devices regulate the energy flow from solar panels to batteries based on ……
#9 [Ultimate Guide] MPPT vs. PWM Solar Charge Controller
Domain Est. 2021
Website: redodopower.com
Key Highlights: PWM, or Pulse Width Modulation, is a more basic and cost-effective technology used in solar charge controllers. It regulates the charging process by rapidly ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pulse Width Modulation Charge Controller

H2: Market Trends for Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Charge Controllers in 2026
As the global renewable energy sector matures in 2026, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) charge controllers continue to maintain a significant presence in the solar power ecosystem, particularly within niche and cost-sensitive markets. While increasingly challenged by the rise of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology, PWM charge controllers are adapting through innovation, cost optimization, and strategic market positioning. The following trends are shaping the PWM charge controller landscape in 2026:
-
Resilient Demand in Off-Grid and Emerging Markets
PWM charge controllers remain popular in off-grid applications, rural electrification projects, and developing regions due to their affordability and reliability. Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of Latin America continue to deploy PWM-based solar systems for small-scale residential, agricultural, and community power needs. The low initial cost and simplicity of installation make PWM controllers ideal for entry-level solar kits and government-funded energy access programs. -
Integration with Smart Features and IoT
To remain competitive, manufacturers are enhancing traditional PWM controllers with smart functionalities. By 2026, many PWM models include Bluetooth connectivity, mobile app monitoring, data logging, and remote diagnostics. These features improve user experience and provide real-time performance insights without significantly increasing cost, allowing PWM systems to serve semi-professional applications. -
Hybrid System Compatibility
There is a growing trend toward hybrid solar systems that combine solar with battery storage and sometimes backup generators. While MPPT dominates in high-efficiency hybrid setups, PWM controllers are being designed to work within simplified hybrid configurations, especially in microgrid applications where cost efficiency is prioritized over peak performance. -
Focus on Durability and Environmental Resilience
With deployments in harsh climates—ranging from desert regions to tropical zones—PWM charge controllers in 2026 are engineered for enhanced durability. Improved heat dissipation, dust resistance, and corrosion protection ensure longevity in extreme conditions. This reliability reinforces their appeal in remote and rugged environments. -
Competition and Coexistence with MPPT Controllers
While MPPT technology offers higher efficiency (especially in variable weather or large arrays), PWM controllers hold ground in small-scale systems (typically under 300W) where the efficiency gap is less impactful. The price-performance balance keeps PWM relevant, especially in markets where return on investment is measured in years rather than months. -
Regulatory and Standardization Developments
International and regional standards (e.g., IEC, UL) are increasingly mandating safety and performance benchmarks for charge controllers. By 2026, compliant PWM models are more widespread, improving consumer confidence and enabling broader adoption in regulated markets. -
Sustainability and End-of-Life Management
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers are exploring recyclable materials and energy-efficient production methods for PWM units. While not as advanced as in other electronics sectors, early efforts toward circular design principles are emerging.
In conclusion, while the PWM charge controller market is not experiencing explosive growth in 2026, it remains a vital segment of the solar ecosystem. Its evolution reflects a strategic adaptation to market needs—balancing cost, reliability, and incremental innovation. As long as affordable, reliable solar solutions are in demand, PWM charge controllers will continue to play a foundational role in global energy access.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pulse Width Modulation Charge Controllers (Quality, IP)
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) charge controllers is the variance in build quality. Low-cost models often use substandard components such as inferior capacitors, low-grade PCB materials, and poorly rated MOSFETs. These components degrade quickly under heat and continuous load, leading to premature failure. Additionally, inadequate soldering and lack of protective coatings increase susceptibility to environmental stress, especially in humid or dusty conditions.
Misrepresented IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
Many PWM charge controllers are marketed with high IP ratings (e.g., IP65 or IP67), suggesting full dust and water resistance. However, in practice, these claims are often exaggerated or unverified. Seals may degrade over time, enclosures may not be properly gasketed, and cable entries may lack strain relief—compromising the unit’s ability to withstand outdoor conditions. Purchasing based solely on stated IP ratings without independent verification or third-party certification can lead to equipment damage and safety hazards.
Inaccurate Voltage and Current Regulation
Low-quality PWM controllers may lack precise voltage sensing and regulation, leading to undercharging or overcharging of batteries. This is often due to poorly calibrated internal circuitry or lack of temperature compensation. Over time, improper charging reduces battery lifespan and may create safety risks such as thermal runaway or gassing in lead-acid batteries.
Lack of Overload and Reverse Polarity Protection
Some budget PWM charge controllers omit essential safety features like reverse polarity protection, overcurrent protection, or short-circuit shutdown. This increases the risk of permanent damage during installation errors or load faults. Always verify that the controller includes robust protection mechanisms, especially in off-grid or remote applications where maintenance is difficult.
Insufficient Heat Dissipation and Overheating
PWM controllers generate heat during operation, especially when regulating high currents. Poorly designed models often lack adequate heat sinks or thermal management, leading to thermal shutdowns or component failure. Units that become excessively hot during normal operation are likely to have reduced lifespans and unreliable performance.
Counterfeit or Clone Products
The solar market includes numerous counterfeit or cloned PWM charge controllers falsely branded as reputable models. These clones often mimic the appearance of well-known brands but use inferior internal designs. They may lack proper certifications, fail safety tests, and provide inconsistent performance. Buyers should source from authorized distributors and verify product authenticity through serial numbers and compliance markings.
Absence of Compliance and Certification
Reputable PWM charge controllers should carry certifications such as CE, RoHS, or IEC 62109 (safety of power converters for use in photovoltaic systems). Many low-cost units lack these certifications or display fake marks. Without proper compliance, there is no assurance of safety, electromagnetic compatibility, or performance under standard conditions.
Inadequate Documentation and Support
Poorly documented controllers—missing datasheets, unclear wiring diagrams, or lack of multilingual support—can lead to incorrect installation and system malfunctions. Limited manufacturer support or warranty coverage further compounds the risk, especially in commercial or industrial deployments where downtime is costly.
To avoid these pitfalls, always prioritize suppliers with verifiable product testing, transparent specifications, and proven track records. Consider investing in slightly higher-cost, certified units to ensure long-term reliability and system safety.
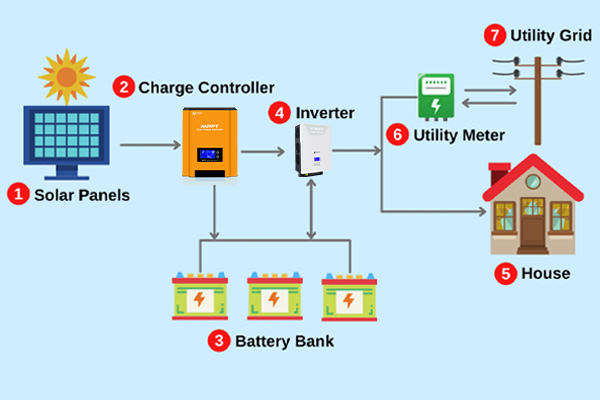
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Charge Controller
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) charge controllers are electronic devices used in solar power systems to regulate the voltage and current flowing from solar panels to batteries, preventing overcharging. These fall under the broader categories of renewable energy equipment and power conversion devices. Proper classification is essential for international shipping and regulatory compliance. Typically, PWM charge controllers are classified under Harmonized System (HS) Code 8504.40 (electronic power converters) or 8537.10 (control panels for electrical circuits), though exact codes may vary by country and specific product specifications.
Safety & Electrical Standards Compliance
PWM charge controllers must comply with regional electrical safety standards to ensure user safety and product reliability. Key certifications include:
– IEC 62109-1 & IEC 62109-2: Safety standards for power converters used in photovoltaic systems.
– UL 1741: Standard for inverters, converters, and controllers in the United States.
– EN 62109: European counterpart to IEC standards, required for CE marking.
– AS/NZS 4777.2: Applicable in Australia and New Zealand.
Manufacturers must provide test reports and certification documentation from accredited laboratories to validate compliance.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Requirements
Due to their switching nature, PWM charge controllers can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). Compliance with EMC directives is mandatory in most markets:
– EU: Must meet EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, typically demonstrated via EN 61000-6-3 (emissions) and EN 61000-6-1 (immunity).
– USA: FCC Part 15, Subpart B, governs unintentional radiators.
– Other Regions: Include KC EMC in South Korea and VCCI in Japan.
Shielding, proper PCB layout, and filtering are commonly used to meet these requirements.
Environmental & RoHS Compliance
PWM charge controllers must comply with environmental regulations restricting hazardous substances:
– EU RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU): Restricts the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials.
– China RoHS: Requires labeling and compliance with substance restrictions.
– REACH (EU): Addresses the registration, evaluation, and restriction of chemicals.
Suppliers must provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) and material disclosure data (e.g., IPC-1752) to support compliance.
Packaging, Labeling & Shipping Guidelines
Proper packaging and labeling are critical for safe logistics and customs clearance:
– Packaging: Use anti-static, shock-resistant materials to protect sensitive electronics. Include moisture barriers if shipping to humid climates.
– Labeling: Include product name, model number, input/output ratings, manufacturer details, safety warnings, and applicable certification marks (e.g., CE, UL, FCC).
– Battery Shipping Note: If the controller is shipped with batteries, additional IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium or lead-acid batteries may apply.
– Documentation: Include user manuals, compliance certificates, commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill.
Import & Customs Considerations
Importers must verify country-specific requirements:
– Tariff Classification: Confirm correct HS code with local customs authorities to determine duties and taxes.
– Energy Efficiency Regulations: Some markets (e.g., California under Title 20) may impose energy efficiency standards on solar equipment.
– Local Representation: In regions like the EU, a Manufacturer’s Authorized Representative (EC REP) may be required for CE-marked products.
– Product Registration: Certain countries (e.g., Saudi Arabia, UAE) require pre-shipment certification (SASO, G-Mark) or local testing.
Warranty, Documentation & After-Sales Support
To ensure long-term compliance and customer satisfaction:
– Maintain technical documentation (including design files, test reports, and risk assessments) for at least 10 years (per EU requirements).
– Provide multilingual user manuals with safety instructions, installation guidance, and troubleshooting.
– Offer warranty services in accordance with local consumer protection laws (e.g., 2-year minimum in the EU).
– Register products with relevant national databases where required (e.g., WEEE in Europe for end-of-life recycling).
Conclusion
Successfully distributing PWM charge controllers globally requires strict adherence to safety, environmental, and logistical standards. Proactive compliance with international regulations not only facilitates market access but also enhances product reliability and customer trust. Always consult with local regulatory experts or certification bodies to ensure alignment with evolving requirements.
Conclusion:
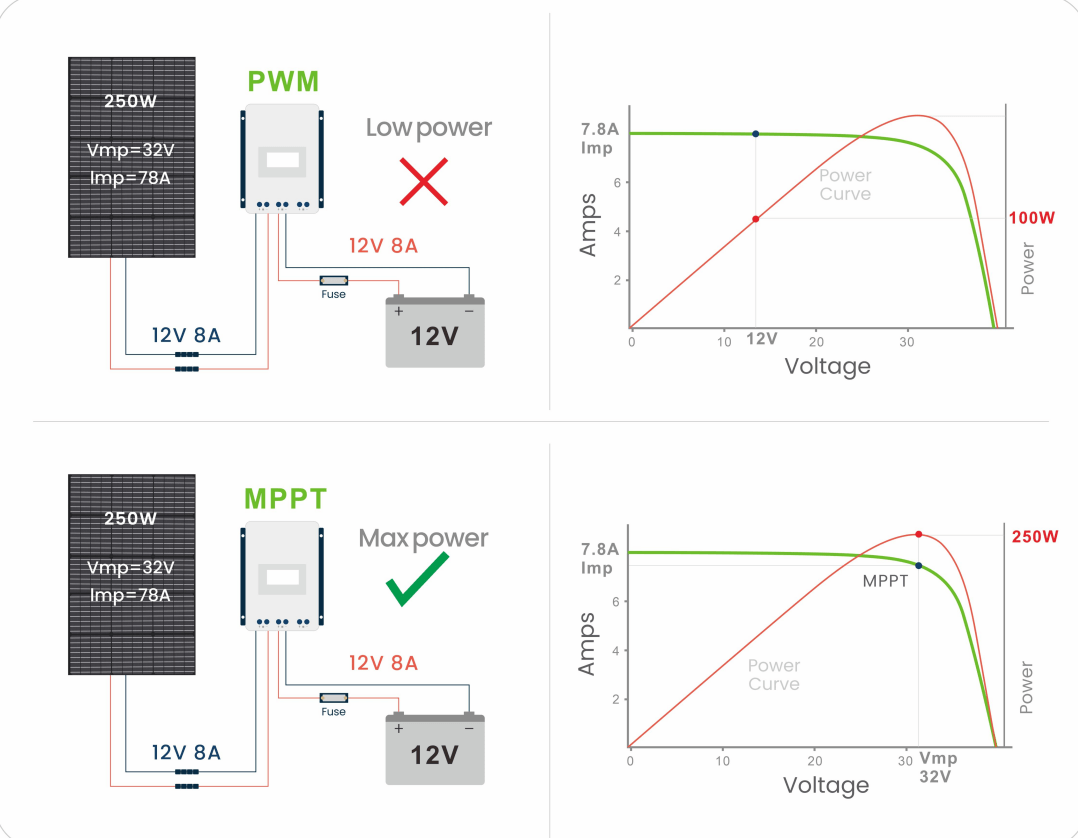
In conclusion, sourcing a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) charge controller is a cost-effective and reliable solution for small to medium-scale solar energy systems where battery charging efficiency and longevity are priorities. PWM controllers offer proven performance in regulating voltage and current from solar panels to batteries, preventing overcharging and extending battery life through precise, pulsating charging cycles. While they are less efficient than Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers—especially in systems with significant voltage mismatches—they remain an ideal choice for simpler, lower-voltage applications due to their durability, ease of installation, and affordability.
When sourcing a PWM charge controller, it is essential to consider factors such as system voltage (12V/24V), current rating (based on solar array output), load capacity, battery compatibility, and protection features (overload, reverse polarity, lightning, etc.). Opting for reputable brands and certified products ensures reliability and safety.
Overall, for off-grid setups, RVs, small cabins, or backup power systems where budget constraints and system simplicity are key considerations, a well-sourced PWM charge controller provides an efficient and dependable energy management solution, supporting sustainable and uninterrupted power supply.
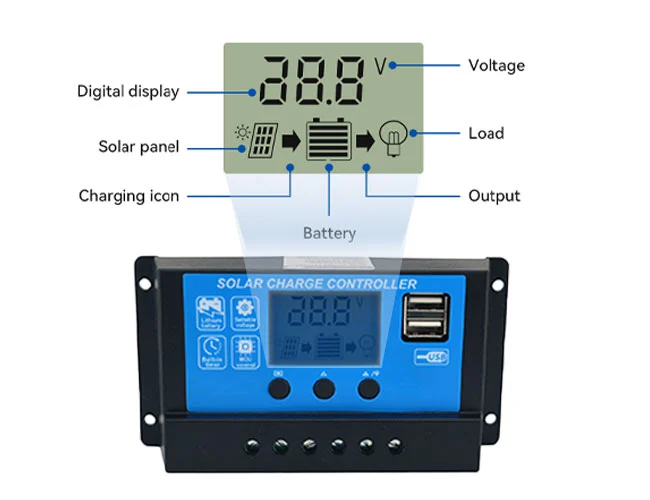





![[Ultimate Guide] MPPT vs. PWM Solar Charge Controller](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/ultimate-guide-mppt-vs-pwm-solar-charge-controller-484.png)

