The global laser cleaning market, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and precision surface treatment solutions, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. A key driver behind this expansion is the rising adoption of pulse laser technology for rust and contaminant removal in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing, where non-abrasive, efficient, and sustainable methods are becoming essential. As regulatory pressures mount against traditional cleaning techniques like sandblasting and chemical treatments, manufacturers are turning to pulsed laser systems for their precision, minimal waste generation, and low operational costs over time. This shift has catalyzed innovation and competition among technology providers, resulting in a dynamic landscape of pulse laser rust removal manufacturers. Based on market presence, technological capability, and customer adoption rates, the following ten companies represent the leaders shaping this high-growth sector.
Top 10 Pulse Laser Rust Removal Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Explore PULSAR Laser P CL laser cleaning machines for industrial rust removal and paint stripping. Compare SHARK P CL, PANDA P CL and FOX P CL….
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#4 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers
Website: fortunelaser.com
Key Highlights: Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine Rust Removal Machine · Fortune Laser Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine · Portable 50W 100W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine · Pulse ……
#5 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our Laser Ablation is the most cost-effective, efficient, and safest method of industrial cleaning, rust removal, paint removal, and surface preparation….
#6 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturer
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: Use pulse laser cleaning machines for delicate materials. They remove contamination with virtually no heat-affected zone (HAZ) and no substrate damage….
#7 Laser cleaning
Website: narran.cz
Key Highlights: We can design and integrate a laser cleaning system into production, build a robotic workstation or supply a mobile laser for a wide range of applications….
#8 Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: triumphlaser.com
Key Highlights: A pulse laser cleaning machine is an advanced, highly efficient tool designed for precision cleaning and removal of contaminants such as rust, paint, oil, and ……
#9 Pulse Wave Laser Machines
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Pulse Wave Laser Cleaning Machines are versatile tools for removing rust, paint, oil stains, oxide films, and other pollutants from metal surfaces, as well ……
#10 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pulse Laser Rust Removal

H2: Emerging Market Trends in Pulse Laser Rust Removal (2026 Outlook)
By 2026, the pulse laser rust removal market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental awareness, and shifting industrial demands. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the sector over the next few years:
1. Accelerated Adoption Across Heavy Industries:
Pulse laser rust removal is moving beyond niche applications into mainstream industrial processes. By 2026, sectors such as shipbuilding, automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and infrastructure maintenance are expected to increase adoption rates significantly. The technology’s precision, non-abrasive nature, and ability to preserve underlying substrates (like sensitive alloys or composites) make it highly attractive for high-value asset maintenance, reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
2. Technological Innovation Driving Efficiency and Affordability:
Advancements in fiber laser technology—particularly in pulse control, beam quality, and energy efficiency—are expected to yield more compact, powerful, and cost-effective systems. Integration with AI-powered scanning and adaptive optics will enable faster, fully automated rust detection and removal, minimizing operator dependency and improving consistency. By 2026, expect next-generation systems with real-time monitoring and closed-loop feedback to enhance process control and reduce operational costs.
3. Regulatory and Environmental Pressures as Key Growth Catalysts:
Stringent global regulations on chemical waste, sandblasting emissions, and worker safety are pushing industries toward cleaner alternatives. Pulse laser rust removal, which generates no secondary waste or hazardous chemicals, aligns perfectly with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. As carbon footprint reporting and sustainability mandates intensify, companies are likely to prioritize laser solutions to meet compliance and enhance corporate sustainability profiles.
4. Expansion of Service-Based Business Models:
While capital expenditure on laser systems remains a barrier for smaller players, the market is witnessing a rise in laser rust removal-as-a-service (LRaaS) models. By 2026, specialized service providers offering on-demand, mobile laser cleaning solutions are expected to capture a growing share, particularly in infrastructure, heritage restoration, and field maintenance. This reduces entry barriers and allows broader access to the technology.
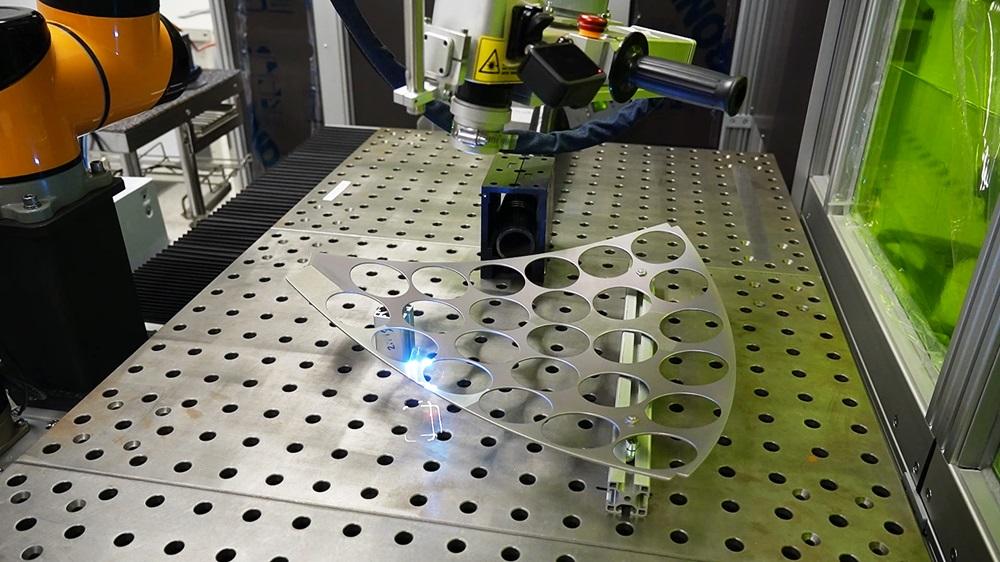
5. Integration with Robotics and Industry 4.0 Ecosystems:
The convergence of pulse laser systems with robotic arms and IoT-enabled platforms will enable fully automated surface treatment cells. In smart factories, laser rust removal units will be seamlessly integrated into production lines, communicating with digital twins and MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) to optimize workflows. This trend supports predictive maintenance and just-in-time surface preparation, boosting overall operational efficiency.
6. Regional Market Divergence and Investment Hotspots:
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, will remain dominant due to strong manufacturing bases and government support for green technologies. North America and Western Europe will see steady growth, driven by defense, aerospace, and renewable energy infrastructure projects. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and the Middle East are also expected to increase investments in laser cleaning as part of modernization initiatives.
Conclusion:
By 2026, pulse laser rust removal is projected to evolve from a premium alternative to a standard solution in surface preparation and maintenance. The convergence of environmental imperatives, technological maturity, and automation will drive widespread adoption, reshaping industrial cleaning practices with cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable outcomes.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Pulse Laser Rust Removal Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing pulse laser rust removal systems, businesses often encounter significant challenges related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Falling into these pitfalls can result in operational inefficiencies, financial losses, and legal complications. Below are the most common issues to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Many suppliers, particularly those offering lower-cost systems from certain regions, compromise on component quality to reduce prices. This can lead to lasers with unstable pulse output, inadequate cooling systems, or substandard optical components. As a result, users may experience inconsistent rust removal efficiency, frequent maintenance needs, and shortened equipment lifespan. Always verify the specifications of core components (e.g., laser source brand, cooling mechanism, beam delivery system) and request third-party test reports or on-site demonstrations.
Lack of Technical Support and Service Infrastructure
Pulse laser systems require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance. Sourcing from vendors without reliable technical support—especially in your region—can leave you stranded during downtime. Be cautious of suppliers who offer limited warranties, unresponsive customer service, or no local service partners. Ensure the supplier provides comprehensive documentation, training, and accessible after-sales support before finalizing procurement.
Misrepresentation of Laser Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate key performance metrics such as peak power, pulse frequency, or effective working distance. For example, advertised “500W” lasers may refer to average power rather than the peak power critical for effective rust ablation. This misrepresentation can lead to underperforming systems that fail to meet industrial requirements. Always request detailed technical documentation and, if possible, performance validation under real-world conditions.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
A major concern when sourcing from certain manufacturers—especially in competitive markets—is the potential use of copied or reverse-engineered technology. Systems that appear unusually low-priced may incorporate patented designs, software algorithms, or optical configurations without proper licensing. Purchasing such equipment exposes your business to legal risks, including infringement claims, import seizures, or forced equipment recall. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio, request proof of original design, and consider legal review of contracts to include IP indemnification clauses.
Inadequate Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser systems must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825) and regional regulations (e.g., FDA in the U.S., CE in Europe). Some sourced units may lack proper safety interlocks, labeling, or certification documentation. Non-compliant equipment poses safety hazards and may be barred from operation in regulated environments. Confirm that the system includes all required certifications and adheres to local regulatory requirements.
Hidden Costs from Lack of Integration Support
While the initial purchase price may seem attractive, some suppliers offer minimal integration support. This can result in unexpected costs related to custom mounting, software interfacing, or automation compatibility. Ensure the supplier provides SDKs, communication protocols, and engineering support for integration into your existing production line or robotic systems.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, businesses can make informed sourcing decisions and deploy reliable, legally compliant pulse laser rust removal solutions.
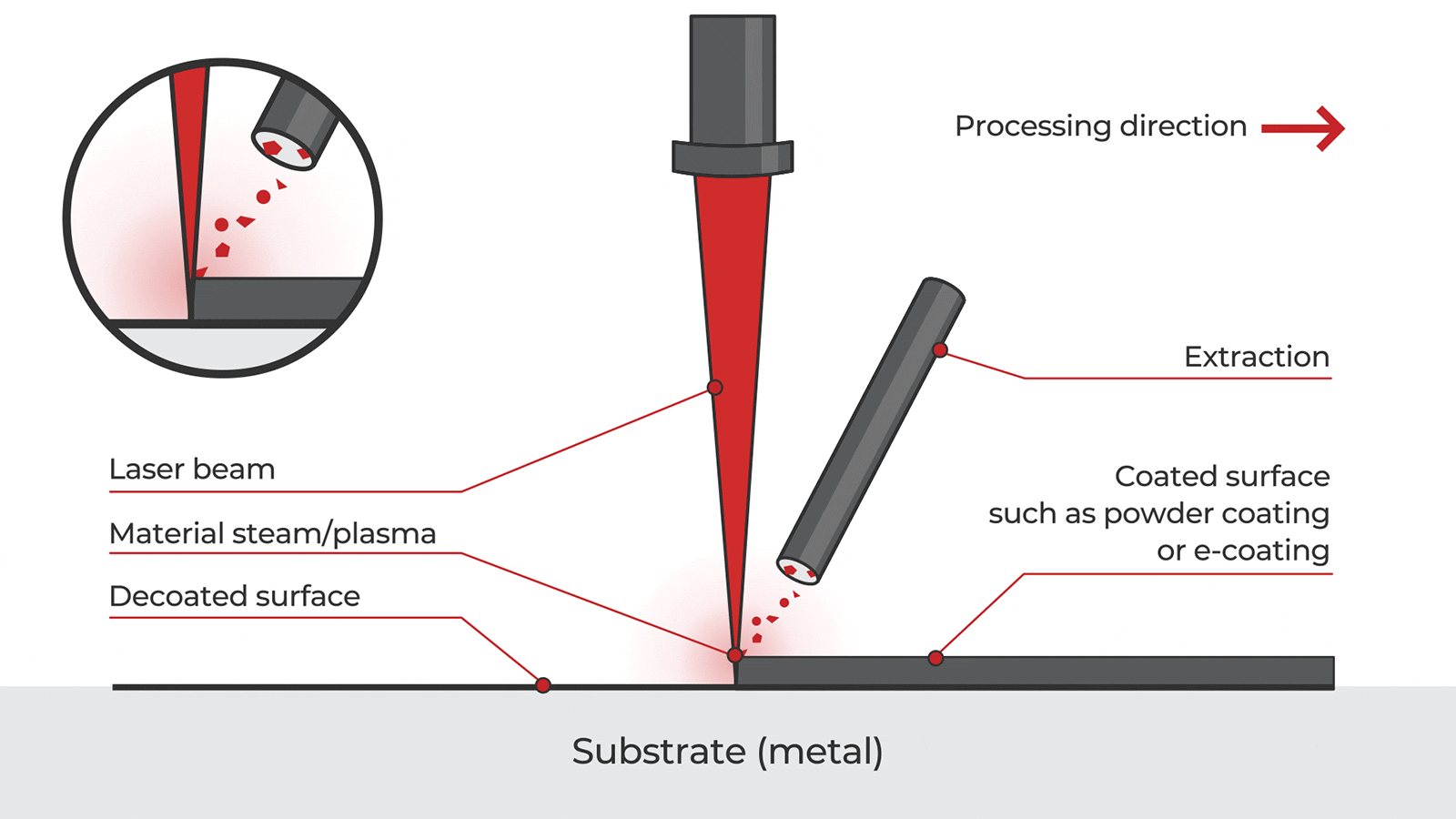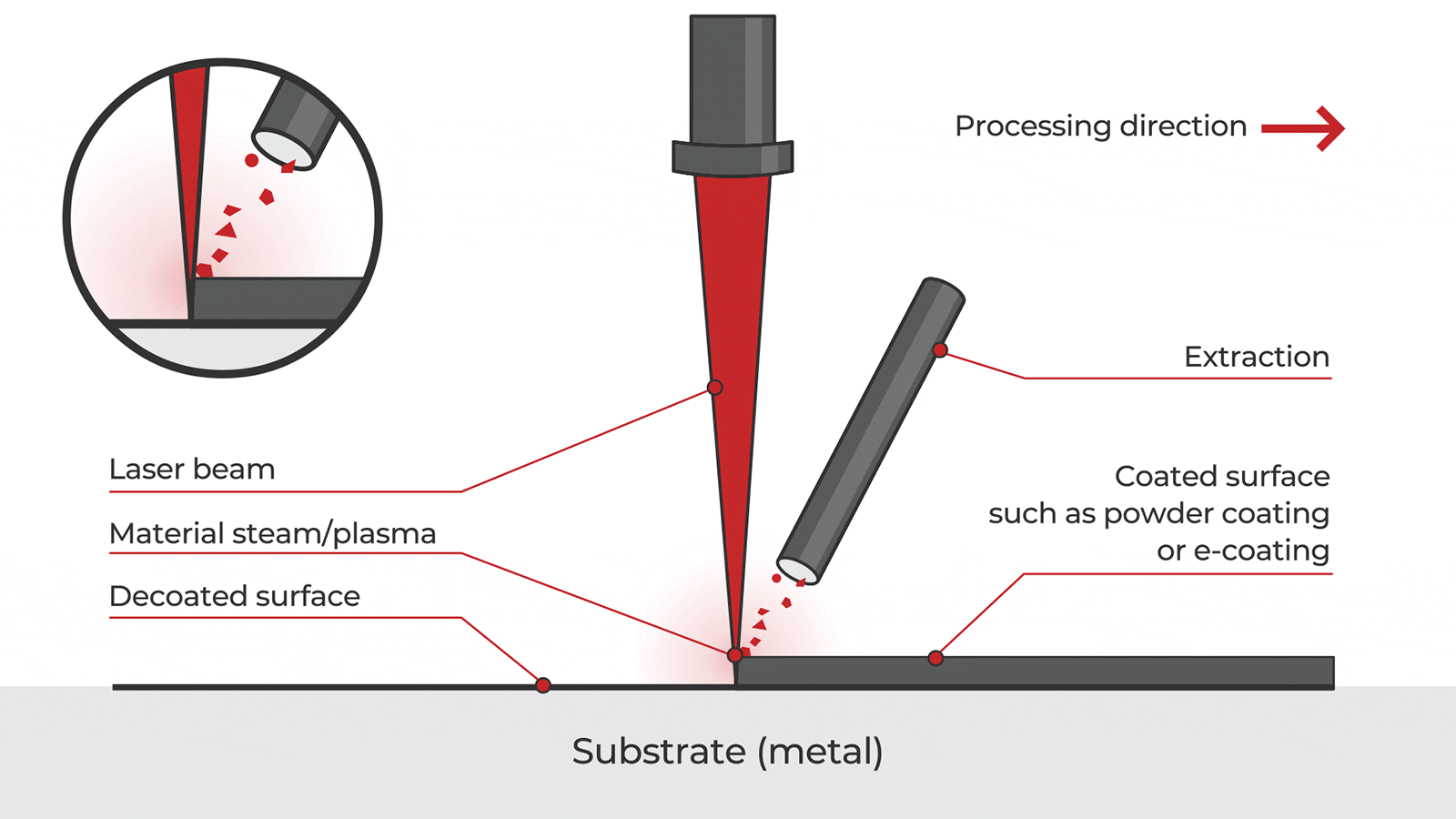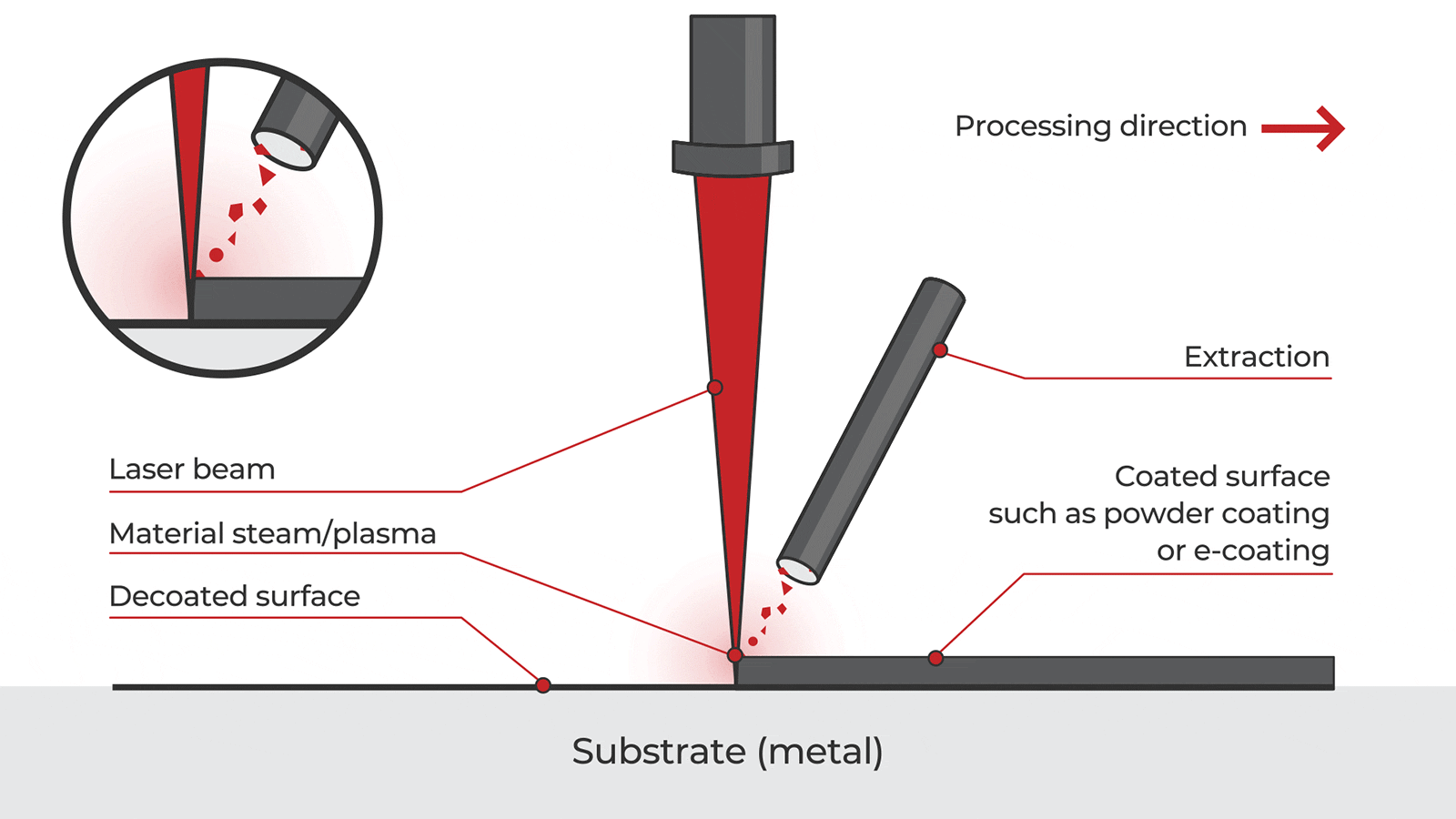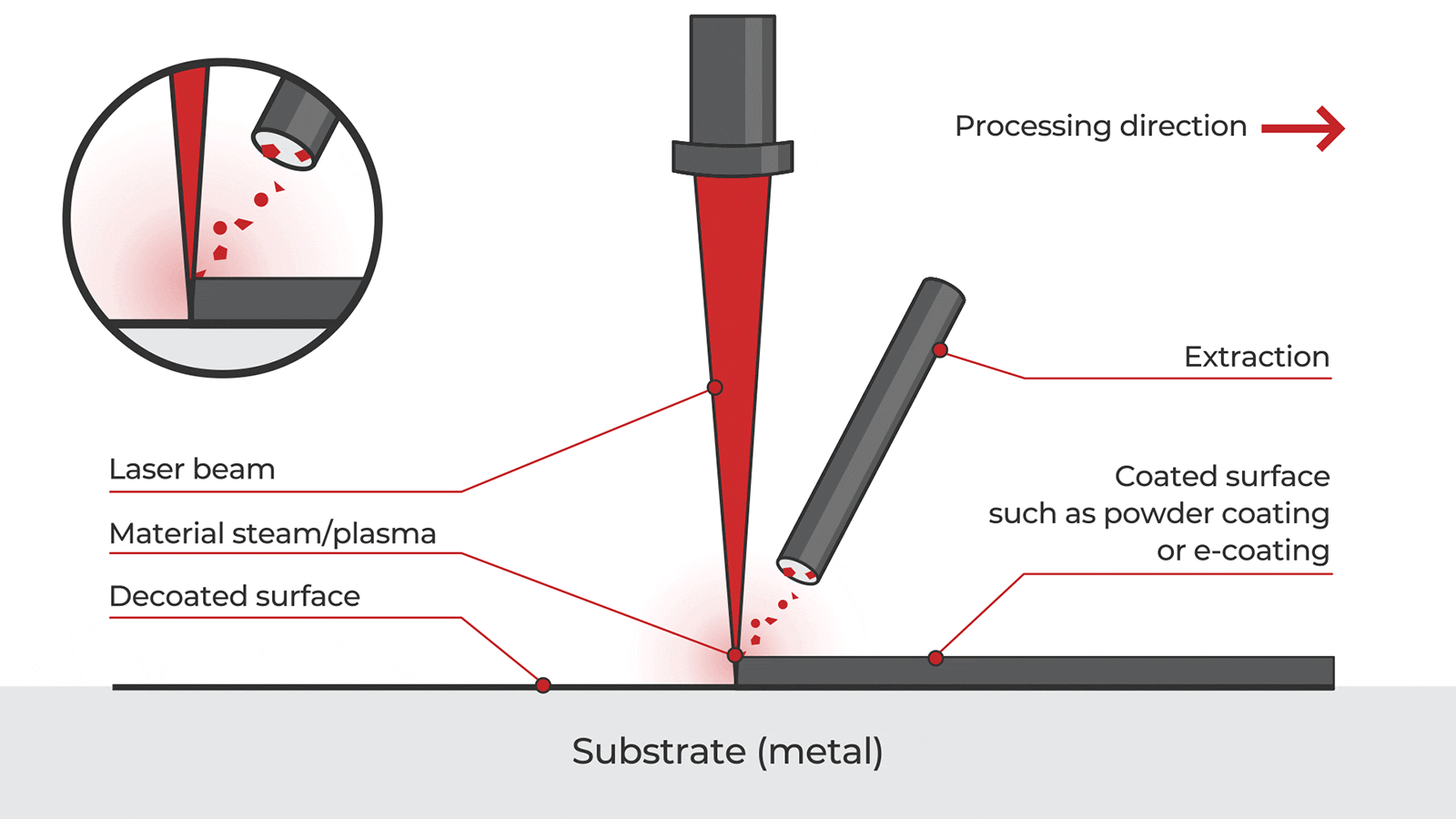
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pulse Laser Rust Removal Equipment
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Pulse laser rust removal systems are precision industrial tools requiring careful handling during transit and setup. Always transport the equipment in its original packaging or a custom protective case designed to absorb shock and vibration. Ensure the laser unit, power supply, control panel, and handheld or robotic arm components are secured separately to prevent internal movement. Use only certified freight carriers experienced in handling sensitive electronic and optical machinery. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust during transit. For international shipping, comply with IATA/ICAO regulations for electronic equipment and include all necessary documentation such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and export declarations.
Installation and Site Requirements
Install pulse laser rust removal systems in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment with stable power supply (typically 110–240 V AC, 50/60 Hz, depending on model). Ensure adequate ventilation and space for operator movement and exhaust fume management, if applicable. The floor must support the equipment weight and be free of vibrations. Connect the system according to the manufacturer’s instructions, verifying proper grounding to avoid electrical hazards. Calibration of the laser optics should be performed by trained technicians post-installation. Always conduct a test run under supervision to confirm operational functionality before full deployment.
Safety Compliance and Operator Training
Pulse laser systems operate with high-intensity beams classified under international laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825-1). Ensure the equipment is labeled with appropriate laser warning signs (Class 4 laser product). Operators must undergo certified training covering laser safety, emergency shutdown procedures, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles with the correct optical density (OD) for the laser’s wavelength (typically 1064 nm for fiber lasers). Implement engineering controls such as interlocks, beam enclosures, and fume extraction systems. Maintain a controlled access zone during operation to prevent accidental exposure.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Verify that the pulse laser rust removal system complies with relevant regional and international regulations:
– CE Marking: Required for sale in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental standards (e.g., Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, and RoHS).
– FDA/CDRH Registration: Mandatory in the United States for laser products; ensure the manufacturer has submitted a Report of Compliance (Form FDA 2877).
– Laser Safety Standards: Adherence to ANSI Z136.1 (US) or IEC 60825 (international) for safe use and classification.
– RoHS and REACH: Confirm compliance with restrictions on hazardous substances and chemical registration (EU).
– Local Permits: Check for additional requirements from occupational safety bodies (e.g., OSHA in the US, HSE in the UK).
Environmental and Waste Management
Laser rust removal produces minimal waste compared to abrasive blasting, but particulate matter (ablated rust and coating residues) must be captured and disposed of properly. Use an industrial-grade fume extractor with HEPA filtration to collect airborne particles. Collected waste should be classified according to local environmental regulations—some metal oxides may be considered hazardous waste. Store waste in sealed, labeled containers and dispose of through licensed hazardous waste handlers if required. Maintain records of waste disposal for audit and compliance purposes.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive documentation for compliance and traceability:
– Equipment manual and safety data sheets (SDS) for any consumables.
– Proof of certifications (CE, FDA, ISO, etc.).
– Records of operator training and safety drills.
– Maintenance logs, including laser alignment and filter replacements.
– Incident reports and corrective actions.
– Waste disposal manifests and environmental compliance records.
Ensure all documents are stored securely and accessible for regulatory inspections or audits.
Conclusion for Sourcing Pulse Laser Rust Removal Equipment:
Sourcing pulse laser technology for rust removal presents a forward-thinking, efficient, and environmentally sustainable solution compared to traditional methods such as sandblasting or chemical treatments. The precision, minimal substrate damage, and elimination of secondary waste make pulse laser systems highly attractive for industries requiring high-standard surface preparation, including automotive, aerospace, cultural heritage restoration, and precision manufacturing.
While the initial investment cost remains relatively high and technical expertise is required for optimal operation, the long-term benefits—such as reduced maintenance, lower consumable use, and compliance with environmental regulations—justify the adoption, particularly for specialized or high-value applications. Additionally, ongoing advancements in fiber laser technology are driving down costs and improving accessibility.
When sourcing, it is essential to evaluate laser specifications (pulse energy, frequency, beam quality), system integration capabilities, vendor support, and safety certifications. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and considering total cost of ownership will ensure a successful implementation.
In conclusion, pulse laser rust removal is a transformative technology with significant operational and environmental advantages. Organizations that strategically invest in this solution today will gain a competitive edge through improved efficiency, sustainability, and service quality in surface treatment processes.