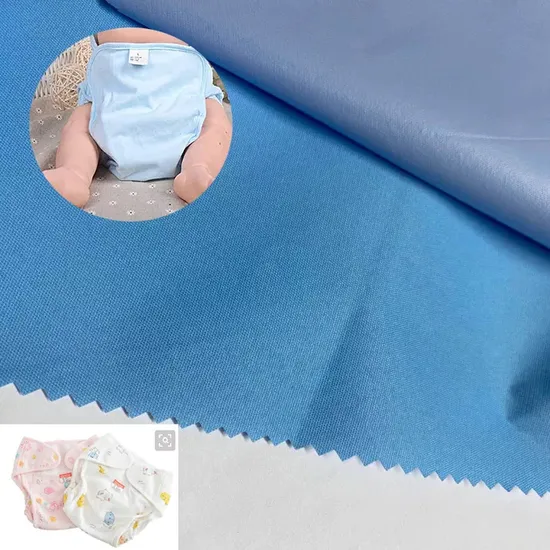
The global demand for sustainable and reusable hygiene products has fueled significant growth in the cloth diaper market, with parents increasingly favoring eco-friendly alternatives to disposable options. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global cloth diaper market was valued at USD 1.65 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. A key driver behind this growth is the rising consumer preference for high-performance, breathable, and leak-resistant materials—particularly polyurethane laminate (PUL), known for its waterproof yet flexible properties. As demand for quality PUL fabric surges, manufacturers specializing in this material are playing a pivotal role in supporting the production of modern cloth diapers. This growing reliance has positioned several suppliers as industry leaders, distinguished by their innovation, production scale, and fabric performance. Below are the top 8 PUL fabric manufacturers contributing to the advancement and scalability of the global cloth diaper industry.
Top 8 Pul Fabric For Cloth Diapers Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PU Laminated Fabric
Domain Est. 2011
Website: waterproofbreathablefabric.com
Key Highlights: The PUL fabric is manufactured using latest TRP technology in colloboration with our German partners to ensure high efficiency & quality….
#2 PUL Fabric Prints
Domain Est. 1998
#3 Diaper Cover Fabric
Domain Est. 1999
Website: greenmountaindiapers.com
Key Highlights: Trucks diaper print PUL also called TPU diaper cover fabric in celery green. Make your own wet bag, changing pad or diaper covers with real cloth diaper ……
#4 Diaper Fabrics: What are PUL and TPU?
Domain Est. 2012
Website: zephyrhillblog.com
Key Highlights: It stands for Polyurethane Laminate and is used to create waterproof fabrics such as cloth diapers, wet bags, cloth menstrual pads, and […]….
#5 PUL
Domain Est. 2019
#6 ProSoft PUL: Eco
Domain Est. 2022
Website: prosoftpulfabrics.com
Key Highlights: ProSoft PUL Fabric is a premium, eco-friendly soft, strong, and waterproof fabric for any application. Versatile, long-lasting and has a life-cycle of 300+ ……
#7 Eco-PUL
Website: ecopultextiles.wixsite.com
Key Highlights: Eco-PUL™ is a special type of laminated material. Our PUL fabric is waterproof, breathable and soft, making it the most comfortable PUL fabric to wear. Eco-PUL™ ……
#8 Pul Fabric Waterproof By The Meter
Website: og-eichenwies.ch
Key Highlights: The material is seriously smart – it’s waterproof but still breathable, which means less heat buildup and reduced diaper rash. We’ve got these cute patterns ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pul Fabric For Cloth Diapers
H2: 2026 Market Trends for PU Fabric in Cloth Diapers
The global market for polyurethane (PU) fabric used in cloth diapers is expected to witness steady growth and notable innovation by 2026, driven by rising environmental awareness, advancements in sustainable materials, and shifting consumer preferences toward reusable baby products. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the PU fabric segment for cloth diapers in 2026:
-
Increased Demand for Eco-Friendly and Biodegradable PU Fabrics
As sustainability becomes a central concern for parents and manufacturers alike, there is a growing shift toward bio-based and biodegradable PU fabrics. Innovations in plant-derived polyols and water-based PU coatings are reducing the environmental footprint of traditional petroleum-based PU. By 2026, leading cloth diaper brands are expected to increasingly adopt eco-conscious PU laminates that maintain performance while aligning with green certifications. -
Enhanced Performance Features
Performance-driven innovation remains a priority. PU fabrics for cloth diapers in 2026 are likely to offer improved breathability, superior waterproofing, and enhanced durability after repeated washing. Advanced microporous PU membranes allow moisture vapor to escape while blocking liquid—improving baby comfort and reducing rashes. These technical improvements are helping cloth diapers compete more effectively with disposable alternatives. -
Growth in Emerging Markets
While North America and Western Europe currently dominate the cloth diaper market, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa are emerging as high-growth regions. Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and growing awareness of environmental issues are fueling demand for sustainable baby care products. Local manufacturing of PU laminated fabrics is expected to increase to meet regional demand and reduce supply chain dependencies. -
Integration with Smart Diaper Technology
A niche but expanding trend is the integration of smart textiles into cloth diapers. Some manufacturers are experimenting with PU-coated fabrics that incorporate moisture-sensing threads or antimicrobial treatments. While still in early stages, this convergence of smart fabrics and sustainable diapering could influence PU fabric development by 2026, especially in premium product segments. -
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Stricter global regulations on chemical use in baby products are impacting PU fabric production. Certifications such as OEKO-TEX® Standard 100, CPSIA (U.S.), and REACH (EU) are becoming mandatory for market access. By 2026, manufacturers of PU fabric for cloth diapers will need to ensure compliance with these standards, favoring non-toxic, phthalate-free, and heavy-metal-free formulations. -
Customization and Aesthetic Appeal
Consumers are increasingly seeking stylish, customizable cloth diapers. In response, PU fabric suppliers are offering a wider array of colors, prints, and textures. Digital printing on PU laminates allows for vibrant, long-lasting designs without compromising waterproof integrity—making cloth diapers more appealing to modern parents. -
Competitive Pressure from Alternatives
While PU remains dominant, alternatives like TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) and PUL (polyurethane laminate) with recycled content are gaining traction due to their higher durability and recyclability. By 2026, competition may push traditional PU fabric producers to innovate or risk losing market share to next-generation materials.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for PU fabric in cloth diapers will be defined by sustainability, performance, and innovation. Manufacturers who invest in eco-friendly production, comply with safety standards, and respond to regional and technological trends are likely to lead the market. As the global push for circular economy principles intensifies, PU fabric will need to evolve to remain a cornerstone of the reusable diaper industry.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing PU Fabric for Cloth Diapers (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing polyurethane (PU) laminated fabric for cloth diapers requires careful attention to both material performance and legal compliance. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to product failures, customer dissatisfaction, and potential legal disputes. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Fabric Breathability and Moisture Management
One of the most critical quality issues is selecting a PU laminate that lacks adequate breathability. While PU provides a waterproof barrier, low-quality or improperly engineered fabrics can trap heat and moisture, leading to diaper rash and discomfort. Ensure the fabric has a high moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) to allow skin to breathe, especially for overnight or heavy-use diapers.
Inadequate Durability and Delamination
Low-grade PU fabrics may delaminate after repeated washing and drying cycles. This occurs when the bond between the fabric backing (typically polyester or cotton) and the PU coating weakens, causing bubbling or peeling. Always request wash-test data (e.g., 50+ hot washes) and verify the lamination method (e.g., adhesive vs. direct coating) to ensure long-term performance.
Use of Non-Phthalate or Non-Certified Materials
Safety is paramount in baby products. Some cheaper PU fabrics may contain hazardous substances such as phthalates, heavy metals, or restricted solvents. Always source fabrics that are CPSIA-compliant and certified by recognized standards like OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 or CPSR testing. Request up-to-date chemical compliance documentation from suppliers.
Misrepresentation of Fabric Specifications
Suppliers—especially those on global marketplaces—may exaggerate fabric performance (e.g., “breathable,” “medical-grade”) without supporting evidence. Verify specifications with independent lab reports and request physical samples for real-world testing before placing bulk orders.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
A significant but often overlooked pitfall is the risk of infringing on patented fabric technologies. Major cloth diaper brands often use proprietary PU laminates (e.g., unique textures like “stay-dry” suedes or microfiber with bonded PU). Sourcing a fabric that visually or functionally mimics a patented material can lead to cease-and-desist letters or lawsuits. Always conduct due diligence on the fabric’s original manufacturer and avoid copying branded textures or performance claims.
Lack of Supply Chain Transparency
Many suppliers act as middlemen without direct access to manufacturing records. This lack of transparency can obscure the true origin of the fabric and increase the risk of receiving inconsistent or substandard batches. Establish relationships with manufacturers who can provide traceability, batch testing, and consistent quality control.
Failure to Secure Usage Rights or Exclusivity
If developing a branded diaper line, confirm whether the PU fabric can be used exclusively or if the supplier sells the same material to competitors. Additionally, clarify whether design or performance aspects of the fabric are protected and whether your use requires licensing.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, businesses can source PU fabric that ensures product safety, performance, and legal compliance—ultimately building trust with customers and protecting brand integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for PU Fabric for Cloth Diapers
Product Overview and Intended Use
PU (Polyurethane) fabric used in cloth diapers is typically a laminated or coated textile designed to provide a waterproof yet breathable barrier. It is commonly used as the outer layer (shell) or as a backing on diaper inserts to prevent leaks while maintaining comfort. Understanding the material’s composition—typically a polyester or cotton knit with a thin polyurethane coating—is critical for ensuring compliance and managing logistics effectively.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
PU fabric for cloth diapers must meet several regulatory standards, particularly concerning safety, environmental impact, and labeling. Key compliance areas include:
- CPSIA (Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act) – Applies to children’s products in the U.S., including limits on lead and phthalates. PU fabric must be tested and certified to ensure it does not exceed allowable levels.
- REACH (EU Regulation) – Regulates the use of hazardous chemicals in products sold in the European Union. Ensure the PU coating does not contain SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern).
- OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 – While voluntary, certification to Class I (for baby articles) is highly recommended to demonstrate the fabric is free from harmful levels of toxic substances.
- Flammability Standards (e.g., 16 CFR Part 1610) – Though less common for diaper fabrics, ensure the material meets basic flammability requirements if applicable.
Manufacturers and importers should obtain valid test reports and certifications from accredited laboratories for each fabric batch.
Import and Export Documentation
When shipping PU fabric internationally, proper documentation ensures smooth customs clearance:
- Commercial Invoice – Must detail product description, quantity, value, country of origin, and harmonized system (HS) code.
- Packing List – Includes weight, dimensions, and packaging details.
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill – Proof of shipment and carrier agreement.
- Certificate of Origin – Required by many countries for duty assessment and trade agreement eligibility.
- Test Reports & Certifications – Attach copies of CPSIA, REACH, or OEKO-TEX® reports to demonstrate compliance upon request.
Use the correct HS code—commonly 5903.20 (textiles impregnated or coated with plastics)—to classify PU-laminated fabric accurately.
Labeling and Packaging Standards
Proper labeling ensures consumer safety and regulatory compliance:
- Fiber Content Labeling – Clearly state the fabric composition (e.g., “92% Polyester, 8% Polyurethane”).
- Care Instructions – Include washing, drying, and temperature guidelines to maintain fabric integrity.
- Country of Origin – Legally required in markets like the U.S. and EU.
- Safety & Warning Labels – If applicable, include warnings about heat exposure (e.g., avoid high-heat drying to prevent delamination).
Packaging should protect the fabric from moisture, tearing, and contamination during transit. Use moisture-resistant wrapping and sturdy cartons suitable for stacking.
Storage and Handling Guidelines
To preserve PU fabric quality:
- Temperature & Humidity Control – Store in a cool, dry place (ideally 15–25°C, <60% humidity) to prevent adhesive degradation or mold.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight – Prolonged UV exposure can weaken the polyurethane layer.
- Roll Orientation – Store fabric rolls vertically to prevent deformation or edge crushing.
- Shelf Life – Most PU laminated fabrics have a shelf life of 12–24 months; rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) principles.
Transportation Considerations
- Mode of Transport – Choose sea freight for large volumes (cost-effective) or air freight for urgent, smaller shipments.
- Container Conditions – For sea freight, use dry containers with desiccants to control humidity. Avoid refrigerated containers unless necessary.
- Transit Time & Insurance – Account for potential delays and insure shipments against damage, moisture, or loss.
Supplier and Quality Assurance
- Audit Suppliers – Verify that fabric suppliers follow ethical labor practices and environmental standards (e.g., ISO 14001, BSCI).
- Pre-Shipment Inspection – Conduct quality checks for width, weight, coating uniformity, and defects.
- Batch Traceability – Maintain records linking fabric rolls to test reports and production batches for recall readiness.
Sustainability and End-of-Life Considerations
- Recyclability Challenges – PU-coated fabrics are difficult to recycle due to composite construction. Inform customers about proper disposal.
- Environmental Claims – Avoid unsubstantiated “eco-friendly” claims unless backed by certifications (e.g., GRS, Bluesign®).
- Waste Reduction – Optimize cutting patterns to minimize fabric waste during diaper manufacturing.
By adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines, businesses can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient handling of PU fabric for cloth diapers across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing PUL Fabric for Cloth Diapers:
Sourcing high-quality PUL (Polyurethane Laminate) fabric is a critical factor in the production of durable, reliable, and safe cloth diapers. After evaluating various suppliers, materials, and manufacturing practices, it is evident that choosing the right PUL fabric involves balancing performance, safety, sustainability, and cost. Key considerations include fabric weight (typically 55–65gsm), breathability, stretch, seam-sealability, and compliance with safety standards such as Oeko-Tex® or CPSIA, especially for baby products.
Suppliers from regions like South Korea, China, and the USA offer varying levels of quality and innovation, with some providing eco-conscious options like recycled fibers or low-impact lamination processes. Building relationships with reputable vendors, requesting samples, and conducting rigorous testing for durability and waterproofing are essential steps to ensure consistency and product integrity.
Ultimately, investing in premium PUL fabric not only enhances the functionality and longevity of cloth diapers but also supports brand reputation and customer satisfaction. As the demand for sustainable and high-performance baby products continues to grow, a well-considered sourcing strategy for PUL fabric positions manufacturers to meet market needs effectively and responsibly.