The global temperature sensor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision monitoring across industrial automation, healthcare, automotive, and HVAC applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. A key contributor to this expansion is the increasing adoption of high-accuracy sensors such as Pt1000 resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), which offer superior stability and repeatability compared to traditional sensing technologies. Pt1000 sensors, known for their 1000-ohm base resistance at 0°C, are especially favored in applications requiring fine temperature resolution, including medical diagnostics equipment, battery thermal management in electric vehicles, and process control systems. As industries continue to prioritize data accuracy and system reliability, the demand for high-performance Pt1000 temperature sensors has intensified, prompting a competitive landscape of manufacturers focused on innovation, durability, and compliance with international standards. This growing market momentum underscores the importance of identifying leading suppliers capable of meeting evolving technical and scalability requirements.
Top 10 Pt1000 Temperature Sensor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pt1000 Temperature Sensor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tc-inc.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading manufacturer of Platinum Resistance Thermometers (RTD sensors / Pt100 sensors). We have an enormous range of components in stock means we can ……
#2 PK temperature sensor (PT1000)
Domain Est. 1998
Website: seweurodrive.com
Key Highlights: The PT1000 temperature sensors serve as a replacement for the KTY sensors, which were discontinued by the manufacturer, and will be available for selection in ……
#3 Temperature sensors
Domain Est. 1986
Website: ti.com
Key Highlights: Our temperature sensors allow you to overcome common design challenges and continue innovating with high-accuracy, low-power consumption, and small, flexible ……
#4 Pt1000 RTD Thin Film Element
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsThe Pt1000 RTD thin film element is an RTD sensor with a base resistance value of 1000 Ohms at 0°C. Complies with DIN EN 60751….
#5 Resistance thermometer Pt100 or Pt1000
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wika.com
Key Highlights: Pt100/Pt1000 resistance thermometers by WIKA. The sensor of a resistance thermometer features a temperature-dependent electrical resistance….
#6 PT1000 RTD Temperature Sensor
Domain Est. 1999
Website: thermometricscorp.com
Key Highlights: PT1000 Sensor. Platinum resistance thermometers (PRTs) offer excellent accuracy over a wide temperature range (from -200 to +850 °C)….
#7 Standard Pt1000 (232) class F0.1
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ist-ag.com
Key Highlights: Standard Pt1000 (232) class F0.1 ; Nominal resistance. 1000 Ω at 0 °C ; Operating temperature range. -200 °C to +600 °C ; TCR. Pt 3850 ppm/K ; Chip size/dimensions….
#8 Sensor RTD Pt1000 SMD for Precision Tempe Sensing
Domain Est. 2012
Website: dxmht.com
Key Highlights: The PT1000 SMD Sensor RTD is used in components like motor heaters, transmission systems, and charging stations. The RTD temperature sensors ……
#9 PT1000 Temperature Sensor
Domain Est. 2012
#10 PT1000 Temperature Sensor
Domain Est. 2022
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pt1000 Temperature Sensor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Pt1000 Temperature Sensors
Based on current technological advancements, industrial demands, and macroeconomic factors, the Pt1000 temperature sensor market in 2026 is poised for significant growth and transformation, driven by increased precision needs, integration with smart systems, and expansion into emerging applications.
1. Dominance of High-Precision & Miniaturization:
The demand for higher accuracy and stability in critical applications (e.g., medical devices, semiconductor manufacturing, and advanced R&D) will solidify the Pt1000’s position over alternatives like Pt100. Its lower lead-wire resistance impact and higher signal output (compared to Pt100) make it ideal for precision environments. Concurrently, advancements in thin-film and micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technologies will drive the miniaturization of Pt1000 sensors, enabling integration into compact and portable devices.
2. Integration into IoT and Industry 4.0 Ecosystems:
Pt1000 sensors will increasingly serve as foundational components in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) networks. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of Pt1000s with integrated signal conditioning, digital interfaces (e.g., IO-Link, Modbus), and wireless connectivity. This enables real-time temperature monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven process optimization in smart factories, energy systems, and building automation.
3. Growth in Renewable Energy and EV Sectors:
The rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy infrastructure (solar inverters, battery storage systems) will be a major growth driver. Pt1000 sensors are critical for precise thermal management in EV battery packs and power electronics, where temperature directly impacts safety, efficiency, and lifespan. Their stability and accuracy make them preferred for these demanding environments.
4. Enhanced Focus on Sustainability and Efficiency:
Manufacturers will prioritize energy-efficient sensor designs and sustainable production processes to meet regulatory standards and corporate ESG goals. Pt1000s, known for their long-term stability and low drift, contribute to system efficiency by reducing calibration frequency and maintenance costs, aligning with broader industrial sustainability trends.
5. Regional Market Expansion and Supply Chain Resilience:
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the largest market due to advanced manufacturing and electronics industries. However, diversification of supply chains will accelerate, with increased investment in regional manufacturing (e.g., in India and Southeast Asia) to mitigate geopolitical risks and reduce lead times. This will foster localized innovation and customization.
6. Competitive Landscape and Innovation:
The market will see intensified competition between established players (e.g., TE Connectivity, Amphenol, WIKA) and emerging specialty sensor manufacturers. Innovation will focus on hybrid sensors (e.g., Pt1000 combined with humidity or pressure sensing), AI-enabled diagnostics, and improved packaging for harsh environments (high vibration, corrosive atmospheres).
Conclusion:
By 2026, the Pt1000 temperature sensor market will be characterized by a shift toward smarter, smaller, and more integrated solutions. Driven by the convergence of precision requirements, digitalization, and green technologies, Pt1000 sensors will play an increasingly vital role in enabling efficient, reliable, and intelligent systems across key industrial and consumer sectors.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pt1000 Temperature Sensors (Quality & IP Protection)
Sourcing Pt1000 temperature sensors requires careful attention to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings to ensure reliability, accuracy, and longevity in the intended application. Overlooking these factors can lead to sensor failure, measurement inaccuracies, and increased maintenance costs.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Sensor Accuracy and Tolerance
Many low-cost Pt1000 sensors deviate from standard tolerance classes (e.g., Class B, Class A, or 1/3 B). Sourcing sensors without verified calibration certificates or traceable documentation may result in inconsistent readings, especially in precision-critical applications such as medical devices or industrial process control.
2. Poor Construction Materials and Build Quality
Inferior materials—such as low-grade stainless steel sheaths or substandard ceramic substrates—can lead to mechanical failure, corrosion, or drift in resistance values over time. Sensors exposed to harsh environments (chemicals, high pressure, thermal cycling) are particularly vulnerable when built with cost-cutting materials.
3. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable suppliers provide calibration certificates, RoHS compliance, and traceable test reports. Sourcing from uncertified or unknown manufacturers may result in non-compliant sensors that fail regulatory audits or do not meet industry standards (e.g., IEC 60751).
IP Protection Pitfalls
1. Misunderstanding IP Rating Requirements
The IP rating (e.g., IP65, IP67, IP68) defines protection against dust and water ingress. A common mistake is selecting a sensor with insufficient IP protection for the operating environment—such as using an IP54 sensor in a washdown application—which leads to moisture ingress, short circuits, and sensor failure.
2. Incomplete or Misrepresented IP Claims
Some suppliers advertise “industrial-grade” or “water-resistant” sensors without specifying a valid IP rating. Others may claim high IP ratings that are not independently verified. Always request test reports or certification from accredited bodies to confirm IP compliance.
3. Poor Sealing at Critical Junctions
Even with a high IP rating, poor manufacturing practices—such as inadequate cable gland seals, weak potting compounds, or improper assembly—can compromise protection. Moisture ingress at the cable entry point or connector is a frequent cause of sensor failure in humid or outdoor installations.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, prioritize suppliers with proven quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), clear technical specifications, and verifiable IP certification. Request sample testing and documentation to validate performance claims before full-scale procurement.
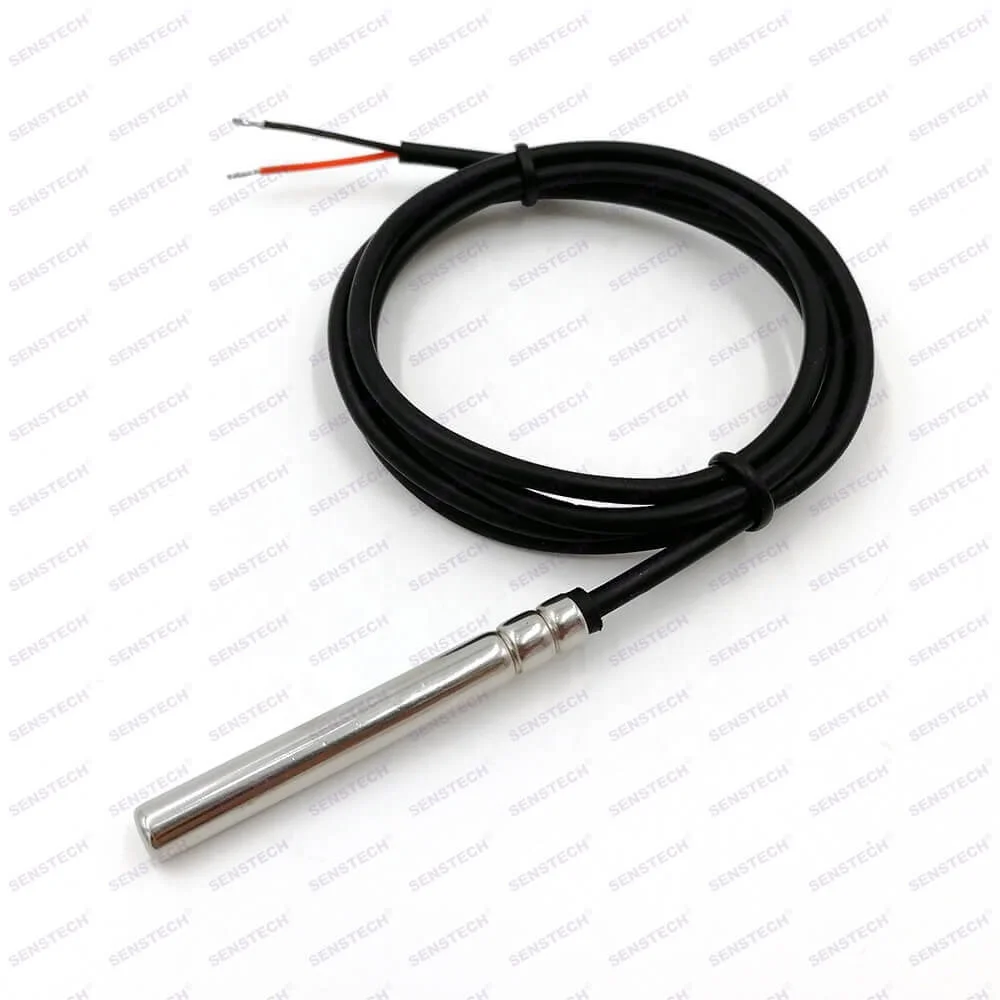

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pt1000 Temperature Sensor
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the shipment, handling, and regulatory adherence of Pt1000 temperature sensors. Proper attention to these factors ensures safe transportation, legal compliance, and product integrity.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Pt1000 temperature sensors are typically passive electronic components used for temperature measurement. They generally fall under HS (Harmonized System) code 9025.19.00 (Electrical resistance thermometers) or 8533.21.00 (Fixed resistors, including precision types), depending on construction and regional classification practices. Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance and duty assessment.
Ensure all shipments are accompanied by a commercial invoice detailing:
– Full product description: “Pt1000 Temperature Sensor, Platinum Resistance Thermometer, Class B Accuracy”
– Quantity and unit value
– Harmonized System (HS) code
– Country of origin
– ECCN (Export Control Classification Number): Typically EAR99 under the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, indicating minimal export restrictions, but verify based on end-use and destination
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Use anti-static packaging (e.g., static-shielded bags) to protect sensors from electrostatic discharge (ESD), especially during transit and storage. Individual sensors should be secured to prevent mechanical stress or bending of leads.
Packaging must meet international standards for shock and vibration resistance (e.g., ISTA 3A). Include cushioning materials such as foam inserts or bubble wrap to absorb impact. Mark outer boxes with handling labels:
– “Fragile – Handle with Care”
– “Electrostatic Sensitive Device – Do Not Open with Bare Hands”
– “This Side Up”
Shipping & Transportation
Ship via reliable couriers (e.g., DHL, FedEx, UPS) or freight forwarders experienced in handling electronic components. For air transport, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations—Pt1000 sensors are generally non-hazardous and do not require special labeling unless integrated with hazardous materials.
Maintain temperature-controlled environments during transit if specified by the manufacturer, particularly for calibrated sensors. Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures (>60°C or <–20°C) and high humidity (>85% RH) to preserve accuracy and performance.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify export restrictions based on destination country. While Pt1000 sensors are widely exportable, certain end-uses (e.g., military, nuclear) or embargoed regions (e.g., sanctioned countries) may require licenses.
Comply with REACH (EU) and RoHS (EU) directives:
– RoHS Compliance: Confirm the sensor is lead-free and free of restricted substances (e.g., Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr⁶⁺, PBB, PBDE)
– REACH: Ensure no SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) are present above threshold levels
For shipments to the EU, provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) affirming compliance with applicable directives. In the U.S., ensure compliance with FCC Part 15 if the sensor is part of a larger system emitting radio frequencies.
Certifications & Traceability
Maintain records of:
– Calibration certificates (if applicable)
– Material declarations (RoHS, REACH)
– Country of origin documentation
– Lot or batch numbers for traceability
Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) in the manufacturing process enhance compliance credibility.
End-of-Life & Environmental Considerations
Pt1000 sensors contain small amounts of platinum and copper/nickel leads. Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU for proper disposal or recycling. Provide customers with take-back or recycling instructions where applicable.
Avoid landfill disposal; return to manufacturer or authorized e-waste handlers for precious metal recovery and environmental protection.
Summary
Adherence to logistics best practices and regulatory standards ensures the Pt1000 temperature sensor reaches its destination safely, legally, and in optimal condition. Always verify regional requirements and maintain thorough documentation for audit readiness.
Conclusion for Sourcing PT1000 Temperature Sensor:
After evaluating various suppliers, specifications, and cost considerations, the PT1000 temperature sensor has been identified as a reliable and accurate solution for precision temperature measurement applications. Its higher resistance compared to the PT100 (1000 Ω at 0°C) offers improved signal stability and reduced sensitivity to lead wire resistance, making it particularly suitable for applications requiring high accuracy over long cable runs or in electrically noisy environments.
Sourcing options have been assessed based on key criteria such as sensor accuracy (e.g., Class A or B), packaging (probe type, material, length), operating temperature range, long-term stability, and compatibility with existing measurement systems. Suppliers offering RoHS compliance, calibration certification, and technical support have been prioritized to ensure quality and traceability.
Additionally, cost-effectiveness, lead times, and minimum order quantities were balanced to identify vendors that provide the best value without compromising on performance. Reputable manufacturers and distributors—both global and regionally available—have been shortlisted to ensure supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, the PT1000 sensor meets the project’s technical requirements, and a sourcing strategy has been established that ensures high-quality, reliable, and scalable procurement. Proceeding with a pilot order from the top-ranked supplier is recommended to validate performance before full-scale integration.