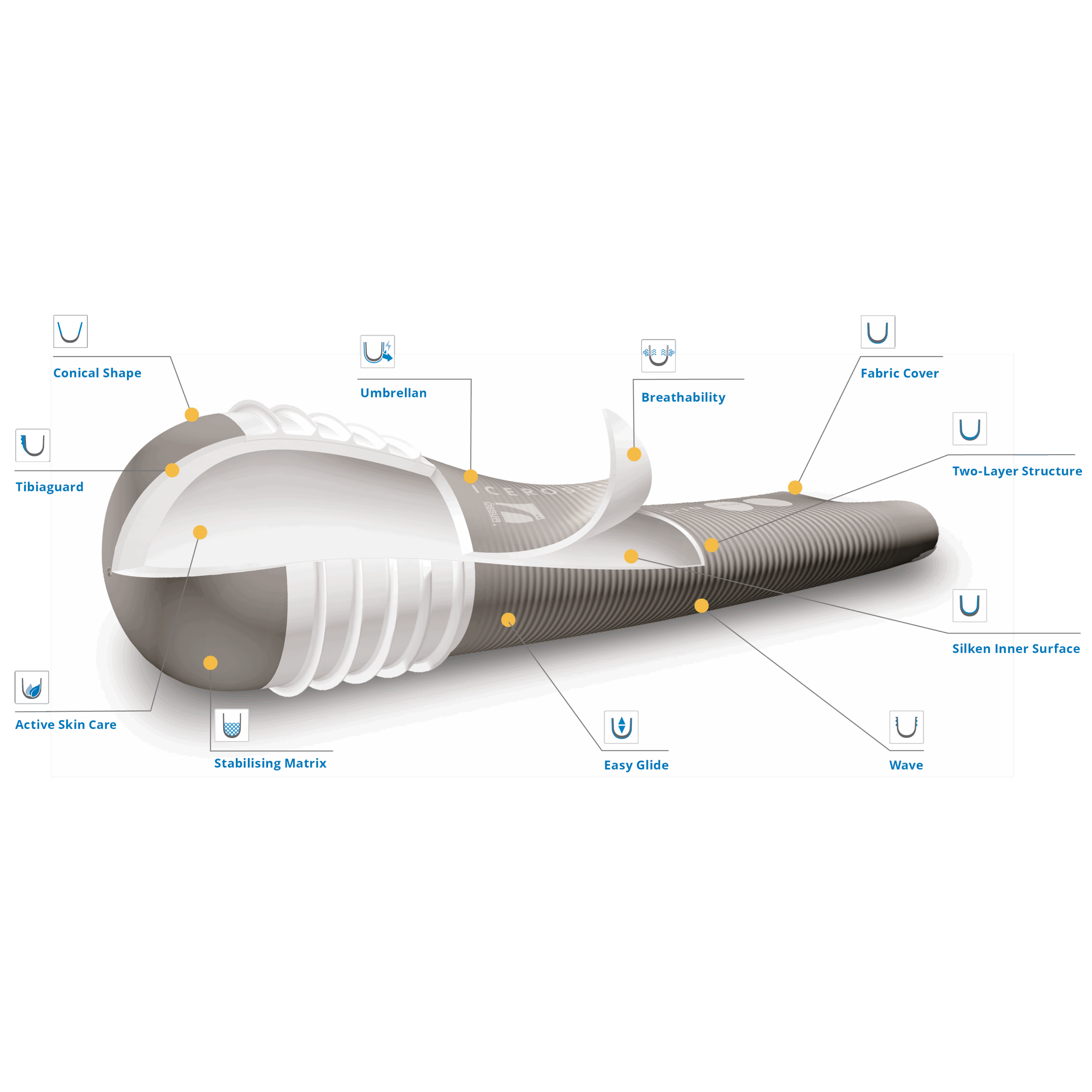
The global prosthetic liners market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising amputations due to vascular diseases, diabetes, and traumatic injuries, along with increasing demand for advanced prosthetic solutions that enhance user comfort and mobility. According to Grand View Research, the global prosthetics and orthotics market was valued at USD 5.57 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence projects a similar upward trajectory, with the prosthetics market anticipated to grow at a CAGR of over 7% during the forecast period of 2023–2028. A critical component within this ecosystem is the prosthetic gel liner—a soft, silicone or urethane-based interface that improves socket fit, reduces friction, and enhances skin protection. As technological advancements continue to prioritize user comfort and biomechanical efficiency, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovating and scaling gel liner production. Below, we explore the top seven prosthetic gel liner manufacturers shaping the future of limb prosthetics through clinical excellence, material science, and data-backed product performance.
Top 7 Prosthetic Gel Liners Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ALPS South
Domain Est. 1999
Website: easyliner.com
Key Highlights: A leading U.S. manufacturer specializing in gel-based prosthetic liners and sleeves….
#2 “It’s a perfect part of me!”. Ossur.com
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ossur.com
Key Highlights: A prosthetic liner is the protective interface that sits between the skin of your residual limb and the inner socket wall of your prosthetic leg….
#3 Orthotic & Prosthetic Supplier
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cascade-usa.com
Key Highlights: Extreme Gel Liner. By ALPS. Card image cap. Smart Picks. Superior Performance … Custom Logo Coolmax® Prosthetic Sock Bundle. By ALPS. Card image cap….
#4 Prosthetics
Domain Est. 1998
Website: silipos.com
Key Highlights: Silipos Pin Liners are built for stability and strength, using a superior gel bond to provide resistance to even the most extreme abrasion. Proven to last, ……
#5 Liners
Domain Est. 2001
Website: willowwood.com
Key Highlights: WillowWood’s Alpha Liners are engineered to optimize patient comfort and fit and offer a wide range of solutions (in both thermoplastic elastomer (TPE Gel) ……
#6 Thermo
Domain Est. 2015
Website: thermoplygel.com
Key Highlights: Thermo-ply is a prosthetic company that manufactures and sells prosthetic liners and prosthetic sleeves. The Encore prosthetic product line includes the ……
#7 Design and Manufacturing of Prosthetic Solutions
Website: easyliner.eu
Key Highlights: For almost 30 years Alps® has been dedicated to designing and manufacturing only the highest-quality prosthetic liners to provide users with all the mobility ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Prosthetic Gel Liners

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Prosthetic Gel Liners
The global market for prosthetic gel liners is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, demographic shifts, and evolving patient expectations. As critical components in modern prosthetic systems, gel liners enhance comfort, suspension, and skin protection for amputees. Key trends shaping the 2026 landscape include:
-
Increased Demand Due to Rising Amputation Rates
The growing prevalence of diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and trauma-related limb loss—particularly in aging populations across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia—is fueling demand for advanced prosthetic solutions. By 2026, this demographic pressure is expected to expand the prosthetic gel liner market, especially in emerging economies with improving healthcare access. -
Advancements in Smart and Sensor-Integrated Liners
A major trend is the integration of smart technologies into gel liners, including moisture sensors, pressure mapping, and gait monitoring systems. These innovations aim to improve fit, reduce skin breakdown, and enable real-time feedback for clinicians. By 2026, smart liners are likely to gain regulatory approvals and insurance reimbursement, accelerating adoption. -
Personalization and 3D Printing
Customization is becoming a standard expectation. Advances in 3D scanning and additive manufacturing allow for patient-specific liner designs that conform precisely to residual limb anatomy. This trend is expected to grow by 2026, supported by falling costs of 3D printing and increasing digital workflow adoption in orthotics and prosthetics (O&P) clinics. -
Focus on Skin Health and Material Innovation
Manufacturers are investing in new gel formulations—such as hydrogel composites and antimicrobial silicones—to reduce skin irritation and infection risks. These materials improve breathability and durability, addressing long-standing user complaints. By 2026, eco-friendly and biocompatible materials may become industry benchmarks. -
Expansion of Telehealth and Remote Fitting Solutions
The rise of tele-rehabilitation and digital health platforms is influencing how gel liners are prescribed and monitored. Remote fitting assessments and AI-driven fit prediction tools are expected to become more prevalent by 2026, improving access for rural and underserved populations. -
Reimbursement and Regulatory Developments
As payer awareness grows, there is increasing pressure to demonstrate cost-effectiveness and clinical outcomes. In markets like the U.S. and EU, value-based healthcare models may drive coverage expansion for premium gel liners, especially those that reduce secondary complications and hospitalizations. -
Growing Patient Empowerment and Aesthetic Preferences
End-users are demanding not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing and lifestyle-compatible products. Liners with improved cosmetic finishes, color options, and athletic performance features are emerging to meet these needs, particularly among younger amputees.
In conclusion, the 2026 prosthetic gel liner market will be defined by smarter, more personalized, and patient-centered innovations. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, clinicians, and payers—will need to adapt to these trends to remain competitive and improve long-term outcomes for amputees globally.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Prosthetic Gel Liners: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing prosthetic gel liners—critical interface components between a residual limb and a prosthetic socket—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to compromised patient safety, legal exposure, and reputational damage. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Biocompatibility Testing
Sourcing gel liners without verified biocompatibility data (e.g., ISO 10993 compliance) risks skin irritation, allergic reactions, or long-term tissue damage. Many low-cost suppliers use substandard silicone or gel formulations that degrade quickly or contain harmful additives.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Poorly controlled production processes can result in variable wall thickness, inconsistent gel distribution, or weak bonding between gel and fabric layers. These inconsistencies impact comfort, durability, and suspension reliability.
Lack of Validation for Durability and Wear Resistance
Without third-party testing data on tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and fatigue life, liners may fail prematurely under daily use. Some suppliers provide only anecdotal evidence instead of standardized testing (e.g., ISO 7206 or ASTM F2772).
Absence of Sterility and Packaging Controls
Non-sterile or poorly sealed packaging increases infection risk, especially for post-operative or sensitive users. Suppliers in unregulated environments may lack cleanroom facilities or validated sterilization methods.
Failure to Meet Regulatory Standards
Sourcing from manufacturers unfamiliar with FDA 510(k), CE Marking (MDR), or other regional medical device regulations can result in non-compliant products. This may lead to shipment rejections, recalls, or market access delays.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Patented Designs or Technologies
Many advanced gel liner features—such as proprietary gel formulations, suspension mechanisms, or interface geometries—are protected by patents. Sourcing from suppliers using these without licensing exposes importers to infringement lawsuits, especially in the U.S. or EU.
Copying Aesthetic or Functional Design Elements
Even if a product isn’t an exact replica, mimicking protected design elements (e.g., specific ridge patterns, valve placements, or layered construction) can violate design patents or trade dress rights.
Lack of IP Due Diligence in Supplier Contracts
Failing to require suppliers to warrant IP ownership and indemnify buyers against infringement claims leaves the sourcing party legally and financially exposed.
Risk of Counterfeit or “Clone” Products
Some suppliers market products under misleading names or packaging that mimic established brands. These clones often lack quality control and may infringe on multiple IP rights, increasing liability.
Unprotected Custom Development
If you co-develop a liner design with a supplier, failing to formalize IP ownership in writing may result in the manufacturer claiming rights to the innovation or selling it to competitors.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: verify certifications, audit manufacturing facilities, request test reports, perform IP clearance searches, and secure comprehensive contractual protections. Partnering with reputable, transparent suppliers aligned with medical device standards is essential for safe, compliant, and legally sound sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Prosthetic Gel Liners
Overview
Prosthetic gel liners are medical devices designed to interface between a prosthetic limb and the user’s residual limb, providing cushioning, comfort, and improved fit. Ensuring efficient logistics and strict regulatory compliance is critical for manufacturers, distributors, and healthcare providers. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, legal, and timely handling of prosthetic gel liners across the supply chain.
Regulatory Classification & Standards
Prosthetic gel liners are typically classified as Class I or Class II medical devices under the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations, depending on design and claims. Similar classifications apply under the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and other global frameworks.
– FDA (United States): Must comply with 21 CFR Part 890 (Physical Medicine Devices). Registration with FDA, establishment listing, and adherence to Quality System Regulation (QSR) 21 CFR Part 820 are required. Most gel liners are exempt from premarket notification (510(k)) but must follow general controls.
– EU MDR (Europe): Classified as Class I (non-sterile, non-measuring) or higher. Requires CE marking, Technical Documentation, and involvement of a Notified Body if applicable.
– ISO 13485: Certification to this quality management standard is essential for international market access and demonstrates compliance with design, manufacturing, and distribution requirements.
– Other Regions: Countries such as Canada (Health Canada), Australia (TGA), and Japan (PMDA) have their own regulatory pathways. Local authorization may be required before import or sale.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Proper labeling ensures patient safety and regulatory compliance:
– Mandatory Information: Include product name, model/size, manufacturer name and address, lot number, expiration date (if applicable), sterile status, and regulatory markings (e.g., CE, FDA Establishment Number).
– Language: Labels and instructions for use (IFU) must be in the official language(s) of the destination country (e.g., English and French in Canada; German in Germany).
– Barcoding: Use of UDI (Unique Device Identification) is required in the U.S. and EU. Include UDI on packaging in both human-readable and machine-readable (e.g., GS1 barcode) formats.
– Storage Conditions: Clearly indicate temperature and humidity requirements on packaging (e.g., “Store at room temperature, 15–30°C”).
Import and Export Compliance
Cross-border shipment of prosthetic gel liners requires compliance with international trade and customs regulations:
– HS Codes: Use appropriate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 9021.10 or 9021.29 for prostheses) for customs declarations.
– Import Permits: Some countries require medical device import licenses or prior notification. Verify with local regulatory agencies before shipping.
– Export Controls: Confirm that products are not subject to dual-use or sanctions restrictions. No major export licenses are typically required for gel liners, but documentation must be accurate.
– Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and regulatory compliance certificates (e.g., Certificate to Foreign Government, Certificate of Free Sale).
Storage and Handling
Gel liners are sensitive to environmental conditions:
– Temperature Control: Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment within the manufacturer’s specified range (typically 15–30°C). Avoid freezing and direct sunlight.
– Shelf Life Management: Monitor expiration dates and implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory practices. Inspect for degradation (e.g., hardening, discoloration) before distribution.
– Sterility: If sterile, ensure packaging integrity is maintained. Do not distribute if seals are compromised.
– Transport Conditions: Use insulated packaging if shipping through extreme climates. Monitor with temperature loggers when necessary.
Distribution and Traceability
Maintain full traceability throughout the supply chain:
– Serialization: Utilize lot and UDI tracking to enable recalls and improve patient safety.
– Chain of Custody: Document all transfers from manufacturer to distributor to provider.
– Authorized Channels: Distribute only through licensed medical device distributors or healthcare providers, especially in regulated markets.
– E-Commerce Compliance: If selling online, ensure platforms comply with medical device advertising and data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
Ongoing monitoring is required after product release:
– Adverse Event Reporting: Report malfunctions, injuries, or deaths related to gel liners to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EU Eudamed) per regulatory timelines.
– Field Safety Notices: Issue recalls or corrections promptly if non-conformities are identified.
– Customer Feedback: Maintain systems to collect and analyze user complaints and performance data.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for prosthetic gel liners demand attention to regulatory details, precise documentation, and robust quality systems. By adhering to international standards, maintaining proper storage and traceability, and staying current with evolving regulations, stakeholders can ensure patient safety and market access worldwide. Regular training and audits are recommended to sustain compliance across the product lifecycle.
Conclusion on Sourcing Prosthetic Gel Liners
Sourcing prosthetic gel liners requires careful consideration of multiple factors to ensure optimal patient outcomes, comfort, and long-term satisfaction. Key aspects such as material quality, fit customization, durability, and moisture management must be prioritized when selecting suppliers. It is essential to partner with reputable manufacturers and distributors that comply with medical device regulations and offer evidence-based product performance. Additionally, evaluating cost-effectiveness, warranty support, and availability of clinical training for prosthetists contributes to sustainable and reliable supply chains. As advancements in materials and smart technologies continue to evolve, staying informed about innovations will enable providers to offer the most suitable solutions tailored to individual patient needs. Ultimately, a strategic and patient-centered sourcing approach ensures improved mobility, comfort, and quality of life for prosthetic users.